2017 Vol. 46, No. 1
2017, 46(1): 1-8.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.001
Abstract:
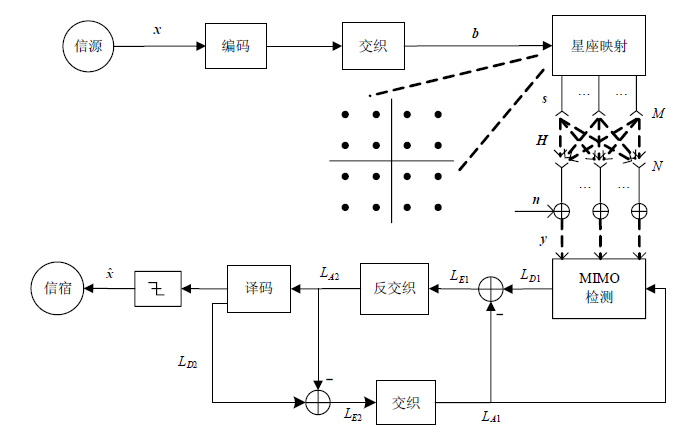
In this paper, an enhanced Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm based on max-log updating is proposed for multiple input multiple output (MIMO) system. The max-log updating can generate the list vectors to simply the complexity of the calculation of the extrinsic log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) efficiently. Meanwhile, it avoids calculating probability distribution per bit in conventional MCMC. However, the proposed MCMC detection suffers from the so called "stalling" problem, where the Markov chain may be trapped into local optimal state. Thus, we also propose three enhancement technologies:1) biased processing, i.e., updating randomly in a given biased interval; 2) reinitialized processing, i.e., reinitialize the Markov chain under the sub-optimal states; 3) clipped processing, i.e., reprocessing the LLR with clipping. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can remedy the "stalling" problem efficiently with reduced complexity, and can achieve 2 dB performance gains with 10% less complexity than MMSE-PIC.
In this paper, an enhanced Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm based on max-log updating is proposed for multiple input multiple output (MIMO) system. The max-log updating can generate the list vectors to simply the complexity of the calculation of the extrinsic log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) efficiently. Meanwhile, it avoids calculating probability distribution per bit in conventional MCMC. However, the proposed MCMC detection suffers from the so called "stalling" problem, where the Markov chain may be trapped into local optimal state. Thus, we also propose three enhancement technologies:1) biased processing, i.e., updating randomly in a given biased interval; 2) reinitialized processing, i.e., reinitialize the Markov chain under the sub-optimal states; 3) clipped processing, i.e., reprocessing the LLR with clipping. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can remedy the "stalling" problem efficiently with reduced complexity, and can achieve 2 dB performance gains with 10% less complexity than MMSE-PIC.
2017, 46(1): 15-20.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.003
Abstract:
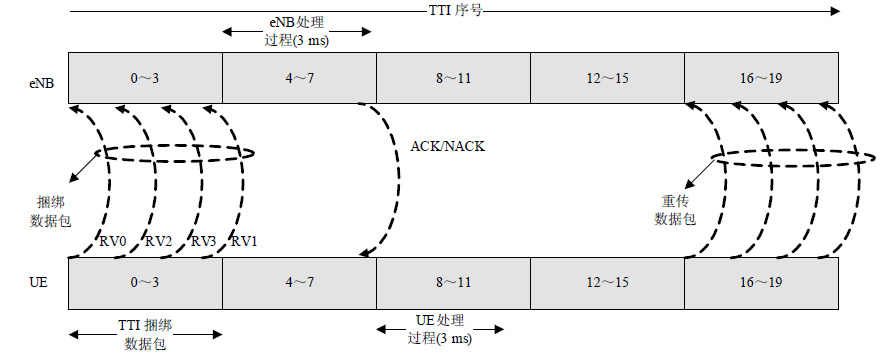
In order to improve the cell coverage performance, transmission time interval (TTI) bundling technique is employed in long term evolution (LTE) uplink for the voice over internet protocol (VoIP) service. Recently, a coverage-enhanced scheme makes user equipment (UE) transmitting up to five bundles under the same delay budget. However, the coverage-enhanced scheme lacks time for feedback processing, in which the UE transmitting power may be wasted for an unnecessary retransmission. Taking the issue into account, we propose a scheme based on preprocessing of TTI bundling for adaptive transmission in LTE uplink. Our scheme uses block error rate (BLER) versus signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) mapping mechanism to reduce unnecessary retransmission bundles and save UE power consumption, yielding higher throughput.
