2017 Vol. 46, No. 2
Compositional Modeling and Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics Extracting for Missile Targets
2017, 46(2): 321-329.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.001
Abstract:
In this paper, conventional missile targets are divided into basic scattering cells, such as disks, cylinders, cones and ellipsoids. By carrying on the parameterized compositional modeling, analytical calculation of integrals, and superposition the field contribution of each unit, we can obtain the scattering fields of missile-like objects in time. Consequently, the electromagnetic scattering characteristics such as RCS, the range profile and ISAR images are available. The numerical results demonstrate the proposed method can meet the real-time requirement as well as the high precision. Numerical software is developed and it gives a best support to the RCS calculation and design evaluation of missile targets in engineering application.
In this paper, conventional missile targets are divided into basic scattering cells, such as disks, cylinders, cones and ellipsoids. By carrying on the parameterized compositional modeling, analytical calculation of integrals, and superposition the field contribution of each unit, we can obtain the scattering fields of missile-like objects in time. Consequently, the electromagnetic scattering characteristics such as RCS, the range profile and ISAR images are available. The numerical results demonstrate the proposed method can meet the real-time requirement as well as the high precision. Numerical software is developed and it gives a best support to the RCS calculation and design evaluation of missile targets in engineering application.
2017, 46(2): 330-334.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.002
Abstract:
In this paper, the construction of polar codes with multiple quadrature amplitude modulation (M-QAM) modulation is studied. To solve the problem of the various noise power of the coded bits caused by M-QAM modulation, we propose a method to divide the channel of M-QAM modulation into a several of parallel binary-input channels with constant noise power so that the traditional construction method for binary-input channel is available for the M-QAM modulation case. We also give the design in detail for M-PAM/M-QAM modulation. Our numerical results show that the proposed scheme has good performance.
In this paper, the construction of polar codes with multiple quadrature amplitude modulation (M-QAM) modulation is studied. To solve the problem of the various noise power of the coded bits caused by M-QAM modulation, we propose a method to divide the channel of M-QAM modulation into a several of parallel binary-input channels with constant noise power so that the traditional construction method for binary-input channel is available for the M-QAM modulation case. We also give the design in detail for M-PAM/M-QAM modulation. Our numerical results show that the proposed scheme has good performance.
2017, 46(2): 335-339.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.003
Abstract:
Hybrid LFM-frequency encoding low probability of interception (LPI) waveform combines the techniques of LFM and FSK, which can obtain a large time-bandwith product, thus enhancing the capability of LPI. However, hybrid LFM/FSK LPI signal suffers from high range sidelobes, resulting in the decrease of radar detectability. To this end, this paper deals with the problem of sidelobe suppression. Specifically, the specific sidelobe suppression filter selected from its library which is designed off-line, instead of matched filter or correlation, is exploited on the echo signal. This operation can accomplish the compression pulse while achieving low sidelobes, and its engineering implementation is simple. Simulation results illustrate the effectiveness of the devised filter, showing its ability to obtain lower sidelobes in comparison with the traditional process.
Hybrid LFM-frequency encoding low probability of interception (LPI) waveform combines the techniques of LFM and FSK, which can obtain a large time-bandwith product, thus enhancing the capability of LPI. However, hybrid LFM/FSK LPI signal suffers from high range sidelobes, resulting in the decrease of radar detectability. To this end, this paper deals with the problem of sidelobe suppression. Specifically, the specific sidelobe suppression filter selected from its library which is designed off-line, instead of matched filter or correlation, is exploited on the echo signal. This operation can accomplish the compression pulse while achieving low sidelobes, and its engineering implementation is simple. Simulation results illustrate the effectiveness of the devised filter, showing its ability to obtain lower sidelobes in comparison with the traditional process.
2017, 46(2): 340-345.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.004
Abstract:
Quantum key agreement (QKA) protocols allow participants to negotiate a classical shared secret key fairly via public quantum channels. Furthermore, the shared key cannot be determined independently by any subset of the participants. Their security is assured by the quantum mechanics principles, so they can achieve unconditional security and have drawn considerable attention. Based on four-particle entangled states and logical qubits, two robust two-party quantum key agreement protocols against collective-dephasing noise and collective-rotation noise are proposed. The security analysis shows that the two protocols can not only resist against participant attacks and outsider attacks, but also resist against two kinds of Trojan horse attacks. Furthermore, the two protocols also achieve higher qubit efficiency.
