2017 Vol. 46, No. 3
2017, 46(3): 481-484, 536.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.001
Abstract:
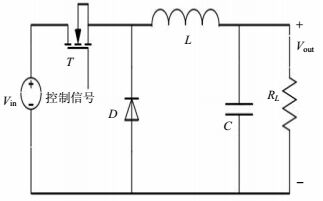
In order to meet the requirements of modern electronic systems, the DC-DC converter needs to have such characteristics as small, light and high reliability. In this paper, a DC-DC converter substrate with embedded inductor is designed by using low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology. The embedded power inductor is modeled and simulated, and the DC characteristics are studied with Anosft Maxwell. The input output circuits and feedback circuit have also been designed. At last, a DC-DC converter with the size 20 mm×15 mm×1 mm and the saturation current more than 2 A has been fabricated.
In order to meet the requirements of modern electronic systems, the DC-DC converter needs to have such characteristics as small, light and high reliability. In this paper, a DC-DC converter substrate with embedded inductor is designed by using low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology. The embedded power inductor is modeled and simulated, and the DC characteristics are studied with Anosft Maxwell. The input output circuits and feedback circuit have also been designed. At last, a DC-DC converter with the size 20 mm×15 mm×1 mm and the saturation current more than 2 A has been fabricated.
2017, 46(3): 485-491.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.002
Abstract:
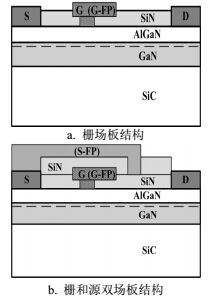
An electro-thermal large-signal model including a nonlinear thermal network for Gallium Nitride high electron mobility transistors (GaN HEMTs) with gate and source field plates is presented in this paper. This model including the nonlinear thermal network with respect to power dissipation is embedded in the improved Angelov model. Based on the electro-thermal principle, the thermal resistance and capacitance for the two field plates of the devices are identified by utilizing the electro-thermal finite element method (FEM) simulations. And the characteristics of small signal and load impedance for the two devices with different field plates have been analyzed in microwave frequency range. Accurate predictions of the quiescent currents, S-parameters up to 40 GHz, and large-signal harmonic performance for the devices with different gate peripheries have been achieved by the proposed model.
An electro-thermal large-signal model including a nonlinear thermal network for Gallium Nitride high electron mobility transistors (GaN HEMTs) with gate and source field plates is presented in this paper. This model including the nonlinear thermal network with respect to power dissipation is embedded in the improved Angelov model. Based on the electro-thermal principle, the thermal resistance and capacitance for the two field plates of the devices are identified by utilizing the electro-thermal finite element method (FEM) simulations. And the characteristics of small signal and load impedance for the two devices with different field plates have been analyzed in microwave frequency range. Accurate predictions of the quiescent currents, S-parameters up to 40 GHz, and large-signal harmonic performance for the devices with different gate peripheries have been achieved by the proposed model.
2017, 46(3): 492-497.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.003
Abstract:
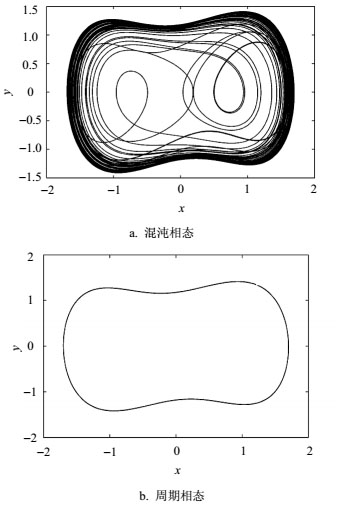
Recent studies suggest that noise could cause the occurrence of Duffing oscillator's phase-state transition, which is one of the most important reasons for the low system detection reliability and has been restricting the application of chaos theory in practical engineering. And hence one novel detection model containing nonlinear damping term is proposed in the paper based on generalized Van der Pol oscillator. And then it is proved feasible for weak signal detection by theoretical analyses. Compared to classical chaotic oscillators, the new model has stronger state robustness and noise immunity with equal complexity. Finally, Simulation results show that the application of the new model can reduce the impacts of noise on the phase-state transition and improve the detection reliability of weak signals.
Recent studies suggest that noise could cause the occurrence of Duffing oscillator's phase-state transition, which is one of the most important reasons for the low system detection reliability and has been restricting the application of chaos theory in practical engineering. And hence one novel detection model containing nonlinear damping term is proposed in the paper based on generalized Van der Pol oscillator. And then it is proved feasible for weak signal detection by theoretical analyses. Compared to classical chaotic oscillators, the new model has stronger state robustness and noise immunity with equal complexity. Finally, Simulation results show that the application of the new model can reduce the impacts of noise on the phase-state transition and improve the detection reliability of weak signals.
2017, 46(3): 498-504.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.004
Abstract:
Ultra-wideband (UWB) channel estimation based on the theory of compressive sensing needs to predict sparsity of the channel. Considering the sparseness of the UWB channel in time domain, the problem of channel estimation can be transformed into the reconstruction of the sparse vector in compressive sensing theory. Sparsity adaptive regularization compressive sampling matching pursuit (SARCoSaMP) algorithm is proposed in this paper. The ideas of adaptive and regularization are introduced based on compressive sampling matching pursuit (CoSaMP) algorithm. The number of the selected atoms is controlled automatically in order to approach channel sparsity K gradually. The UWB channel is estimated accurately although the sparsity of the channel is not available. Results show that the proposed algorithm can be effectively used in ultra-wideband channel estimation and it is significantly superior to CoSaMP and sparsity adaptive matching pursuit (SAMP) algorithm.
