2016 Vol. 45, No. 4
2016, 45(4): 481-481.
Abstract:
2016, 45(4): 482-501.
Abstract:
2016, 45(4): 502-510.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.002
Abstract:
In order to overcome a number of challenges in CMOS millimeter-wave integrated circuit design, the millimeter-wave device modeling, antenna design, circuit block, and multi-channel transceiver system are introduced in this paper. The equivalent-circuit models of millimeter-wave on-chip interconnected lines, multiple-coupled inductors, six-port M:N transformers, and the model of terahertz active device are studied and proposed, respectively. Moreover, a low noise amplifier with noise canceling and a power amplifier with a fully symmetrical distributed active transformer are introduced in this paper. Furthermore, the CMOS 60 GHz receiver with on-chip antenna and the multi-channel phase array transceiver are described, respectively.
In order to overcome a number of challenges in CMOS millimeter-wave integrated circuit design, the millimeter-wave device modeling, antenna design, circuit block, and multi-channel transceiver system are introduced in this paper. The equivalent-circuit models of millimeter-wave on-chip interconnected lines, multiple-coupled inductors, six-port M:N transformers, and the model of terahertz active device are studied and proposed, respectively. Moreover, a low noise amplifier with noise canceling and a power amplifier with a fully symmetrical distributed active transformer are introduced in this paper. Furthermore, the CMOS 60 GHz receiver with on-chip antenna and the multi-channel phase array transceiver are described, respectively.
2016, 45(4): 511-519.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.003
Abstract:
Airborne cognitive radar uses priori clutter knowledge-aided adaptive technique to suppress the clutter. Thus, the authenticity and validity of clutter model has a great influence on the detection performance of airborne cognitive radar. Considering the characteristics of signal processing technologies in airborne cognitive radar, this paper designs a clutter modeling method based on the digital elevation model data. The new method extracts the terrain factors influencing the power spectrum of clutter from DEM data. By combining the geographical landscape theory with the terrain factors, the real landforms provided by DEM are quantifiably classified. In order to increase the real-time in modeling clutter, a dynamic database is designed to store the quantized landform information. Finally, the ground clutter model is constructed based on the topography information and backscattering coefficient model. The simulation results show that the ground clutter model we constructed fits with the actual topography where the airborne radar locates. The model has the real, stable and reliable advantages when it is used to obtain the priori information of airborne cognitive radar and it can effectively aid airborne cognitive radar to improve detection performance and survivability.
Airborne cognitive radar uses priori clutter knowledge-aided adaptive technique to suppress the clutter. Thus, the authenticity and validity of clutter model has a great influence on the detection performance of airborne cognitive radar. Considering the characteristics of signal processing technologies in airborne cognitive radar, this paper designs a clutter modeling method based on the digital elevation model data. The new method extracts the terrain factors influencing the power spectrum of clutter from DEM data. By combining the geographical landscape theory with the terrain factors, the real landforms provided by DEM are quantifiably classified. In order to increase the real-time in modeling clutter, a dynamic database is designed to store the quantized landform information. Finally, the ground clutter model is constructed based on the topography information and backscattering coefficient model. The simulation results show that the ground clutter model we constructed fits with the actual topography where the airborne radar locates. The model has the real, stable and reliable advantages when it is used to obtain the priori information of airborne cognitive radar and it can effectively aid airborne cognitive radar to improve detection performance and survivability.
2016, 45(4): 520-527.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.004
Abstract:
Information theory is the mathematic foundation for communication systems. The existing researches focus on low energy consumption bound analysis with the equivalent model of the symmetry circuits from the view point of information theory, and there are few works which focus on the analysis of the relationship among the information transmission, the reliability, and the supply voltage for the asymmetry circuits. The main contribution of this paper provides an analysis methodology for the reliability and supply voltage of asymmetry-based digital circuits with information theory. We use the new Markov random field (MRF) circuits, which can achieve ultra low power and high fault tolerance, as the analysis case. We demonstrate that the low supply voltage bound of MRF circuits is lower than that of traditional CMOS circuits through the proof of four lemmas of entropy, conditional entropy, and mutual information. This work can provide a theoretical basis for the research and design of the asymmetry-based MRF.