Quantum key agreement (QKA) protocols allow participants to negotiate a classical shared secret key fairly via public quantum channels. Furthermore, the shared key cannot be determined independently by any subset of the participants. Their security is assured by the quantum mechanics principles, so they can achieve unconditional security and have drawn considerable attention. Based on four-particle entangled states and logical qubits, two robust two-party quantum key agreement protocols against collective-dephasing noise and collective-rotation noise are proposed. The security analysis shows that the two protocols can not only resist against participant attacks and outsider attacks, but also resist against two kinds of Trojan horse attacks. Furthermore, the two protocols also achieve higher qubit efficiency.
2017, 46(2): 346-351.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.005
Abstract:
In heterogeneous cellular networks, traditional user association schemes based on reference signal power result in load imbalances between macro cell base stations (MBSs) and small cell base stations (SBSs). Meanwhile, offloading users to SBSs face the quality of service (QoS) degradation. In this paper, we propose a utility maximization framework to address the user association problem. In order to strike a tradeoff between load balancing and user QoS experiences, a bi-criterion optimization problem is formulated to solve the user association problem. The bi-criterion optimization problem is then linearized as a utility maximization problem with a tunable parameter. In addition, we show that the utility maximization problem can be reformulated as a maximum bi-partite matching problem and can be solved in polynomial time by using the Hungarian method. Simulation results show that our proposed method achieves load balancing and can strike tradeoffs between load balancing and user QoS by tuning the optimization parameter.
In heterogeneous cellular networks, traditional user association schemes based on reference signal power result in load imbalances between macro cell base stations (MBSs) and small cell base stations (SBSs). Meanwhile, offloading users to SBSs face the quality of service (QoS) degradation. In this paper, we propose a utility maximization framework to address the user association problem. In order to strike a tradeoff between load balancing and user QoS experiences, a bi-criterion optimization problem is formulated to solve the user association problem. The bi-criterion optimization problem is then linearized as a utility maximization problem with a tunable parameter. In addition, we show that the utility maximization problem can be reformulated as a maximum bi-partite matching problem and can be solved in polynomial time by using the Hungarian method. Simulation results show that our proposed method achieves load balancing and can strike tradeoffs between load balancing and user QoS by tuning the optimization parameter.
2017, 46(2): 352-356.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.006
Abstract:
The performance of fast fixed-point algorithm of independent component analysis (ICA) is influenced by noise significantly. However, the method of noisy ICA proposed by Hyvärinen did not discuss the impulsive noise. In this study, we extend the algorithm proposed by Hyvärinen for noisy ICA to the more general situation in which the signals are observed in the presence of Gaussian and impulsive noise. We use the non-polynomial function to analyze the impulsive noise, which is to guarantee the impulsive noise can be distinguished from the observed data. Furthermore, combined with the noisy ICA method, a modification to the algorithm for multi-noise is introduced. The proposed technique improves the performance of Hyvärinen's algorithm for cases where the observed signals contain Gaussian and impulsive noise. We also perform simulations to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
The performance of fast fixed-point algorithm of independent component analysis (ICA) is influenced by noise significantly. However, the method of noisy ICA proposed by Hyvärinen did not discuss the impulsive noise. In this study, we extend the algorithm proposed by Hyvärinen for noisy ICA to the more general situation in which the signals are observed in the presence of Gaussian and impulsive noise. We use the non-polynomial function to analyze the impulsive noise, which is to guarantee the impulsive noise can be distinguished from the observed data. Furthermore, combined with the noisy ICA method, a modification to the algorithm for multi-noise is introduced. The proposed technique improves the performance of Hyvärinen's algorithm for cases where the observed signals contain Gaussian and impulsive noise. We also perform simulations to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2017, 46(2): 357-362.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.007
Abstract:
An infrared and visible image fusion algorithm is proposed based on visual saliency and non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT). At first, the frequency tuned saliency detection method is improved by guided filter and applied to detect the saliency of infrared image. Then the infrared and visible light images are decomposed into low frequency and high-frequency sub-bands by NSCT. Finally the saliency map of infrared image is used to guide the fusion in low frequency sub-band, and the rule of maximum absolute value selection is used for the fusion in high frequency sub-band. Experimental results demonstrate that compared to several other algorithms, the proposed method highlights the IR targets and at the same time makes the fusion images have rich background information, and better visual fusion effects and objective quality evaluations are obtained.