In order to improve the cell coverage performance, transmission time interval (TTI) bundling technique is employed in long term evolution (LTE) uplink for the voice over internet protocol (VoIP) service. Recently, a coverage-enhanced scheme makes user equipment (UE) transmitting up to five bundles under the same delay budget. However, the coverage-enhanced scheme lacks time for feedback processing, in which the UE transmitting power may be wasted for an unnecessary retransmission. Taking the issue into account, we propose a scheme based on preprocessing of TTI bundling for adaptive transmission in LTE uplink. Our scheme uses block error rate (BLER) versus signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) mapping mechanism to reduce unnecessary retransmission bundles and save UE power consumption, yielding higher throughput.
2017, 46(1): 21-26.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.004
Abstract:
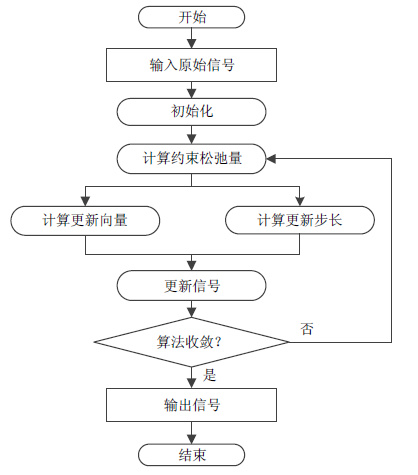
Since cubic metric (CM) can more accurately predict the power de-rating of power amplifier (PA), it is recognized as a better metric to characterize the envelope fluctuations of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signals than peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). To improve the PA efficiency, a common scheme is minimizing the CM value of signals. However, this aggravates the in-band distortion, resulting in bit error ratio (BER) degradation of systems. This paper formulates the problem as an in-band distortion optimization subject to CM constraint, and a customized interior-point algorithm is developed to solve the optimization problem. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm provides better BER and CM-reduction performance than existing optimization schemes.
Since cubic metric (CM) can more accurately predict the power de-rating of power amplifier (PA), it is recognized as a better metric to characterize the envelope fluctuations of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signals than peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). To improve the PA efficiency, a common scheme is minimizing the CM value of signals. However, this aggravates the in-band distortion, resulting in bit error ratio (BER) degradation of systems. This paper formulates the problem as an in-band distortion optimization subject to CM constraint, and a customized interior-point algorithm is developed to solve the optimization problem. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm provides better BER and CM-reduction performance than existing optimization schemes.
2017, 46(1): 27-31,60.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.005
Abstract:
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) sky-wave over-the-horizon radar (OTHR) transmits the wide beams with low gain at the transmitter, and achieves receiver beam-forming to get narrow beams with high gain. The MIMO technique is an ideal choice for OTHR to detect the target through the multi-layer ionosphere and suppress the strong clutters. This paper applies a two-layer ionospheric model in MIMO-OTHR, and proposes a mutual information method to adaptively optimize the waveforms in order to suppress strong clutters with high clutter-to-noise ratio (CNR). Numerical experiments show that this method improves range resolution and detection probability significantly. It also demonstrates that, by applying the optimization method, the multipath propagation can be utilized to enhance the radar performance.
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) sky-wave over-the-horizon radar (OTHR) transmits the wide beams with low gain at the transmitter, and achieves receiver beam-forming to get narrow beams with high gain. The MIMO technique is an ideal choice for OTHR to detect the target through the multi-layer ionosphere and suppress the strong clutters. This paper applies a two-layer ionospheric model in MIMO-OTHR, and proposes a mutual information method to adaptively optimize the waveforms in order to suppress strong clutters with high clutter-to-noise ratio (CNR). Numerical experiments show that this method improves range resolution and detection probability significantly. It also demonstrates that, by applying the optimization method, the multipath propagation can be utilized to enhance the radar performance.
