2016 Vol. 45, No. 6
2016, 45(6): 873-887.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.001
Abstract:
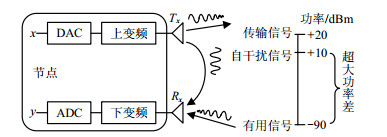
In-band full-duplex (IBFD) wireless communication, which allows nodes to transmit and receive simultaneously in the same frequency band, can double spectral efficiency theoretically compared with conventional duplex. The survey presents an analysis of the main technical problems of IBFD wireless full duplex communication to be solved, and summarizes the research progress systematically. The system models and key technologies of IBFD wireless communication are introduced, especially emphasizing the research of self-interference cancellation methods, MAC (Medium Access Control) protocols and scheduling mechanisms. Finally, combined with current research and application focuses, the future trends and main research directions of IBFD wireless communication are discussed.
In-band full-duplex (IBFD) wireless communication, which allows nodes to transmit and receive simultaneously in the same frequency band, can double spectral efficiency theoretically compared with conventional duplex. The survey presents an analysis of the main technical problems of IBFD wireless full duplex communication to be solved, and summarizes the research progress systematically. The system models and key technologies of IBFD wireless communication are introduced, especially emphasizing the research of self-interference cancellation methods, MAC (Medium Access Control) protocols and scheduling mechanisms. Finally, combined with current research and application focuses, the future trends and main research directions of IBFD wireless communication are discussed.
2016, 45(6): 888-892.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.002
Abstract:
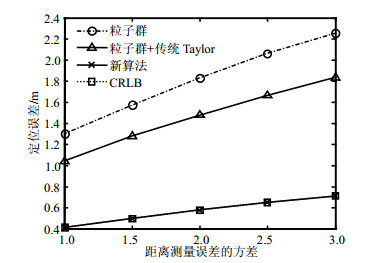
Conventional Taylor series expansion model only considers the distances between unknown nodes and anchor nodes, without considering the distances between unknown nodes. As a result, the location information is not comprehensive enough to result in lower positioning accuracy. Thus, a novel localization algorithm based on multivariable Taylor series expansion model is proposed to further enhance positioning accuracy. Firstly, the new positioning model which considers the distances between unknown nodes in multivariable Taylor series expansion is established. In the process of model solution, the particle swarm algorithm is used to obtain the estimated position values of the unknown nodes. Then, the optimal position values are obtained by the weighted least squares method. Finally, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the positioning result is derived to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm obtains a higher positioning accuracy, and its positioning error is very close to the CRLB.
Conventional Taylor series expansion model only considers the distances between unknown nodes and anchor nodes, without considering the distances between unknown nodes. As a result, the location information is not comprehensive enough to result in lower positioning accuracy. Thus, a novel localization algorithm based on multivariable Taylor series expansion model is proposed to further enhance positioning accuracy. Firstly, the new positioning model which considers the distances between unknown nodes in multivariable Taylor series expansion is established. In the process of model solution, the particle swarm algorithm is used to obtain the estimated position values of the unknown nodes. Then, the optimal position values are obtained by the weighted least squares method. Finally, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the positioning result is derived to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm obtains a higher positioning accuracy, and its positioning error is very close to the CRLB.
2016, 45(6): 893-897.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.003
Abstract:
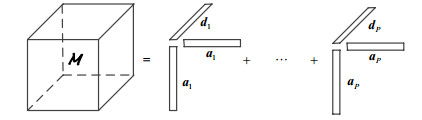
In view of the estimation problem of mixing matrix in the underdetermined blind source separation (UBSS), a novel underdetermined blind identification algorithm is proposed. This proposed algorithm employs the statistical and structure properties of generalized covariance and the compressive characteristic of Tucker decomposition. Firstly, the core functions are built based on generalized covariance matrix. Then the core functions are stacked as a three-order tensor, and the tucker decomposition of constructed tensor is executed to estimate the mixing matrix. The proposed algorithm has not only the better identification performance, but also the lower computational complexity. At last, the simulation experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
In view of the estimation problem of mixing matrix in the underdetermined blind source separation (UBSS), a novel underdetermined blind identification algorithm is proposed. This proposed algorithm employs the statistical and structure properties of generalized covariance and the compressive characteristic of Tucker decomposition. Firstly, the core functions are built based on generalized covariance matrix. Then the core functions are stacked as a three-order tensor, and the tucker decomposition of constructed tensor is executed to estimate the mixing matrix. The proposed algorithm has not only the better identification performance, but also the lower computational complexity. At last, the simulation experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
2016, 45(6): 898-904.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.004
Abstract:
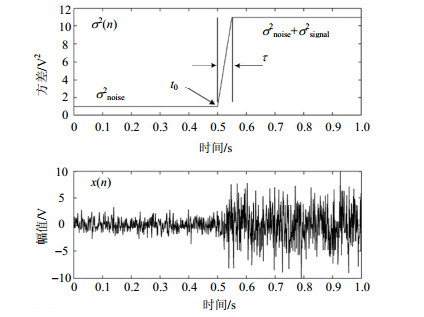
Recognizing hand movements by using surface electromyography (sEMG) signal in real time and accurately is an important aspect of the application of sEMG signal. Hand movements onset detection from sEMG signals is the precondition of real-time hand movements recognizing. In this paper, The study aims at detecting the hand movement onset based on the consecutive sEMG signal. The sEMG signal is preprocessed by using the teager-kaiser energy (TKE) operator and a sEMG signal state binary function is designed to detect the hand movement onset from the consecutive sEMG signal. Then we design a heuristic filter according to the actual sEMG signal character. The detected results are filtered further by the heuristic filter which can cancel the effects of noise. We compare the application several methods for the simulation model. It proves the validity of TKE operator method. In the end, using sEMG signal acquisition and processing system for experimental verification, the results show that the detection method can rival action initiated for high precision of real-time detection.