An infrared and visible image fusion algorithm is proposed based on visual saliency and non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT). At first, the frequency tuned saliency detection method is improved by guided filter and applied to detect the saliency of infrared image. Then the infrared and visible light images are decomposed into low frequency and high-frequency sub-bands by NSCT. Finally the saliency map of infrared image is used to guide the fusion in low frequency sub-band, and the rule of maximum absolute value selection is used for the fusion in high frequency sub-band. Experimental results demonstrate that compared to several other algorithms, the proposed method highlights the IR targets and at the same time makes the fusion images have rich background information, and better visual fusion effects and objective quality evaluations are obtained.
2017, 46(2): 363-368, 406.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.008
Abstract:
We present a novel on-line algorithm for target segmentation and tracking in video. Superpixels, which are abstracted in every frame, are treated as data points in this paper. The object in current frame is represented as sparse linear combination of dictionary templates, which are generated based on the segmentation result in the previous frame. Then the algorithm capitalizes on the inherent low-rank structure of representation that are learned jointly. A low-rank sparse matrix optimal solution results in the construction of the trimap. At last, a simple energy minimization solution is adopted in segmented stage, leading to a binary pixel-wise segmentation. Experiments demonstrate that our approach is effective.
We present a novel on-line algorithm for target segmentation and tracking in video. Superpixels, which are abstracted in every frame, are treated as data points in this paper. The object in current frame is represented as sparse linear combination of dictionary templates, which are generated based on the segmentation result in the previous frame. Then the algorithm capitalizes on the inherent low-rank structure of representation that are learned jointly. A low-rank sparse matrix optimal solution results in the construction of the trimap. At last, a simple energy minimization solution is adopted in segmented stage, leading to a binary pixel-wise segmentation. Experiments demonstrate that our approach is effective.
2017, 46(2): 369-374.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.009
Abstract:
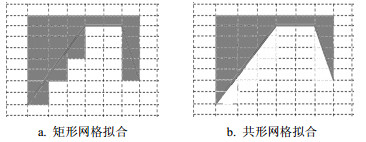
The calculation errors of particle-in-cell (PIC) method at the conformal boundary are analyzed, especially for the conformal boundary at the THz cyclotron oscillator. The condition of stability and two general treatment methods for the conformal grid are put forward. And the stability and accuracy of these two conformal treatment methods are analyzed. Based on these analysis, an adaptive conformal cell subdivision method is developed. With this method, the problems of the limitation of the conformal grid are solved. The method is implemented on the electromagnetic particle simulation software CHIPIC and is verified by simulating a cylindrical waveguide. Finally, using this method, the THz cyclotron maser with TE26 and the quasi optical cavity cyclotron oscillator with HE06 are simulated successfully.
The calculation errors of particle-in-cell (PIC) method at the conformal boundary are analyzed, especially for the conformal boundary at the THz cyclotron oscillator. The condition of stability and two general treatment methods for the conformal grid are put forward. And the stability and accuracy of these two conformal treatment methods are analyzed. Based on these analysis, an adaptive conformal cell subdivision method is developed. With this method, the problems of the limitation of the conformal grid are solved. The method is implemented on the electromagnetic particle simulation software CHIPIC and is verified by simulating a cylindrical waveguide. Finally, using this method, the THz cyclotron maser with TE26 and the quasi optical cavity cyclotron oscillator with HE06 are simulated successfully.
2017, 46(2): 375-379.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.010
Abstract:
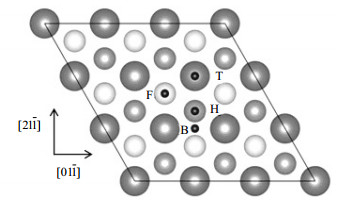
The interactions of hydrogen molecules (H2) and the Cu (111) surface have been studied by using density functional theory based first-principles calculations. The results show that the dissociation of H2 depends mainly on the initial distance from H2 to the surface (hH) and the initial H2 configurations. The H2 molecules of vertical adsorption on Cu (111) are not dissociated for the initial hH of 0.3-4.0 Å, and the undissociated H2 is physically adsorbed on the Cu (111) surface. When H2 molecules are adsorbed on Cu (111) surface in parallel, some of the H2 are dissociated into two hydrogen atoms, which occupy hcp and fcc sites and form stable chemisorption on the Cu (111) surface. The critical distance of H2 dissociation at bri sites is 1.35 Å for parallel adsorption along the[211] direction and 0.65-0.86 Å for other cases.
