2018 Vol. 47, No. 1
2018, 47(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.001
Abstract:
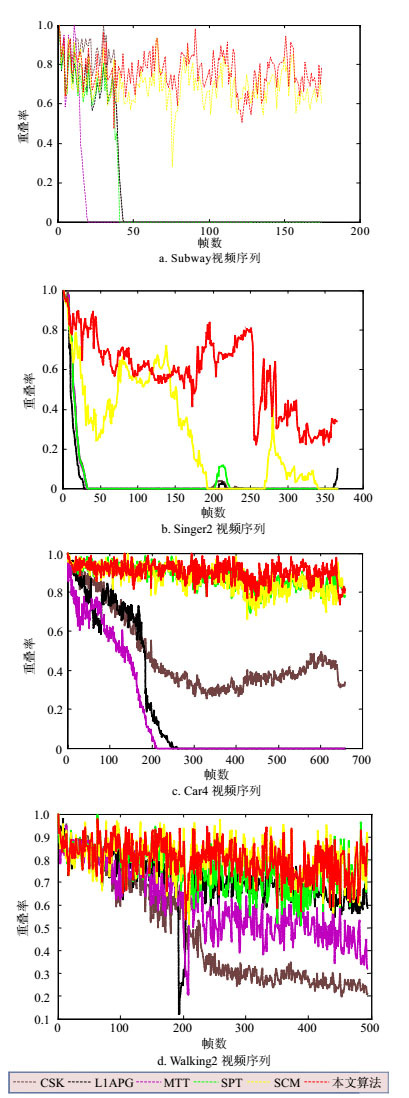
Sparse representation has already been successfully applied to the visual tracking, but it also faces with unstable factors. In this paper, we propose an adaptive tracking algorithm based on simultaneous sparse representation which considers the Gaussian noise and Laplace noise. The sparse model is chosen adaptively according to the energy of Laplace noise. The proposed algorithm can better solve the problem of targets such as occlusion, pose change, illumination variation and background clutter, and the algorithm has better robustness. Secondly, the template update method based on the subspace learning and unsupervised learning (K-means) is given to respond the target state in a timely and effective manner and to avoid the template update too fast and introduce significant error. Then, the LASSO algorithm is used to further improve the model. Finally, comparing the current nine state-of-the-art tracking algorithms with the proposed algorithm in this paper, the experimental results illustrate that the proposed algorithm have the better performance in terms of robustness, accuracy and real time.
Sparse representation has already been successfully applied to the visual tracking, but it also faces with unstable factors. In this paper, we propose an adaptive tracking algorithm based on simultaneous sparse representation which considers the Gaussian noise and Laplace noise. The sparse model is chosen adaptively according to the energy of Laplace noise. The proposed algorithm can better solve the problem of targets such as occlusion, pose change, illumination variation and background clutter, and the algorithm has better robustness. Secondly, the template update method based on the subspace learning and unsupervised learning (K-means) is given to respond the target state in a timely and effective manner and to avoid the template update too fast and introduce significant error. Then, the LASSO algorithm is used to further improve the model. Finally, comparing the current nine state-of-the-art tracking algorithms with the proposed algorithm in this paper, the experimental results illustrate that the proposed algorithm have the better performance in terms of robustness, accuracy and real time.
2018, 47(1): 13-18.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.002
Abstract:
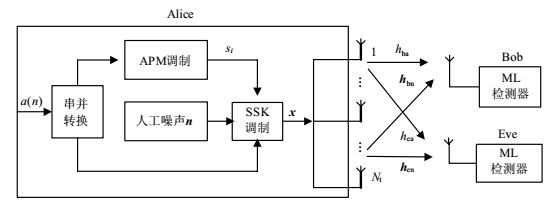
This paper proposes a security method in the physical layer by using artificial noise and spatial modulation technique. The information is conveyed by the transmitting antenna index and amplitude-phase modulated symbol. The other antennas transmit the artificial noise located in the null space of the legitimate channel to interfere with the eavesdropper's signal detection without affecting that of the legitimate receiver. The achievable secrecy rate and bit error rate bound of both the legitimate receiver and the eavesdropper are analyzed, and the simulation is done to verify the secrecy performance of the scheme. The results show that the legitimate receiver has a much lower bit error rate than the eavesdropper, whose bit error rate is about 0.5. Thus the secrecy rate can be improved considerably.
This paper proposes a security method in the physical layer by using artificial noise and spatial modulation technique. The information is conveyed by the transmitting antenna index and amplitude-phase modulated symbol. The other antennas transmit the artificial noise located in the null space of the legitimate channel to interfere with the eavesdropper's signal detection without affecting that of the legitimate receiver. The achievable secrecy rate and bit error rate bound of both the legitimate receiver and the eavesdropper are analyzed, and the simulation is done to verify the secrecy performance of the scheme. The results show that the legitimate receiver has a much lower bit error rate than the eavesdropper, whose bit error rate is about 0.5. Thus the secrecy rate can be improved considerably.
2018, 47(1): 19-24, 36.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.003
Abstract:
Terahertz radar features high frequency, large bandwidth, and other characteristics, thus helpful to improve the micro-motion target detection accuracy of radar systems, and feasible to extract the feature of micro-motion target. Combing with the typical micro-motion feature model, we propose a curve extraction algorithm based on the edge detection technique for the extracting the spectrum curves and further obtaining the parameters of micro-motion targets. Real data show that the proposed technique can effectively extract the feature parameters of the micro-motion target with multiple scattering centers. This research provides effective approach for further micro-motion target signal processing and target recognition.
