2017 Vol. 46, No. 4
2017, 46(4): 481-487.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.001
Abstract:
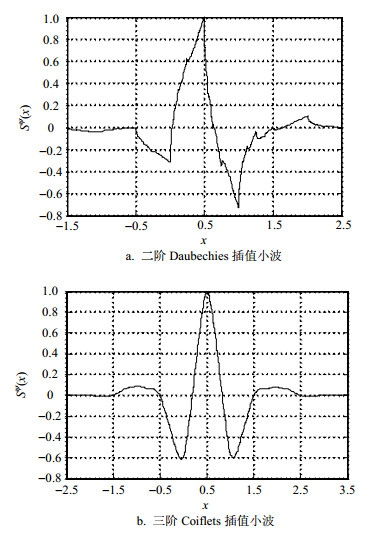
In classical wavelet sampling theory, interpolatory wavelets are constructed by using orthogonal wavelets. Since the analytic expressions of orthogonal wavelets are usually complex or unavailable, interpolatory wavelet construction has become an important topic in signal processing and harmonic analysis. In this paper, a new method is proposed to construct interpolating wavelets from scaling functions. Since this method has avoided using orthogonal wavelets in construction of interpolation wavelets, it can greatly improve efficiency of interpolating wavelet construction. Taking Daubechies and Coiflets MRAs as examples, our method is verified to be effective for interpolatory wavelet construction.
In classical wavelet sampling theory, interpolatory wavelets are constructed by using orthogonal wavelets. Since the analytic expressions of orthogonal wavelets are usually complex or unavailable, interpolatory wavelet construction has become an important topic in signal processing and harmonic analysis. In this paper, a new method is proposed to construct interpolating wavelets from scaling functions. Since this method has avoided using orthogonal wavelets in construction of interpolation wavelets, it can greatly improve efficiency of interpolating wavelet construction. Taking Daubechies and Coiflets MRAs as examples, our method is verified to be effective for interpolatory wavelet construction.
2017, 46(4): 488-494.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.002
Abstract:
Blind recognition of space-time block coding (STBC) is an important issue in the non-cooperative scenario. However, few literatures on blind recognition in multiple input single output system are reported. An efficient algorithm for STBC recognition is proposed when a single antenna is employed at the receiver. The algorithm exploits the discrimination features provided by the empirical cumulative distributions (CDFs) of the received signal. The distance between CDFs employed relies on the two-sample Kolmogrov-Smirnov(K-S) test. The proposed algorithm does not need the estimation of channel, noise statistics and modulation type, but only need fewer samples. The simulation shows that the proposed algorithm performs well, and is robust to modulation and carrier frequency offset, even with non-Gaussian noise.
Blind recognition of space-time block coding (STBC) is an important issue in the non-cooperative scenario. However, few literatures on blind recognition in multiple input single output system are reported. An efficient algorithm for STBC recognition is proposed when a single antenna is employed at the receiver. The algorithm exploits the discrimination features provided by the empirical cumulative distributions (CDFs) of the received signal. The distance between CDFs employed relies on the two-sample Kolmogrov-Smirnov(K-S) test. The proposed algorithm does not need the estimation of channel, noise statistics and modulation type, but only need fewer samples. The simulation shows that the proposed algorithm performs well, and is robust to modulation and carrier frequency offset, even with non-Gaussian noise.
2017, 46(4): 495-500.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.003
Abstract:
A novel algorithm for high-speed multi-target detection and parameters estimation with narrowband radar is proposed in this paper. Firstly, base on cyclostationarity, moving parameters are roughly estimated with the joint Keystone transform and ambiguity searching. And then, according to the coarse estimation, the joint compensating range migration in frequency domain and fractional Fourier transform are utilized to conduct the targets detection and parameters estimation. In the case of multi-target, range migration, Doppler spread and Doppler ambiguity, this algorithm is suitable, and retains the merit of low computational complexity of cyclostationarity. Compared with existing cyclostationarity based algorithms, the weaknesses of low estimation precision and limited range of moving parameters are conquered in engineering applications. The validity of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated by computer simulation and raw radar data results.
A novel algorithm for high-speed multi-target detection and parameters estimation with narrowband radar is proposed in this paper. Firstly, base on cyclostationarity, moving parameters are roughly estimated with the joint Keystone transform and ambiguity searching. And then, according to the coarse estimation, the joint compensating range migration in frequency domain and fractional Fourier transform are utilized to conduct the targets detection and parameters estimation. In the case of multi-target, range migration, Doppler spread and Doppler ambiguity, this algorithm is suitable, and retains the merit of low computational complexity of cyclostationarity. Compared with existing cyclostationarity based algorithms, the weaknesses of low estimation precision and limited range of moving parameters are conquered in engineering applications. The validity of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated by computer simulation and raw radar data results.
2017, 46(4): 501-504, 512.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.004
Abstract:
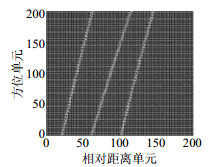
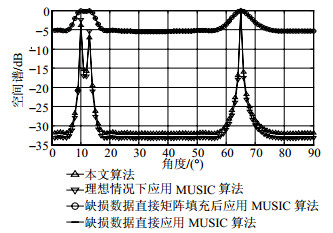
In order to solve the accuracy decrease in angle estimation caused by the undersampling or the damage of the array elements in the uniform linear array, the matrix completion theory and Hankel matrix characteristic are exploited to transform the undersampling data matrix into a two-fold Hankel matrix. The completed data matrix is reconstructed by inexact augmented Lagrange multiplier method and the accurate angle estimation is achieved. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method is still effective with damaged and missing elements and show the tendency of the proposed method versus the different elements damage of the uniform linear array.