Recognizing hand movements by using surface electromyography (sEMG) signal in real time and accurately is an important aspect of the application of sEMG signal. Hand movements onset detection from sEMG signals is the precondition of real-time hand movements recognizing. In this paper, The study aims at detecting the hand movement onset based on the consecutive sEMG signal. The sEMG signal is preprocessed by using the teager-kaiser energy (TKE) operator and a sEMG signal state binary function is designed to detect the hand movement onset from the consecutive sEMG signal. Then we design a heuristic filter according to the actual sEMG signal character. The detected results are filtered further by the heuristic filter which can cancel the effects of noise. We compare the application several methods for the simulation model. It proves the validity of TKE operator method. In the end, using sEMG signal acquisition and processing system for experimental verification, the results show that the detection method can rival action initiated for high precision of real-time detection.
2016, 45(6): 905-910, 916.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.005
Abstract:
The heterogeneous clutter results in degradation of clutter suppression performance of space-time adaptive processing (STAP). To solve this problem, a subspace method is proposed based on the radar parameters and the time-limited and band-limited features of the prolate spheroidal wave functions. The method can improve the clutter suppression performance in heterogeneous environment, reduce the computational complexity and demand for homogeneous samples. However, it is hard to estimate the precise clutter rank if the proposed method suffers from crab angle. Therefore, with the radar parameters and the detection environment geometry, a pre-process method is presented to eliminate the crab influence and improve the clutter suppression performance in heterogeneous environment. Finally, simulation attests its effectiveness.
The heterogeneous clutter results in degradation of clutter suppression performance of space-time adaptive processing (STAP). To solve this problem, a subspace method is proposed based on the radar parameters and the time-limited and band-limited features of the prolate spheroidal wave functions. The method can improve the clutter suppression performance in heterogeneous environment, reduce the computational complexity and demand for homogeneous samples. However, it is hard to estimate the precise clutter rank if the proposed method suffers from crab angle. Therefore, with the radar parameters and the detection environment geometry, a pre-process method is presented to eliminate the crab influence and improve the clutter suppression performance in heterogeneous environment. Finally, simulation attests its effectiveness.
2016, 45(6): 911-916.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.006
Abstract:
In the process of ballistic missile defense, the key to carry out missile intercept is whether the phased array radar could capture the target rapidly under the guidance of early warning satellite. Some key problems are studied in this paper, aiming at the problem of search area definition of precision tracking radar under the guidance of low earth orbit (LEO) early warning satellite. Taking the space transportation system (STSS) of the USA as the study object, the detecting precision of multi-satellite is analyzed firstly, the CramérRao Bound of position error is taken to express detection precision of tracking satellite, and then the expression and transmission of measurement error under different coordinates system are discussed. Finally, the search area of phased array radar under pointing coordinate system is proposed and deduced when searching type of phased array radar is taking into account. The simulation results indicate that when the method is adopted, the search area of phased array radar is reduced, making radar searching more purposeful.
In the process of ballistic missile defense, the key to carry out missile intercept is whether the phased array radar could capture the target rapidly under the guidance of early warning satellite. Some key problems are studied in this paper, aiming at the problem of search area definition of precision tracking radar under the guidance of low earth orbit (LEO) early warning satellite. Taking the space transportation system (STSS) of the USA as the study object, the detecting precision of multi-satellite is analyzed firstly, the CramérRao Bound of position error is taken to express detection precision of tracking satellite, and then the expression and transmission of measurement error under different coordinates system are discussed. Finally, the search area of phased array radar under pointing coordinate system is proposed and deduced when searching type of phased array radar is taking into account. The simulation results indicate that when the method is adopted, the search area of phased array radar is reduced, making radar searching more purposeful.
2016, 45(6): 917-922.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.007
Abstract:
The staring observation of a certain region for geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) is very important application. Due to the big SAR echo range migration in staring imaging which makes the signal reception window be difficult to choose, a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) variation method for geosynchronous orbit staring imaging is put forward. Firstly, the design criterion of pulse repetition frequency variation is given, and then both of the location of the missing pulse and the influence on imaging quality owing to pulse repetition frequency (PRF) variation are deduced in detail. The back projection (BP) algorithm is adapted to non-uniform sampling signal imaging focusing. Finally, the simulation is used to verify the effectiveness of the PRF variation. Numerical simulations have demonstrated the effectiveness of the approach proposed.
The staring observation of a certain region for geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) is very important application. Due to the big SAR echo range migration in staring imaging which makes the signal reception window be difficult to choose, a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) variation method for geosynchronous orbit staring imaging is put forward. Firstly, the design criterion of pulse repetition frequency variation is given, and then both of the location of the missing pulse and the influence on imaging quality owing to pulse repetition frequency (PRF) variation are deduced in detail. The back projection (BP) algorithm is adapted to non-uniform sampling signal imaging focusing. Finally, the simulation is used to verify the effectiveness of the PRF variation. Numerical simulations have demonstrated the effectiveness of the approach proposed.
2016, 45(6): 923-928.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.008
Abstract:
Conventional forecasting methods cannot systematically analyze the aggregation of space and time in multidimensional parameter analysis. To solve the problem, a prediction method based on discrete process neural networks is proposed in this paper. In order to avoid choosing a local optimal solution during the training of the net, the chaotic particle swarm optimization algorithm is introduced in the process of training. Finally, a case study is presented to illustrate the validity of the proposed method.