The interactions of hydrogen molecules (H2) and the Cu (111) surface have been studied by using density functional theory based first-principles calculations. The results show that the dissociation of H2 depends mainly on the initial distance from H2 to the surface (hH) and the initial H2 configurations. The H2 molecules of vertical adsorption on Cu (111) are not dissociated for the initial hH of 0.3-4.0 Å, and the undissociated H2 is physically adsorbed on the Cu (111) surface. When H2 molecules are adsorbed on Cu (111) surface in parallel, some of the H2 are dissociated into two hydrogen atoms, which occupy hcp and fcc sites and form stable chemisorption on the Cu (111) surface. The critical distance of H2 dissociation at bri sites is 1.35 Å for parallel adsorption along the[211] direction and 0.65-0.86 Å for other cases.
2017, 46(2): 380-385.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.011
Abstract:
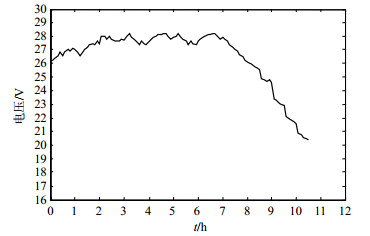
The estimation accuracy of the battery state of charge (SOC) is one of the key factors that affect the performance of new energy vehicles. Owing to the large accumulated error, traditional ampere-hour method cannot meet the precise estimate of the aluminum-air battery SOC. In this paper, the approach based on hidden semi-Markov models (HSMM) of SOC prediction is applied as a complement for the ampere-hour method, making the latter estimation precision of aluminum air battery be guaranteed. Each of the different states of the model produces multiple sets of observations. According to the transition probability between the various states and the residence time, the model can more accurately predict the remaining time of each state. Through the experimental simulation and comparison with the single ampere-hour method, SOC estimation error combined with HSMM promotes the prediction accuracy when the battery is running out.
The estimation accuracy of the battery state of charge (SOC) is one of the key factors that affect the performance of new energy vehicles. Owing to the large accumulated error, traditional ampere-hour method cannot meet the precise estimate of the aluminum-air battery SOC. In this paper, the approach based on hidden semi-Markov models (HSMM) of SOC prediction is applied as a complement for the ampere-hour method, making the latter estimation precision of aluminum air battery be guaranteed. Each of the different states of the model produces multiple sets of observations. According to the transition probability between the various states and the residence time, the model can more accurately predict the remaining time of each state. Through the experimental simulation and comparison with the single ampere-hour method, SOC estimation error combined with HSMM promotes the prediction accuracy when the battery is running out.
2017, 46(2): 386-391.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.012
Abstract:
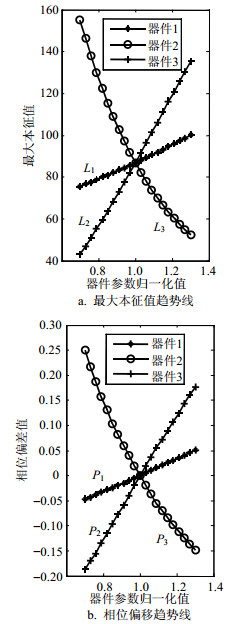
This paper proposes a new model for parametric fault diagnosis in analog circuits, which is one of the most challenging problems in circuits and systems. This new model is based on the eigenvalue and phase difference from the time series of the output voltage of the circuit under test (CUT). The phase deviation information of the circuit is obtained via the sampling voltage time series. The sampling voltage time series is reorganized to be a matrix, and dominant eigenvalue of this matrix is obtained accordingly. Finally, by comparing the phase deviation and the dominant eigenvalue of the CUT with those of the fault free circuit in absolute relative error criteria, fault location and parameter identification can be accomplished. Experimental results show that the proposed method performs well in both fault location and parameter identification with very few access points and relatively low computation cost, moreover, fault location and parameter identification can be realized simultaneously, which makes it an effective and efficient method for fault diagnosis of analog circuits.
This paper proposes a new model for parametric fault diagnosis in analog circuits, which is one of the most challenging problems in circuits and systems. This new model is based on the eigenvalue and phase difference from the time series of the output voltage of the circuit under test (CUT). The phase deviation information of the circuit is obtained via the sampling voltage time series. The sampling voltage time series is reorganized to be a matrix, and dominant eigenvalue of this matrix is obtained accordingly. Finally, by comparing the phase deviation and the dominant eigenvalue of the CUT with those of the fault free circuit in absolute relative error criteria, fault location and parameter identification can be accomplished. Experimental results show that the proposed method performs well in both fault location and parameter identification with very few access points and relatively low computation cost, moreover, fault location and parameter identification can be realized simultaneously, which makes it an effective and efficient method for fault diagnosis of analog circuits.