In order to solve the accuracy decrease in angle estimation caused by the undersampling or the damage of the array elements in the uniform linear array, the matrix completion theory and Hankel matrix characteristic are exploited to transform the undersampling data matrix into a two-fold Hankel matrix. The completed data matrix is reconstructed by inexact augmented Lagrange multiplier method and the accurate angle estimation is achieved. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method is still effective with damaged and missing elements and show the tendency of the proposed method versus the different elements damage of the uniform linear array.
2017, 46(4): 505-512.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.005
Abstract:
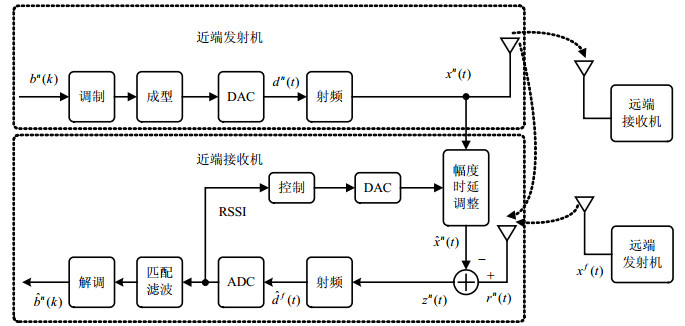
In a full-duplex transceiver which transmits and receives at the same frequency simultaneously, a radiofrequency (RF) adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm based on quick search is proposed to cancel the single path self-interference. By analyzing the impact of the magnitude and phase estimation errors on the residual received signal power after the self-interference cancellation, the RF quick adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm is derived, and its convergence performance is discussed. By analysis and simulation, the RF adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm based on quick search can effectively cancel the self-interference at the RF domain, and its convergence time decreases by 60% compared with the existing RF adaptive self-interference canceller.
In a full-duplex transceiver which transmits and receives at the same frequency simultaneously, a radiofrequency (RF) adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm based on quick search is proposed to cancel the single path self-interference. By analyzing the impact of the magnitude and phase estimation errors on the residual received signal power after the self-interference cancellation, the RF quick adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm is derived, and its convergence performance is discussed. By analysis and simulation, the RF adaptive self-interference cancellation algorithm based on quick search can effectively cancel the self-interference at the RF domain, and its convergence time decreases by 60% compared with the existing RF adaptive self-interference canceller.
2017, 46(4): 513-519.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.006
Abstract:
Netted radar has excellent performance for anti-jamming, especially for the deception jamming. According to the difference in spatial correlation, it can discriminate deceptive false targets by utilizing the method of data fusion. To solve the problem of optimal allocation of netted radar under deception jamming, we first analyze the anti-jamming ability of the fusion-based method in theory and obtain the theoretical expression for the cheated probability of netted radar. Based on the obtained theoretical expression, we propose an optimal deployment algorithm which can achieve the minimization of the cheated probability of netted radar and the maximization of its detection area. The simulations illustrate the locations of optimal deployment in different conditions.
Netted radar has excellent performance for anti-jamming, especially for the deception jamming. According to the difference in spatial correlation, it can discriminate deceptive false targets by utilizing the method of data fusion. To solve the problem of optimal allocation of netted radar under deception jamming, we first analyze the anti-jamming ability of the fusion-based method in theory and obtain the theoretical expression for the cheated probability of netted radar. Based on the obtained theoretical expression, we propose an optimal deployment algorithm which can achieve the minimization of the cheated probability of netted radar and the maximization of its detection area. The simulations illustrate the locations of optimal deployment in different conditions.
2017, 46(4): 520-524.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.007
Abstract:
To further improve the ability of analyzing electromagnetic scattering from electrically large perfect electric conducting objects, an efficient domain decomposition method is presented. In this method, the approximated current density is expanded with the phase-extracted basis functions defined over curvilinear triangular patches, and the number of unknowns to be solved is significantly reduced. Meanwhile, to further reduce the memory requirement, the original problem domain is divided into a number of small overlapped sub-domains and the sub-domain problems are solved one by one. In addition, the buffer regions introduced in this method are limited to only a single layer of jagged triangular mesh cells whose edges are about half a wavelength long, leading to a simplified construction process of buffer zones as well as a smaller number of additional variables to be solved. A good convergence behavior is observed. The multilevel fast multipole algorithm is applied to accelerate the matrix-vector products. Numerical examples are given to show the efficiency and robustness of the proposed approach.