Ultra-wideband (UWB) channel estimation based on the theory of compressive sensing needs to predict sparsity of the channel. Considering the sparseness of the UWB channel in time domain, the problem of channel estimation can be transformed into the reconstruction of the sparse vector in compressive sensing theory. Sparsity adaptive regularization compressive sampling matching pursuit (SARCoSaMP) algorithm is proposed in this paper. The ideas of adaptive and regularization are introduced based on compressive sampling matching pursuit (CoSaMP) algorithm. The number of the selected atoms is controlled automatically in order to approach channel sparsity K gradually. The UWB channel is estimated accurately although the sparsity of the channel is not available. Results show that the proposed algorithm can be effectively used in ultra-wideband channel estimation and it is significantly superior to CoSaMP and sparsity adaptive matching pursuit (SAMP) algorithm.
2017, 46(3): 505-510.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.005
Abstract:
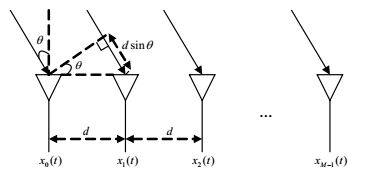
The actual steering vector with errors is usually modeled as an uncertainty set in most robust adaptive beamforming (RAB) against the steering vector mismatch. However, it is commonly difficult to determine the constraint parameter in practice. In this paper, a RAB based on modified noncircular complex fast independent component analysis (MNC-FastICA) algorithm is proposed. The weight vector of beamformer can be constructed with the separation matrix found by MNC-FastICA algorithm and the amplitude and phase ambiguities of estimations resulted from separation are also calibrated. Thus, the signal directions of arrival (DOA) do not need to be predestinated, which voids the mismatch of signal steering vector due to the error of DOA in classical RAB methods. Moreover, the proposed method is not sensitive to the amplitude and phase errors of array channel so that array calibration is not necessary. Simulations are run and the performances are compared with classical methods such as worst-case performance optimization (WCPO). Results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method.
The actual steering vector with errors is usually modeled as an uncertainty set in most robust adaptive beamforming (RAB) against the steering vector mismatch. However, it is commonly difficult to determine the constraint parameter in practice. In this paper, a RAB based on modified noncircular complex fast independent component analysis (MNC-FastICA) algorithm is proposed. The weight vector of beamformer can be constructed with the separation matrix found by MNC-FastICA algorithm and the amplitude and phase ambiguities of estimations resulted from separation are also calibrated. Thus, the signal directions of arrival (DOA) do not need to be predestinated, which voids the mismatch of signal steering vector due to the error of DOA in classical RAB methods. Moreover, the proposed method is not sensitive to the amplitude and phase errors of array channel so that array calibration is not necessary. Simulations are run and the performances are compared with classical methods such as worst-case performance optimization (WCPO). Results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method.
2017, 46(3): 511-515.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.006
Abstract:
Restoring Poisson noise images has been drawn a lot of attention in recent years. To solve this problem, several regularization methods have been put forward. One of the most famous methods is the Total variation (TV) model. However, the TV model will cause staircasing effects. The total generalized variation (TGV) is the extension of TV. Using TGV as a regularization term to recover the Poission image can eliminate staircase effects but the edge details will not preserved very well. In order to overcome this drawback, based on TGV and Shearlet transform, we propose a new regularization method. The proposed model is solved by the alternating direction method of multiplier (ADMM). The numerical results reflect the efficiency of the new model in dealing with Poisson noise image.
Restoring Poisson noise images has been drawn a lot of attention in recent years. To solve this problem, several regularization methods have been put forward. One of the most famous methods is the Total variation (TV) model. However, the TV model will cause staircasing effects. The total generalized variation (TGV) is the extension of TV. Using TGV as a regularization term to recover the Poission image can eliminate staircase effects but the edge details will not preserved very well. In order to overcome this drawback, based on TGV and Shearlet transform, we propose a new regularization method. The proposed model is solved by the alternating direction method of multiplier (ADMM). The numerical results reflect the efficiency of the new model in dealing with Poisson noise image.
2017, 46(3): 516-521.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.007
Abstract:
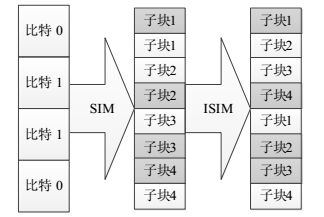
In order to reduce the interference and improve the system performances, this paper utilizes the idea of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with interleaved subcarrier-index modulation (OFDM-ISIM) into Generalized frequency division multiplexing (GFDM), which is referred as interleaved subcarrier-index modulation GFDM (ISIM-GFDM). In the ISIM-GFDM, the data are mapped by the interleaved subcarrier-index modulation in each ISIM-GFDM subsymbol, which can enlarge the average Euclidean distance of the received symbols and improve the error performance of the signal recovery in the receiver. Simulation results show that ISIM-GFDM outperforms GFDM and SIM-GFDM in wireless mobile communication channel in terms of bit error rate (BER).