2017, 46(2): 392-398.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.013
Abstract:
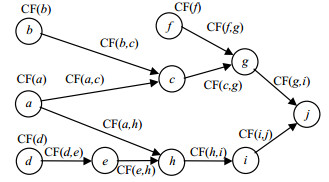
Due to the mix and uncertainty of the microblog information data, the credibility assessment has difficulty to distinguish. An argumentation directedgraphical model for microblog credibility assessment is presented. From the point of view of argumentation, the model, the argument deduction process is described intuitively by graphical model. In the credibility assessment process, we create the argument node based on the relevant topic corpus, define the rule credibility by the thematic sentiment and potential logical relationship, set the weights on the edges, and represent the defense and attack strength between arguments for this reason. The conclusion credibility is achieved and the argumentation graphical with recursion is evolved according to the relevant algorithm. At last the distinguish information could get the credibility. Experimental results show that this model obtains an accuracy up to 6% in comprehensive indexmeasure compared to the traditional methods.
Due to the mix and uncertainty of the microblog information data, the credibility assessment has difficulty to distinguish. An argumentation directedgraphical model for microblog credibility assessment is presented. From the point of view of argumentation, the model, the argument deduction process is described intuitively by graphical model. In the credibility assessment process, we create the argument node based on the relevant topic corpus, define the rule credibility by the thematic sentiment and potential logical relationship, set the weights on the edges, and represent the defense and attack strength between arguments for this reason. The conclusion credibility is achieved and the argumentation graphical with recursion is evolved according to the relevant algorithm. At last the distinguish information could get the credibility. Experimental results show that this model obtains an accuracy up to 6% in comprehensive indexmeasure compared to the traditional methods.
2017, 46(2): 399-406.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.014
Abstract:
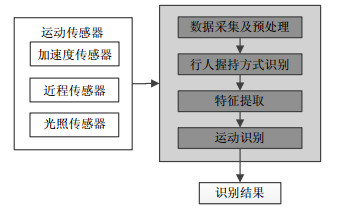
Traditional activity recognition methods are based on sensors at the fixed positions of users. Once the sensors' positions are changed, the performance of the methods will be degraded. Unlike most of these studies, the proposed system firstly detects the holding mode of the phone, and then recognizes the human activities. Our work contains preprocessing, feature extraction and classification. By using wavelet transform and singular value decomposition to extract and reduce features dimension and using RBF-based SVM (support vector machine) for classification, the system is able to recognize 5 holding modes (close to body on the side, swing, holding at the front, close to ear) and 5 activities (stationary, slow walking, normal walking, fast walking and running). Comparing with 4 common classifiers, the result shows that the proposed method performs the best and its detection accuracy is about 93%.
Traditional activity recognition methods are based on sensors at the fixed positions of users. Once the sensors' positions are changed, the performance of the methods will be degraded. Unlike most of these studies, the proposed system firstly detects the holding mode of the phone, and then recognizes the human activities. Our work contains preprocessing, feature extraction and classification. By using wavelet transform and singular value decomposition to extract and reduce features dimension and using RBF-based SVM (support vector machine) for classification, the system is able to recognize 5 holding modes (close to body on the side, swing, holding at the front, close to ear) and 5 activities (stationary, slow walking, normal walking, fast walking and running). Comparing with 4 common classifiers, the result shows that the proposed method performs the best and its detection accuracy is about 93%.
2017, 46(2): 407-411.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.015
Abstract:
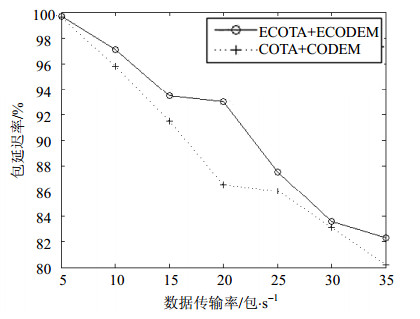
An enhanced congestion traffic allocation (ECOTA) and an efficient congestion detection and mitigation (ECODEM) algorithm are proposed in this paper, based on the traffic allocation and reallocation algorithm. After measuring the energy consumption and transmission delay of all paths, some low energy consumption and short delay paths are selected to increase the success rate of data transmission. The congested area is detected by methods of setting the threshold and prediction. Once the congestion occurs, nodes can quickly recover from congested situations by using reasonable traffic reallocation. And traffic in the congested area can be transferred to the non-congested area as soon as possible. Simulation results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can improve the success rate of packet delivery, reduce the end to end delay and improve the overall performance of the network.