To further improve the ability of analyzing electromagnetic scattering from electrically large perfect electric conducting objects, an efficient domain decomposition method is presented. In this method, the approximated current density is expanded with the phase-extracted basis functions defined over curvilinear triangular patches, and the number of unknowns to be solved is significantly reduced. Meanwhile, to further reduce the memory requirement, the original problem domain is divided into a number of small overlapped sub-domains and the sub-domain problems are solved one by one. In addition, the buffer regions introduced in this method are limited to only a single layer of jagged triangular mesh cells whose edges are about half a wavelength long, leading to a simplified construction process of buffer zones as well as a smaller number of additional variables to be solved. A good convergence behavior is observed. The multilevel fast multipole algorithm is applied to accelerate the matrix-vector products. Numerical examples are given to show the efficiency and robustness of the proposed approach.
2017, 46(4): 525-529.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.008
Abstract:
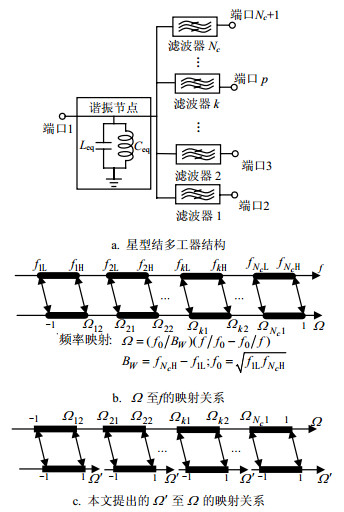
This paper presents a method for synthesizing coupled resonator multiplexers with a star-junction (an extra resonant junction in addition to the channel filters). A linear frequency transformation is proposed for the evaluation of the characteristic polynomials of the each channel filter composed of star-junction multiplexers, and then coupling matrix of overall multiplexers can be obtained by using the proposed linear frequency transformation and well-established method. The evaluation of group delay in the physical frequency f domain and S-parameters based on coupling matrix are derived. To illustrate the validation of the method, two examples, including 25-poles multiplexers and 7-poles diplexer, have been synthesized, and the 7-poles diplexer has been further designed, manufactured and measured. The measured resuts are in good agreement with the synthetic results, which further verify the accuracy of the proposed method.
This paper presents a method for synthesizing coupled resonator multiplexers with a star-junction (an extra resonant junction in addition to the channel filters). A linear frequency transformation is proposed for the evaluation of the characteristic polynomials of the each channel filter composed of star-junction multiplexers, and then coupling matrix of overall multiplexers can be obtained by using the proposed linear frequency transformation and well-established method. The evaluation of group delay in the physical frequency f domain and S-parameters based on coupling matrix are derived. To illustrate the validation of the method, two examples, including 25-poles multiplexers and 7-poles diplexer, have been synthesized, and the 7-poles diplexer has been further designed, manufactured and measured. The measured resuts are in good agreement with the synthetic results, which further verify the accuracy of the proposed method.
2017, 46(4): 530-533.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.009
Abstract:
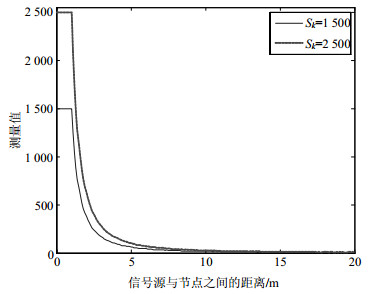
In this paper, we focus on the multi-acoustic source localization algorithm based on wireless sensor networks. First, the logarithm quantization strategy is proposed for the propagation characteristics of the ultrasonic source. The nodes calculate the quantized data according to the quantization strategy and the measured value, and transmit the quantized data to the base station. The base station then estimates the localization of the acoustic source with the proposed multi-acoustic source localization algorithm based on the likelihood C-means clustering algorithm. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm under different parameters is verified and the simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can estimate the position of the multi-acoustic source more accurately and has some robustness to packet loss rate.
In this paper, we focus on the multi-acoustic source localization algorithm based on wireless sensor networks. First, the logarithm quantization strategy is proposed for the propagation characteristics of the ultrasonic source. The nodes calculate the quantized data according to the quantization strategy and the measured value, and transmit the quantized data to the base station. The base station then estimates the localization of the acoustic source with the proposed multi-acoustic source localization algorithm based on the likelihood C-means clustering algorithm. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm under different parameters is verified and the simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can estimate the position of the multi-acoustic source more accurately and has some robustness to packet loss rate.
2017, 46(4): 534-539, 599.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.010
Abstract:
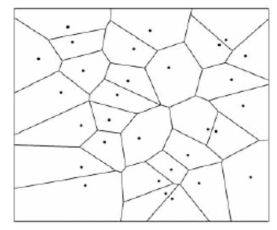
This paper proposes two improved recovery algorithms on the base of Voronoi algorithm (VOR):priority-based VOR (VORP) and V complex priority-based VOR (ORCP) of coverage holes in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) in view of the existing problems in traditional VOR. Through the simulations and analyses of these two improved algorithms, as well as the vertical and horizontal comparisons and analyses of recovery algorithms unused and VOR, VORP, VORCP used, the results demonstrate that the proposed algorithms have better performances and efficiency than traditional recovery algorithms of coverage holes in WSNs.
This paper proposes two improved recovery algorithms on the base of Voronoi algorithm (VOR):priority-based VOR (VORP) and V complex priority-based VOR (ORCP) of coverage holes in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) in view of the existing problems in traditional VOR. Through the simulations and analyses of these two improved algorithms, as well as the vertical and horizontal comparisons and analyses of recovery algorithms unused and VOR, VORP, VORCP used, the results demonstrate that the proposed algorithms have better performances and efficiency than traditional recovery algorithms of coverage holes in WSNs.
