2018 Vol. 47, No. 2
2018, 47(2): 161-168.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.001
Abstract:
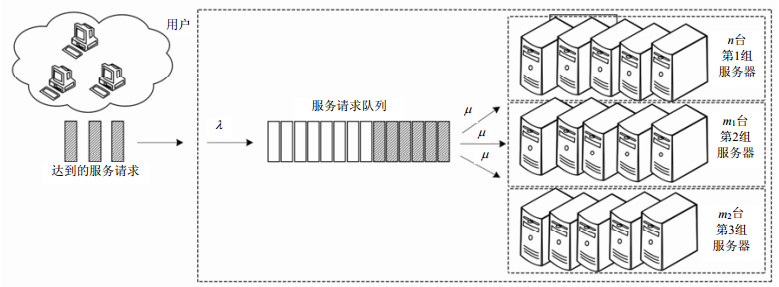
With the increasing popularity of Internet services and cloud computing, both energy efficiency and performance guarantees are major concerns for data center operators. However, most of the previous works only address this problem in homogeneous data center environments. This paper investigates how to guarantee performance requirement in terms of waiting time so as to minimize power consumption among multiple types of servers with different processing capabilities in a data center. We address the problem of minimizing the energy consumption of a data center by means of dynamic management policies that switch on/off a certain quantity of servers necessary under given performance requirements in terms of waiting time. We develop a mathematical model using queuing theory to determine the number of servers that should be used i.e., powered on. Experiment results show that our scheme can reduce power consumption compared with the non-group division strategy. Our scheme provides an analytical approach for studying the power-performance tradeoff in the heterogeneous data center.
With the increasing popularity of Internet services and cloud computing, both energy efficiency and performance guarantees are major concerns for data center operators. However, most of the previous works only address this problem in homogeneous data center environments. This paper investigates how to guarantee performance requirement in terms of waiting time so as to minimize power consumption among multiple types of servers with different processing capabilities in a data center. We address the problem of minimizing the energy consumption of a data center by means of dynamic management policies that switch on/off a certain quantity of servers necessary under given performance requirements in terms of waiting time. We develop a mathematical model using queuing theory to determine the number of servers that should be used i.e., powered on. Experiment results show that our scheme can reduce power consumption compared with the non-group division strategy. Our scheme provides an analytical approach for studying the power-performance tradeoff in the heterogeneous data center.
2018, 47(2): 169-177.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.002
Abstract:
TCP incast congestion happens in data center networks with high-bandwidth and low-latency, when multiple synchronized servers send data to a single receiver in parallel. The existing improved methods focus on the congestion control algorithm in the congestion avoidance phase, ignoring the aggressive exponential increasing window in the slow start phase that is a key reason for incast problem. Therefore, this paper proposes an ECN-based slow-start of transmission control protocol (TCP) congestion control strategy, which dynamically feedbacks congestion status by using the existing congestion flags to adjust the window-increasing speed during the slow start phase. Experimental results show that our approach helps the existing data center TCP effectively avoid the throughput collapse in concurrent transmissions. The number of concurrent flow and network throughput are increased by 3.4×and 85×, respectively.
TCP incast congestion happens in data center networks with high-bandwidth and low-latency, when multiple synchronized servers send data to a single receiver in parallel. The existing improved methods focus on the congestion control algorithm in the congestion avoidance phase, ignoring the aggressive exponential increasing window in the slow start phase that is a key reason for incast problem. Therefore, this paper proposes an ECN-based slow-start of transmission control protocol (TCP) congestion control strategy, which dynamically feedbacks congestion status by using the existing congestion flags to adjust the window-increasing speed during the slow start phase. Experimental results show that our approach helps the existing data center TCP effectively avoid the throughput collapse in concurrent transmissions. The number of concurrent flow and network throughput are increased by 3.4×and 85×, respectively.