2017, 46(1): 32-37.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.006
Abstract:
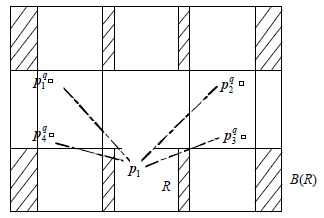
In order to implement multi-floor buildings accurate location, the map information based indoor position scheme is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the map information model and affinity propagation method for fingerprints clustering are explored in offline phase. Then, the received signal strength indication (RSSI) threshold based floor identification method is put forward. Finally, the terminal positions are obtained by using the map information model and maximum posteriori position estimation method. Experimental results show that the proposed indoor position scheme can effectively enhance the location estimation accuracy and reduce the computation complexity for multi-floor buildings.
In order to implement multi-floor buildings accurate location, the map information based indoor position scheme is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the map information model and affinity propagation method for fingerprints clustering are explored in offline phase. Then, the received signal strength indication (RSSI) threshold based floor identification method is put forward. Finally, the terminal positions are obtained by using the map information model and maximum posteriori position estimation method. Experimental results show that the proposed indoor position scheme can effectively enhance the location estimation accuracy and reduce the computation complexity for multi-floor buildings.
2017, 46(1): 38-45.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.007
Abstract:
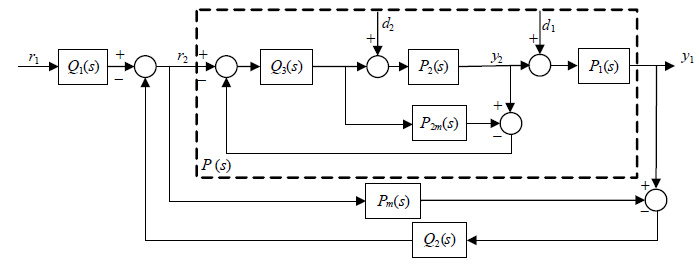
A design method of internal model control (IMC) controllers for unstable cascade processes with time delay is presented. The cascade proposed structure contains two control loops, a secondary loop and a primary loop. In the secondary loop, an analytical design method is derived based on the traditional IMC, it can quickly reject the disturbance in the inner loop. In order to decouple the set-point tracking characteristic from disturbance rejection characteristic, a 2 degree of freedom (DOF) IMC structure is used in the primary loop. Then the set point tracking controller and the disturbance rejection controller can be tuned independently, which overcomes the shortage of a traditional IMC. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can reduce the number of controller effectively, meanwhile provide good performance of set-point tracking and disturbance rejection as well as robustness simultaneously.
A design method of internal model control (IMC) controllers for unstable cascade processes with time delay is presented. The cascade proposed structure contains two control loops, a secondary loop and a primary loop. In the secondary loop, an analytical design method is derived based on the traditional IMC, it can quickly reject the disturbance in the inner loop. In order to decouple the set-point tracking characteristic from disturbance rejection characteristic, a 2 degree of freedom (DOF) IMC structure is used in the primary loop. Then the set point tracking controller and the disturbance rejection controller can be tuned independently, which overcomes the shortage of a traditional IMC. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can reduce the number of controller effectively, meanwhile provide good performance of set-point tracking and disturbance rejection as well as robustness simultaneously.
2017, 46(1): 46-54.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.008
Abstract:
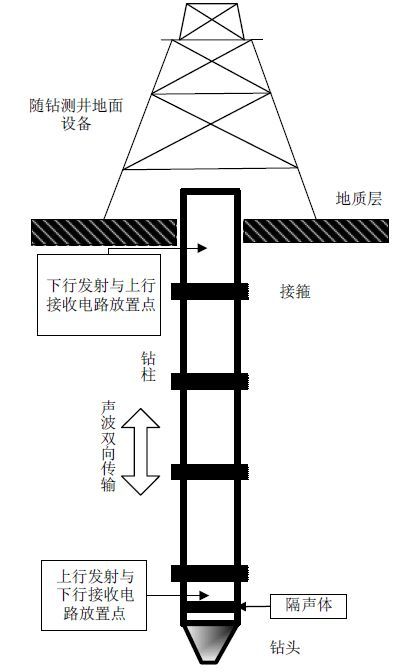
Data transmission system of logging while drilling achieves real-time communication between ground and under well accurately and effectively by acoustic wave transmitting along the drillstring. A drillstring channel is periodically constructed by pipes and joints. By theoretical analysis and modeling simulation, the spectrum of drillstring channel is a comb-filtering-like transfer function composed of alternating passed bands and stop bands. A finite impulse response (FIR) filter is used to approximate the spectrum and to build a simulation platform of the channel. Vector orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technology (V-OFDM) can convert the multipath fading channel into a number of vector sub-channels. The number of error bits which are leaded by channel spectral nulls can be reduced and the robustness can be increased by diversity gain when eliminating symbol interference by adding right amount of cyclic prefix. Simulation and test results show that this technology can reduce data redundancy and increase transmission efficiency extremely when meeting the need of low bit error rate.