Information theory is the mathematic foundation for communication systems. The existing researches focus on low energy consumption bound analysis with the equivalent model of the symmetry circuits from the view point of information theory, and there are few works which focus on the analysis of the relationship among the information transmission, the reliability, and the supply voltage for the asymmetry circuits. The main contribution of this paper provides an analysis methodology for the reliability and supply voltage of asymmetry-based digital circuits with information theory. We use the new Markov random field (MRF) circuits, which can achieve ultra low power and high fault tolerance, as the analysis case. We demonstrate that the low supply voltage bound of MRF circuits is lower than that of traditional CMOS circuits through the proof of four lemmas of entropy, conditional entropy, and mutual information. This work can provide a theoretical basis for the research and design of the asymmetry-based MRF.
2016, 45(4): 528-532.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.005
Abstract:
Underwater very low frequency (VLF) minimum shift keying (MSK) signals are distorted by the impulsive noise, the propagation attenuation of sea water and the fluctuation of sea wave. In order to reduce the requirement for carrier phase synchronization and improve the robustness of demodulation algorithm, the differential demodulation algorithm of the underwater VLF MSK signal is investigated in this paper. The propagation attenuation of sea water is first modeled. By considering the impact of suppressing impulsive noise, the multiple-symbols differential demodulation of the underwater VLF MSK signal is then derived based on the principle of maximum likelihood (ML) detection. Extensive simulation results show that the performance of the ML multiple-symbols differential demodulation algorithm can closely approach that of the coherent demodulation algorithm if the carrier phase is recovered and a relative large amount of symbols are utilized. On the other hand, the differential demodulation algorithm is superior to the coherent demodulation algorithm if the carrier phase is not recovered.
Underwater very low frequency (VLF) minimum shift keying (MSK) signals are distorted by the impulsive noise, the propagation attenuation of sea water and the fluctuation of sea wave. In order to reduce the requirement for carrier phase synchronization and improve the robustness of demodulation algorithm, the differential demodulation algorithm of the underwater VLF MSK signal is investigated in this paper. The propagation attenuation of sea water is first modeled. By considering the impact of suppressing impulsive noise, the multiple-symbols differential demodulation of the underwater VLF MSK signal is then derived based on the principle of maximum likelihood (ML) detection. Extensive simulation results show that the performance of the ML multiple-symbols differential demodulation algorithm can closely approach that of the coherent demodulation algorithm if the carrier phase is recovered and a relative large amount of symbols are utilized. On the other hand, the differential demodulation algorithm is superior to the coherent demodulation algorithm if the carrier phase is not recovered.
2016, 45(4): 533-550.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.001
Abstract:
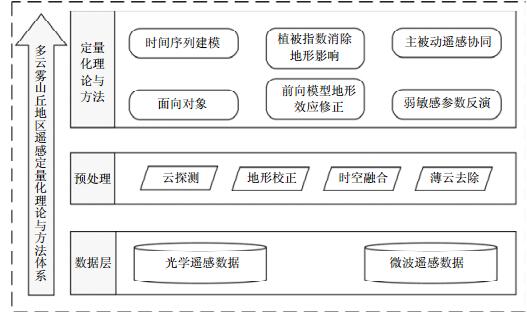
With the rapid development of the Earth observation technologies, remote sensing plays an increasingly important role in the applications of global change, ecological environment, territorial resources, natural disasters, national defense, smart city, and other applications. Accompanied by the development and improvement for the theories and applications of the quantitative remote sensing, there are still many unprecedented challenges. Because of the Earth complexity of the surface and the limitation of the remote sensing information, the quantitative applications of remote sensing generally are hampered by ill-posed inversion, scale effect, and other problems. Especially for cloudy and hilly regions, sufficiently influenced by the cloud, topography, and spatial heterogeneity, the quantitative applications of remote sensing becomes more difficult. Based on the analysis of the application status and the challenges faced by optical and microwave remote sensing, this paper reviews the theory and approaches applied for cloudy and hilly regions from the perspective of remote sensing data, preprocessing, and the quantitative theory and approaches, which include object-oriented inversion strategy, synergy of active and passive remote sensing, time series modeling, topographic correction of the forward model, and inversion of weak sensitive parameters. In addition, specific application examples are presented based on the recent research and practice achieved by the team of the authors, including continuous change detection of land cover, forest fire risk assessment, drought monitoring, and soil moisture retrieval under vegetation cover from active and passive remote sensing in the southwest China.