Terahertz radar features high frequency, large bandwidth, and other characteristics, thus helpful to improve the micro-motion target detection accuracy of radar systems, and feasible to extract the feature of micro-motion target. Combing with the typical micro-motion feature model, we propose a curve extraction algorithm based on the edge detection technique for the extracting the spectrum curves and further obtaining the parameters of micro-motion targets. Real data show that the proposed technique can effectively extract the feature parameters of the micro-motion target with multiple scattering centers. This research provides effective approach for further micro-motion target signal processing and target recognition.
2018, 47(1): 25-29.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.004
Abstract:
The orthogonal block matrix is needed in the generalized sidelobe canceller algorithm to offset the received signal and the desired signal. But there is a limitation on constructing the orthogonal block matrix in the actual pattern synthesis processing. In this paper, an improved sidelobe cancellation algorithm is proposed. The wavelet filter bank is used to block the desired signal component in received signals of antenna array for adaptive beamforming. The covariance matrix of array signal does not contain the desired signal component in the improved algorithm. So the desired signal cancellation problem in adaptive beamforming with the system error can be overcome. Also the proposed algorithm solves the problem that the generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) beamforming algorithm needs to construct the blocking matrix which is orthogonal with the desired signal, thus the robust performance of the system is achieved. The effectiveness of the improved algorithm is verified by the simulation results. The simulation results show that the performance of the improved algorithm is better than the traditional minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) method and the diagonal loading method based on MVDR algorithm.
The orthogonal block matrix is needed in the generalized sidelobe canceller algorithm to offset the received signal and the desired signal. But there is a limitation on constructing the orthogonal block matrix in the actual pattern synthesis processing. In this paper, an improved sidelobe cancellation algorithm is proposed. The wavelet filter bank is used to block the desired signal component in received signals of antenna array for adaptive beamforming. The covariance matrix of array signal does not contain the desired signal component in the improved algorithm. So the desired signal cancellation problem in adaptive beamforming with the system error can be overcome. Also the proposed algorithm solves the problem that the generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) beamforming algorithm needs to construct the blocking matrix which is orthogonal with the desired signal, thus the robust performance of the system is achieved. The effectiveness of the improved algorithm is verified by the simulation results. The simulation results show that the performance of the improved algorithm is better than the traditional minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) method and the diagonal loading method based on MVDR algorithm.
2018, 47(1): 30-36.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.005
Abstract:
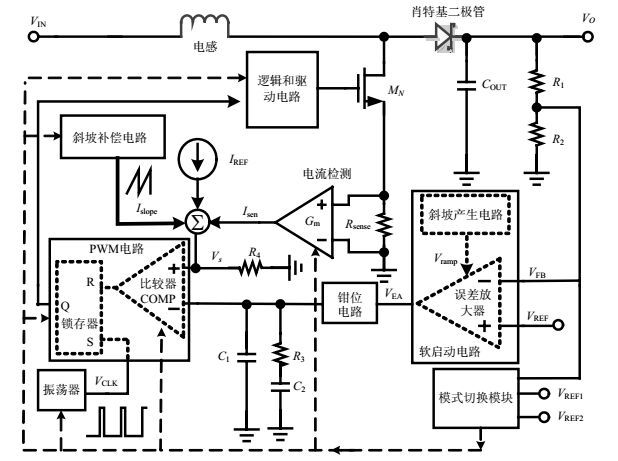
An on-chip soft-start circuit consisting of a ramp-up voltage generator and an error amplifier with soft-start function is presented. The ramp-up voltage with slow ramp rate is achieved with small capacitors by using techniques of pulse swallowing and pulse current charging. The ramp-up voltage generator shuts down automatically to save power after the start-up has finished. The controlling scheme of start-up is realized by just adding two extra transistors to the conventional error amplifier circuit. In the start-up period, the output voltage of the converter and the current of the inductor rise are slowly controlled by the error amplifier output voltage which follows the ramp-up voltage. When the start-up finishes, a smooth transition from start-up to the steady states is achieved without disturbance to the current of the inductor, which always happens in the conventional method by using transferring switch. The soft-start circuit is applied to a peak-current mode boost DC-DC converter implemented with CSMC 0.5 μm BCD process. Simulation results show that the inrush current during start-up is eliminated effectively, and the output voltage rises smoothly without overshoot. Moreover, a smooth transition to the steady states without disturbance is achieved. The soft-start circuit is compact and suitable for on-chip implementation.
An on-chip soft-start circuit consisting of a ramp-up voltage generator and an error amplifier with soft-start function is presented. The ramp-up voltage with slow ramp rate is achieved with small capacitors by using techniques of pulse swallowing and pulse current charging. The ramp-up voltage generator shuts down automatically to save power after the start-up has finished. The controlling scheme of start-up is realized by just adding two extra transistors to the conventional error amplifier circuit. In the start-up period, the output voltage of the converter and the current of the inductor rise are slowly controlled by the error amplifier output voltage which follows the ramp-up voltage. When the start-up finishes, a smooth transition from start-up to the steady states is achieved without disturbance to the current of the inductor, which always happens in the conventional method by using transferring switch. The soft-start circuit is applied to a peak-current mode boost DC-DC converter implemented with CSMC 0.5 μm BCD process. Simulation results show that the inrush current during start-up is eliminated effectively, and the output voltage rises smoothly without overshoot. Moreover, a smooth transition to the steady states without disturbance is achieved. The soft-start circuit is compact and suitable for on-chip implementation.