An enhanced congestion traffic allocation (ECOTA) and an efficient congestion detection and mitigation (ECODEM) algorithm are proposed in this paper, based on the traffic allocation and reallocation algorithm. After measuring the energy consumption and transmission delay of all paths, some low energy consumption and short delay paths are selected to increase the success rate of data transmission. The congested area is detected by methods of setting the threshold and prediction. Once the congestion occurs, nodes can quickly recover from congested situations by using reasonable traffic reallocation. And traffic in the congested area can be transferred to the non-congested area as soon as possible. Simulation results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can improve the success rate of packet delivery, reduce the end to end delay and improve the overall performance of the network.
2017, 46(2): 412-418.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.016
Abstract:
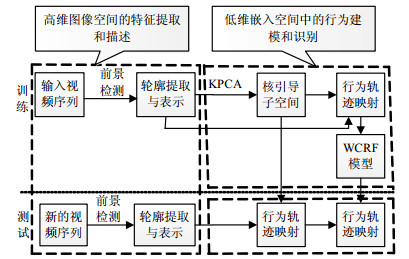
For human behavior recognition in monocular video, a method for recognizing human behavior based on action subspace and weighted condition random field is presented in this paper. This method combines kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) based on feature extraction and weighted conditional random field (WCRF) based on activity modeling. Silhouette data of human is represented more compactly by nonlinear dimensionality reduction that explores the basic structure of action space and preserves explicit temporal orders in the course of projection trajectories of motions. Temporal sequences are modeled in WCRF by using multiple interacting ways, thus increasing joint accuracy by information sharing, and this model has superiority over generative ones (e.g., relaxing independence assumption between observations and the ability to effectively incorporate both overlapping features and long-range dependencies). The experimental results show that the proposed behavior recognition method can not only accurately recognize human activities with temporal, external and internal person variations, but also considerably robust to noise and other factors.
For human behavior recognition in monocular video, a method for recognizing human behavior based on action subspace and weighted condition random field is presented in this paper. This method combines kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) based on feature extraction and weighted conditional random field (WCRF) based on activity modeling. Silhouette data of human is represented more compactly by nonlinear dimensionality reduction that explores the basic structure of action space and preserves explicit temporal orders in the course of projection trajectories of motions. Temporal sequences are modeled in WCRF by using multiple interacting ways, thus increasing joint accuracy by information sharing, and this model has superiority over generative ones (e.g., relaxing independence assumption between observations and the ability to effectively incorporate both overlapping features and long-range dependencies). The experimental results show that the proposed behavior recognition method can not only accurately recognize human activities with temporal, external and internal person variations, but also considerably robust to noise and other factors.
2017, 46(2): 419-425.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.017
Abstract:
An adaptive mixed culture artificial bee colony algorithm (AMC-ABC) is proposed to solve continuous space optimization problem. In the algorithm, community space is evolved by the improved group update way with optimal foraging theory; the knowledge of belief space is updated by the cloud model algorithm and optimal sorting differential mutation strategy; the outer space is evolved by chaos algorithm and opposition-based learning algorithm; and the knowledge exchange of three kinds of spatial is realized by adaptive acceptance operation and effect of operation. Simulation results of the typical complex functions show that the algorithm has fine the convergence precision and computing speed, particularly suitable for optimization the multimodal function.
An adaptive mixed culture artificial bee colony algorithm (AMC-ABC) is proposed to solve continuous space optimization problem. In the algorithm, community space is evolved by the improved group update way with optimal foraging theory; the knowledge of belief space is updated by the cloud model algorithm and optimal sorting differential mutation strategy; the outer space is evolved by chaos algorithm and opposition-based learning algorithm; and the knowledge exchange of three kinds of spatial is realized by adaptive acceptance operation and effect of operation. Simulation results of the typical complex functions show that the algorithm has fine the convergence precision and computing speed, particularly suitable for optimization the multimodal function.
2017, 46(2): 426-433.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.018
Abstract:
Aho-Corasick automata algorithm is a famous multi-string matching algorithm, which backtracks to the effective subsequence state through the fail pointer when it fails in one pattern matching, where one or more effective subsequent states may exist. According to the above characteristics, this paper proposes an automata algorithm suitable for Chinese segmentation. The algorithm calculates the context matching probability of the current pattern by dynamic programming method, and backtracks to the optimal subsequent state of maximum probability, namely, it can realize the combination of the mechanical Chinese segmentation and statistics and probability model. The experimental result shows that a high accuracy rate in Chinese segmentation can be obtained through this algorithm.