Data transmission system of logging while drilling achieves real-time communication between ground and under well accurately and effectively by acoustic wave transmitting along the drillstring. A drillstring channel is periodically constructed by pipes and joints. By theoretical analysis and modeling simulation, the spectrum of drillstring channel is a comb-filtering-like transfer function composed of alternating passed bands and stop bands. A finite impulse response (FIR) filter is used to approximate the spectrum and to build a simulation platform of the channel. Vector orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technology (V-OFDM) can convert the multipath fading channel into a number of vector sub-channels. The number of error bits which are leaded by channel spectral nulls can be reduced and the robustness can be increased by diversity gain when eliminating symbol interference by adding right amount of cyclic prefix. Simulation and test results show that this technology can reduce data redundancy and increase transmission efficiency extremely when meeting the need of low bit error rate.
2017, 46(1): 55-60.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.009
Abstract:
Security and privacy are main restriction factors in the development of the Internet of Things(IOT). The external users need to directly access the sensor nodes to get data in IOT. In order to protect the security of data, we propose a user authentication and key agreement scheme based on heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. The proposed scheme can verify the identity of participants and establish a shared key between the user and senor node.The detailed analysis of the proposed scheme shows that the scheme is secure and efficient.
Security and privacy are main restriction factors in the development of the Internet of Things(IOT). The external users need to directly access the sensor nodes to get data in IOT. In order to protect the security of data, we propose a user authentication and key agreement scheme based on heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. The proposed scheme can verify the identity of participants and establish a shared key between the user and senor node.The detailed analysis of the proposed scheme shows that the scheme is secure and efficient.
2017, 46(1): 61-68.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.010
Abstract:
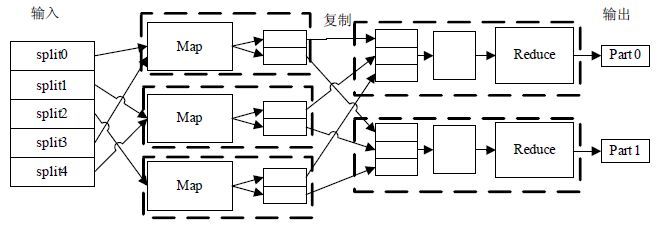
Following with the growth of massive data, clustering research, one of the core problems of big dataisfaced with more and more problems such as high computing complexity and lack of resource. It has proposed an improved parallel K-means algorithm based on Hadoop. To overcomethe problem that the traditional K-means algorithm often has local optimal solution due to the randomness choice of initial center, we introduce Canopy algorithm to initialize clustering center andapply K-means algorithm on canopy. Meanwhile, clusters are merged among canopies. The result is stable and iteration number is less. In addition, the parallel implementation methods and strategies of the improved algorithm are presented, combining with the distributed computing model of MapReduce. And a new method of text clustering is introduced by improving the similarity of measurement. The experiment results indicate the validity and scalability of our method.
Following with the growth of massive data, clustering research, one of the core problems of big dataisfaced with more and more problems such as high computing complexity and lack of resource. It has proposed an improved parallel K-means algorithm based on Hadoop. To overcomethe problem that the traditional K-means algorithm often has local optimal solution due to the randomness choice of initial center, we introduce Canopy algorithm to initialize clustering center andapply K-means algorithm on canopy. Meanwhile, clusters are merged among canopies. The result is stable and iteration number is less. In addition, the parallel implementation methods and strategies of the improved algorithm are presented, combining with the distributed computing model of MapReduce. And a new method of text clustering is introduced by improving the similarity of measurement. The experiment results indicate the validity and scalability of our method.