2018, 47(1): 37-42.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.006
Abstract:
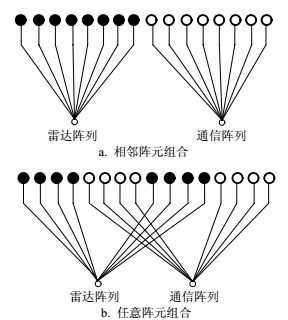
The traditional single aperture antenna can only schedule the task in time, but the large loss rate easily appear when the task is more. Under the condition of dynamic aperture segmentation, the task management and execution of the antenna can be carried out in two dimensions of time and aperture, and it is easier to complete the task. In this paper, the characteristics of the dynamic aperture segmentation task is first analyzed and the resource management problem is proposed under the condition of two-dimensional time and aperture after introducing the rectangular layout idea in mechanical engineering. The data structure is then designed and the resource scheduling method of radar-communication integrated system is proposed based on the update rules of first in first out. Simulation results show that the algorithm has lower task loss rate and higher resource utilization ratio.
The traditional single aperture antenna can only schedule the task in time, but the large loss rate easily appear when the task is more. Under the condition of dynamic aperture segmentation, the task management and execution of the antenna can be carried out in two dimensions of time and aperture, and it is easier to complete the task. In this paper, the characteristics of the dynamic aperture segmentation task is first analyzed and the resource management problem is proposed under the condition of two-dimensional time and aperture after introducing the rectangular layout idea in mechanical engineering. The data structure is then designed and the resource scheduling method of radar-communication integrated system is proposed based on the update rules of first in first out. Simulation results show that the algorithm has lower task loss rate and higher resource utilization ratio.
2018, 47(1): 43-50.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.007
Abstract:
Offset error, gain error and time error greatly degrade the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and effective number of bits (ENOB) in time-interleaved analog to digital converter (ADC) systems. This paper discusses mathematical statistics and spectrum analysis calibration method for time-interleaved ADC systems. Mathematical statistics is used for offset error, through mathematical statistics of the sampled data of each sub ADC, the estimation of the offset error can be obtained, and the calibration can be carried out. Meanwhile, a second time calibration is applied to improve the calibration accuracy, the spectrum analysis is used for gain error and time error. The gain error and time error can be estimated by the magnitude and phase of the specific frequency point, so the calibration can be achieved. The comparison of the signal spectrums before and after calibration proves the effectiveness of the calibration algorithm. The algorithm is simple and easy to implement. The experiment result shows that the SNR can reach to 41.019 4 dB, and ENOB to 6.52 bit. Moreover, the results is equal or better than the sine fitting algorithm.
Offset error, gain error and time error greatly degrade the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and effective number of bits (ENOB) in time-interleaved analog to digital converter (ADC) systems. This paper discusses mathematical statistics and spectrum analysis calibration method for time-interleaved ADC systems. Mathematical statistics is used for offset error, through mathematical statistics of the sampled data of each sub ADC, the estimation of the offset error can be obtained, and the calibration can be carried out. Meanwhile, a second time calibration is applied to improve the calibration accuracy, the spectrum analysis is used for gain error and time error. The gain error and time error can be estimated by the magnitude and phase of the specific frequency point, so the calibration can be achieved. The comparison of the signal spectrums before and after calibration proves the effectiveness of the calibration algorithm. The algorithm is simple and easy to implement. The experiment result shows that the SNR can reach to 41.019 4 dB, and ENOB to 6.52 bit. Moreover, the results is equal or better than the sine fitting algorithm.
2018, 47(1): 51-59.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.008
Abstract:
Arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) is a instrument which can generate arbitrary excitation signal. Output bandwidth, the number of channels and synchronous accuracy between different channels are the key specifications of AWG. In order to achieve high bandwidth, a multi-memories parallel structure is proposed to break through operation speed limitation of phase accumulator and look-up table. However, this structure introduces more complex synchronous error than traditional structures. The synchronization requirements of AWG with multi-memories parallel is analyzed emphatically in this article. The random initial phase of data clock and random trigger position are eliminated by deliberate distributing clock and trigger signal. The design of embedded phase calibration module is used to eliminate the random phase difference. Finally, the specifications of AWG are verified.
Arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) is a instrument which can generate arbitrary excitation signal. Output bandwidth, the number of channels and synchronous accuracy between different channels are the key specifications of AWG. In order to achieve high bandwidth, a multi-memories parallel structure is proposed to break through operation speed limitation of phase accumulator and look-up table. However, this structure introduces more complex synchronous error than traditional structures. The synchronization requirements of AWG with multi-memories parallel is analyzed emphatically in this article. The random initial phase of data clock and random trigger position are eliminated by deliberate distributing clock and trigger signal. The design of embedded phase calibration module is used to eliminate the random phase difference. Finally, the specifications of AWG are verified.
2018, 47(1): 60-65.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.009
Abstract:
In recent years, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is widely used in power industry transmission line inspection. Power transmission lines UAV automation inspection technology has been attracted extensive attention from domestic and foreign research institutions because of its unique advantages. However, the rapid growth of inspection task demand and more and more choices for UAV platforms make it difficult to complete the UAV platform selection rapidly, which usually cost a lot of manpower. For solving this problem, this paper proposes a three-phase framework based on various types neural networks for rapid selection. In the first phase, the adjusted one-hot vector algorithm is presented to transform the description of inspection task into task matrix; in the second phase, the relationship between task matrix and load parameters is constructed by using long short term memory (LSTM) neural network; in the last phase, the UAV platform selection is achieved with decision tree network. Finally, the real-world data are used to validate the effectiveness of the proposed model.