With the rapid development of the Earth observation technologies, remote sensing plays an increasingly important role in the applications of global change, ecological environment, territorial resources, natural disasters, national defense, smart city, and other applications. Accompanied by the development and improvement for the theories and applications of the quantitative remote sensing, there are still many unprecedented challenges. Because of the Earth complexity of the surface and the limitation of the remote sensing information, the quantitative applications of remote sensing generally are hampered by ill-posed inversion, scale effect, and other problems. Especially for cloudy and hilly regions, sufficiently influenced by the cloud, topography, and spatial heterogeneity, the quantitative applications of remote sensing becomes more difficult. Based on the analysis of the application status and the challenges faced by optical and microwave remote sensing, this paper reviews the theory and approaches applied for cloudy and hilly regions from the perspective of remote sensing data, preprocessing, and the quantitative theory and approaches, which include object-oriented inversion strategy, synergy of active and passive remote sensing, time series modeling, topographic correction of the forward model, and inversion of weak sensitive parameters. In addition, specific application examples are presented based on the recent research and practice achieved by the team of the authors, including continuous change detection of land cover, forest fire risk assessment, drought monitoring, and soil moisture retrieval under vegetation cover from active and passive remote sensing in the southwest China.
2016, 45(4): 551-556.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.007
Abstract:
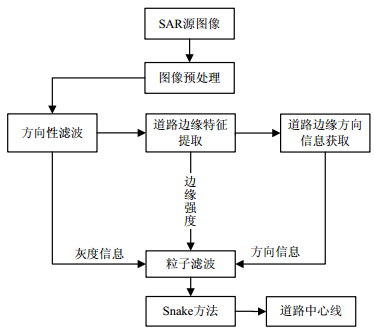
In this paper, an approach for road damage information extraction based on multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images is proposed. The road centerline is obtained by using particle filtering. According to complex mountainous terrains, the image pre-processing and the filtering process are adjusted and the road centerline can identified correctly. A road damage model is then developed in terms of the features of the road damage in SAR images, thus the road damage information is attained. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method can achieve the accuracy of road damage information above 80%.
In this paper, an approach for road damage information extraction based on multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images is proposed. The road centerline is obtained by using particle filtering. According to complex mountainous terrains, the image pre-processing and the filtering process are adjusted and the road centerline can identified correctly. A road damage model is then developed in terms of the features of the road damage in SAR images, thus the road damage information is attained. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method can achieve the accuracy of road damage information above 80%.
2016, 45(4): 557-563.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.008
Abstract:
There are quite long interconnection lines between the nodes of a network-on-chip (NoC) based on the globally asynchronous locally synchronous (GALS) structure. It is difficult to match the delay requirement for the communication with the asynchronous ways. In this paper, we propose a build-in self-test (BIST) method to solve the problem of interconnection delay fault across different clock domains. The test circuit and the module of automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) are designed and simulated. The circuit with FPGA is realized to verify the function and performance of the test circuit. The results of simulation and hardware verification indicate that test circuit and the module of ATPG can carry out the function of interconnection delay fault diagnosis of NoC, and the proposed method of interconnection delay fault diagnosis can detect the delay fault existed in the interconnection line rapidly and accurately.
There are quite long interconnection lines between the nodes of a network-on-chip (NoC) based on the globally asynchronous locally synchronous (GALS) structure. It is difficult to match the delay requirement for the communication with the asynchronous ways. In this paper, we propose a build-in self-test (BIST) method to solve the problem of interconnection delay fault across different clock domains. The test circuit and the module of automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) are designed and simulated. The circuit with FPGA is realized to verify the function and performance of the test circuit. The results of simulation and hardware verification indicate that test circuit and the module of ATPG can carry out the function of interconnection delay fault diagnosis of NoC, and the proposed method of interconnection delay fault diagnosis can detect the delay fault existed in the interconnection line rapidly and accurately.
2016, 45(4): 564-572.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.009
Abstract:
With the emergence of complex network control systems (NCSs), such as smart grid, big data, cloud control system and teleoperation system, NCSs possess the new characteristics of wide area, wide range, and large data etc. This paper focuses on the network induced-delay and packet dropouts in the complex NCSs, which need more attention to. The research status of predictive control algorithm is examined and summarized, and also the future development directions of network control systems are discussed. This paper aimed to provide theoretical basis and research ways to predictive control of the complex network control systems.