In order to reduce the interference and improve the system performances, this paper utilizes the idea of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with interleaved subcarrier-index modulation (OFDM-ISIM) into Generalized frequency division multiplexing (GFDM), which is referred as interleaved subcarrier-index modulation GFDM (ISIM-GFDM). In the ISIM-GFDM, the data are mapped by the interleaved subcarrier-index modulation in each ISIM-GFDM subsymbol, which can enlarge the average Euclidean distance of the received symbols and improve the error performance of the signal recovery in the receiver. Simulation results show that ISIM-GFDM outperforms GFDM and SIM-GFDM in wireless mobile communication channel in terms of bit error rate (BER).
2017, 46(3): 522-528.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.008
Abstract:
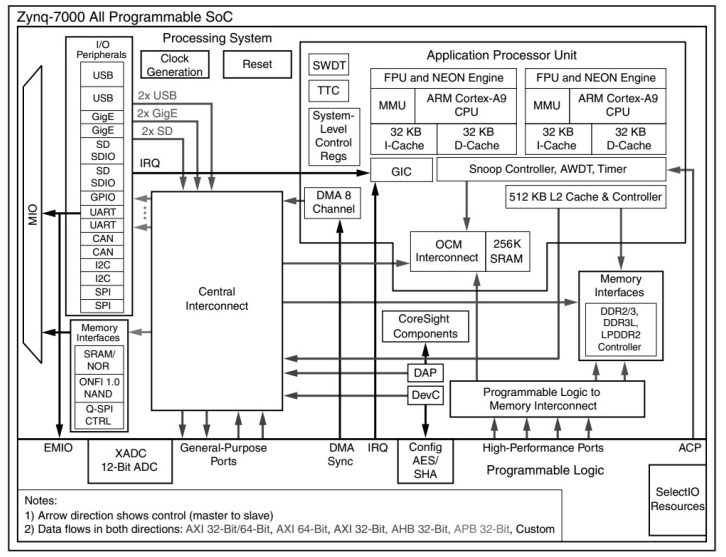
In order to use the excellent transmission performance of peripheral component interconnect express (PCIE) interface to carry out high-speed communication between peripherals and the host effectively, a multi-channel and high-speed PCIE interface scheme is designed based on Zynq family chip of Xilinx. The DMA hardcore controller, device driver and application program are designed on the basis of PCI express 2.0 hardcore using the FPGA+ARM architecture of Zynq-7000 platform. Test results show that the transfer rate in our project almost can reach 3.3 Gbps in PCIE×1 lane and single logical channel, which increases about 20% compared with the traditional existing designs. Our scheme owns higher expansibility and wide application prospect, it is an important design reference for external equipment and PCIE interface.
In order to use the excellent transmission performance of peripheral component interconnect express (PCIE) interface to carry out high-speed communication between peripherals and the host effectively, a multi-channel and high-speed PCIE interface scheme is designed based on Zynq family chip of Xilinx. The DMA hardcore controller, device driver and application program are designed on the basis of PCI express 2.0 hardcore using the FPGA+ARM architecture of Zynq-7000 platform. Test results show that the transfer rate in our project almost can reach 3.3 Gbps in PCIE×1 lane and single logical channel, which increases about 20% compared with the traditional existing designs. Our scheme owns higher expansibility and wide application prospect, it is an important design reference for external equipment and PCIE interface.
2017, 46(3): 529-536.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.009
Abstract:
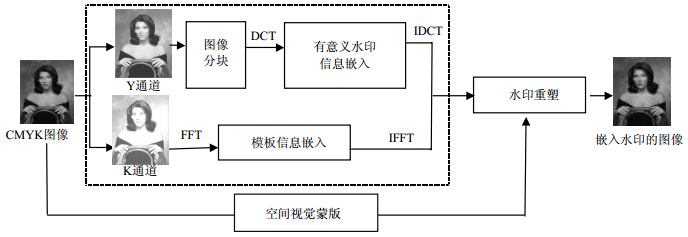
The challenges faced with printed image watermarking applications mainly are the robustness against distortion caused by print-scanning processing and the color fidelity of printed images. Based on the feature of CMYK color space and human visual system, this paper presents a robust CMYK printed image watermarking, which embeds the informative watermark and the structure template signal respectively in the Y color information channel and K color information channel. The embedded template enables the necessary robustness against geometric distortions in print-scanning process. A spatial perceptual mask is used to reshape the embedded energy after it is inverted to the spatial domain, which significantly improves the color fidelity and the image quality. A series of proof tests have been carried out on lithographic printing presses and shows that the watermark embedded in the CMYK images is well preserved and can be extracted with a high quality, and simultaneously, a remarkable fidelity of color and tones on printed copies is also well preserved.
The challenges faced with printed image watermarking applications mainly are the robustness against distortion caused by print-scanning processing and the color fidelity of printed images. Based on the feature of CMYK color space and human visual system, this paper presents a robust CMYK printed image watermarking, which embeds the informative watermark and the structure template signal respectively in the Y color information channel and K color information channel. The embedded template enables the necessary robustness against geometric distortions in print-scanning process. A spatial perceptual mask is used to reshape the embedded energy after it is inverted to the spatial domain, which significantly improves the color fidelity and the image quality. A series of proof tests have been carried out on lithographic printing presses and shows that the watermark embedded in the CMYK images is well preserved and can be extracted with a high quality, and simultaneously, a remarkable fidelity of color and tones on printed copies is also well preserved.