2017, 46(4): 540-546.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.011
Abstract:
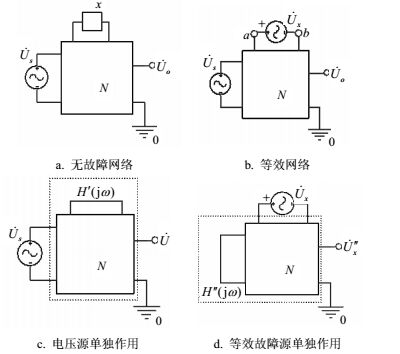
Parameter fault and tolerance are two challenging problems in analog circuit fault diagnosis. This paper proposes approaches to solve such problems. First, a new fault modeling method and its theoretical proof are presented. In analog circuits, both the real part and the imaginary part of output voltage are the functions of fault component parameters. By eliminating component parameters from the simultaneous formulas, a new equation is achieved. It is independent from the value of component parameters and uniquely determined by the component locations and the topological structure. Hence, the function can be used as the fault model, which is applicable to both hard (open or short) and soft (parametric) faults. It is also applicable to either linear or nonlinear analog circuits. Then, the parameter tolerance is taken into consideration. A frequency selection method is proposed to maximize the difference between fault signatures. Hence, the aliasing problem arise from tolerance can be mitigated. The effectiveness of the proposed approaches is verified by simulated results.
Parameter fault and tolerance are two challenging problems in analog circuit fault diagnosis. This paper proposes approaches to solve such problems. First, a new fault modeling method and its theoretical proof are presented. In analog circuits, both the real part and the imaginary part of output voltage are the functions of fault component parameters. By eliminating component parameters from the simultaneous formulas, a new equation is achieved. It is independent from the value of component parameters and uniquely determined by the component locations and the topological structure. Hence, the function can be used as the fault model, which is applicable to both hard (open or short) and soft (parametric) faults. It is also applicable to either linear or nonlinear analog circuits. Then, the parameter tolerance is taken into consideration. A frequency selection method is proposed to maximize the difference between fault signatures. Hence, the aliasing problem arise from tolerance can be mitigated. The effectiveness of the proposed approaches is verified by simulated results.
2017, 46(4): 547-553.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.012
Abstract:
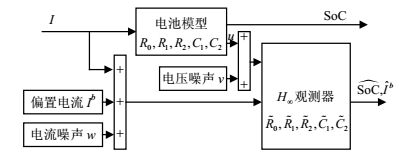
In battery management systems, there are always colored noises in the sampled battery current signals and voltage signals, which make it hard to achieve the accurate battery state of charge estimation. Regarding these noises as distributions, an H∞ observer with current debasing for online batter state of charge (SoC) estimation is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the battery stated model with current debasing and noise distribution is built. Secondly, H∞ observer is designed with current debasing. The estimation accuracy, performance, robust to model errors and parameter adaptation of the observer are analyzed by simulation. At last, experiment results demonstrate its effectiveness.
In battery management systems, there are always colored noises in the sampled battery current signals and voltage signals, which make it hard to achieve the accurate battery state of charge estimation. Regarding these noises as distributions, an H∞ observer with current debasing for online batter state of charge (SoC) estimation is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the battery stated model with current debasing and noise distribution is built. Secondly, H∞ observer is designed with current debasing. The estimation accuracy, performance, robust to model errors and parameter adaptation of the observer are analyzed by simulation. At last, experiment results demonstrate its effectiveness.
2017, 46(4): 554-558.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.013
Abstract:
Aiming at the problems that the reactor interturn short circuit can not be perceived timely, this paper presents dry-type air-core reactor interturn short circuit model, and studies on-line monitoring and protection from the angle of the magnetic field. The method combining Ansoft software and hardware is employed to convert the magnetic signal to the electric signal. The influence of different positions of the detected coil on the reactor interturn short circuit fault is researched. Comparing the calculated result of detected coil voltage with the threshold amount, we can judge the status of the internal insulated structure of the reactor and estimate whether the fault will occur. Therefore, the misoperation of the protector can be avoided. Experimental data shows that the method using detected coil voltage to monitor the short circuit condition is accurate and feasible, the fault can be found in time and fault expansion can also be effectively avoided.
Aiming at the problems that the reactor interturn short circuit can not be perceived timely, this paper presents dry-type air-core reactor interturn short circuit model, and studies on-line monitoring and protection from the angle of the magnetic field. The method combining Ansoft software and hardware is employed to convert the magnetic signal to the electric signal. The influence of different positions of the detected coil on the reactor interturn short circuit fault is researched. Comparing the calculated result of detected coil voltage with the threshold amount, we can judge the status of the internal insulated structure of the reactor and estimate whether the fault will occur. Therefore, the misoperation of the protector can be avoided. Experimental data shows that the method using detected coil voltage to monitor the short circuit condition is accurate and feasible, the fault can be found in time and fault expansion can also be effectively avoided.