With the emergence of complex network control systems (NCSs), such as smart grid, big data, cloud control system and teleoperation system, NCSs possess the new characteristics of wide area, wide range, and large data etc. This paper focuses on the network induced-delay and packet dropouts in the complex NCSs, which need more attention to. The research status of predictive control algorithm is examined and summarized, and also the future development directions of network control systems are discussed. This paper aimed to provide theoretical basis and research ways to predictive control of the complex network control systems.
2016, 45(4): 573-581.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.010
Abstract:
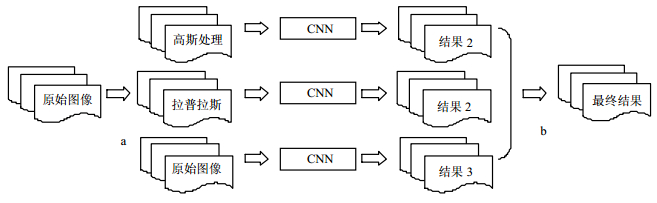
This paper presents a method based on multi-modal convolution neural networks to segment the brain CT angiography image (CTA) for brain vessel. This method firstly processes the original image by adopting the Gaussian and Laplacian filter, respectively, and constructs the multi model image as the input by combining processed images with the original image together. Next, these multi model images will be respectively segmented through a number of parallel convolutional neural networks. Finally, all the segmentation results are fused by employing the linear regression to extract the brain vessel. By evaluating the experiment with the real data acquired from the hospital, it can be proved that the convolution neural network is an effective method for segmenting the cerebral vessels. Moreover, the final result shows that our proposed segmenting method is more accurate than the existing algorithms.
This paper presents a method based on multi-modal convolution neural networks to segment the brain CT angiography image (CTA) for brain vessel. This method firstly processes the original image by adopting the Gaussian and Laplacian filter, respectively, and constructs the multi model image as the input by combining processed images with the original image together. Next, these multi model images will be respectively segmented through a number of parallel convolutional neural networks. Finally, all the segmentation results are fused by employing the linear regression to extract the brain vessel. By evaluating the experiment with the real data acquired from the hospital, it can be proved that the convolution neural network is an effective method for segmenting the cerebral vessels. Moreover, the final result shows that our proposed segmenting method is more accurate than the existing algorithms.
2016, 45(4): 582-588.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.011
Abstract:
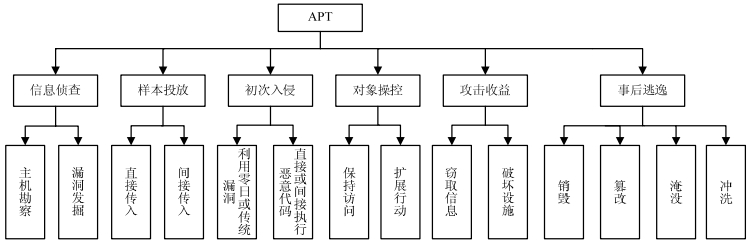
In recent years, advanced persistent threat (APT) has become one of the most important factors threatening cyber security. However, due to the complicated attacking method and strong conceal ability of APT, it is very hard to predict APT using the common boundary protection technique based on feature matching. To solve the problem of APT attack detection and defense, we propose an APT attacks prediction method based on tree structure. An APT exfiltration model of an attack target combing the kill chain model with stage characteristics is first constructed. And then the correlation analysis of massive logs is conducted to formulate attack events context, and the credibility ratio and DS evidence theory are introduced to determine true attack events. Finally, all possible attack paths are calculated. Experimental results show that our proposed method can predict APT attacks, and it can obtain good scalability and practicability.
In recent years, advanced persistent threat (APT) has become one of the most important factors threatening cyber security. However, due to the complicated attacking method and strong conceal ability of APT, it is very hard to predict APT using the common boundary protection technique based on feature matching. To solve the problem of APT attack detection and defense, we propose an APT attacks prediction method based on tree structure. An APT exfiltration model of an attack target combing the kill chain model with stage characteristics is first constructed. And then the correlation analysis of massive logs is conducted to formulate attack events context, and the credibility ratio and DS evidence theory are introduced to determine true attack events. Finally, all possible attack paths are calculated. Experimental results show that our proposed method can predict APT attacks, and it can obtain good scalability and practicability.