2017, 46(3): 537-542.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.010
Abstract:
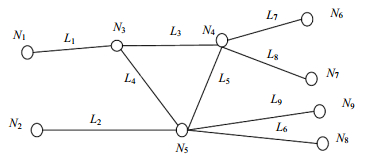
In the method of end-to-end (E2E) path performance active detection (network tomography), the link loss rate solution methods involve the inverse of linear equations, so its large computation complexity may lead to failure. This paper proposes a new congestion link location algorithm based Boolean model. First the nonsingular coefficient matrix of the linear system for solving prior probability is formed; then the prior probability of link congestion is calculated. Finally, based on Bayesian maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimator, the set of congested links can be located. The validity and accuracy of this algorithm is verified by experiments.
In the method of end-to-end (E2E) path performance active detection (network tomography), the link loss rate solution methods involve the inverse of linear equations, so its large computation complexity may lead to failure. This paper proposes a new congestion link location algorithm based Boolean model. First the nonsingular coefficient matrix of the linear system for solving prior probability is formed; then the prior probability of link congestion is calculated. Finally, based on Bayesian maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimator, the set of congested links can be located. The validity and accuracy of this algorithm is verified by experiments.
2017, 46(3): 543-548.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.011
Abstract:
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a key technology for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) autonomous flight and navigation. This paper presents a visual localization and environment mapping method for micro UAV. In the method, the point-plane ICP point cloud matching algorithm is used to achieve visual localization based on RGB-D sensor, the parallel computing acceleration is applied to meet the real-time requirements of UAV control, then the truncated signed distance function (TSDF) algorithm is used for multi-frame point cloud data fusion to achieve environment model reconstruction for an unknown environment, and at last the fusion of visual SLAM system and UAV IMU sensor data is applied to enhance the precision of autonomous localization and model reconstruction. Finally, we set up a micro UAV system with full visual SLAM algorithm and test the whole system in a typical indoor environment. The result shows a 0.092 m positioning deviation and 60 Hz update rate, capable for real-time UAV controlling accuracy requirement, thus verifying the effectiveness of the method.
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a key technology for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) autonomous flight and navigation. This paper presents a visual localization and environment mapping method for micro UAV. In the method, the point-plane ICP point cloud matching algorithm is used to achieve visual localization based on RGB-D sensor, the parallel computing acceleration is applied to meet the real-time requirements of UAV control, then the truncated signed distance function (TSDF) algorithm is used for multi-frame point cloud data fusion to achieve environment model reconstruction for an unknown environment, and at last the fusion of visual SLAM system and UAV IMU sensor data is applied to enhance the precision of autonomous localization and model reconstruction. Finally, we set up a micro UAV system with full visual SLAM algorithm and test the whole system in a typical indoor environment. The result shows a 0.092 m positioning deviation and 60 Hz update rate, capable for real-time UAV controlling accuracy requirement, thus verifying the effectiveness of the method.
2017, 46(3): 549-554.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.012
Abstract:
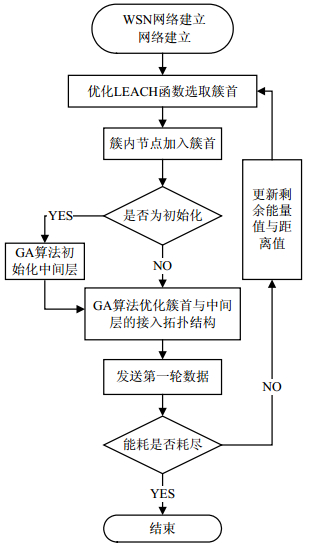
To solve the problems of unbalanced energy consumption and the high energy consumption of header cluster effectively in the wireless sensor networks (WSN), the paper proposes an optimized transportation layer algorithm which is based on the genetic algorithm (GA), low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (LEACH) algorithm, and ZigBee protocol. The algorithm introduces a new type of topological structure and improves the threshold function based on distance and energy consumption for WSN. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve a 95% reduction of communication energy consumption of key cluster head with 9% increase of overall energy consumption, thus effectively improving the uniformity of the energy consumption of WSN, and extending 1~3 times working life of the whole WSN.
To solve the problems of unbalanced energy consumption and the high energy consumption of header cluster effectively in the wireless sensor networks (WSN), the paper proposes an optimized transportation layer algorithm which is based on the genetic algorithm (GA), low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (LEACH) algorithm, and ZigBee protocol. The algorithm introduces a new type of topological structure and improves the threshold function based on distance and energy consumption for WSN. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve a 95% reduction of communication energy consumption of key cluster head with 9% increase of overall energy consumption, thus effectively improving the uniformity of the energy consumption of WSN, and extending 1~3 times working life of the whole WSN.