2018, 47(2): 178-182.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.003
Abstract:
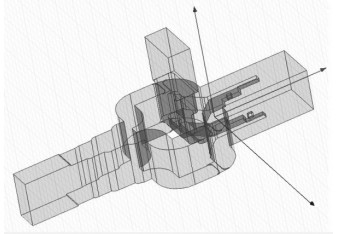
This paper describes a wideband orthomode transducer (OMT) based on the ridged waveguide connection, the center frequency of OMT is 40 GHz, relative bandwidth is 50%. The transducer is aimed to work in Q-band receiver system in radio telescope. This OMT is composed of dual ridged waveguide connection joint, Y type joint and E type elbow, the structure of OMT is compact, and the influence of processing and assembling errors on the electrical performance is reduced. After testing the actual machining of the OMT, the reflection loss of Y type joint output S11 ≤ -22.7dB, the reflection loss of direct arm output ≤ -21.0dB, and the isolation between Y type joint output and direct arm output ≤ -43.4dB. The trend of curve change between actual measure and simulation result is very similar, and this OMT can satisfy the requirements of radio astronomic observation in (30~50) GHz bandwidth.
This paper describes a wideband orthomode transducer (OMT) based on the ridged waveguide connection, the center frequency of OMT is 40 GHz, relative bandwidth is 50%. The transducer is aimed to work in Q-band receiver system in radio telescope. This OMT is composed of dual ridged waveguide connection joint, Y type joint and E type elbow, the structure of OMT is compact, and the influence of processing and assembling errors on the electrical performance is reduced. After testing the actual machining of the OMT, the reflection loss of Y type joint output S11 ≤ -22.7dB, the reflection loss of direct arm output ≤ -21.0dB, and the isolation between Y type joint output and direct arm output ≤ -43.4dB. The trend of curve change between actual measure and simulation result is very similar, and this OMT can satisfy the requirements of radio astronomic observation in (30~50) GHz bandwidth.
2018, 47(2): 183-188.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.004
Abstract:
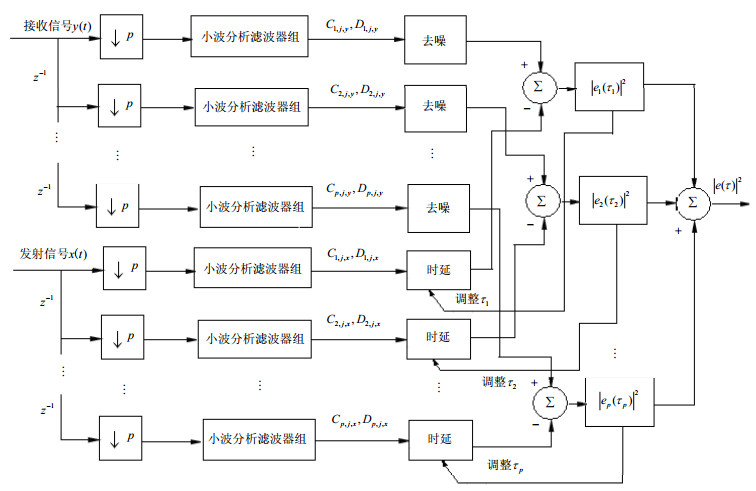
In the array signal receiving, the different time delay of the desired signal is received by the array antenna because of the signal multipath effect. So high accuracy beamforming with time delay signals is an intractable problem in the signal processing. In this paper, a beamforming algorithm considering the time delay signal is proposed. The time delay estimation value is calculated by the wavelet algorithm at first. And then the time delay estimate is compared with the prestored time delay value to choose the desired signal direction. The spatial multi-beam with approximate desired signal direction is optimized by iteration to implement overall adaptive beam in space. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the improved algorithm.
In the array signal receiving, the different time delay of the desired signal is received by the array antenna because of the signal multipath effect. So high accuracy beamforming with time delay signals is an intractable problem in the signal processing. In this paper, a beamforming algorithm considering the time delay signal is proposed. The time delay estimation value is calculated by the wavelet algorithm at first. And then the time delay estimate is compared with the prestored time delay value to choose the desired signal direction. The spatial multi-beam with approximate desired signal direction is optimized by iteration to implement overall adaptive beam in space. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the improved algorithm.