2016, 45(4): 589-606.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.012
Abstract:
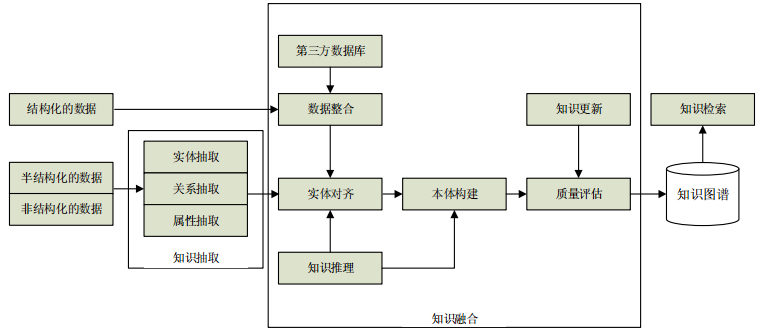
Knowledge graph technology is a critical part of artificial intelligence research. It establishes a knowledge base with the capacity of semantic processing and open interconnection in order to provide intelligent information service, such as search, question-answering, personalized recommendation, and so on. This article first presents a comprehensive study on definitions and architectures of knowledge graphs. Then we summarizes recent advances in knowledge graphs, including knowledge extraction, knowledge representation, knowledge fusion, and knowledge reasoning, with typical applications. Finally, this article concludes with future challenges of knowledge graphs.
Knowledge graph technology is a critical part of artificial intelligence research. It establishes a knowledge base with the capacity of semantic processing and open interconnection in order to provide intelligent information service, such as search, question-answering, personalized recommendation, and so on. This article first presents a comprehensive study on definitions and architectures of knowledge graphs. Then we summarizes recent advances in knowledge graphs, including knowledge extraction, knowledge representation, knowledge fusion, and knowledge reasoning, with typical applications. Finally, this article concludes with future challenges of knowledge graphs.
2016, 45(4): 607-615.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.013
Abstract:
The wrapper feature selection methods can achieve high classification accuracy, however, its cross-validation scheme in evaluation phase is very expensive in terms of computing resource consumption. In this paper, we propose a new statistical LW-measure which can replace the cross-validation scheme to evaluate feature sets. Furthermore, two improved wrapper algorithms, i.e. sequential forward selection-LW (SFS-LW) and sequential backward selection-LW (SBS-LW), are presented for feature selection, on the basis of combination of LW-measure and sequence search algorithms. Three groups of experiments conducted on two University of California, Irvine (UCI) datasets show that the proposed algorithms can not only obtain the similar classification accuracy to that of the traditional wrapper methods, but also are nearly ten times faster than the traditional ones.
The wrapper feature selection methods can achieve high classification accuracy, however, its cross-validation scheme in evaluation phase is very expensive in terms of computing resource consumption. In this paper, we propose a new statistical LW-measure which can replace the cross-validation scheme to evaluate feature sets. Furthermore, two improved wrapper algorithms, i.e. sequential forward selection-LW (SFS-LW) and sequential backward selection-LW (SBS-LW), are presented for feature selection, on the basis of combination of LW-measure and sequence search algorithms. Three groups of experiments conducted on two University of California, Irvine (UCI) datasets show that the proposed algorithms can not only obtain the similar classification accuracy to that of the traditional wrapper methods, but also are nearly ten times faster than the traditional ones.
2016, 45(4): 616-624.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.014
Abstract:
This paper reviews some advances in network science from the perspective of the Internet plus.In retrospect, the first wave of network science studies, Internet plus big data, was set off by foreign scholars in the eve of the new millennium. Next, the second wave of network science studies, Internet plus dynamics, was launched by Chinese scholars. We predict that the third wave of network science studies, Internet plus game theory and pure math, may be about to come. We hope that the young scholars in China will be able to make greater contributions to the future network science.