2017, 46(1): 69-74.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.011
Abstract:
In order to organize, manage and browse large-scale image databases effectively, an image classification algorithm based on local features is proposed. After analyzing of several fashionable local features at present, we choose the suitable features to construct the visual vocabulary. These visual words are invariant to image scale and rotation, and are shown robust to addition of noise and changes in 3D viewpoint. We also describe two approaches to represent objects using these visual words. As baselines for comparison, some additional classification systems also have been implemented. The performance analysis on the obtained experimental results demonstrates that the proposed methods are effective and highly valuable in practice.
In order to organize, manage and browse large-scale image databases effectively, an image classification algorithm based on local features is proposed. After analyzing of several fashionable local features at present, we choose the suitable features to construct the visual vocabulary. These visual words are invariant to image scale and rotation, and are shown robust to addition of noise and changes in 3D viewpoint. We also describe two approaches to represent objects using these visual words. As baselines for comparison, some additional classification systems also have been implemented. The performance analysis on the obtained experimental results demonstrates that the proposed methods are effective and highly valuable in practice.
2017, 46(1): 75-80.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.012
Abstract:
With the rapidly growth of online social networks such as microblog and WeChat, the false information breaks out on the social network and often brings serious consequences. How to locate the rumor source is of great importance for many applications. This paper proposes a source localization algorithm on online social network. We consider the characteristic that the information often contains some partial spreading, and design a more accurate algorithm to locate the information source. The results show that the improved algorithm can provide a more accurate spreading trees and improve the localization accuracy. Experiments on model and real network show the effectiveness of the improved algorithm.
With the rapidly growth of online social networks such as microblog and WeChat, the false information breaks out on the social network and often brings serious consequences. How to locate the rumor source is of great importance for many applications. This paper proposes a source localization algorithm on online social network. We consider the characteristic that the information often contains some partial spreading, and design a more accurate algorithm to locate the information source. The results show that the improved algorithm can provide a more accurate spreading trees and improve the localization accuracy. Experiments on model and real network show the effectiveness of the improved algorithm.
2017, 46(1): 81-87.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.013
Abstract:
A new MEME-based motif discovery algorithm for uncertain data stream is proposed by using the idea of sequential pattern discovery in bioinformatics. According to features of uncertain data stream, the new algorithm designs a simplified calculation method for uncertain sliding window and modifies the SAX symbolic strategy. The feasibility of the proposed algorithm is verified by one uncertain test data stream from air and missile defense sensors. And its accuracy is measured through planting different number motifs. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm is validated by comparing with existing algorithms in the condition that the existence probability of tuples is set to 1.
A new MEME-based motif discovery algorithm for uncertain data stream is proposed by using the idea of sequential pattern discovery in bioinformatics. According to features of uncertain data stream, the new algorithm designs a simplified calculation method for uncertain sliding window and modifies the SAX symbolic strategy. The feasibility of the proposed algorithm is verified by one uncertain test data stream from air and missile defense sensors. And its accuracy is measured through planting different number motifs. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm is validated by comparing with existing algorithms in the condition that the existence probability of tuples is set to 1.