2018, 47(2): 189-193.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.005
Abstract:
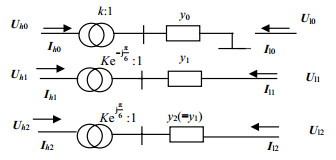
Impedance matching technology is the key to designing high-frequency electronic circuits. In order to solve the problem of impedance matching of transmission lines with special structures, the basic characteristics of the transmission line with multi-branch structure are studied based on the principle of impedance matching of transmission lines, and signal transmission characteristics of transmission line with multi-branch structure are analyzed in depth. Combined with the zero-order model of transmission line, the impedance matching conditions of multi-branch structure are obtained, and the simulation results are given. This paper summarizes the main factors influencing the signal characteristics in the model. As well, it further optimizes the solution to the impedance matching of the transmission line with multi-branch structure.
Impedance matching technology is the key to designing high-frequency electronic circuits. In order to solve the problem of impedance matching of transmission lines with special structures, the basic characteristics of the transmission line with multi-branch structure are studied based on the principle of impedance matching of transmission lines, and signal transmission characteristics of transmission line with multi-branch structure are analyzed in depth. Combined with the zero-order model of transmission line, the impedance matching conditions of multi-branch structure are obtained, and the simulation results are given. This paper summarizes the main factors influencing the signal characteristics in the model. As well, it further optimizes the solution to the impedance matching of the transmission line with multi-branch structure.
2018, 47(2): 194-202.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.006
Abstract:
The state estimation of complex distribution networks is the most basic function of power grid intelligent operation. The state estimation algorithm of transmission networks usually cannot be directly applied to the distribution networks, it is needed to provide accurate and efficient state estimation in the face of the basic data of distribution networks with different qualities on the condition of power grid operation states. The complex distribution network considered in this paper is modelled according to the characteristics of three-phase unbalance. A state estimation method based on load classification and complex network pruning is presented in detail, the problems of lack of measured data in the distribution network is better solved. Through the field test in an actual distribution network, it is proved that the proposed algorithm is robust, accurate and efficient, and can meet the actual application needs.
The state estimation of complex distribution networks is the most basic function of power grid intelligent operation. The state estimation algorithm of transmission networks usually cannot be directly applied to the distribution networks, it is needed to provide accurate and efficient state estimation in the face of the basic data of distribution networks with different qualities on the condition of power grid operation states. The complex distribution network considered in this paper is modelled according to the characteristics of three-phase unbalance. A state estimation method based on load classification and complex network pruning is presented in detail, the problems of lack of measured data in the distribution network is better solved. Through the field test in an actual distribution network, it is proved that the proposed algorithm is robust, accurate and efficient, and can meet the actual application needs.
2018, 47(2): 203-208.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.007
Abstract:
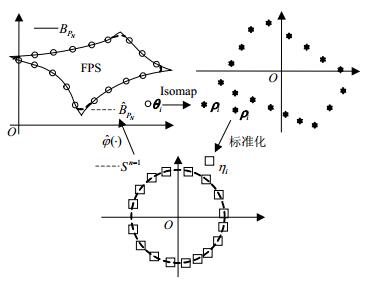
This paper proposes a novel set membership parameter estimation method for nonlinear systems. According to the theory of geometry and topology, the boundary of the feasible parameter set (FPS) is homeomorphic to an n-1-sphere (n is the number of parameters). From the viewpoint of manifold learning, the proposed method constructs a mapping which can approximate the homeomorphism between the FPS boundary and the n-1-sphere. Once this mapping is established, it can be used to map the n-1-sphere into an approximation of the FPS boundary. The following technologies are used to build the mapping. First, a data set consisting of vectors uniformly sampled from the FPS boundary is mapped into a data set contained by the n-1-sphere. This is achieved by Isomap followed by the data normalization. Then, a non-parametric method based on the two data sets is used to build a mapping which approximates the homeomorphism between the FPS boundary and the n-1-sphere. The simulation results show that the proposed method exhibits superior accuracy compared with the support vector machine method.
This paper proposes a novel set membership parameter estimation method for nonlinear systems. According to the theory of geometry and topology, the boundary of the feasible parameter set (FPS) is homeomorphic to an n-1-sphere (n is the number of parameters). From the viewpoint of manifold learning, the proposed method constructs a mapping which can approximate the homeomorphism between the FPS boundary and the n-1-sphere. Once this mapping is established, it can be used to map the n-1-sphere into an approximation of the FPS boundary. The following technologies are used to build the mapping. First, a data set consisting of vectors uniformly sampled from the FPS boundary is mapped into a data set contained by the n-1-sphere. This is achieved by Isomap followed by the data normalization. Then, a non-parametric method based on the two data sets is used to build a mapping which approximates the homeomorphism between the FPS boundary and the n-1-sphere. The simulation results show that the proposed method exhibits superior accuracy compared with the support vector machine method.