This paper reviews some advances in network science from the perspective of the Internet plus.In retrospect, the first wave of network science studies, Internet plus big data, was set off by foreign scholars in the eve of the new millennium. Next, the second wave of network science studies, Internet plus dynamics, was launched by Chinese scholars. We predict that the third wave of network science studies, Internet plus game theory and pure math, may be about to come. We hope that the young scholars in China will be able to make greater contributions to the future network science.
2016, 45(4): 625-633.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.015
Abstract:
With the advent of the era of big data, both the quantity and quality of economic activity related data have been enormously enriched and improved. By analyzing these large-scale data from socio-economic systems, we have the opportunity to quantify the status of economic development instantaneously and accurately with nearly no cost. In this paper, focusing on how big data reveal the status of economic development, we briefly summary the applications of different types of big data on quantifying macro-economic structures and micro-social status. Further, we discuss and provide some promising ways to apply big data to improve regional economic development strategies and upgrade macro industrial structures.
With the advent of the era of big data, both the quantity and quality of economic activity related data have been enormously enriched and improved. By analyzing these large-scale data from socio-economic systems, we have the opportunity to quantify the status of economic development instantaneously and accurately with nearly no cost. In this paper, focusing on how big data reveal the status of economic development, we briefly summary the applications of different types of big data on quantifying macro-economic structures and micro-social status. Further, we discuss and provide some promising ways to apply big data to improve regional economic development strategies and upgrade macro industrial structures.
2016, 45(4): 634-649.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.016
Abstract:
Materials genome is an emerging technology to accelerate materials discovery, development, and deployment. In the past two decades, high-throughput materials experimentation tools have been developed and applied successfully to the discovery of a number of materials, ranging from advanced catalysts, dielectrics, electrodes, to high-temperature alloys. Materials computation and database technologies have also made remarkable progresses, particularly represented by the integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) developed in the past decade. Materials genome research integrates high-throughput computation and simulation, high-throughput experimentation, and materials database, throughout the materials discovery-to-deployment process, targeting to cut the materials development time and cost significantly. This review, is trying to give a brief and comprehensive introduction to materials genome technologies, with emphasis on high-throughput materials experimentation, as well as applications of materials computation and database. University of Electronics Science and Technology of China is one of the most active institutes in China in the filed of materials genome research, and some progresses are also highlighted in this review.
Materials genome is an emerging technology to accelerate materials discovery, development, and deployment. In the past two decades, high-throughput materials experimentation tools have been developed and applied successfully to the discovery of a number of materials, ranging from advanced catalysts, dielectrics, electrodes, to high-temperature alloys. Materials computation and database technologies have also made remarkable progresses, particularly represented by the integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) developed in the past decade. Materials genome research integrates high-throughput computation and simulation, high-throughput experimentation, and materials database, throughout the materials discovery-to-deployment process, targeting to cut the materials development time and cost significantly. This review, is trying to give a brief and comprehensive introduction to materials genome technologies, with emphasis on high-throughput materials experimentation, as well as applications of materials computation and database. University of Electronics Science and Technology of China is one of the most active institutes in China in the filed of materials genome research, and some progresses are also highlighted in this review.
2016, 45(4): 664-673.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.019
Abstract:
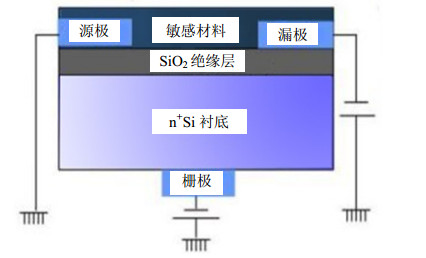
This paper discusses the research progress of organic thin film transistors (OTFT) gas sensors in the State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, under the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China. In this work, organic thin film transistor with a bottom-gate bottom-contact type structure was used as the sensor element, the preparation process and structure parameters of the device were optimized, and the sensing properties of copper phthalocyanine (CuPc) film to H2S were studied. Besides, the OTFT gas sensor based on P3HT-ZnO nanorods composite film, P3HT single-layer film, P3HT-MoS2 composite and layered film was fabricated. Furthermore, the electrical properties and gas sensing performance of OTFT device were analyzed systematically.