Conventional forecasting methods cannot systematically analyze the aggregation of space and time in multidimensional parameter analysis. To solve the problem, a prediction method based on discrete process neural networks is proposed in this paper. In order to avoid choosing a local optimal solution during the training of the net, the chaotic particle swarm optimization algorithm is introduced in the process of training. Finally, a case study is presented to illustrate the validity of the proposed method.
2016, 45(6): 929-933.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.009
Abstract:
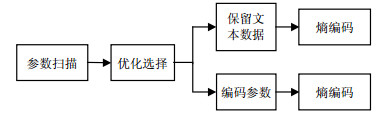
A novel algorithm for text data compression is proposed based on arithmetic codec. The global parameters optimization is converted into the local parameter optimization, then Glomb code principle is used to solve the local optimization, and a parameter choice method is derived. The LZ77 scanning algorithm is improved in which a prediction code is proposed, and the prediction data is preserved. The parameters such as prediction data, offset, match data length and preserved text data are loaded into MQ codec in which the data can be compressed. To improve the compression efficiency, the corresponding compression algorithms and the context design algorithm are proposed. The proposed algorithm for text data compression is simulated and compared with Winzip and WinRAR. The results show that our compression algorithm has an advantage in compression effect over the Winzip for the data such as texts, word documents, C language program codes and images. Compared with WinRar, our algorithm achieved almost the same compression results for texts, word documents, C language program codes except images.
A novel algorithm for text data compression is proposed based on arithmetic codec. The global parameters optimization is converted into the local parameter optimization, then Glomb code principle is used to solve the local optimization, and a parameter choice method is derived. The LZ77 scanning algorithm is improved in which a prediction code is proposed, and the prediction data is preserved. The parameters such as prediction data, offset, match data length and preserved text data are loaded into MQ codec in which the data can be compressed. To improve the compression efficiency, the corresponding compression algorithms and the context design algorithm are proposed. The proposed algorithm for text data compression is simulated and compared with Winzip and WinRAR. The results show that our compression algorithm has an advantage in compression effect over the Winzip for the data such as texts, word documents, C language program codes and images. Compared with WinRar, our algorithm achieved almost the same compression results for texts, word documents, C language program codes except images.
2016, 45(6): 934-938.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.010
Abstract:
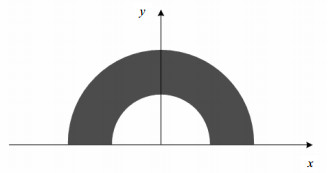
The design and detection of landmark and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) pose estimation are key points in the process of UAV autonomous landing based on computer vision. This paper proposes a pose estimation algorithm based on polar coordinates transform and designs a new landmark. Firstly, the polar coordinates transform is applied to the pose estimation algorithm for its related parameters are few and low computational complexity, then a landmark with hemi-toroidal shape is designed. Secondly, the saliency detection algorithm is used to detect the landmark, which is accurate, fast and robust to clutter background. Then the Hough transform algorithm is used to extract the lines of the detected landmark. Lastly, the experimental results show that the landmark is feasible in the process of UAV autonomous landing.
The design and detection of landmark and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) pose estimation are key points in the process of UAV autonomous landing based on computer vision. This paper proposes a pose estimation algorithm based on polar coordinates transform and designs a new landmark. Firstly, the polar coordinates transform is applied to the pose estimation algorithm for its related parameters are few and low computational complexity, then a landmark with hemi-toroidal shape is designed. Secondly, the saliency detection algorithm is used to detect the landmark, which is accurate, fast and robust to clutter background. Then the Hough transform algorithm is used to extract the lines of the detected landmark. Lastly, the experimental results show that the landmark is feasible in the process of UAV autonomous landing.
2016, 45(6): 939-943.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.011
Abstract:
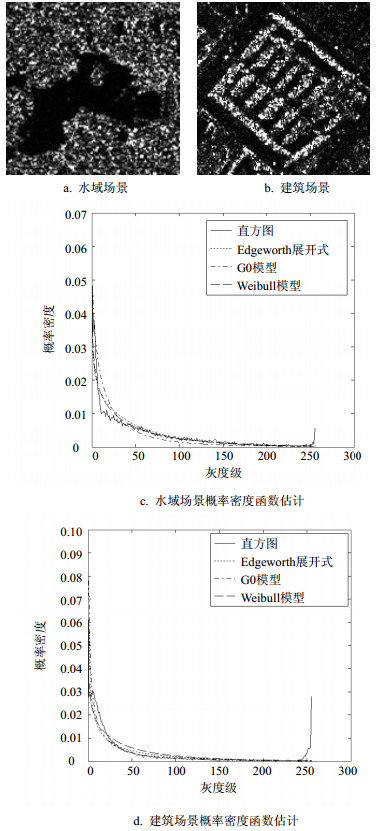
In this paper, a multi-region segmentation method for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images based on a parametric model is proposed. The modified Edgeworth expansion series method is employed to fit the statistical information of the SAR image adaptively. Since the estimation of the probability density function of the SAR image is not required, it is more suited for the multi-region segmentation. Based on the number of the segmentation, the modified Edgeworth expansion series is introduced to the corresponding energy functional model and then the solution based on the level set and its numerical method are developed, thus attaining the segmentation. The experimental results indicate that the higher accuracy of the segmentation is achieved by the proposed method compared with those by the other methods, and the proposed method is more suitable for the multi-region segmentation.