2018, 47(2): 209-215, 241.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.008
Abstract:
Zigbee-based space charge density measurement system is widely used in space charge density measurements of high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission project. In practice, the power consumption of the space charge density measurement system is a key constraint of the device performance. According to the distribution characteristics of wireless communication unit of space charge density measurement system, the low-power operation status transition mechanism and the influence of communication distance and working environment on power consumption are analyzed. At the end, the low-power energy management strategy is developed. The proposed strategy effectively improves the performance of space charge density measurement system.
Zigbee-based space charge density measurement system is widely used in space charge density measurements of high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission project. In practice, the power consumption of the space charge density measurement system is a key constraint of the device performance. According to the distribution characteristics of wireless communication unit of space charge density measurement system, the low-power operation status transition mechanism and the influence of communication distance and working environment on power consumption are analyzed. At the end, the low-power energy management strategy is developed. The proposed strategy effectively improves the performance of space charge density measurement system.
2018, 47(2): 216-223.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.009
Abstract:
The disturbance-suppression methods are discussed for solving the severe disturbance from the automatic three-coordinate positioning and installation system of a certain type of motor test equipment. Firstly, a kinetic model of the Z-axis lifting system with complicated internal disturbance factors and significant external load is established, and then an AC driven full closed-loop electromechanical position servo system is established to prevent the initial impact of various closed-loop internal disturbances. In order to further improve the system's anti-disturbance abilities, the advanced active-disturbances rejection controller (ADRC) is introduced in the positional loop controller of the fully closed-loop control system. A MATLAB/Simulink simulation test was carried out based on this full closed-loop position servo system and a contrast analysis was made between the disturbance resistance effects of ADRC control and PID control for the position loop. The results show that for the position tracking performance under the external disturbance of a constant load and the position holding performance under the internal disturbance of electrical impedance, the ADRC control is better than the PID control. Finally, the corresponding tests were completed using the test equipment, and the simulation results were further verified.
The disturbance-suppression methods are discussed for solving the severe disturbance from the automatic three-coordinate positioning and installation system of a certain type of motor test equipment. Firstly, a kinetic model of the Z-axis lifting system with complicated internal disturbance factors and significant external load is established, and then an AC driven full closed-loop electromechanical position servo system is established to prevent the initial impact of various closed-loop internal disturbances. In order to further improve the system's anti-disturbance abilities, the advanced active-disturbances rejection controller (ADRC) is introduced in the positional loop controller of the fully closed-loop control system. A MATLAB/Simulink simulation test was carried out based on this full closed-loop position servo system and a contrast analysis was made between the disturbance resistance effects of ADRC control and PID control for the position loop. The results show that for the position tracking performance under the external disturbance of a constant load and the position holding performance under the internal disturbance of electrical impedance, the ADRC control is better than the PID control. Finally, the corresponding tests were completed using the test equipment, and the simulation results were further verified.
2018, 47(2): 224-229.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.010
Abstract:
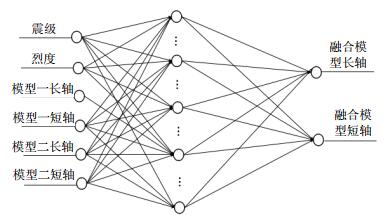
It is the hotpot and challenge in the field of earthquake for charactering seismic intensity attenuation relationship. Many scholars have established some prediction models of seismic intensity attenuation. In order to further improve the prediction accuracy of the seismic intensity attenuation models, 243 isoseismics from 107 earthquake cases are collected from Sichuan-Yunnan to establish a new comprehensive prediction model base on back propagation (BP) neural network. This prediction model fuses the merits of the Western China intensity attenuation relation based on the traditional model and the matrix attenuation relation based on matrix model. The experimental result shows that the prediction accuracy of the proposed fusion model is better than that of the matrix attenuation relationship and the western Chinese intensity attenuation relationship.