2017, 46(3): 555-561.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.013
Abstract:
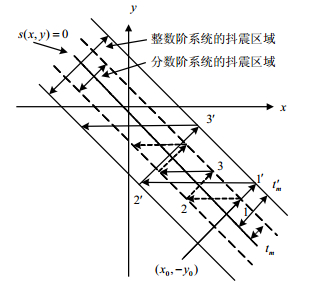
A novel adaptive sliding mode synchronization controller for uncertain fractional order chaotic systems is proposed in this paper. The proposed controller can realize the synchronization of systems with parameters perturbation, function uncertainties, and exterior disturbance. The new sliding mode surface with fractional order has advantages of week chattering and high convergent rate. A novel fractional order adaptive updating law is proposed to prevent the estimations from increasing infinitely. The sliding mode surface and the parameter estimation error of the controller are modelled by utilizing frequency distribution model, and the convergence of the error system is verified by Lyapunov functions, avoiding the mistake caused by directly applying pseudo state variables for the analysis of system synchronization error. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
A novel adaptive sliding mode synchronization controller for uncertain fractional order chaotic systems is proposed in this paper. The proposed controller can realize the synchronization of systems with parameters perturbation, function uncertainties, and exterior disturbance. The new sliding mode surface with fractional order has advantages of week chattering and high convergent rate. A novel fractional order adaptive updating law is proposed to prevent the estimations from increasing infinitely. The sliding mode surface and the parameter estimation error of the controller are modelled by utilizing frequency distribution model, and the convergence of the error system is verified by Lyapunov functions, avoiding the mistake caused by directly applying pseudo state variables for the analysis of system synchronization error. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
2017, 46(3): 562-568.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.014
Abstract:
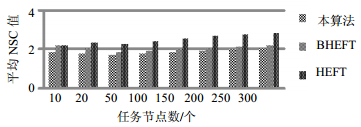
The existing cloud workflow scheduling algorithms, using the global search for resource selection, exist a high computational cost and poor adaptability for large-scale cloud systems. Aimed at solving these problem, a multi-constrained cloud workflow scheduling algorithm based on resource grouping is proposed in this paper. It uses the direct acyclic graph to model the multi-task in cloud workflow and characterize the execution sequences and data transfer requirement between tasks with the DAG's node and edge's attributes. Then, fuzzy clustering method is employed to classify resources based on multidimensional features and reduce the computational load from workflow tasks to resource selection. By introducing execution time and cost budget constraints, the proposed algorithm transforms the scheduling problem into a minimax problem. Simulation results show that our algorithm significantly reduces the task execution time and cost.
The existing cloud workflow scheduling algorithms, using the global search for resource selection, exist a high computational cost and poor adaptability for large-scale cloud systems. Aimed at solving these problem, a multi-constrained cloud workflow scheduling algorithm based on resource grouping is proposed in this paper. It uses the direct acyclic graph to model the multi-task in cloud workflow and characterize the execution sequences and data transfer requirement between tasks with the DAG's node and edge's attributes. Then, fuzzy clustering method is employed to classify resources based on multidimensional features and reduce the computational load from workflow tasks to resource selection. By introducing execution time and cost budget constraints, the proposed algorithm transforms the scheduling problem into a minimax problem. Simulation results show that our algorithm significantly reduces the task execution time and cost.
2017, 46(3): 569-576.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.015
Abstract:
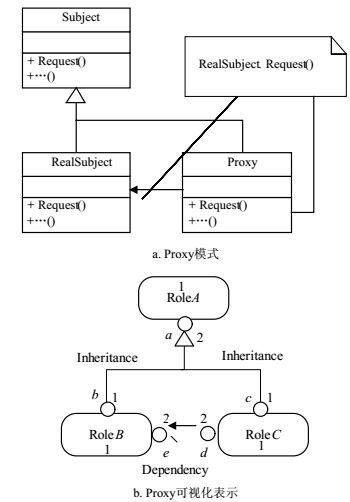
Aiming at obtaining the accurate detection results of design pattern, an optimization method for design pattern identification based on the grammar production is presented for solving the variant problem of design pattern. The method focuses on role attributes of participants and relationships of design pattern instances by visual grammar production, and identifies the overlapping patterns and the additional relations between the participant roles by adding the feature information of grammar production. Experiment results show that the proposed method can reduce the false positive results and the false negative results. F-score index comparison with other well-known algorithms indicates the effectiveness and merits of the proposed method.
Aiming at obtaining the accurate detection results of design pattern, an optimization method for design pattern identification based on the grammar production is presented for solving the variant problem of design pattern. The method focuses on role attributes of participants and relationships of design pattern instances by visual grammar production, and identifies the overlapping patterns and the additional relations between the participant roles by adding the feature information of grammar production. Experiment results show that the proposed method can reduce the false positive results and the false negative results. F-score index comparison with other well-known algorithms indicates the effectiveness and merits of the proposed method.
2017, 46(3): 577-582.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.016
Abstract:
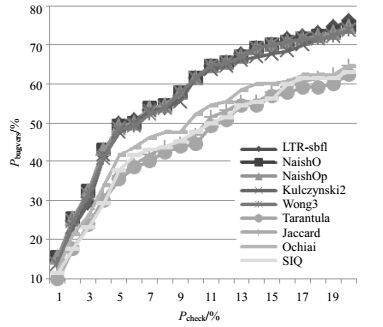
Spectrum-based fault localization (SBFL) has been proven to be the promising technique during software debugging. SBFL combined various factors in the execution profile to form different fault localization models. However, these models are still agnostic to the particular program and dataset. In this paper we propose a learning to rank method referred to as LTR-sbfl which automatically constructs the SBFL model for each program. Like the existing SBFL methods, we first collect program execution traces and results of test cases. Next, it is directly mapped from the coverage difference in a pair of faulty statement and non-faulty statement to an instance in supervised learning. Finally, the conventional classification algorithm is applied to learn a ranking model for a program based on the training data. The proposed method on three benchmark datasets is evaluated through experiment. Results show that LTR-sbfl can outperform other SBFL approaches in the precision of fault localization.