This paper discusses the research progress of organic thin film transistors (OTFT) gas sensors in the State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, under the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China. In this work, organic thin film transistor with a bottom-gate bottom-contact type structure was used as the sensor element, the preparation process and structure parameters of the device were optimized, and the sensing properties of copper phthalocyanine (CuPc) film to H2S were studied. Besides, the OTFT gas sensor based on P3HT-ZnO nanorods composite film, P3HT single-layer film, P3HT-MoS2 composite and layered film was fabricated. Furthermore, the electrical properties and gas sensing performance of OTFT device were analyzed systematically.
2016, 45(4): 674-683.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.020
Abstract:
Establishing system equivalences for event structures such as trace and testing equivalences, require the observed actions to be exactly identical. However, an accurate measurement is impossible when interacting with the physical world, hence exact equivalence is restrictive and not robust. Using Baire metric, this paper proposes a generalized framework of event structures approximation by developing the notions of approximate interleaving (trace and singleton failures) equivalence and approximate step (trace and singleton failures) equivalence. The proposed framework captures the traditional exact equivalence as a special case. These approximate equivalences satisfy the transitive property, consequently, they can be successively used in event structures approximations.
Establishing system equivalences for event structures such as trace and testing equivalences, require the observed actions to be exactly identical. However, an accurate measurement is impossible when interacting with the physical world, hence exact equivalence is restrictive and not robust. Using Baire metric, this paper proposes a generalized framework of event structures approximation by developing the notions of approximate interleaving (trace and singleton failures) equivalence and approximate step (trace and singleton failures) equivalence. The proposed framework captures the traditional exact equivalence as a special case. These approximate equivalences satisfy the transitive property, consequently, they can be successively used in event structures approximations.
2016, 45(4): 684-688.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.021
Abstract:
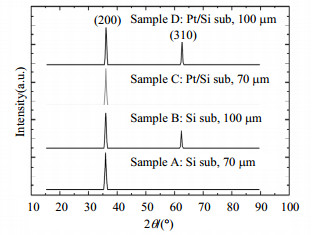
Thallium doped cesium iodide (CsI(Tl)) scintillator films are widely used for their dense micro-columnar structure. In this work, CsI(Tl) films with different thickness were fabricated on monocrystalline silicon substrate and polycrystalline Pt/Si substrate by the thermal deposition method. These scintillator films with different thickness were manufactured under the same process conditions and prepared for experiments. The microcrystalline column structures were different during the thickness of films. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to investigate the crystal quality and microcrystalline column morphology. The microstructure model of the CsI(Tl) film was built to illustrate the influence of the interplanar spacing on microcrystalline column structures of the monocrystalline film.
Thallium doped cesium iodide (CsI(Tl)) scintillator films are widely used for their dense micro-columnar structure. In this work, CsI(Tl) films with different thickness were fabricated on monocrystalline silicon substrate and polycrystalline Pt/Si substrate by the thermal deposition method. These scintillator films with different thickness were manufactured under the same process conditions and prepared for experiments. The microcrystalline column structures were different during the thickness of films. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to investigate the crystal quality and microcrystalline column morphology. The microstructure model of the CsI(Tl) film was built to illustrate the influence of the interplanar spacing on microcrystalline column structures of the monocrystalline film.
2016, 45(4): 689-695.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.022
Abstract:
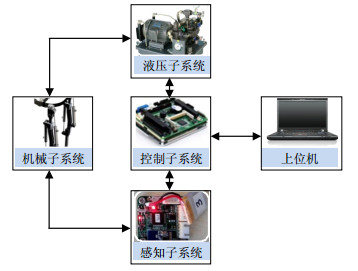
A learning-based adaptive impedance control algorithm for a human-powered augmentation lower exoskeleton (HUALEX) is presented. The HUALEX system architecture is introduced first, which is divided into three parts including the mechanical subsystems, the sensing subsystem and the control subsystem. By using impedance control method, the inverse dynamics model of HUALEX is established and the control effect of impedance parameters is studied. And then, a reinforcement learning-based adaptive impedance control algorithm, including the reinforcement learning, PI2 (policy improvement with path integrals) learning algorithm and adaptive impedance control, is proposed. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified simulation experiment.
A learning-based adaptive impedance control algorithm for a human-powered augmentation lower exoskeleton (HUALEX) is presented. The HUALEX system architecture is introduced first, which is divided into three parts including the mechanical subsystems, the sensing subsystem and the control subsystem. By using impedance control method, the inverse dynamics model of HUALEX is established and the control effect of impedance parameters is studied. And then, a reinforcement learning-based adaptive impedance control algorithm, including the reinforcement learning, PI2 (policy improvement with path integrals) learning algorithm and adaptive impedance control, is proposed. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified simulation experiment.