It is the hotpot and challenge in the field of earthquake for charactering seismic intensity attenuation relationship. Many scholars have established some prediction models of seismic intensity attenuation. In order to further improve the prediction accuracy of the seismic intensity attenuation models, 243 isoseismics from 107 earthquake cases are collected from Sichuan-Yunnan to establish a new comprehensive prediction model base on back propagation (BP) neural network. This prediction model fuses the merits of the Western China intensity attenuation relation based on the traditional model and the matrix attenuation relation based on matrix model. The experimental result shows that the prediction accuracy of the proposed fusion model is better than that of the matrix attenuation relationship and the western Chinese intensity attenuation relationship.
2018, 47(2): 230-234.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.011
Abstract:
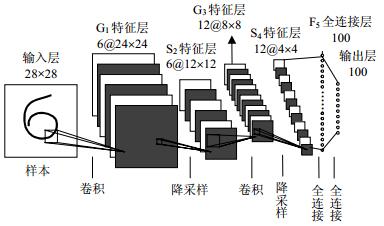
In order to make convolutional neural network get optimal connection automatically without experienced guidance and improve the optimizing effectiveness for parameters of convolutional neural network, a new method using both particle swarm optimization algorithm and discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm is proposed to optimize parameters and feature maps connecting structure of convolutional neural network. The particle swarm optimization is applied to optimize the weights of convolutional neural network at first, and then the discrete particle swarm optimization is applied to optimize feature maps connections between sub-sampling layer and convolutional layer. The method is applied to MNIST database and CIFAR-10 database, compared to convolutional neural networks of other connecting structures and other recognition methods, results shown that this method can optimize the parameters and structure of the network effectively, accelerate network convergence and improve the recognition accuracy.
In order to make convolutional neural network get optimal connection automatically without experienced guidance and improve the optimizing effectiveness for parameters of convolutional neural network, a new method using both particle swarm optimization algorithm and discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm is proposed to optimize parameters and feature maps connecting structure of convolutional neural network. The particle swarm optimization is applied to optimize the weights of convolutional neural network at first, and then the discrete particle swarm optimization is applied to optimize feature maps connections between sub-sampling layer and convolutional layer. The method is applied to MNIST database and CIFAR-10 database, compared to convolutional neural networks of other connecting structures and other recognition methods, results shown that this method can optimize the parameters and structure of the network effectively, accelerate network convergence and improve the recognition accuracy.
2018, 47(2): 235-241.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.012
Abstract:
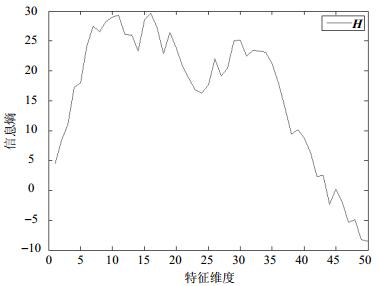
Data dimensionality reduction is a necessary step in mining effective information from high-dimensional data. When applying the traditional principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm to high-dimensional sparse data dimensionality reduction, there is a problem that unable to read all data features at once into memory for analysis and calculation, furthermore, the improved block processing PCA algorithm also can not meet the actual requirements because of the time consuming. In this paper, we propose the E-PCA algorithm by introducing the concept of information entropy to improve the PCA algorithm. First, the useless features are eliminated through feature selection based on information entropy, and then PCA algorithm is used to reduce the dimensionality of large, high-dimensional sparse data. The experimental results show that in the case of keeping the same proportion of raw data, the information entropy-based E-PCA algorithm proposed in this paper is superior to block processing PCA algorithm in terms of memory usage, run time and the results of dimension reduction.
Data dimensionality reduction is a necessary step in mining effective information from high-dimensional data. When applying the traditional principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm to high-dimensional sparse data dimensionality reduction, there is a problem that unable to read all data features at once into memory for analysis and calculation, furthermore, the improved block processing PCA algorithm also can not meet the actual requirements because of the time consuming. In this paper, we propose the E-PCA algorithm by introducing the concept of information entropy to improve the PCA algorithm. First, the useless features are eliminated through feature selection based on information entropy, and then PCA algorithm is used to reduce the dimensionality of large, high-dimensional sparse data. The experimental results show that in the case of keeping the same proportion of raw data, the information entropy-based E-PCA algorithm proposed in this paper is superior to block processing PCA algorithm in terms of memory usage, run time and the results of dimension reduction.