In recent years, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is widely used in power industry transmission line inspection. Power transmission lines UAV automation inspection technology has been attracted extensive attention from domestic and foreign research institutions because of its unique advantages. However, the rapid growth of inspection task demand and more and more choices for UAV platforms make it difficult to complete the UAV platform selection rapidly, which usually cost a lot of manpower. For solving this problem, this paper proposes a three-phase framework based on various types neural networks for rapid selection. In the first phase, the adjusted one-hot vector algorithm is presented to transform the description of inspection task into task matrix; in the second phase, the relationship between task matrix and load parameters is constructed by using long short term memory (LSTM) neural network; in the last phase, the UAV platform selection is achieved with decision tree network. Finally, the real-world data are used to validate the effectiveness of the proposed model.
2018, 47(1): 66-72.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.010
Abstract:
The structure reliability or performance assessment of complex systems with both epistemic and aleatory uncertainties is a challenge problem for engineering systems. In this paper, an implementation framework of systems reliability assessment based on the quantification of margins and uncertainties (QMU) methodology is proposed. The description of QMU concept is introduced first, then the Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence is used to present the presence of aleatory and epistemic uncertainties in the proposed QMU implementation framework. To alleviate the computational costs, the Kriging model has been implemented as the surrogate for the structure response. Then the structure reliability was presented by a QMU metric in terms of confidence factor(CF). The technique is demonstrated by a numerical example to account for the computational efficiency. The difference between QMU metric and non-probabilistic reliability methods is discussed
The structure reliability or performance assessment of complex systems with both epistemic and aleatory uncertainties is a challenge problem for engineering systems. In this paper, an implementation framework of systems reliability assessment based on the quantification of margins and uncertainties (QMU) methodology is proposed. The description of QMU concept is introduced first, then the Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence is used to present the presence of aleatory and epistemic uncertainties in the proposed QMU implementation framework. To alleviate the computational costs, the Kriging model has been implemented as the surrogate for the structure response. Then the structure reliability was presented by a QMU metric in terms of confidence factor(CF). The technique is demonstrated by a numerical example to account for the computational efficiency. The difference between QMU metric and non-probabilistic reliability methods is discussed
2018, 47(1): 73-79.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.011
Abstract:
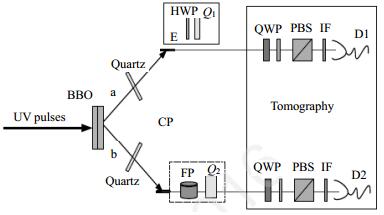
As a way to develop scalable quantum computing and quantum networks, practical quantum teleportation technology is proverbially applied in the fields of finance, government affairs, national defense and military affairs, and long-distance communication (such as space exploration). Quantum entanglement and super-joint measurement not only bring great challenges to the fundamental theory and application technology of quantum teleportation, but also bring the opportunity of fundamental innovation in theory and technology (application). In this paper, the research of quantum teleportation protocol for immune noise is summarized from the following aspects:the quantum teleportation and immune noise model, quantum channel capacity and network coding, and quantum teleportation mechanism of the immune noise of the quantum teleportation protocol. Finally, the trends of future research hotspots and development are summarized.
As a way to develop scalable quantum computing and quantum networks, practical quantum teleportation technology is proverbially applied in the fields of finance, government affairs, national defense and military affairs, and long-distance communication (such as space exploration). Quantum entanglement and super-joint measurement not only bring great challenges to the fundamental theory and application technology of quantum teleportation, but also bring the opportunity of fundamental innovation in theory and technology (application). In this paper, the research of quantum teleportation protocol for immune noise is summarized from the following aspects:the quantum teleportation and immune noise model, quantum channel capacity and network coding, and quantum teleportation mechanism of the immune noise of the quantum teleportation protocol. Finally, the trends of future research hotspots and development are summarized.
2018, 47(1): 80-87.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.012
Abstract:
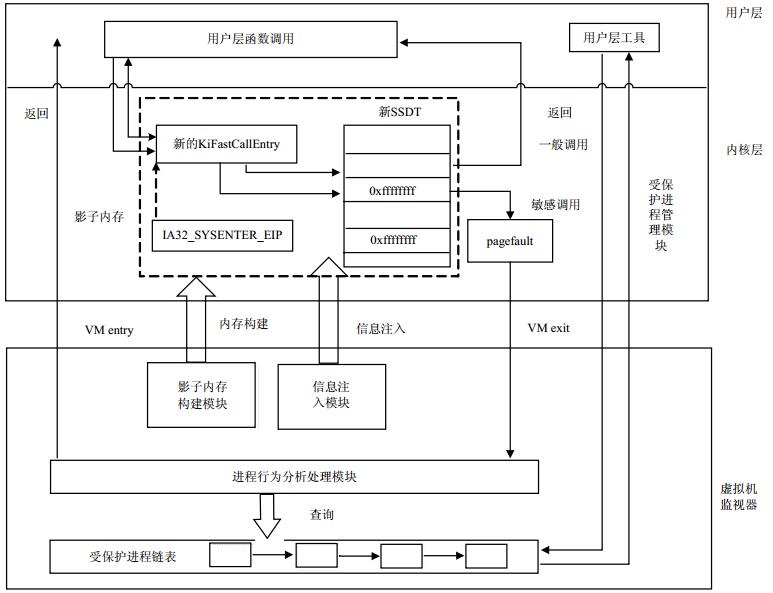
To improve security of process in virtual machine (VM) and avoid system service descriptor table (SSDT) and system call execution path being hooked, a agentless method based on shadow memory of protecting process security in VM is proposed. First, a block of shadow memory is constructed in nonpaged pool of VM by using of high privilege level of virtual machine manager (VMM), then new system service descriptor table (SSDT) and system call execution path are injected to shadow memory. The process sensitive behavior is detected by using of characteristic of hardware virtualization and hook technology, and the invalid operation to targeted process is filtered in VMM so as to implement protecting process security without agent in VM. Analysis and test results show that almost all the attacks from rootkits can be prevented, and the targeted process in VM can be protected well with almost no performance loss.