In this paper, a multi-region segmentation method for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images based on a parametric model is proposed. The modified Edgeworth expansion series method is employed to fit the statistical information of the SAR image adaptively. Since the estimation of the probability density function of the SAR image is not required, it is more suited for the multi-region segmentation. Based on the number of the segmentation, the modified Edgeworth expansion series is introduced to the corresponding energy functional model and then the solution based on the level set and its numerical method are developed, thus attaining the segmentation. The experimental results indicate that the higher accuracy of the segmentation is achieved by the proposed method compared with those by the other methods, and the proposed method is more suitable for the multi-region segmentation.
2016, 45(6): 944-949.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.012
Abstract:
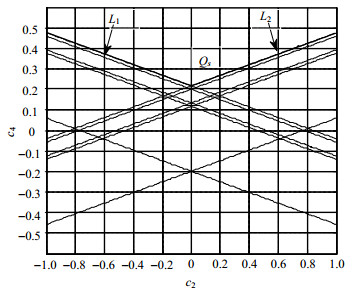
A parametric stabilization method is proposed for the problem of Hopf bifurcation system control. Compared with the existing methods, the controller designed by this method has a lower controller order and a simpler structure, and it does not contain equilibrium points. The method keeps equilibrium of the origin system unchanged. Under the control, the characteristics of the original system will be improved at equilibrium, and the system states of Hopf bifurcation or chaos can be controlled to stable. Using the Hurwitz criterion, the constraints of the parametric controller are derived. The idea of cylindrical algebraic decomposition (CAD) is employed to compute the constraints to find the parameter ranges of the designed controller, and the controller can be designed to stabilize the system by using any feasible control parameters in the ranges. Taking Lorenz system as an example, the controller design process of the method and numerical simulations are discussed. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
A parametric stabilization method is proposed for the problem of Hopf bifurcation system control. Compared with the existing methods, the controller designed by this method has a lower controller order and a simpler structure, and it does not contain equilibrium points. The method keeps equilibrium of the origin system unchanged. Under the control, the characteristics of the original system will be improved at equilibrium, and the system states of Hopf bifurcation or chaos can be controlled to stable. Using the Hurwitz criterion, the constraints of the parametric controller are derived. The idea of cylindrical algebraic decomposition (CAD) is employed to compute the constraints to find the parameter ranges of the designed controller, and the controller can be designed to stabilize the system by using any feasible control parameters in the ranges. Taking Lorenz system as an example, the controller design process of the method and numerical simulations are discussed. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2016, 45(6): 950-957.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.013
Abstract:
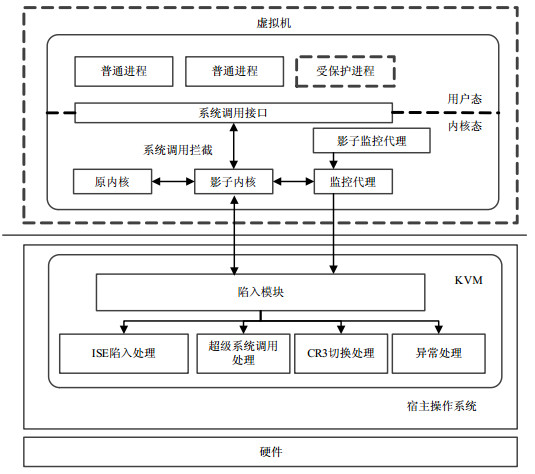
To protect the process memory and execution paths of system calls from the threat of malicious code on Windows virtual machine, a KVM-based virtual machine user process protection solution is proposed. Combined with hardware virtualization technologies, a shadow kernel is built for Windows virtual machine to protect the original kernel system call paths from being hooked by malicious code. Meanwhile, the process memory is secured through filtering out-of-process system calls in the monitoring agent, intercepting the switching behaviors of page tables, monitoring the exceptions of breakpoints, and debugging of the virtual machine. In addition, a shadow monitoring agent is built to safeguard the virtual machine's monitor agent memory. A prototype system VMPPS was thus designed and implemented with its validity tests and analysis results showing that process memory and execution paths of system calls of the virtual machine are effectively protected within an acceptable performance loss range.
To protect the process memory and execution paths of system calls from the threat of malicious code on Windows virtual machine, a KVM-based virtual machine user process protection solution is proposed. Combined with hardware virtualization technologies, a shadow kernel is built for Windows virtual machine to protect the original kernel system call paths from being hooked by malicious code. Meanwhile, the process memory is secured through filtering out-of-process system calls in the monitoring agent, intercepting the switching behaviors of page tables, monitoring the exceptions of breakpoints, and debugging of the virtual machine. In addition, a shadow monitoring agent is built to safeguard the virtual machine's monitor agent memory. A prototype system VMPPS was thus designed and implemented with its validity tests and analysis results showing that process memory and execution paths of system calls of the virtual machine are effectively protected within an acceptable performance loss range.
2016, 45(6): 958-963.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.014
Abstract:
With the widespread use of Linux operating systems, security problems is gradually exposed and become a hot topic because of excessive root privileges. To solve this problem and enhance security of Linux operating system, firstly, we model the separation of privilege, which divides the privilege of Linux system into three roles, system administrator, security administrator, and auditor. Then, this paper designs and implements the separation of privilege mechanism based on the SELinux's mandatory access control technology, which can define fine-grained permissions and security policy for each role and control user's access strictly. Finally, we implement a prototype system based on the embedded platform, which verifies the correctness and feasibility of our approaches presented in this paper. These approaches presented in this paper can be used in Linux operating system to enhance system security.