2017, 46(4): 559-564.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.014
Abstract:
This paper proposes a power cable partial discharge (PD) pulse extraction method. Firstly, the PD pulse peak is located according to the variation of signal kurtosis, and then according to the signal energy's changing the method of sliding energy search is adopted to calculate and search the edge of PD pulse from the centered PH pulse to the both sides, so as to extract the PD pulse in the noise background accurately. This method can distinguish the full noise signal section from the section that contains partial discharge pulse signal in partial discharge detection signal, and won't be constrained by the number of partial discharge pulses and position of pulse, and also has features of simple step and small amount of calculation. By comparing the simulation experiments of two mainstream power cable PD pulse extraction methods (the wavelet threshold de-noising and the empirical mode decomposition) with the actual experiments, the effectiveness and veracity of this method have been verified.
This paper proposes a power cable partial discharge (PD) pulse extraction method. Firstly, the PD pulse peak is located according to the variation of signal kurtosis, and then according to the signal energy's changing the method of sliding energy search is adopted to calculate and search the edge of PD pulse from the centered PH pulse to the both sides, so as to extract the PD pulse in the noise background accurately. This method can distinguish the full noise signal section from the section that contains partial discharge pulse signal in partial discharge detection signal, and won't be constrained by the number of partial discharge pulses and position of pulse, and also has features of simple step and small amount of calculation. By comparing the simulation experiments of two mainstream power cable PD pulse extraction methods (the wavelet threshold de-noising and the empirical mode decomposition) with the actual experiments, the effectiveness and veracity of this method have been verified.
2017, 46(4): 565-571.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.015
Abstract:
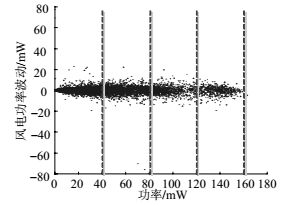
The prediction error of wind power reflects its random characteristic and the fluctuation of wind power describes its step-by-step changing characteristic at a specific time and space scale. In order to determine the reserve capacity needed by the prediction error and the fluctuation of wind power, a novel reserve capacity demand model is proposed through analyzing the randomness and the fluctuation of wind power. By considering the relationship between reserve capacity demand and system operation reserve, the wind power operation risk is defined, and then a dispatch model of wind power operation risk and reserve capacity coordination and optimization is proposed. In this model, the costs of load shedding and wind energy waste due to wind power operation reserve insufficiency are taken into consideration via a penalty function. Case studies based on modified IEEE 6-bus and IEEE 118-bus system show the validity and effectiveness of the proposed model. The proposed model provides a dispatch method which utilizes the wind energy with a more economic and safer way while having higher penetration.
The prediction error of wind power reflects its random characteristic and the fluctuation of wind power describes its step-by-step changing characteristic at a specific time and space scale. In order to determine the reserve capacity needed by the prediction error and the fluctuation of wind power, a novel reserve capacity demand model is proposed through analyzing the randomness and the fluctuation of wind power. By considering the relationship between reserve capacity demand and system operation reserve, the wind power operation risk is defined, and then a dispatch model of wind power operation risk and reserve capacity coordination and optimization is proposed. In this model, the costs of load shedding and wind energy waste due to wind power operation reserve insufficiency are taken into consideration via a penalty function. Case studies based on modified IEEE 6-bus and IEEE 118-bus system show the validity and effectiveness of the proposed model. The proposed model provides a dispatch method which utilizes the wind energy with a more economic and safer way while having higher penetration.
2017, 46(4): 572-578.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.016
Abstract:
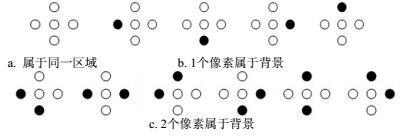
A novel codebook model combined with the superpixel segmentation method is proposed in this paper to improve the efficiency of object detection. The original pixels are clustered based on the similarities of both color and location information to reduce the processing cost. Our revised codebook model based on the superpixel could not only suppress the effect of local noise, but also reduce the redundancy of codebook. Simulation results indicate that, our proposed algorithm could reduce the memory consumption and improve the processing speed significantly without sacrificing the detection precision. Our algorithm could implement the object detection in real time in the embedded video processing system based on the DM6437 processor.
A novel codebook model combined with the superpixel segmentation method is proposed in this paper to improve the efficiency of object detection. The original pixels are clustered based on the similarities of both color and location information to reduce the processing cost. Our revised codebook model based on the superpixel could not only suppress the effect of local noise, but also reduce the redundancy of codebook. Simulation results indicate that, our proposed algorithm could reduce the memory consumption and improve the processing speed significantly without sacrificing the detection precision. Our algorithm could implement the object detection in real time in the embedded video processing system based on the DM6437 processor.
2017, 46(4): 579-584.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.017
Abstract:
To improve the performance of the active contour segmentation algorithm on natural images, a novel segmentation algorithm is proposed. First, combining the level set with the total variation, an edge-preserving smoothing segmentation model is constructed. Then a kind of clustering algorithm is employed to learn the balance parameter adaptively to avoid the level set curve converges at the local optimal point. At last, according to the different smoothing components with different segmentation regions, the segmentation smoothing convergence function based on regional confidence is designed to solve segmentation curve vanishes. Experimental results show that the score of this algorithm is higher than that of the traditional active-contour-based segmentation algorithmsfor the real images, and the algorithm is insensitive to texture and noise.