To improve security of process in virtual machine (VM) and avoid system service descriptor table (SSDT) and system call execution path being hooked, a agentless method based on shadow memory of protecting process security in VM is proposed. First, a block of shadow memory is constructed in nonpaged pool of VM by using of high privilege level of virtual machine manager (VMM), then new system service descriptor table (SSDT) and system call execution path are injected to shadow memory. The process sensitive behavior is detected by using of characteristic of hardware virtualization and hook technology, and the invalid operation to targeted process is filtered in VMM so as to implement protecting process security without agent in VM. Analysis and test results show that almost all the attacks from rootkits can be prevented, and the targeted process in VM can be protected well with almost no performance loss.
2018, 47(1): 88-94.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.013
Abstract:
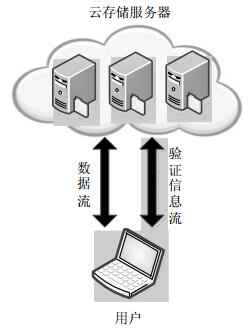
The integrity of user's data is one of the problems which is most concerned when users using cloud storage service to store their data and files. The data users commit to cloud storage servers may be lost and modified. Users need a technology to check the integrity and validity of their data and files when accessing them. By considering the limit of the calculation resource of users and the security request of cloud storage service, an integrity verification protocol based on improved skip lists and short signature is proposed, which can support dynamic operation. By combining accessible counting and skip lists, this protocol can support inserting and deleting data block at any position efficiently. The analysis and experiment show that the proposed protocol is security and efficient.
The integrity of user's data is one of the problems which is most concerned when users using cloud storage service to store their data and files. The data users commit to cloud storage servers may be lost and modified. Users need a technology to check the integrity and validity of their data and files when accessing them. By considering the limit of the calculation resource of users and the security request of cloud storage service, an integrity verification protocol based on improved skip lists and short signature is proposed, which can support dynamic operation. By combining accessible counting and skip lists, this protocol can support inserting and deleting data block at any position efficiently. The analysis and experiment show that the proposed protocol is security and efficient.
2018, 47(1): 95-98, 111.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.014
Abstract:
The BGN (Boneh-Goh-Nissim) cryptosystem is a cryptosystem that permits arbitrary number of additions and one multiplication of ciphertext without growing the size of ciphertext. The scheme of BGV12 is a fully homomorphic encryption from (G)LWE which needs key switching, modulus switching and other technologies for the multiplicative homomorphism. This paper describes a BGN scheme based on BGV12. Although our constructed scheme only permits one multiplication, it does not need other technologies, so it is more efficient. Comparing with the scheme of GVH10, our scheme has better size of parameter. In addition, we extend our scheme to a threshold encryption scheme, which allows parties to cooperatively decrypt a ciphertext without learning anything but the plaintext, and can be protected from related-key attacks.
The BGN (Boneh-Goh-Nissim) cryptosystem is a cryptosystem that permits arbitrary number of additions and one multiplication of ciphertext without growing the size of ciphertext. The scheme of BGV12 is a fully homomorphic encryption from (G)LWE which needs key switching, modulus switching and other technologies for the multiplicative homomorphism. This paper describes a BGN scheme based on BGV12. Although our constructed scheme only permits one multiplication, it does not need other technologies, so it is more efficient. Comparing with the scheme of GVH10, our scheme has better size of parameter. In addition, we extend our scheme to a threshold encryption scheme, which allows parties to cooperatively decrypt a ciphertext without learning anything but the plaintext, and can be protected from related-key attacks.
2018, 47(1): 99-104.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.015
Abstract:
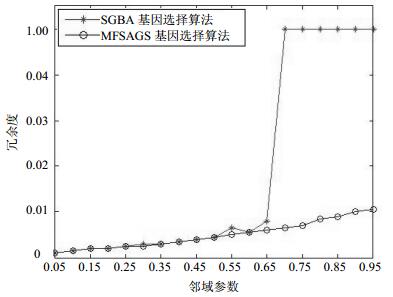
Facing the gene expression data with high dimension, small samples and uncertainty, a gene selection method based on neighborhood rough sets and fish swarm intelligence is proposed by fusing a fuzzy tolerance granulation technology and a fish swarm intelligence algorithm with global optimization ability. Firstly, the neighborhood rough sets are used to granulate the gene data and form some neighborhood particles. Secondly, the neighborhood classification accuracy is presented as an uncertainty evaluation function that aims to judge these neighborhood particles and distinguish key genes. Furthermore, a gene selection algorithm based on artificial fish swarm intelligence is designed. Finally, some gene selection experiments are carried out on two tumor gene data sets. The classification experiments of a small number of selected key genes are conducted by using SVM classifier. The experimental results show that the genes selected by our proposed method have a low redundancy and a better classification performance.