Spectrum-based fault localization (SBFL) has been proven to be the promising technique during software debugging. SBFL combined various factors in the execution profile to form different fault localization models. However, these models are still agnostic to the particular program and dataset. In this paper we propose a learning to rank method referred to as LTR-sbfl which automatically constructs the SBFL model for each program. Like the existing SBFL methods, we first collect program execution traces and results of test cases. Next, it is directly mapped from the coverage difference in a pair of faulty statement and non-faulty statement to an instance in supervised learning. Finally, the conventional classification algorithm is applied to learn a ranking model for a program based on the training data. The proposed method on three benchmark datasets is evaluated through experiment. Results show that LTR-sbfl can outperform other SBFL approaches in the precision of fault localization.
2017, 46(3): 583-587, 611.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.017
Abstract:
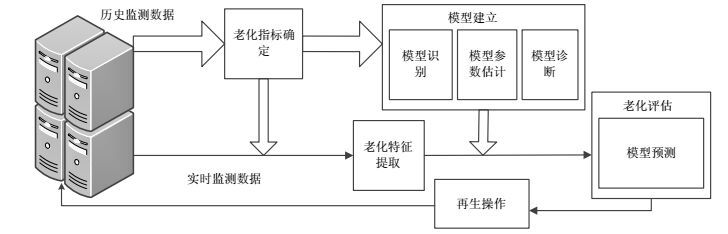
Software aging is a common phenomenon in a system that needs long-term operation. The existing analysis methods based on time series analysis mainly focus on autoregressive moving average (ARMA) models, not fully considered the seasonality or non-stationarity of the key indicators about software aging. This paper proposes a new software aging evaluation method based on seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model. The experimental results show that the method can well fit the software aging trend of seasonal load systems, and can achieve accurate prediction for supporting software rejuvenation.
Software aging is a common phenomenon in a system that needs long-term operation. The existing analysis methods based on time series analysis mainly focus on autoregressive moving average (ARMA) models, not fully considered the seasonality or non-stationarity of the key indicators about software aging. This paper proposes a new software aging evaluation method based on seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model. The experimental results show that the method can well fit the software aging trend of seasonal load systems, and can achieve accurate prediction for supporting software rejuvenation.
2017, 46(3): 588-593.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.018
Abstract:
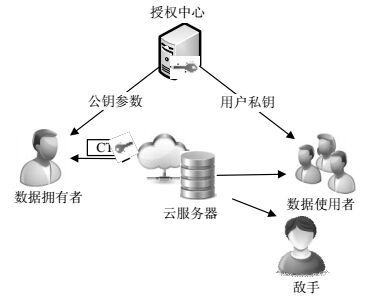
A timed access solution of sensitive data based on dual encryption scheme is proposed to solve the problem of timed deletion of shared sensitive data stored in outsourcing storage. In our solution, the shared sensitive data file is encrypted by symmetric encryption, and the encrypted file is randomly divided to form the extracted cipher component and the encapsulated cipher component. Then, the attribute based timed encryption algorithm is used to encrypt the symmetric key and extracted cipher component, which can generate access control object. Finally, the encapsulated cipher component is combined with the access control object and sent into the cloud server. By this scheme, the authorized user can decrypt the access control object in the time limitation, obtain the symmetric key and extract cipher component, compose the original ciphertext, and recover the plaintext. Once access windows period expire, any users are unable to decrypt the access control object, get the symmetric key, recover the plaintext, so as to realize the timed destruction of sensitive data. The security of the scheme is analyzed and proved by the adversary attack model.
A timed access solution of sensitive data based on dual encryption scheme is proposed to solve the problem of timed deletion of shared sensitive data stored in outsourcing storage. In our solution, the shared sensitive data file is encrypted by symmetric encryption, and the encrypted file is randomly divided to form the extracted cipher component and the encapsulated cipher component. Then, the attribute based timed encryption algorithm is used to encrypt the symmetric key and extracted cipher component, which can generate access control object. Finally, the encapsulated cipher component is combined with the access control object and sent into the cloud server. By this scheme, the authorized user can decrypt the access control object in the time limitation, obtain the symmetric key and extract cipher component, compose the original ciphertext, and recover the plaintext. Once access windows period expire, any users are unable to decrypt the access control object, get the symmetric key, recover the plaintext, so as to realize the timed destruction of sensitive data. The security of the scheme is analyzed and proved by the adversary attack model.
2017, 46(3): 594-599.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.019
Abstract:
Noise is a serious challenge that militates against the security of quantum dialogue, quantum information fidelity, quantum channel capacity, and quantum information disclosure. In order to solve this problem, we propose a robust quantum dialogue protocol that is immune against joint rotation noise, establish a logical quantum state that is immune to the combined rotation noise in the cluster state which also serves as a quantum carrier, and then construct the corresponding decoherence free subspace (DFS). With advantages of the entangled exchange of quantum cryptography, steganography, and eavesdropping detection, etc, a quantum fidelity dialogue model is realized which is resistant against rotational noise. This model therefore ensures the accuracy and security of the exchange of confidential information through a quantum channel. By comparison, the proposed protocol has the highest quantum bit efficiency, and the measurement requires only a single photon.