2017, 46(1): 88-95.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.014
Abstract:
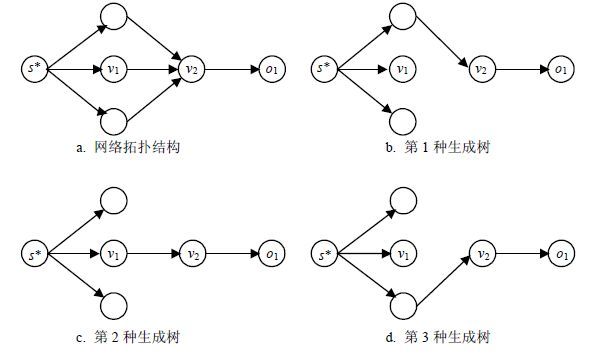
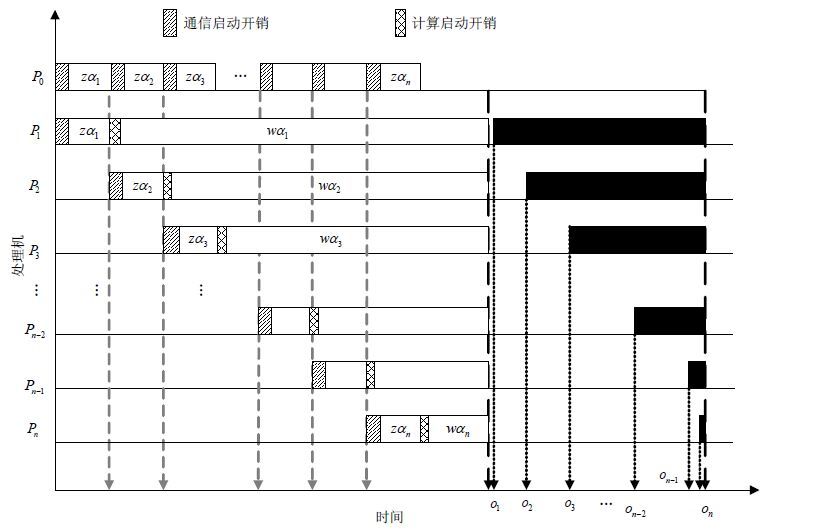
As scientific applications become more data intensive, finding an efficient scheduling strategy for massive computing in parallel and distributed systems has drawn increasingly attention. Most existing scheduling models assume that all processors can 100% finish computing, that is, they keep online during the completion of assigned workload fractions. In fact, in the real parallel and distributed environments, different processors have different off-line time. Therefore, off-line time constraints of processors should be taken into account before distributing of the workload fractions; otherwise, some processors may not be able to fish computing their assignments. To solve the above issue, this paper proposes an off-line time aware divisible-load scheduling model and designs an effective global optimization genetic algorithm to solve it. Finally, experimental results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed model and the efficiency of the proposed algorithm.
As scientific applications become more data intensive, finding an efficient scheduling strategy for massive computing in parallel and distributed systems has drawn increasingly attention. Most existing scheduling models assume that all processors can 100% finish computing, that is, they keep online during the completion of assigned workload fractions. In fact, in the real parallel and distributed environments, different processors have different off-line time. Therefore, off-line time constraints of processors should be taken into account before distributing of the workload fractions; otherwise, some processors may not be able to fish computing their assignments. To solve the above issue, this paper proposes an off-line time aware divisible-load scheduling model and designs an effective global optimization genetic algorithm to solve it. Finally, experimental results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed model and the efficiency of the proposed algorithm.
2017, 46(1): 96-101.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.015
Abstract:
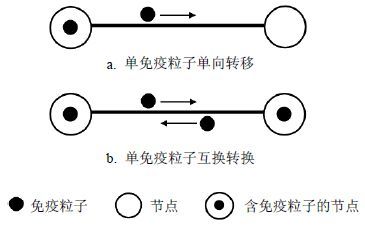
For the problems of traditional immune models arising in collectingand analyzing network topology information in temporal networks, an immune strategy based on random walk mechanism is put forward and itcan be implemented withoutcollectingnetwork topology information. A certain number of immune particles were randomly assigned to the network nodes.When a nodewith immune particles has one or more activated links,the immune particles on the node will walk to another node along anactivated link of the node.The nodes with immune particlesacquire the immunity,but thenodes losingimmune particleswill betransformed into the susceptible state. Considering whether the random walkers exert impact upon each other when they move, the dependent random walk immune model and the P_independent random walk immune model are established,respectively, in which the network transmission overhead of the immune particle is limited by a given immune particle density. Experiments show the two random walk immune models are characterized by their better immune effects with lower immune particle density and the network overhead when compared with acquaintances immune model. In addition, the comparative result with the target immune model depends on heterogeneity of network topology.
For the problems of traditional immune models arising in collectingand analyzing network topology information in temporal networks, an immune strategy based on random walk mechanism is put forward and itcan be implemented withoutcollectingnetwork topology information. A certain number of immune particles were randomly assigned to the network nodes.When a nodewith immune particles has one or more activated links,the immune particles on the node will walk to another node along anactivated link of the node.The nodes with immune particlesacquire the immunity,but thenodes losingimmune particleswill betransformed into the susceptible state. Considering whether the random walkers exert impact upon each other when they move, the dependent random walk immune model and the P_independent random walk immune model are established,respectively, in which the network transmission overhead of the immune particle is limited by a given immune particle density. Experiments show the two random walk immune models are characterized by their better immune effects with lower immune particle density and the network overhead when compared with acquaintances immune model. In addition, the comparative result with the target immune model depends on heterogeneity of network topology.