2018, 47(2): 242-246.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.013
Abstract:
In 2014, Yuan et al. proposed a new multivariate public key cryptosystem by combining "small field-big field" and "stepwise triangular" methods. The authors claimed that their scheme can be secure against rank attack, linearization equation attack and differential attack. Through analysis, we found that there are a lot of linearization equations satisfied by this scheme. We can transform it to an equivalent square encryption scheme by linearization equation method and then recover corresponding plaintext for any given cipheretext by differential attack. As to two recommended parameters, for given public key, the complexities of recovering plaintext are 233 and 235, respectively. The results above are further confirmed by computer experiments.
In 2014, Yuan et al. proposed a new multivariate public key cryptosystem by combining "small field-big field" and "stepwise triangular" methods. The authors claimed that their scheme can be secure against rank attack, linearization equation attack and differential attack. Through analysis, we found that there are a lot of linearization equations satisfied by this scheme. We can transform it to an equivalent square encryption scheme by linearization equation method and then recover corresponding plaintext for any given cipheretext by differential attack. As to two recommended parameters, for given public key, the complexities of recovering plaintext are 233 and 235, respectively. The results above are further confirmed by computer experiments.
2018, 47(2): 256-261.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.015
Abstract:
A novel method for group activity recognition in crowd is proposed using causality analysis. The Granger Causality Test is used to analyze the causality between individual actions. On this basis, we adopt a dominant set based clustering algorithm to detect interacting groups in crowded scenes using causality, spatial and directional relationships among people. To effectively represent group activity, low level visual features and causality features are used. The low level visual features, which included histograms of oriented gradients (HOG) and histograms of optical flow (HOF), are applied to describe the properties of individual activity, and the causality features obtained by causality analysis are introduced to depict the interaction information of people. Sparse representation is employed to recognize group activities in crowd. Experiments are performed on the BEHAVE and collective activity databases to test and evaluate the proposed method. The experiments results show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods.
A novel method for group activity recognition in crowd is proposed using causality analysis. The Granger Causality Test is used to analyze the causality between individual actions. On this basis, we adopt a dominant set based clustering algorithm to detect interacting groups in crowded scenes using causality, spatial and directional relationships among people. To effectively represent group activity, low level visual features and causality features are used. The low level visual features, which included histograms of oriented gradients (HOG) and histograms of optical flow (HOF), are applied to describe the properties of individual activity, and the causality features obtained by causality analysis are introduced to depict the interaction information of people. Sparse representation is employed to recognize group activities in crowd. Experiments are performed on the BEHAVE and collective activity databases to test and evaluate the proposed method. The experiments results show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods.
2018, 47(2): 262-266.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.016
Abstract:
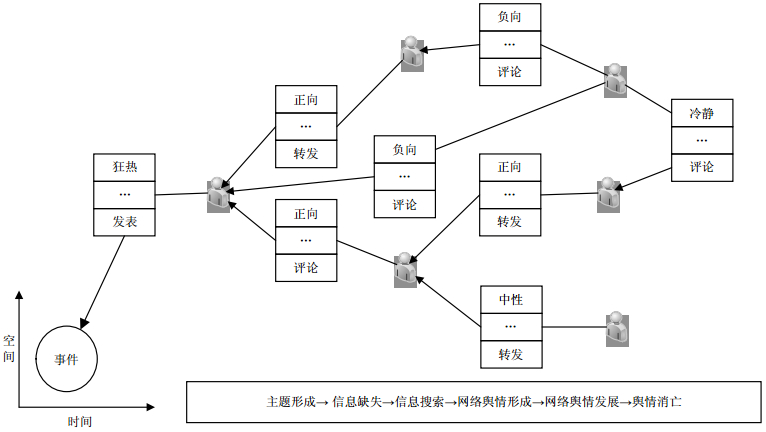
To construct the social network of Micro-blog users has become one of the most important method to analyze micro-blog data. However, due to the uncertainty of the behavior of users in the process of information release and dissemination, it is hard to construct effectively the social network of Micro-blog users. Based on the uncertainty theory, the paper proposes a rough set based dynamic cognitive technology to handle the incomplete and massive information of micro-blog, complete the calculation and analysis of behavior of users, and construct the social network of Micro-blog users. On this basis, the development of network events in micro-blog is analyzed combined with the method with operation, theme and emotion analysis.