Aho-Corasick automata algorithm is a famous multi-string matching algorithm, which backtracks to the effective subsequence state through the fail pointer when it fails in one pattern matching, where one or more effective subsequent states may exist. According to the above characteristics, this paper proposes an automata algorithm suitable for Chinese segmentation. The algorithm calculates the context matching probability of the current pattern by dynamic programming method, and backtracks to the optimal subsequent state of maximum probability, namely, it can realize the combination of the mechanical Chinese segmentation and statistics and probability model. The experimental result shows that a high accuracy rate in Chinese segmentation can be obtained through this algorithm.
2017, 46(2): 434-440.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.019
Abstract:
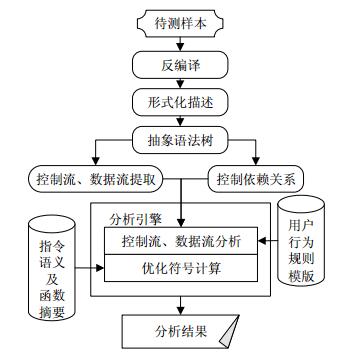
This paper proposes a semantic-based sensitive behavior analysis method for Android. With sample statistics results, the method firstly adopts a simple-Dalvik intermediate language (SDIL) as the intermediate language for text analysis, thus giving a symbolic semantics description for instructions. Then the method uses SDIL to detect sensitive calls from the samples and traces the call paths according to the control dependence. Then based on control-flow analysis, the method adopts constraint solving to obtain path conditions. At last, the method finds the background behaviors with trigger conditions, thus the whole process of background behavior execution will be showed as well. This method can release the path explosion problem in the process of symbolic execution. With experiment under our platform, it proves that the method can analyze the background behaviors of mobile application efficiently, and find the unknown mobile malicious applications which can not be found by traditional feature detection methods in time.
This paper proposes a semantic-based sensitive behavior analysis method for Android. With sample statistics results, the method firstly adopts a simple-Dalvik intermediate language (SDIL) as the intermediate language for text analysis, thus giving a symbolic semantics description for instructions. Then the method uses SDIL to detect sensitive calls from the samples and traces the call paths according to the control dependence. Then based on control-flow analysis, the method adopts constraint solving to obtain path conditions. At last, the method finds the background behaviors with trigger conditions, thus the whole process of background behavior execution will be showed as well. This method can release the path explosion problem in the process of symbolic execution. With experiment under our platform, it proves that the method can analyze the background behaviors of mobile application efficiently, and find the unknown mobile malicious applications which can not be found by traditional feature detection methods in time.
2017, 46(2): 441-448.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.020
Abstract:
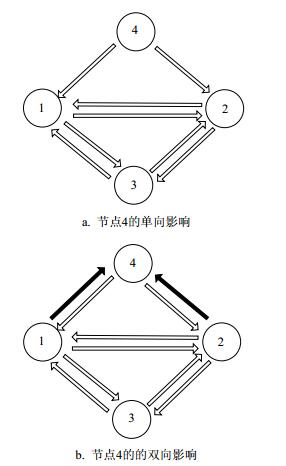
The effect of important nodes in complex networks on the structure and function of the networks causes widespread concern. This paper presents a SRank algorithm based on LeaderRank and nodes similarity which is used to measure the interaction between nodes. The simulation of SIR model and Spearman's correlation coefficient on real social networks show that the SRankalgorithm preforms better on identifying influential nodes both in directed and undirected networks, compared with the other four classical algorithms.
The effect of important nodes in complex networks on the structure and function of the networks causes widespread concern. This paper presents a SRank algorithm based on LeaderRank and nodes similarity which is used to measure the interaction between nodes. The simulation of SIR model and Spearman's correlation coefficient on real social networks show that the SRankalgorithm preforms better on identifying influential nodes both in directed and undirected networks, compared with the other four classical algorithms.
2017, 46(2): 449-457.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.021
Abstract:
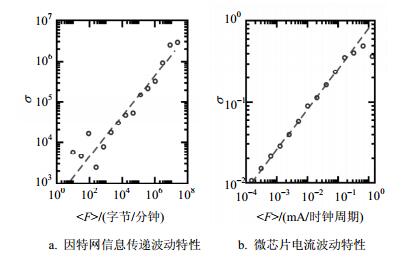
Flux-fluctuation law means the scaling relationship between the mean and the stand errors of traffic in networks. This law has been observed in a wide range of complex systems. Understanding the origin of flux-fluctuation law is fundamental and significant to the dynamics of complex systems. This review article summarizes the state-of-the-art progresses of flux-fluctuation law in complex systems, and give a detailed description of typical models and major results in this area. Moreover, we propose an easy mathematical model, with which we use the mathematic language to provide a universal framework for previous major models. Furthermore, this article reviews the advanced and insufficient points of related works, and points out some unsolved challenges in both theoretical and practical aspects.