2016, 45(4): 701-706.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.024
Abstract:
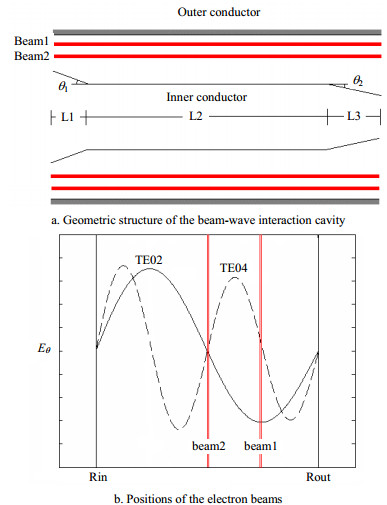
The dual-frequency operation coaxial gyrotron with two electron beams is investigated in this paper. The results of the numerical calculation and particle in cell (PIC) simulation show that the coaxial gyrotron with two electron beams (CGTB) can operate at two different frequencies simultaneously. In addition, the power of the high harmonic can be enhanced due to the nonlinear coupling between two electron beams. The prototype of CGTB was fabricated and the verification experiment was conducted. The operation frequencies are at 0.11 THz and 0.22 THz, and the output power is about 20 kW. A method to separate the radiations from a dual-frequency operation gyrotron is also proposed.
The dual-frequency operation coaxial gyrotron with two electron beams is investigated in this paper. The results of the numerical calculation and particle in cell (PIC) simulation show that the coaxial gyrotron with two electron beams (CGTB) can operate at two different frequencies simultaneously. In addition, the power of the high harmonic can be enhanced due to the nonlinear coupling between two electron beams. The prototype of CGTB was fabricated and the verification experiment was conducted. The operation frequencies are at 0.11 THz and 0.22 THz, and the output power is about 20 kW. A method to separate the radiations from a dual-frequency operation gyrotron is also proposed.
2016, 45(4): 707-711.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.025
Abstract:
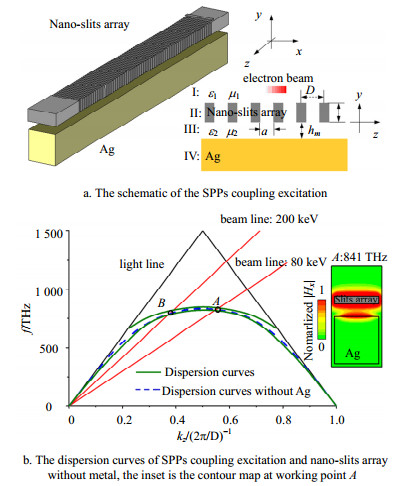
A novel mechanism of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) electron beam excitation is presented in this paper. The mimicking surface plasmon polaritons (MSPPs) on the nano-slits array excited by parallel moving electron beam are used to couple coherent and tunable SPPs on the metal surface. The results of numerical calculations and particle-in-cell simulations show that it brings many significant advantages to SPPs excitation. Based on this mechanism, SPPs can be coupled efficiently, regardless of the distance between the metal surface and the electron beam. The decay time of the coupled SPPs is as long as that of the excited MSPPs, and the amplitudes of the coupled SPPs are two orders of magnitude larger than that of SPPs excited by electron beam directly. Accordingly, this mechanism may bring great significances for the applications of SPPs.
A novel mechanism of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) electron beam excitation is presented in this paper. The mimicking surface plasmon polaritons (MSPPs) on the nano-slits array excited by parallel moving electron beam are used to couple coherent and tunable SPPs on the metal surface. The results of numerical calculations and particle-in-cell simulations show that it brings many significant advantages to SPPs excitation. Based on this mechanism, SPPs can be coupled efficiently, regardless of the distance between the metal surface and the electron beam. The decay time of the coupled SPPs is as long as that of the excited MSPPs, and the amplitudes of the coupled SPPs are two orders of magnitude larger than that of SPPs excited by electron beam directly. Accordingly, this mechanism may bring great significances for the applications of SPPs.

 ISSN
ISSN