2017, 46(1): 102-108.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.016
Abstract:
Server as an important part of the institutions or organizations usually carries a particular network service, for the security protection, it usually adopts rule-based approaches to detecting attacks according to the specific characters. However, due to the new network attacks emerge in endlessly and network anomaly is difficult to define, anomaly-feature-based detection is more and more difficult to meet the needs of the increasingly complex network environment. To cope with it, we propose the concept of traffic structure stability based on both the inherent stability of normal traffic attributes and the stability of a specific service, and profile the normal network behavior model for the server to detect traffic abnormality. To describe the difference between current traffic structure and the normal profile, we propose a novel visualization measurement method based on Spie Chart. Finally, we implement the system on a mail server and confirm the validity of the model by experiments.
Server as an important part of the institutions or organizations usually carries a particular network service, for the security protection, it usually adopts rule-based approaches to detecting attacks according to the specific characters. However, due to the new network attacks emerge in endlessly and network anomaly is difficult to define, anomaly-feature-based detection is more and more difficult to meet the needs of the increasingly complex network environment. To cope with it, we propose the concept of traffic structure stability based on both the inherent stability of normal traffic attributes and the stability of a specific service, and profile the normal network behavior model for the server to detect traffic abnormality. To describe the difference between current traffic structure and the normal profile, we propose a novel visualization measurement method based on Spie Chart. Finally, we implement the system on a mail server and confirm the validity of the model by experiments.
2017, 46(1): 109-125.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.017
Abstract:
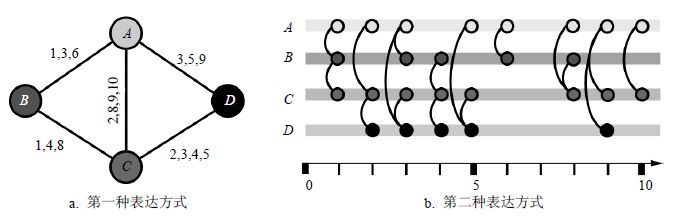
In temporal networks, the temporal structure of edge activations can remarkably affect dynamics of systems interacting through the network at the same time scale, which is one of hot research topics in complex networks. The research progress is reviewed in this paper, covering the temporal network modeling, temporal network structure and related statistical mechanics, temporal network propagation dynamics, the combination statistical characteristics of temporal network and human behaviors, as well as some theoretical analysis methods of dealing with temporal networks. In addition, some significant scientific problems are put forward by analyzing the current research situation at home and aboard. Finally, the future research direction and development trend of this field are prospected.
In temporal networks, the temporal structure of edge activations can remarkably affect dynamics of systems interacting through the network at the same time scale, which is one of hot research topics in complex networks. The research progress is reviewed in this paper, covering the temporal network modeling, temporal network structure and related statistical mechanics, temporal network propagation dynamics, the combination statistical characteristics of temporal network and human behaviors, as well as some theoretical analysis methods of dealing with temporal networks. In addition, some significant scientific problems are put forward by analyzing the current research situation at home and aboard. Finally, the future research direction and development trend of this field are prospected.
2017, 46(1): 126-132.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.018
Abstract:
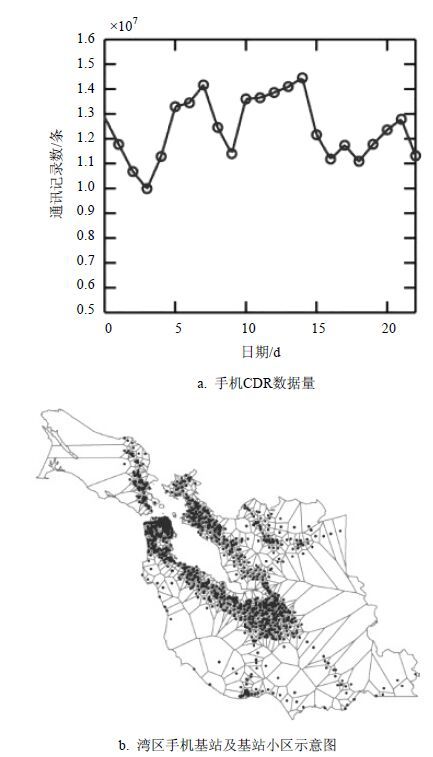
This paper presents an urban population sensing method based on mobile phone dataset and applies it to San Francisco Bay Area. The difference of mobile phone market shares in different tracts is considered. We introduce the potential application of dynamic population sensing using mobile phone data and calculate the relative difference of daytime population and nighttime population in different tracts in Bay Area. The knowledge of urban population distribution has great importance of the early-warning of city emergency, urban traffic control, and the allocation of city public resources.