With the widespread use of Linux operating systems, security problems is gradually exposed and become a hot topic because of excessive root privileges. To solve this problem and enhance security of Linux operating system, firstly, we model the separation of privilege, which divides the privilege of Linux system into three roles, system administrator, security administrator, and auditor. Then, this paper designs and implements the separation of privilege mechanism based on the SELinux's mandatory access control technology, which can define fine-grained permissions and security policy for each role and control user's access strictly. Finally, we implement a prototype system based on the embedded platform, which verifies the correctness and feasibility of our approaches presented in this paper. These approaches presented in this paper can be used in Linux operating system to enhance system security.
2016, 45(6): 964-968.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.015
Abstract:
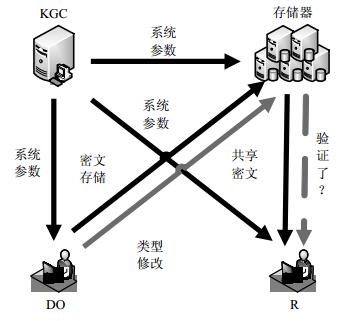
Dynamic type information of ciphertext can be modified properly so that it can be well applied in a practical cloud storage environment. In order to meet the application requirements, Liu et al proposed a dynamic type and identity-based proxy re-encryption (PRE) scheme based on Ibraimi et al's scheme. Their scheme not only keeps the traditional core function of PRE scheme, but also makes sure that the owner of ciphertext can modify the type information at any time. However, after careful security analysis it found that Liu et al.'s scheme has two security flaws. Firstly, the dynamic type information lacks of verification, the adversary can modify the type tag. Secondly, the dynamic type information causes a conditional chosen plaintext attack. Thus we further improve Liu et al.'s scheme and give the security analysis.
Dynamic type information of ciphertext can be modified properly so that it can be well applied in a practical cloud storage environment. In order to meet the application requirements, Liu et al proposed a dynamic type and identity-based proxy re-encryption (PRE) scheme based on Ibraimi et al's scheme. Their scheme not only keeps the traditional core function of PRE scheme, but also makes sure that the owner of ciphertext can modify the type information at any time. However, after careful security analysis it found that Liu et al.'s scheme has two security flaws. Firstly, the dynamic type information lacks of verification, the adversary can modify the type tag. Secondly, the dynamic type information causes a conditional chosen plaintext attack. Thus we further improve Liu et al.'s scheme and give the security analysis.
2016, 45(6): 969-973.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.016
Abstract:
Witness encryption (WE) is a new type of encryption scheme without key generation. It can be used for construction of many other cryptosystems such as public key encryption, IBE, ABE, etc. A new WE application is presented, i.e., the construction of revocable broadcast encryption (BE) based on WE. The constructed BE scheme also supports a simple re-membership function, which is suitable for applications like pay-TV etc. In the construction, we also point out that the original security definition of WE is not strong enough. So we strengthen the original WE security definition and construct a WE scheme satisfying this new definition based on the original WE scheme, hard subset membership problem and random oracle model.
Witness encryption (WE) is a new type of encryption scheme without key generation. It can be used for construction of many other cryptosystems such as public key encryption, IBE, ABE, etc. A new WE application is presented, i.e., the construction of revocable broadcast encryption (BE) based on WE. The constructed BE scheme also supports a simple re-membership function, which is suitable for applications like pay-TV etc. In the construction, we also point out that the original security definition of WE is not strong enough. So we strengthen the original WE security definition and construct a WE scheme satisfying this new definition based on the original WE scheme, hard subset membership problem and random oracle model.
2016, 45(6): 974-980.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.017
Abstract:
The existing workflow task scheduling schemes in cloud computing environment are analyzed, For the issues of the long operation time and low resource utilization, a workflow task scheduling scheme base on hybrid improved cuckoo search and decision tree in cloud computing is proposed. First, the deadline is assigned according to the work-flow task attribute; then, the improved cuckoo search algorithm is used to split the workflow into several sub workflow, minimizing data dependent; then, the decision tree is used to choose the resources which meet the QoS constraints of tasks; finally, the deadline constraints to be satisfied is judged according to satisfy according to the sum of task computing time, queuing time and communication delay, so as to configure the appropriate resources. Experimental results show that the proposed scheme has shorter total running time and higher task completion rate.
The existing workflow task scheduling schemes in cloud computing environment are analyzed, For the issues of the long operation time and low resource utilization, a workflow task scheduling scheme base on hybrid improved cuckoo search and decision tree in cloud computing is proposed. First, the deadline is assigned according to the work-flow task attribute; then, the improved cuckoo search algorithm is used to split the workflow into several sub workflow, minimizing data dependent; then, the decision tree is used to choose the resources which meet the QoS constraints of tasks; finally, the deadline constraints to be satisfied is judged according to satisfy according to the sum of task computing time, queuing time and communication delay, so as to configure the appropriate resources. Experimental results show that the proposed scheme has shorter total running time and higher task completion rate.
2016, 45(6): 981-985.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.018
Abstract:
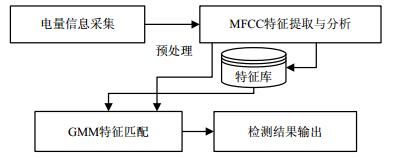
This paper proposes a malicious software detection method based on power consumption. Firstly, the mobile terminal's power consumption status is obtained, and the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is built by using Mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). Then the GMM is used to analyze power consumption, and then identify malicious applications through the application software classification processing. Experiments show that an application software function and its power consumption have a close relationship, and some malicious applications in mobile terminals can be detected accurately through analyzing software power consumption information.