Facing the gene expression data with high dimension, small samples and uncertainty, a gene selection method based on neighborhood rough sets and fish swarm intelligence is proposed by fusing a fuzzy tolerance granulation technology and a fish swarm intelligence algorithm with global optimization ability. Firstly, the neighborhood rough sets are used to granulate the gene data and form some neighborhood particles. Secondly, the neighborhood classification accuracy is presented as an uncertainty evaluation function that aims to judge these neighborhood particles and distinguish key genes. Furthermore, a gene selection algorithm based on artificial fish swarm intelligence is designed. Finally, some gene selection experiments are carried out on two tumor gene data sets. The classification experiments of a small number of selected key genes are conducted by using SVM classifier. The experimental results show that the genes selected by our proposed method have a low redundancy and a better classification performance.
2018, 47(1): 105-111.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.016
Abstract:
A novel bi-histogram equalization algorithm is proposed for keeping image brightness preservation. Based on the grayscale histogram of the given image, the corresponding relation between the grayscale threshold and the output brightness is established; all the thresholds are calculated to meet the requirements of the output brightness, then the best one is chosen for bi-histogram equalization so that the biggest histogram similarity exists between the output image and the result by the brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization (BBHE) method. Experimental results of several images with different brightness show that by using the proposed algorithm the margin of relative error between output brightness and expected value reaches 0.43%~2.56%, but only-36.94%~8.85% by using the BBHE method. We conclude that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the accuracy of brightness control target for bi-histogram equalization, and the operating speed meets real-time requirements.
A novel bi-histogram equalization algorithm is proposed for keeping image brightness preservation. Based on the grayscale histogram of the given image, the corresponding relation between the grayscale threshold and the output brightness is established; all the thresholds are calculated to meet the requirements of the output brightness, then the best one is chosen for bi-histogram equalization so that the biggest histogram similarity exists between the output image and the result by the brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization (BBHE) method. Experimental results of several images with different brightness show that by using the proposed algorithm the margin of relative error between output brightness and expected value reaches 0.43%~2.56%, but only-36.94%~8.85% by using the BBHE method. We conclude that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the accuracy of brightness control target for bi-histogram equalization, and the operating speed meets real-time requirements.
An Improved Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithm with Weighted Heterogeneous Information
2018, 47(1): 112-116, 152.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.017
Abstract:
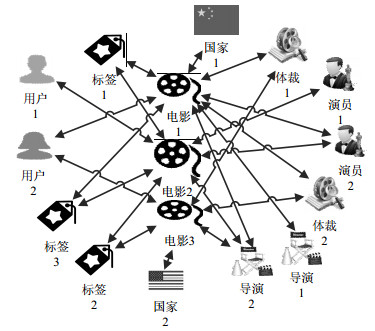
Collaborative filtering is oneofthe most successful recommendation technologies, and the quality of collaborative filtering is determinedby the accuracy of the nearest neighbors. Data sparsity problem and similarity metricsseriously affect the choice of the nearest neighbors. Different from traditional recommendation tasks, in this paper, we propose an improved meta path-based collaborative filtering algorithm for weighted heterogeneous information networks. Firstly, we calculate the similarity among users based on different meta path by utilizing the rich semantic information and attribute information in weighted heterogeneous networks. Then we apply the similarity to user-based collaborative filtering algorithm and get multiple predicted rating scores based on different similarity. Finally we calculate the final predicted scores by combining various meta path information using supervised machine learning algorithms. The method is evaluated with the extended MovieLens dataset and experimental results show that our approach outperforms several traditional algorithms and make the result of recommendation more accurate in terms of accuracy.
Collaborative filtering is oneofthe most successful recommendation technologies, and the quality of collaborative filtering is determinedby the accuracy of the nearest neighbors. Data sparsity problem and similarity metricsseriously affect the choice of the nearest neighbors. Different from traditional recommendation tasks, in this paper, we propose an improved meta path-based collaborative filtering algorithm for weighted heterogeneous information networks. Firstly, we calculate the similarity among users based on different meta path by utilizing the rich semantic information and attribute information in weighted heterogeneous networks. Then we apply the similarity to user-based collaborative filtering algorithm and get multiple predicted rating scores based on different similarity. Finally we calculate the final predicted scores by combining various meta path information using supervised machine learning algorithms. The method is evaluated with the extended MovieLens dataset and experimental results show that our approach outperforms several traditional algorithms and make the result of recommendation more accurate in terms of accuracy.
2018, 47(1): 117-124.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.018
Abstract:
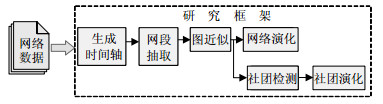
Aiming at the mining problem for evolutionary community patterns, which restricts the development of evolution analysis methods for dynamic network, this paper designs a static community detection algorithm based on a kind of directed mutation strategy and variable neighborhood search algorithm, and a community evolution analysis algorithm based on compatibility and community {\rm{lifetime}}. Through adopting a strategy that runs static community detection algorithm on the moment and community evolution analysis algorithm on the sequential, a new community detection and evolution analysis method for dynamic network is proposed. In the experiment, the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by Zachary karate club network and power network.
Aiming at the mining problem for evolutionary community patterns, which restricts the development of evolution analysis methods for dynamic network, this paper designs a static community detection algorithm based on a kind of directed mutation strategy and variable neighborhood search algorithm, and a community evolution analysis algorithm based on compatibility and community {\rm{lifetime}}. Through adopting a strategy that runs static community detection algorithm on the moment and community evolution analysis algorithm on the sequential, a new community detection and evolution analysis method for dynamic network is proposed. In the experiment, the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by Zachary karate club network and power network.