This paper presents an urban population sensing method based on mobile phone dataset and applies it to San Francisco Bay Area. The difference of mobile phone market shares in different tracts is considered. We introduce the potential application of dynamic population sensing using mobile phone data and calculate the relative difference of daytime population and nighttime population in different tracts in Bay Area. The knowledge of urban population distribution has great importance of the early-warning of city emergency, urban traffic control, and the allocation of city public resources.
2017, 46(1): 151-155.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.020
Abstract:
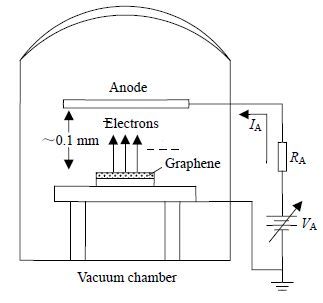
Stable aqueous graphene dispersion with sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) surfactant was prepared by using an ultrasonic dispersing process. Graphene films were deposited on glass and silicon substrate as functional layers by the spray coating method. The study of the influence of SDBS concentration on graphene dispersing performance show that SDBS concentration of 15% is adequate for preparing stable graphene dispersion. Optical and morphological properties of the resulting graphene films are also investigated by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. The results indicate that the visible light transmittance of graphene coating is higher than 82% and the graphene film shows a cluster structure with blade-like edges. The field emission analyses were carried out by a diode test cell in a vacuum system, which confirms that this graphene functional layer has good field-emission performance with low turn-on field of 3 V/μm and large enhancement factor of 3 580. Collectively, this deposition method may be a viable and cost-effective route for fabricating graphene films.
Stable aqueous graphene dispersion with sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) surfactant was prepared by using an ultrasonic dispersing process. Graphene films were deposited on glass and silicon substrate as functional layers by the spray coating method. The study of the influence of SDBS concentration on graphene dispersing performance show that SDBS concentration of 15% is adequate for preparing stable graphene dispersion. Optical and morphological properties of the resulting graphene films are also investigated by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. The results indicate that the visible light transmittance of graphene coating is higher than 82% and the graphene film shows a cluster structure with blade-like edges. The field emission analyses were carried out by a diode test cell in a vacuum system, which confirms that this graphene functional layer has good field-emission performance with low turn-on field of 3 V/μm and large enhancement factor of 3 580. Collectively, this deposition method may be a viable and cost-effective route for fabricating graphene films.
2017, 46(1): 156-160.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.01.021
Abstract:
A new method for testing the distribution of the microwave surface resistance (Rs) of high temperature superconductor (HTS) is introduced in this paper. By using the mirror method and its relevant principles, the energy convergence of dielectric resonator and cavity is achieved and the incompatible problem between the versatility and high resolution of Rs of HTS thin film is solved through a metal ring. A testing device working at 32 GHz with TE012+δ mode is developed according to this method. The resolution of the device can reach a circle with 5 mm in diameter and 19.6 mm2 in area. In this paper, the distribution test of Rs with thirteen points is conducted on a piece of two inch YBCO/LAO/YBCO superconductor thin film sample by this new testing device.
A new method for testing the distribution of the microwave surface resistance (Rs) of high temperature superconductor (HTS) is introduced in this paper. By using the mirror method and its relevant principles, the energy convergence of dielectric resonator and cavity is achieved and the incompatible problem between the versatility and high resolution of Rs of HTS thin film is solved through a metal ring. A testing device working at 32 GHz with TE012+δ mode is developed according to this method. The resolution of the device can reach a circle with 5 mm in diameter and 19.6 mm2 in area. In this paper, the distribution test of Rs with thirteen points is conducted on a piece of two inch YBCO/LAO/YBCO superconductor thin film sample by this new testing device.

 ISSN
ISSN