This paper proposes a malicious software detection method based on power consumption. Firstly, the mobile terminal's power consumption status is obtained, and the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is built by using Mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). Then the GMM is used to analyze power consumption, and then identify malicious applications through the application software classification processing. Experiments show that an application software function and its power consumption have a close relationship, and some malicious applications in mobile terminals can be detected accurately through analyzing software power consumption information.
2016, 45(6): 986-991.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.019
Abstract:
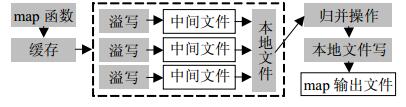
It is difficult to predict the amount of memory for a mapreduce job. Based on the fact that Java virtual machine (JVM) divides the heap space managed by the JVM garbage collector into young and old generations, a generational memory prediction method is put forward. We build up a function that models the relationship between the amount of young generation and the total garbage collection time, and then we use a constrained nonlinear optimization model to find the rational footprint of young generation. The memory model for the map phase is established, the phase of a mapreduce job is reduced, then a relationship between map/reduce tasks' performance (runtime of a task) and the amount of memory of the old generation is set up, and finally, the reasonable old generation memory size is obtained. The experimental results show that the proposed approach can accurately predict the memory size of map and reduce the tasks of a mapreduce job. In comparison with the default configuration, the proposed approach can give us 6 times performance improvement than default settings.
It is difficult to predict the amount of memory for a mapreduce job. Based on the fact that Java virtual machine (JVM) divides the heap space managed by the JVM garbage collector into young and old generations, a generational memory prediction method is put forward. We build up a function that models the relationship between the amount of young generation and the total garbage collection time, and then we use a constrained nonlinear optimization model to find the rational footprint of young generation. The memory model for the map phase is established, the phase of a mapreduce job is reduced, then a relationship between map/reduce tasks' performance (runtime of a task) and the amount of memory of the old generation is set up, and finally, the reasonable old generation memory size is obtained. The experimental results show that the proposed approach can accurately predict the memory size of map and reduce the tasks of a mapreduce job. In comparison with the default configuration, the proposed approach can give us 6 times performance improvement than default settings.
2016, 45(6): 992-996.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.020
Abstract:
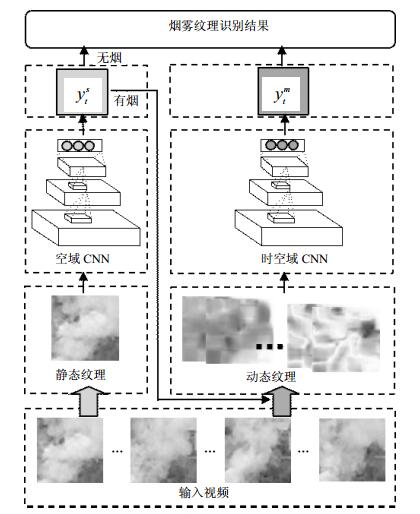
The extraction of stable smoke features in complex scenes is a challenging task for video based smoke detection. For this issue, a convolutional neural network (CNN) framework which employs both static and dynamic features of the smoke is proposed. On the basis of analyzing the static features of individual frame, we further explore the dynamic features in spatial-temporal domain to reduce the influence of the noise from environment. Experimental results show that the proposed cascaded convolutional neural network framework performs well in real-time video based smoke detection for complex scenes.
The extraction of stable smoke features in complex scenes is a challenging task for video based smoke detection. For this issue, a convolutional neural network (CNN) framework which employs both static and dynamic features of the smoke is proposed. On the basis of analyzing the static features of individual frame, we further explore the dynamic features in spatial-temporal domain to reduce the influence of the noise from environment. Experimental results show that the proposed cascaded convolutional neural network framework performs well in real-time video based smoke detection for complex scenes.
2016, 45(6): 997-1001.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.021
Abstract:
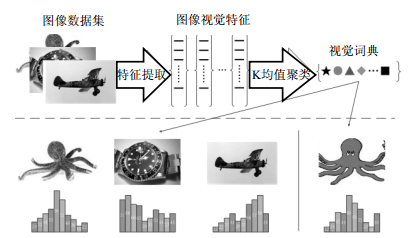
This paper proposes a new framework to improve the efficiency of visual bag-of-words model in large scale image classification. The method is based on the low scale image representation obtained by wavelet transform, and the low scale visual dictionary is built by extracting the SIFT features on the low scale image. Since the feature dimension is reduced, the method can quickly generate the visual dictionary and minimize the time of image classification process. The results of comparison experiments on the 8 677 images of Caltech 101 show that the proposed method can effectively improve the classification performance and efficiency of the traditional visual bag-of-words model and the Pyramid-BOW model.
This paper proposes a new framework to improve the efficiency of visual bag-of-words model in large scale image classification. The method is based on the low scale image representation obtained by wavelet transform, and the low scale visual dictionary is built by extracting the SIFT features on the low scale image. Since the feature dimension is reduced, the method can quickly generate the visual dictionary and minimize the time of image classification process. The results of comparison experiments on the 8 677 images of Caltech 101 show that the proposed method can effectively improve the classification performance and efficiency of the traditional visual bag-of-words model and the Pyramid-BOW model.