2018, 47(1): 125-131.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.019
Abstract:
In the cases of imbalance big datasets, the traditional feature processing method is biased to the large class and ignores the small class, which affects the classification performance. So a text feature gene extraction method is proposed in this paper. First of all, considering the feature selection impact of imbalance distribution of sample categorization, a feature selection method based on the CHI statistical matrix combined with information entropy is used to strengthen the characteristics of the small class. Secondly, based on the high order correlation of multidimensional statistical data, the method of text feature extraction is designed to enhance the generalization ability of feature item. Finally, the two methods are combined to construct a new method of text feature extraction under unbalanced large datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a better performance in early maturity and feature dimension reduction, and is far superior to the common feature selection algorithm in the classification ability of small classes.
In the cases of imbalance big datasets, the traditional feature processing method is biased to the large class and ignores the small class, which affects the classification performance. So a text feature gene extraction method is proposed in this paper. First of all, considering the feature selection impact of imbalance distribution of sample categorization, a feature selection method based on the CHI statistical matrix combined with information entropy is used to strengthen the characteristics of the small class. Secondly, based on the high order correlation of multidimensional statistical data, the method of text feature extraction is designed to enhance the generalization ability of feature item. Finally, the two methods are combined to construct a new method of text feature extraction under unbalanced large datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a better performance in early maturity and feature dimension reduction, and is far superior to the common feature selection algorithm in the classification ability of small classes.
2018, 47(1): 132-138.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.020
Abstract:
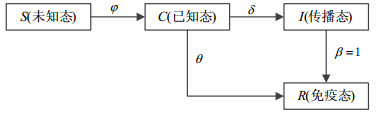
Based on the multilayer coupling network theory and transmission dynamics theory, the paper establishes a single-layer platform information dissemination model (S-SCIR model) and a double-layer platform model (O-SCI2R model) in accordance with the mechanism of information spreading in crowdfunding platform. The transmission of information under different network conditions in the public platform is modelled and simulated. The factors influencing the dissemination of information is explored by simulating the transmission of information in the online and offline networks, providing a new perspective and method for the research of this kind of problems. The results show that the information can be transmitted more quickly under the condition of double layer coupled network, stronger online and offline node correlation is more helpful to the spread of information, and the greater the information value has, the faster the transmission of information will be.
Based on the multilayer coupling network theory and transmission dynamics theory, the paper establishes a single-layer platform information dissemination model (S-SCIR model) and a double-layer platform model (O-SCI2R model) in accordance with the mechanism of information spreading in crowdfunding platform. The transmission of information under different network conditions in the public platform is modelled and simulated. The factors influencing the dissemination of information is explored by simulating the transmission of information in the online and offline networks, providing a new perspective and method for the research of this kind of problems. The results show that the information can be transmitted more quickly under the condition of double layer coupled network, stronger online and offline node correlation is more helpful to the spread of information, and the greater the information value has, the faster the transmission of information will be.
2018, 47(1): 139-146.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.021
Abstract:
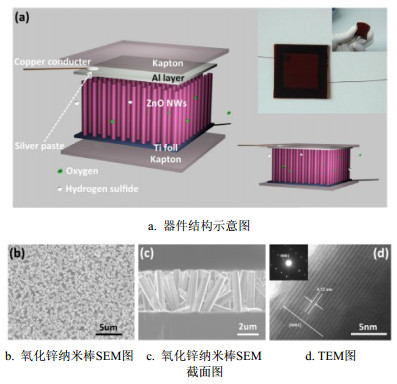
Small, maintenance-free and portable self-powered systems especially self-powered sensors have been widely used. Self-powered systems provide electric energy for various sensors by harvesting environmental energy. Therefore, it is very meaningful to develop self-powered gas sensors by harvesting clean energy, such as wind energy, mechanical energy, solar energy, and so on. The realization of self-powered sensors generally has two approaches:the first approach is to develop environmental energy harvesting devices for driving the traditional sensors; the other is to develop self-powered sensors that can actively generate electrical signal by itself as a response to stimulation from the ambient environment. The structure design, operation principle and performance of several self-powered gas sensors that are driven by wind energy, mechanical energy, and solar energy are introduced systemically. This paper provide a reference for integrative self-powered gas sensors in the future.
Small, maintenance-free and portable self-powered systems especially self-powered sensors have been widely used. Self-powered systems provide electric energy for various sensors by harvesting environmental energy. Therefore, it is very meaningful to develop self-powered gas sensors by harvesting clean energy, such as wind energy, mechanical energy, solar energy, and so on. The realization of self-powered sensors generally has two approaches:the first approach is to develop environmental energy harvesting devices for driving the traditional sensors; the other is to develop self-powered sensors that can actively generate electrical signal by itself as a response to stimulation from the ambient environment. The structure design, operation principle and performance of several self-powered gas sensors that are driven by wind energy, mechanical energy, and solar energy are introduced systemically. This paper provide a reference for integrative self-powered gas sensors in the future.
2018, 47(1): 147-152.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.022
Abstract:
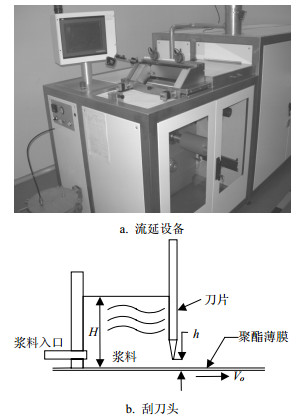
In this paper, the influence on the mechanical properties of green tape from binder, dispersant and plasticizer in the slurry system is studied based on the characteristics of tape casting process in the low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology. Also, the relationships between the heat-treatment temperature and the mass loss, as well as the elongation and tensile strength of the tape are analyzed. Moreover, the effects on structure and microwave characteristics of the green tape generated from the key procedures and technical parameters of tape casting process are discussed. The results show that the tape casting process can be significantly improved and the green tapes with stable quality and high reliability are obtained by adjusting the ratio of binder, dispersant and plasticizer, and using the gradient temperature profile and the method of eliminating cumulative stress, respectively. Finally, by the verification of the experimental microwave capacitors, the green tapes with high stability, performance and reliability are obtained, which can be suitable for the requirements in microwave applications.