To improve the performance of the active contour segmentation algorithm on natural images, a novel segmentation algorithm is proposed. First, combining the level set with the total variation, an edge-preserving smoothing segmentation model is constructed. Then a kind of clustering algorithm is employed to learn the balance parameter adaptively to avoid the level set curve converges at the local optimal point. At last, according to the different smoothing components with different segmentation regions, the segmentation smoothing convergence function based on regional confidence is designed to solve segmentation curve vanishes. Experimental results show that the score of this algorithm is higher than that of the traditional active-contour-based segmentation algorithmsfor the real images, and the algorithm is insensitive to texture and noise.
2017, 46(4): 585-590.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.018
Abstract:
In some specific areas, a single condition of semantic retrieval cannot have the ideal results. A retrieval algorithm based on semantic correlation between different ontologies is presented. The algorithm firstly builds the domain ontology, and then analyzes the existing instances to find out the semantic correlation among ontologies by clustering algorithm. Besides, the evaluation data of the user of the instance which is obtained by the survey is used as the sample, with which the deep belief network (DBN) is trained to obtain the weights of correlation between semantics of different ontologies. Finally, the relevancy between the retrieved models and the model in database is computed and the models with higher relevancy are used as the retrieval results. With the retrieval algorithm, the designer can get more satisfactory model in retrieval homepage, which greatly shortens the retrieval time.
In some specific areas, a single condition of semantic retrieval cannot have the ideal results. A retrieval algorithm based on semantic correlation between different ontologies is presented. The algorithm firstly builds the domain ontology, and then analyzes the existing instances to find out the semantic correlation among ontologies by clustering algorithm. Besides, the evaluation data of the user of the instance which is obtained by the survey is used as the sample, with which the deep belief network (DBN) is trained to obtain the weights of correlation between semantics of different ontologies. Finally, the relevancy between the retrieved models and the model in database is computed and the models with higher relevancy are used as the retrieval results. With the retrieval algorithm, the designer can get more satisfactory model in retrieval homepage, which greatly shortens the retrieval time.
2017, 46(4): 591-599.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.019
Abstract:
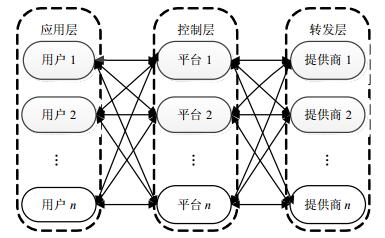
As a new type of network architecture, software defined network (SDN) breaks the closed mode of traditional network, realizes the separation between forwarding and control, and therefore can effectively solve a series of problems of the current Internet. Taking advantage of economic principles and according to the characteristics of the traditional auction model, we propose a price negotiation algorithm, namely multi-homing combinatorial double auction model (MCDAM) algorithm, to curb the waste of SDN resources. MCDAM can solve the problem of reasonable transaction price between the buyers and sellers, make the price as a lever to achieve the purpose of SDN resources reasonable allocation. Simulation results illustrate the superiority and feasibility of the proposed algorithm.
As a new type of network architecture, software defined network (SDN) breaks the closed mode of traditional network, realizes the separation between forwarding and control, and therefore can effectively solve a series of problems of the current Internet. Taking advantage of economic principles and according to the characteristics of the traditional auction model, we propose a price negotiation algorithm, namely multi-homing combinatorial double auction model (MCDAM) algorithm, to curb the waste of SDN resources. MCDAM can solve the problem of reasonable transaction price between the buyers and sellers, make the price as a lever to achieve the purpose of SDN resources reasonable allocation. Simulation results illustrate the superiority and feasibility of the proposed algorithm.
2017, 46(4): 600-606.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.020
Abstract:
A local trajectory-planning algorithm that generates safety and comfort trajectories is described. The obstacles are detected online by receiving cooperative awareness messages (CAMs) and decentralized environmental notification messages (DENMs). Our approach has three main steps. The first step uses a trajectory generation module to generate comfort trajectories. The second step predicts the position and velocity of obstacle vehicles because of transmission delay. The final step chooses a best trajectory to follow by operating the trajectory selection module. A collision probability model is then proposed to help autonomous vehicle make decision. The trajectory-planning algorithm described in this paper was tested on MATLAB, and the simulation results show they are secure and reliable.
A local trajectory-planning algorithm that generates safety and comfort trajectories is described. The obstacles are detected online by receiving cooperative awareness messages (CAMs) and decentralized environmental notification messages (DENMs). Our approach has three main steps. The first step uses a trajectory generation module to generate comfort trajectories. The second step predicts the position and velocity of obstacle vehicles because of transmission delay. The final step chooses a best trajectory to follow by operating the trajectory selection module. A collision probability model is then proposed to help autonomous vehicle make decision. The trajectory-planning algorithm described in this paper was tested on MATLAB, and the simulation results show they are secure and reliable.