2016, 45(6): 1002-1007.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.022
Abstract:
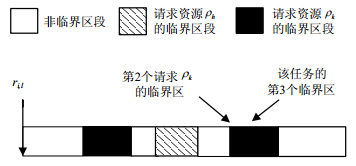
Multiprocessor priority ceiling protocol (MPCP) is a classical suspension-based real-time locking protocol, wildly used in partitioned fixed-priority (P-FP) scheduled multiprocessor/multicore real-time systems. However, prior worst-case task blocking time (WCTBT) analysis is pessimistic, which negatively impacts the system schedulability. Therefore, a novel WCTBT analysis is proposed. In this analysis, a task is modeled to be an alternative sequence of normal and critical section segments. By analyzing the minimum execution time required for a task to request several shared resources, this method improves the accuracy of prior work and provides an upper bound on the cumulative execution time for a task to execute critical sections in any time interval. Schedulability experiments indicate that the proposed method outperforms the existing methods and improves the system schedulability significantly.
Multiprocessor priority ceiling protocol (MPCP) is a classical suspension-based real-time locking protocol, wildly used in partitioned fixed-priority (P-FP) scheduled multiprocessor/multicore real-time systems. However, prior worst-case task blocking time (WCTBT) analysis is pessimistic, which negatively impacts the system schedulability. Therefore, a novel WCTBT analysis is proposed. In this analysis, a task is modeled to be an alternative sequence of normal and critical section segments. By analyzing the minimum execution time required for a task to request several shared resources, this method improves the accuracy of prior work and provides an upper bound on the cumulative execution time for a task to execute critical sections in any time interval. Schedulability experiments indicate that the proposed method outperforms the existing methods and improves the system schedulability significantly.
2016, 45(6): 1008-1013.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.023
Abstract:
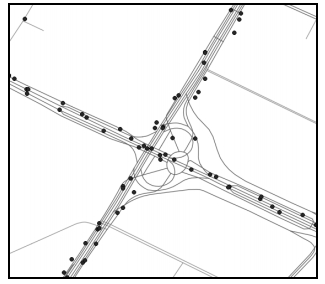
Map-matching for GPS trajectories is a key groundwork in mining transportation data. Reliable matching results are significant for monitoring traffic situation, publishing real-time transportation information, vehicle tracking, smart vehicle dispatching, and routing behavior analysis. In real urban road networks, there are numerous complicated road structures such as elevated roads, frontage roads, and interchange bridges. Traditional map-matching algorithms could not match trajectories on these structures accurately. In this paper, we propose a map-matching algorithm based on the topological structure of the road networks and transform the problem of matching GPS trajectories in road map into the problem of finding the shortest path in a weighted road network. We test the algorithm with the real data of GPS trajectories of tens of thousands of taxis in Chengdu. The results show that the presented algorithm can acquire a high success ratio and accuracy ratio in complicated urban road networks.
Map-matching for GPS trajectories is a key groundwork in mining transportation data. Reliable matching results are significant for monitoring traffic situation, publishing real-time transportation information, vehicle tracking, smart vehicle dispatching, and routing behavior analysis. In real urban road networks, there are numerous complicated road structures such as elevated roads, frontage roads, and interchange bridges. Traditional map-matching algorithms could not match trajectories on these structures accurately. In this paper, we propose a map-matching algorithm based on the topological structure of the road networks and transform the problem of matching GPS trajectories in road map into the problem of finding the shortest path in a weighted road network. We test the algorithm with the real data of GPS trajectories of tens of thousands of taxis in Chengdu. The results show that the presented algorithm can acquire a high success ratio and accuracy ratio in complicated urban road networks.
2016, 45(6): 1014-1019, 1032.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.024
Abstract:
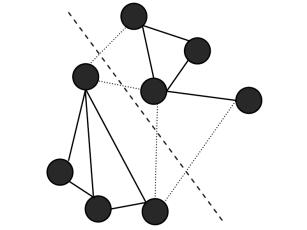
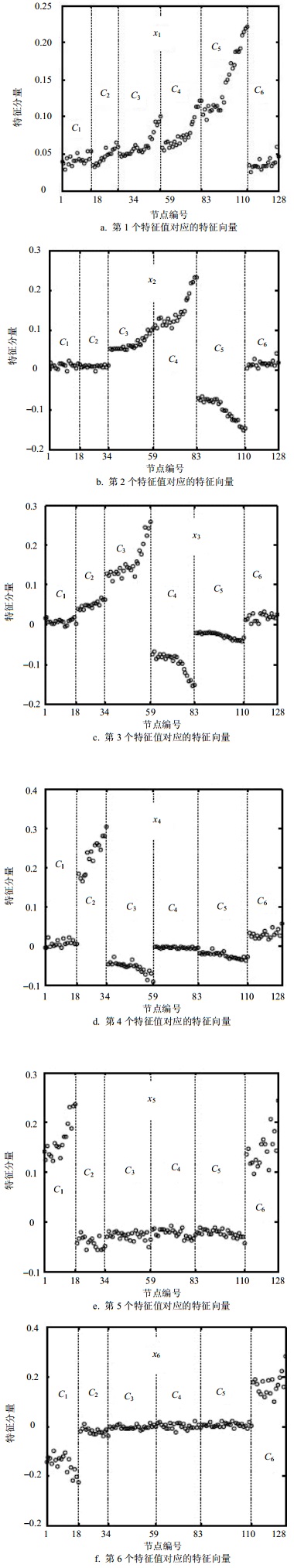
Detecting community structure of directed networks is of significance for understanding the structures and functions of complex systems. In this paper, we develop a spectral algorithm using multiple eigenvectors of the Laplacian matrix (MEL) in directed networks, where the c eigenvectors of the smallest eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix are taken into account. We compare with the spectral optimization method (SOM) and simulated annealing (SA) algorithm of modularity matrix in directed networks on synthetic and empirical networks. The experimental results indicate that, the values of the normalized mutual information (NMI) obtained by our algorithm are approximated 1 when the community structures are clearly. The proposed algorithm outperforms the SOM and SA algorithms when the community structures are not clearly. In addition, the numerical results for empirical data set show that the modularity values Q could be enhanced by 17.28% and 19.21% respectively. This work may be helpful to analyze the relationship between the properties of Laplacian matrix and community structures in directed networks.