Noise is a serious challenge that militates against the security of quantum dialogue, quantum information fidelity, quantum channel capacity, and quantum information disclosure. In order to solve this problem, we propose a robust quantum dialogue protocol that is immune against joint rotation noise, establish a logical quantum state that is immune to the combined rotation noise in the cluster state which also serves as a quantum carrier, and then construct the corresponding decoherence free subspace (DFS). With advantages of the entangled exchange of quantum cryptography, steganography, and eavesdropping detection, etc, a quantum fidelity dialogue model is realized which is resistant against rotational noise. This model therefore ensures the accuracy and security of the exchange of confidential information through a quantum channel. By comparison, the proposed protocol has the highest quantum bit efficiency, and the measurement requires only a single photon.
2017, 46(3): 600-605.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.020
Abstract:
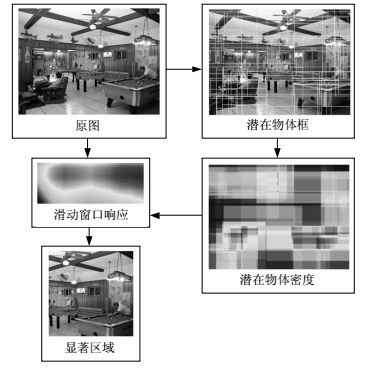
Scene recognition is an important and challenging topic in the research filed of high level image understanding. Traditional researches of scene recognition focused on handcrafted features, which result in limited discriminative and generalization ability. In addition, finding regions in a scene with rich information is always very challenging. This paper presents an effective method for scene recognition based on learned features from multi-scale salient regions. The method first finds multi-scale salient regions in a scene and then extracts the features from the regions via transfer learning using convolutional neural networks (ConvNets). Experiments on two popular scene recognition datasets show that our proposed method is effective and has good generalization ability for scene recognition, compared with the benchmarks on both of the datasets.
Scene recognition is an important and challenging topic in the research filed of high level image understanding. Traditional researches of scene recognition focused on handcrafted features, which result in limited discriminative and generalization ability. In addition, finding regions in a scene with rich information is always very challenging. This paper presents an effective method for scene recognition based on learned features from multi-scale salient regions. The method first finds multi-scale salient regions in a scene and then extracts the features from the regions via transfer learning using convolutional neural networks (ConvNets). Experiments on two popular scene recognition datasets show that our proposed method is effective and has good generalization ability for scene recognition, compared with the benchmarks on both of the datasets.
2017, 46(3): 606-611.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.021
Abstract:
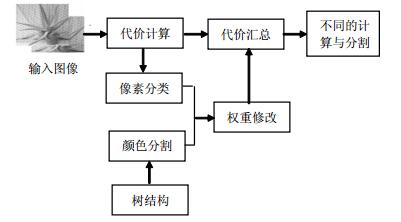
Tree filter matching method will cause wrong matching results since it considers only one single component with color to obtain the weight of support region. This paper presents a local tree filter stereo matching method based on pixel classification and color segmentation. The pixels of an image are classified according to their stability during their initial matching cost computation phase. A tree structure based on color information of reference image is constructed, meanwhile, a segmented image with color segmentation constraint is generated. The weight value of each edge is improved by utilizing the information of segmented color image and classified pixels. Finally, the tree filter is executed and the dense disparity is achieved. The experimental results on Middlebury datasets show that our proposed method has higher accuracy than other original tree filter methods in each special region.
Tree filter matching method will cause wrong matching results since it considers only one single component with color to obtain the weight of support region. This paper presents a local tree filter stereo matching method based on pixel classification and color segmentation. The pixels of an image are classified according to their stability during their initial matching cost computation phase. A tree structure based on color information of reference image is constructed, meanwhile, a segmented image with color segmentation constraint is generated. The weight value of each edge is improved by utilizing the information of segmented color image and classified pixels. Finally, the tree filter is executed and the dense disparity is achieved. The experimental results on Middlebury datasets show that our proposed method has higher accuracy than other original tree filter methods in each special region.
2017, 46(3): 612-617.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.022
Abstract:
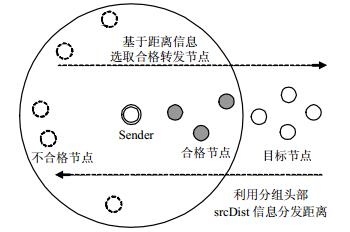
The distinctive features make content-centric networking (CCN) as a potential networking scheme for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs), such as asynchronous communication paradigm, in-network caching and multi-path forwarding, and thus, content-centric mobile ad hoc network (CCM) is becoming a hot issue in the area of CCN. Firstly, a content routing model of CCM is introduced, and then the major content routing schemes are elaborated. Furthermore, the existing issues are concluded in terms of broadcasting and routing model. The work shows the current research progress on content routing in CCM.
The distinctive features make content-centric networking (CCN) as a potential networking scheme for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs), such as asynchronous communication paradigm, in-network caching and multi-path forwarding, and thus, content-centric mobile ad hoc network (CCM) is becoming a hot issue in the area of CCN. Firstly, a content routing model of CCM is introduced, and then the major content routing schemes are elaborated. Furthermore, the existing issues are concluded in terms of broadcasting and routing model. The work shows the current research progress on content routing in CCM.