Flux-fluctuation law means the scaling relationship between the mean and the stand errors of traffic in networks. This law has been observed in a wide range of complex systems. Understanding the origin of flux-fluctuation law is fundamental and significant to the dynamics of complex systems. This review article summarizes the state-of-the-art progresses of flux-fluctuation law in complex systems, and give a detailed description of typical models and major results in this area. Moreover, we propose an easy mathematical model, with which we use the mathematic language to provide a universal framework for previous major models. Furthermore, this article reviews the advanced and insufficient points of related works, and points out some unsolved challenges in both theoretical and practical aspects.
2017, 46(2): 458-468.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.022
Abstract:
The topic analysis on the Sina microblog data is studied by using the Twitter-LDA topic model. The analysis based on correlation of users' topic interests shows that topic interests between users follow the three degrees of correlation. Within the same topic interest when the number of microblogs that users publish increases, the number of microblogs that their fans within three degrees publish also increases in fluctuation, and the similarity of topic interests between users and their multi-degree fans decreases with the increase of degree. Through the analysis and comparison of the diffusion difference of diverse topic categories, we find that users prefer the information with lifestyle topic, reposting probability is significantly different among microblogs within different topic categories, and the average reposting count can be 10 times in difference. In microblog information diffusion trees, diffusion depth, diffusion time interval and users' diffusion ability all show different characteristics for microblogs with different topic categories.
The topic analysis on the Sina microblog data is studied by using the Twitter-LDA topic model. The analysis based on correlation of users' topic interests shows that topic interests between users follow the three degrees of correlation. Within the same topic interest when the number of microblogs that users publish increases, the number of microblogs that their fans within three degrees publish also increases in fluctuation, and the similarity of topic interests between users and their multi-degree fans decreases with the increase of degree. Through the analysis and comparison of the diffusion difference of diverse topic categories, we find that users prefer the information with lifestyle topic, reposting probability is significantly different among microblogs within different topic categories, and the average reposting count can be 10 times in difference. In microblog information diffusion trees, diffusion depth, diffusion time interval and users' diffusion ability all show different characteristics for microblogs with different topic categories.
2017, 46(2): 469-474.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.023
Abstract:
For aerostatic bearing-rotor coupling system of precision centrifuge, the method of computational fluid dynamics is used to calculate flow field with variation of eccentricity and the supply pressure. The bearing load capacity related to eccentricity and the supply pressure is derived by a nonlinear fitting function. The dynamic characteristic of bearing-rotor system is built based on the finite element method and the response under the influences of gravity and unbalanced force and nonlinear gas film force is calculated. The calculated results show that the rotation error can meet the design requirements of 10-6 precision centrifuge.
For aerostatic bearing-rotor coupling system of precision centrifuge, the method of computational fluid dynamics is used to calculate flow field with variation of eccentricity and the supply pressure. The bearing load capacity related to eccentricity and the supply pressure is derived by a nonlinear fitting function. The dynamic characteristic of bearing-rotor system is built based on the finite element method and the response under the influences of gravity and unbalanced force and nonlinear gas film force is calculated. The calculated results show that the rotation error can meet the design requirements of 10-6 precision centrifuge.
2017, 46(2): 475-480.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.024
Abstract:
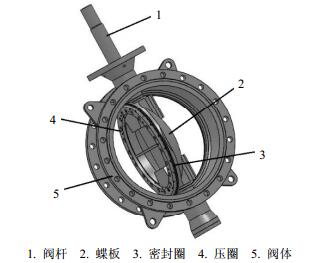
In this study, a series of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were performed with a 100% opening butterfly valve. Grid-adaption processes, including Y plus adaption and gradient adaption, were also applied to refine the meshes. To validate the CFD method, a series of experiments were also conducted according to the national standard of valves-test method of flow coefficient. The results show that the grid-adaption based CFD method can accurately predict the flow coefficients of valves, and the grid-adaption process can effectively improve the simulation accuracy while reducing the workload of mesh refinement.
In this study, a series of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were performed with a 100% opening butterfly valve. Grid-adaption processes, including Y plus adaption and gradient adaption, were also applied to refine the meshes. To validate the CFD method, a series of experiments were also conducted according to the national standard of valves-test method of flow coefficient. The results show that the grid-adaption based CFD method can accurately predict the flow coefficients of valves, and the grid-adaption process can effectively improve the simulation accuracy while reducing the workload of mesh refinement.

 ISSN
ISSN