2017, 46(4): 607-613.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.021
Abstract:
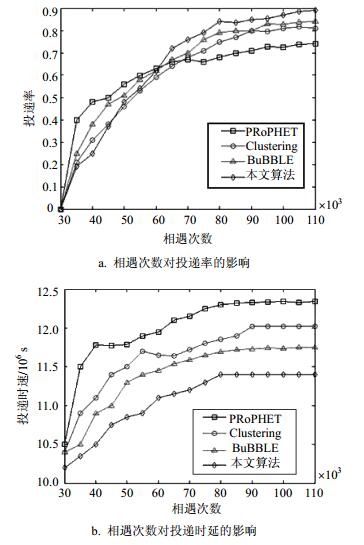
In order to increase the delivery rate and reduce the transmission delay of messages in the process of routing, an opportunistic social networks routing based on two-step clustering is presented. The method of two-step clustering is used to reduce the resource requirements for nodes, and different forwarding strategies are applied to inter-message and intra-message respectively, aiming to optimize the process of message forwarding and relay node choosing. Besides, the chain of events is used in clustering to analyze internal social relationship between nodes, which can improve the accuracy of clustering. Our evaluations show that the protocol can lead to a 5~10% increase in delivery ratio and a 10% at least decrease in delivery delay in large complex networks, and get about 80% of messages delivered in networks with insufficient resources of computing and storage.
In order to increase the delivery rate and reduce the transmission delay of messages in the process of routing, an opportunistic social networks routing based on two-step clustering is presented. The method of two-step clustering is used to reduce the resource requirements for nodes, and different forwarding strategies are applied to inter-message and intra-message respectively, aiming to optimize the process of message forwarding and relay node choosing. Besides, the chain of events is used in clustering to analyze internal social relationship between nodes, which can improve the accuracy of clustering. Our evaluations show that the protocol can lead to a 5~10% increase in delivery ratio and a 10% at least decrease in delivery delay in large complex networks, and get about 80% of messages delivered in networks with insufficient resources of computing and storage.
2017, 46(4): 614-620.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.022
Abstract:
The advancement of data science has been prompting the shift of research paradigms in various fields, including psychology, management etc.Investigations on the large empirical datasets have uncovered astonishing regularities and universalities which cannot be revealed through classic methods. This paper aims to explore the fundamental differences in air traffic controllers' information seeking behavior based on the analysis of their eye movements' data. The faceLAB is used to collect eye movements' data recorded from 14 air traffic controllers. Statistical analysis and multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MF-DFA) are carried out to investigate the fundamental properties of eye movements. The analytical results show that 1) expert controllers have longer mean fixation duration, less fixation points, shorter mean saccadic duration, and smaller mean saccadic velocity than novices; 2) Controllers' fixation time series, saccadic duration time series, and saccadic amplitude time series, allexhibit multifractal characteristics, and multifractal singularity spectrum demonstrates that there are stronger fluctuations in novices' fixation activities. Our workindicates thatcontroller's information seeking dynamics are different.Work experience does have a significant impact on controllers' behavior.
The advancement of data science has been prompting the shift of research paradigms in various fields, including psychology, management etc.Investigations on the large empirical datasets have uncovered astonishing regularities and universalities which cannot be revealed through classic methods. This paper aims to explore the fundamental differences in air traffic controllers' information seeking behavior based on the analysis of their eye movements' data. The faceLAB is used to collect eye movements' data recorded from 14 air traffic controllers. Statistical analysis and multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MF-DFA) are carried out to investigate the fundamental properties of eye movements. The analytical results show that 1) expert controllers have longer mean fixation duration, less fixation points, shorter mean saccadic duration, and smaller mean saccadic velocity than novices; 2) Controllers' fixation time series, saccadic duration time series, and saccadic amplitude time series, allexhibit multifractal characteristics, and multifractal singularity spectrum demonstrates that there are stronger fluctuations in novices' fixation activities. Our workindicates thatcontroller's information seeking dynamics are different.Work experience does have a significant impact on controllers' behavior.
2017, 46(4): 621-624.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.023
Abstract:
The properties and microstructures of SnZnPr solders were studied with the addition of Au nanoparticles. The results indicat that the addition of Au nanoparticles can enhance the wettability of solder and the mechanical property of solder joints, the optimum content of Au nanoparticles is 0.1% with optimal design. However, excessive Au nanoparticles can degrade the wettability of solders, and no variation occurs for mechanical property of solder joints. With the microstructure observation of SnZnPr and SnZnPr-0.1Au solders, the 0.1% Au nanoparticles can refine the matrix microstructure of SnZnPr solder, especially for reduction of rich-Zn phases. Moreover, with the addition of 0.1% Au nanoparticles, nanoindentation testing indicates that the creep-resistance property can be enhanced obviously, thermal fatigue life of solder joints is increased by 12.3% with thermal cycling testing, which can be attributed to dislocation pinning effect of nanoparticles.
The properties and microstructures of SnZnPr solders were studied with the addition of Au nanoparticles. The results indicat that the addition of Au nanoparticles can enhance the wettability of solder and the mechanical property of solder joints, the optimum content of Au nanoparticles is 0.1% with optimal design. However, excessive Au nanoparticles can degrade the wettability of solders, and no variation occurs for mechanical property of solder joints. With the microstructure observation of SnZnPr and SnZnPr-0.1Au solders, the 0.1% Au nanoparticles can refine the matrix microstructure of SnZnPr solder, especially for reduction of rich-Zn phases. Moreover, with the addition of 0.1% Au nanoparticles, nanoindentation testing indicates that the creep-resistance property can be enhanced obviously, thermal fatigue life of solder joints is increased by 12.3% with thermal cycling testing, which can be attributed to dislocation pinning effect of nanoparticles.