Detecting community structure of directed networks is of significance for understanding the structures and functions of complex systems. In this paper, we develop a spectral algorithm using multiple eigenvectors of the Laplacian matrix (MEL) in directed networks, where the c eigenvectors of the smallest eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix are taken into account. We compare with the spectral optimization method (SOM) and simulated annealing (SA) algorithm of modularity matrix in directed networks on synthetic and empirical networks. The experimental results indicate that, the values of the normalized mutual information (NMI) obtained by our algorithm are approximated 1 when the community structures are clearly. The proposed algorithm outperforms the SOM and SA algorithms when the community structures are not clearly. In addition, the numerical results for empirical data set show that the modularity values Q could be enhanced by 17.28% and 19.21% respectively. This work may be helpful to analyze the relationship between the properties of Laplacian matrix and community structures in directed networks.
2016, 45(6): 1020-1026.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.025
Abstract:
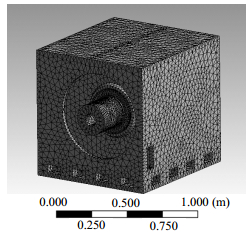
The thermal characteristics of the spindle system has a significant influence on the machining accuracy of the heavy horizontal lathe. The major research object is the spindle system of heavy horizontal lathe. Based on the thermoset coupling analysis of the finite element method, the temperature field and thermal deformation field of the spindle system after reaching the thermal equilibrium state is simulated. And the shift of the spindle's center line that thermal deformation has led is analyzed. According to the structural characteristics of the hydrostatic bearing, the effect of the rotational speed of bearing, viscosity of hydraulic oil, the thickness of the hydrostatic oil film and the oil supply pressure to the thermal deformation of the spindle system are analyzed. The results show that all the factors have different-level influences on the deformation field of the spindle system, and therefore provide a reference for the optimal design and thermal error compensation of the spindle system.
The thermal characteristics of the spindle system has a significant influence on the machining accuracy of the heavy horizontal lathe. The major research object is the spindle system of heavy horizontal lathe. Based on the thermoset coupling analysis of the finite element method, the temperature field and thermal deformation field of the spindle system after reaching the thermal equilibrium state is simulated. And the shift of the spindle's center line that thermal deformation has led is analyzed. According to the structural characteristics of the hydrostatic bearing, the effect of the rotational speed of bearing, viscosity of hydraulic oil, the thickness of the hydrostatic oil film and the oil supply pressure to the thermal deformation of the spindle system are analyzed. The results show that all the factors have different-level influences on the deformation field of the spindle system, and therefore provide a reference for the optimal design and thermal error compensation of the spindle system.
2016, 45(6): 1027-1032.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.06.026
Abstract:
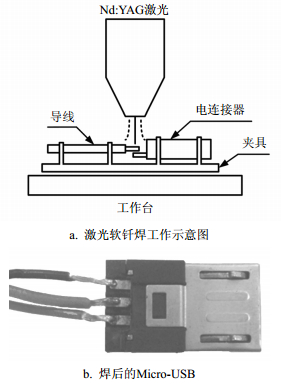
Mechanical properties of Micro-USB electrical connectors is affected by instantaneous power on or off caused by hot-plugging. In order to further understand the failure behavior of electrical connectors under thermal cycling, it is necessary to carry out the fatigue life prediction for laser soldering joints of Micro-USB electrical connectors under heat acceleration test. Firstly, the finite element model of Micro-USB electrical connectors is established. The mechanical behavior of solder joints under cyclic thermal loading is described by using the Anand constitutive equation. Then, the stress or strain distribution is analyzed by means of ANSYS software. Finally, the thermal fatigue life under thermal cycling can be calculated by using the Coffin-Manson equation based on plastic strain. The results show that the maximum stress or strain occurs at the place of the middle solder joint contacting with metal Pin when laser soldering joints of electrical connectors are subjected to thermal cycling. Its fatigue life is lowest, only 1 146 times. Meanwhile, the risk of failure can be determined. The conclusions can provide a theoretical reference for the design, manufacture and testing of electrical connectors.
Mechanical properties of Micro-USB electrical connectors is affected by instantaneous power on or off caused by hot-plugging. In order to further understand the failure behavior of electrical connectors under thermal cycling, it is necessary to carry out the fatigue life prediction for laser soldering joints of Micro-USB electrical connectors under heat acceleration test. Firstly, the finite element model of Micro-USB electrical connectors is established. The mechanical behavior of solder joints under cyclic thermal loading is described by using the Anand constitutive equation. Then, the stress or strain distribution is analyzed by means of ANSYS software. Finally, the thermal fatigue life under thermal cycling can be calculated by using the Coffin-Manson equation based on plastic strain. The results show that the maximum stress or strain occurs at the place of the middle solder joint contacting with metal Pin when laser soldering joints of electrical connectors are subjected to thermal cycling. Its fatigue life is lowest, only 1 146 times. Meanwhile, the risk of failure can be determined. The conclusions can provide a theoretical reference for the design, manufacture and testing of electrical connectors.

 ISSN
ISSN