2017, 46(3): 618-624.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.023
Abstract:
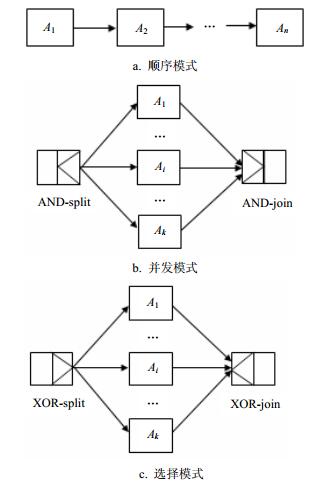
The quality of service (QoS)-aware web service composition problem is a research hotspot. Its objective is to select a composite service which can maximizes the QoS utility while preserving QoS constraints. By giving the definition of usual workflow and the combination rule of virtual tasks, a top-k based web service composition approach is proposed. Its core idea is to transform the original workflow into a virtual task by recursively calling the combination rule of virtual tasks. Moreover, a new scheme is presented to select suitable replaceable services to support the self-healing property. The effectiveness of the k value and the performances of algorithms are analyzed through simulation experiments.
The quality of service (QoS)-aware web service composition problem is a research hotspot. Its objective is to select a composite service which can maximizes the QoS utility while preserving QoS constraints. By giving the definition of usual workflow and the combination rule of virtual tasks, a top-k based web service composition approach is proposed. Its core idea is to transform the original workflow into a virtual task by recursively calling the combination rule of virtual tasks. Moreover, a new scheme is presented to select suitable replaceable services to support the self-healing property. The effectiveness of the k value and the performances of algorithms are analyzed through simulation experiments.
2017, 46(3): 625-630.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.024
Abstract:
Classification algorithm is one of the important tasks and techniques in the field of time series data mining. A classification method for time series data based on center sequences of clusters is proposed in this paper. Time series in the training set are divided into several clusters according to their labels, and every cluster picks out the representation objects using affinity propagation clustering and constructs the representation subset. The barycenter averaging method based on dynamic time warping is used to calculate the center group in which the improved K nearest neighbors method is executed for time series classification. The experimental results demonstrated that the new method, compared to the traditional method, has better classification quality and calculation performance.
Classification algorithm is one of the important tasks and techniques in the field of time series data mining. A classification method for time series data based on center sequences of clusters is proposed in this paper. Time series in the training set are divided into several clusters according to their labels, and every cluster picks out the representation objects using affinity propagation clustering and constructs the representation subset. The barycenter averaging method based on dynamic time warping is used to calculate the center group in which the improved K nearest neighbors method is executed for time series classification. The experimental results demonstrated that the new method, compared to the traditional method, has better classification quality and calculation performance.
2017, 46(3): 631-635.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.025
Abstract:
For most real-time operating systems, only the event-triggered mechanism is supported. This paper proposes a scheduling mechanism which can support not only time-triggered but also event-triggered tasks in μC/OS-Ⅱ. For safety critical tasks in this embedded system, a simple and easy scheduling algorithm is also presented based on criticality degree based priority (CDBP). This algorithm ensures the execution of the emergency tasks at a low level and the execution of the higher critical tasks at the high level while reducing the unnecessary task switching overhead. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is better than own criticality based priority (OCBP) algorithm in improving the system efficiency and provides better support for the criticality tasks and emergency tasks.
For most real-time operating systems, only the event-triggered mechanism is supported. This paper proposes a scheduling mechanism which can support not only time-triggered but also event-triggered tasks in μC/OS-Ⅱ. For safety critical tasks in this embedded system, a simple and easy scheduling algorithm is also presented based on criticality degree based priority (CDBP). This algorithm ensures the execution of the emergency tasks at a low level and the execution of the higher critical tasks at the high level while reducing the unnecessary task switching overhead. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is better than own criticality based priority (OCBP) algorithm in improving the system efficiency and provides better support for the criticality tasks and emergency tasks.
2017, 46(3): 636-640.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.03.026
Abstract:
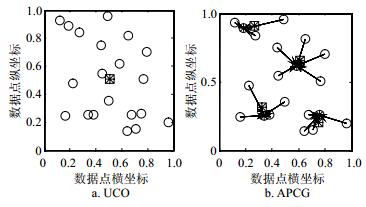
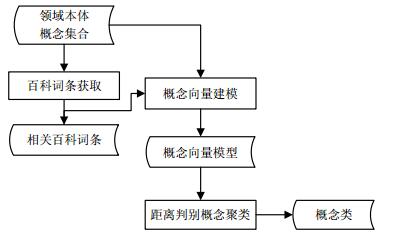
To build the set of ontology relations automatically, this paper presents a preliminary study on a concept clustering method based on encyclopedia entries of obtaining semantic relations among concepts. Given a set of domain ontology concepts, this method clusters concepts in 3 steps: 1) obtaining encyclopedia entries; 2) modeling each of the concepts into a vector; 3) clustering concepts using the distance discrimination method. Clustering experiments on 3 sets of domain ontology concepts demonstrate that the proposed method shows better results compared with classical clustering methods and has good potentials for identifying related concepts automatically in the ontology building tasks.
To build the set of ontology relations automatically, this paper presents a preliminary study on a concept clustering method based on encyclopedia entries of obtaining semantic relations among concepts. Given a set of domain ontology concepts, this method clusters concepts in 3 steps: 1) obtaining encyclopedia entries; 2) modeling each of the concepts into a vector; 3) clustering concepts using the distance discrimination method. Clustering experiments on 3 sets of domain ontology concepts demonstrate that the proposed method shows better results compared with classical clustering methods and has good potentials for identifying related concepts automatically in the ontology building tasks.

 ISSN
ISSN