2017, 46(4): 625-629.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.024
Abstract:
Zinc oxide (ZnO) mocro/nanoporous array thin film-based gas sensors were prepared by the organic template-based solution dipping——monolithic transfer strategy. The research focuses on nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gas sensing properties of different aperture sizes of ZnO micro/nanoporous array thin films under UV irradiation with different intensity. The results show that ZnO micro/nanoporous array thin film can be obtained by 500 nm polystyrene (PS) as template, the film-based sensor has high sensitivity and fast response and recovery time when the intensity of UV light is 0.35 mW/cm3. This kind of sensor shows good anti-disturbance to the other gases, such as acetone, formaldehyde, H2S, SO2, and CH4.
Zinc oxide (ZnO) mocro/nanoporous array thin film-based gas sensors were prepared by the organic template-based solution dipping——monolithic transfer strategy. The research focuses on nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gas sensing properties of different aperture sizes of ZnO micro/nanoporous array thin films under UV irradiation with different intensity. The results show that ZnO micro/nanoporous array thin film can be obtained by 500 nm polystyrene (PS) as template, the film-based sensor has high sensitivity and fast response and recovery time when the intensity of UV light is 0.35 mW/cm3. This kind of sensor shows good anti-disturbance to the other gases, such as acetone, formaldehyde, H2S, SO2, and CH4.
2017, 46(4): 630-635.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.025
Abstract:
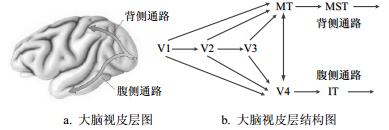
According to side-bias characteristics of motion perception towards random-dot video stimuli among some middle temporal cortex (MT) cells in the experiment, a model for motion feature extraction of random-dot video sequences with the visual cortex mechanism is proposed for exploring the visual cortex mechanism underlying multi-direction motion information processing. First, Von Mises function is used to model receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex (V1). A nonlinear energy model unturned and tuned normalization operation is adopted to simulate the direction perception of V1 complex cells; then, with the feedforward and cascade method, the responses of V1 model are pooled through a set of linear weights, thus giving rise to the responses of MT cells. The simulation results are generally consistent with the experimental data of rhesus monkeys. It can model the motion perception and feature extraction mechanism underlying multi-direction random-dot video sequences at different direction separations in visual cortex. So that it can provide new ideas for extracting features of complex motion sequences and lay the foundation for the visual brain-like computation for the further step.
According to side-bias characteristics of motion perception towards random-dot video stimuli among some middle temporal cortex (MT) cells in the experiment, a model for motion feature extraction of random-dot video sequences with the visual cortex mechanism is proposed for exploring the visual cortex mechanism underlying multi-direction motion information processing. First, Von Mises function is used to model receptive fields of simple cells in primary visual cortex (V1). A nonlinear energy model unturned and tuned normalization operation is adopted to simulate the direction perception of V1 complex cells; then, with the feedforward and cascade method, the responses of V1 model are pooled through a set of linear weights, thus giving rise to the responses of MT cells. The simulation results are generally consistent with the experimental data of rhesus monkeys. It can model the motion perception and feature extraction mechanism underlying multi-direction random-dot video sequences at different direction separations in visual cortex. So that it can provide new ideas for extracting features of complex motion sequences and lay the foundation for the visual brain-like computation for the further step.
2017, 46(4): 636-640.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.04.026
Abstract:
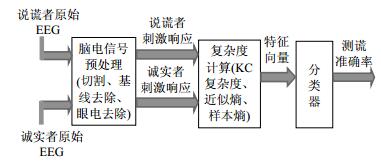
There is great significance in lie detection for the criminal investigation and psychological disease treatment. To distinguish lying, thirty subjects were divided into lying and telling-truth groups randomly and three groups of nonlinear features——complexity measures including Kolmogorov complexity, approximate entropy and sample entropy were extracted. By statistical analysis, the feature vector was constructed by using complexity on the muilti electrodes with significant difference of complexity values between the two groups of subjects. The support vector machine was used to classify and idendify feature samples. The study finds that there are more electrodes with significant difference of complexity values for the sample entropy, and the highest classification accuracy can be observed for the feature vector constructed from the sample entropy, compared with the other two featues. Experimental resutls indicate that sample entropy could be used to classify EEG signals in lying from EEG signals in telling-truth, which provides a new alternative for EEG-based lie detection method.
There is great significance in lie detection for the criminal investigation and psychological disease treatment. To distinguish lying, thirty subjects were divided into lying and telling-truth groups randomly and three groups of nonlinear features——complexity measures including Kolmogorov complexity, approximate entropy and sample entropy were extracted. By statistical analysis, the feature vector was constructed by using complexity on the muilti electrodes with significant difference of complexity values between the two groups of subjects. The support vector machine was used to classify and idendify feature samples. The study finds that there are more electrodes with significant difference of complexity values for the sample entropy, and the highest classification accuracy can be observed for the feature vector constructed from the sample entropy, compared with the other two featues. Experimental resutls indicate that sample entropy could be used to classify EEG signals in lying from EEG signals in telling-truth, which provides a new alternative for EEG-based lie detection method.

 ISSN
ISSN