In this paper, the influence on the mechanical properties of green tape from binder, dispersant and plasticizer in the slurry system is studied based on the characteristics of tape casting process in the low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology. Also, the relationships between the heat-treatment temperature and the mass loss, as well as the elongation and tensile strength of the tape are analyzed. Moreover, the effects on structure and microwave characteristics of the green tape generated from the key procedures and technical parameters of tape casting process are discussed. The results show that the tape casting process can be significantly improved and the green tapes with stable quality and high reliability are obtained by adjusting the ratio of binder, dispersant and plasticizer, and using the gradient temperature profile and the method of eliminating cumulative stress, respectively. Finally, by the verification of the experimental microwave capacitors, the green tapes with high stability, performance and reliability are obtained, which can be suitable for the requirements in microwave applications.
2018, 47(1): 153-156.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.023
Abstract:
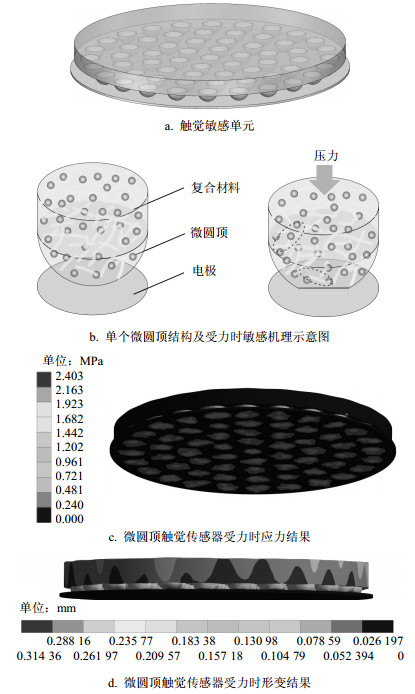
The silicone rubber filled with mass fraction of 3% carbon and 2% of carbon nanotubes was used as the force sensitive conductive composite materials. A flexible tactile sensor with microdome array structures is proposed in this paper. The structure characteristics, fabrication process and micro characterization of the tactile sensor with microdome array structures are researched, and the tactile perception mechanism is also revealed with ANSYS finite element analysis software. The force sensitive characteristic of the microdome array structures flexible tactile is studied and the application of plantar pressure distribution perception is illustrated. The experimental results indicate that the microdome array structures flexible tactile has good force-sensitive property and wearing comfort, and it provides a design proposal for flexible wearable tactile sensor.
The silicone rubber filled with mass fraction of 3% carbon and 2% of carbon nanotubes was used as the force sensitive conductive composite materials. A flexible tactile sensor with microdome array structures is proposed in this paper. The structure characteristics, fabrication process and micro characterization of the tactile sensor with microdome array structures are researched, and the tactile perception mechanism is also revealed with ANSYS finite element analysis software. The force sensitive characteristic of the microdome array structures flexible tactile is studied and the application of plantar pressure distribution perception is illustrated. The experimental results indicate that the microdome array structures flexible tactile has good force-sensitive property and wearing comfort, and it provides a design proposal for flexible wearable tactile sensor.
2018, 47(1): 157-160.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.01.024
Abstract:
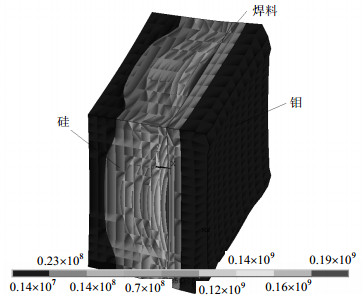
The influence of brazing parameters on the equivalent stress of welding field emission array and molybdenum electrode was simulated by ANSYS and the results of simulation were verified by vacuum brazing technique. Simulating results show that when brazing temperature was 850 ℃, it had the minimum equivalent stress. When the cooling rate was 23 ℃/min, the equivalent stress reached the maximum, and then decreased rapidly with increasing cooling rate. During the cooling process, the high temperature zone gradually extended to the silicon substrate, and the temperature distribution was symmetrical along brazing seam, in accompany with high temperature in brazing seam center and low temperature on both sides. Experimental results show that brazed joint was dense and brazing seam was well combined without any defects such as cracks and voids. Collectively, this method may be a viable and cost-effective route for welding the field emission cathode array with molybdenum electrode.
The influence of brazing parameters on the equivalent stress of welding field emission array and molybdenum electrode was simulated by ANSYS and the results of simulation were verified by vacuum brazing technique. Simulating results show that when brazing temperature was 850 ℃, it had the minimum equivalent stress. When the cooling rate was 23 ℃/min, the equivalent stress reached the maximum, and then decreased rapidly with increasing cooling rate. During the cooling process, the high temperature zone gradually extended to the silicon substrate, and the temperature distribution was symmetrical along brazing seam, in accompany with high temperature in brazing seam center and low temperature on both sides. Experimental results show that brazed joint was dense and brazing seam was well combined without any defects such as cracks and voids. Collectively, this method may be a viable and cost-effective route for welding the field emission cathode array with molybdenum electrode.

 ISSN
ISSN