To construct the social network of Micro-blog users has become one of the most important method to analyze micro-blog data. However, due to the uncertainty of the behavior of users in the process of information release and dissemination, it is hard to construct effectively the social network of Micro-blog users. Based on the uncertainty theory, the paper proposes a rough set based dynamic cognitive technology to handle the incomplete and massive information of micro-blog, complete the calculation and analysis of behavior of users, and construct the social network of Micro-blog users. On this basis, the development of network events in micro-blog is analyzed combined with the method with operation, theme and emotion analysis.
2018, 47(2): 267-271.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.017
Abstract:
In the network intrusion detection, because of the high dimensionality and redundant features of the original data, the storage burden of the intrusion detection system is increased, and the performance of the classifier is reduced. Aiming at this problem, this paper proposes an intrusion detection feature extraction method based on information theory model. The method starts with the feature of maximum information gain, and then iteratively adjusts the correlation among the classification mark of the data set, selected feature subset and candidate feature by search strategies and evaluation functions. Finally, the feature subset is determined by terminating conditions. In the experiment, we chose sample dataset for intrusion detection as the experimental data, and apply feature vector selected by the method to the support vector machine classification algorithm. It is found that the detection accuracy is almost unchanged, in the case that the dimension of the feature is greatly reduced. The results show the validity of the method.
In the network intrusion detection, because of the high dimensionality and redundant features of the original data, the storage burden of the intrusion detection system is increased, and the performance of the classifier is reduced. Aiming at this problem, this paper proposes an intrusion detection feature extraction method based on information theory model. The method starts with the feature of maximum information gain, and then iteratively adjusts the correlation among the classification mark of the data set, selected feature subset and candidate feature by search strategies and evaluation functions. Finally, the feature subset is determined by terminating conditions. In the experiment, we chose sample dataset for intrusion detection as the experimental data, and apply feature vector selected by the method to the support vector machine classification algorithm. It is found that the detection accuracy is almost unchanged, in the case that the dimension of the feature is greatly reduced. The results show the validity of the method.
2018, 47(2): 272-278.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.018
Abstract:
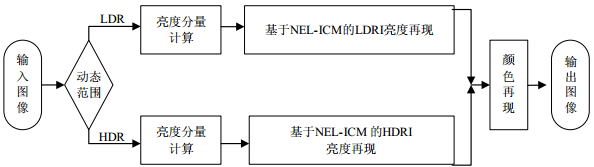
Realistic image rendition (RIR) aims to realize the realistic cognition of the world, including two main topics:low dynamic range image enhancement and high dynamic range image visualization. The RIR methods on the basis of visual system are firstly reviewed and analyzed. A general framework for RIR based on a modified neighborhood-enhanced-linking intersecting cortical model (NEL-ICM) is presented. The ideal image rendition on display is achieved through meticulous designs. The simulation results show high contrast enhancement effects for non-uniform lighting images, and HDR images gain good visualization with high-quality.
Realistic image rendition (RIR) aims to realize the realistic cognition of the world, including two main topics:low dynamic range image enhancement and high dynamic range image visualization. The RIR methods on the basis of visual system are firstly reviewed and analyzed. A general framework for RIR based on a modified neighborhood-enhanced-linking intersecting cortical model (NEL-ICM) is presented. The ideal image rendition on display is achieved through meticulous designs. The simulation results show high contrast enhancement effects for non-uniform lighting images, and HDR images gain good visualization with high-quality.
2018, 47(2): 247-255.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.014
Abstract:
Due to the different effects of different features on multidimensional data during the clustering, this paper proposes an affinity propagation clustering algorithm based on adaptive feature weight. This method introduces a feature weight similarity measure to affinity propagation by considering different importance of different features. During the clustering the new method evaluates the objective function according to current data partition, and calculates the contribution of each features made to current clustering. Then the feature weights will be self-adaptive updated according to the contribution, and the two messages passing between data points in affinity propagation will be recalculated on the basis of feature weight similarity matrix to enhance the clustering results. The experimental results show that feature updating works well on the new algorithm, and compared to the affinity propagation and other traditional clustering algorithm the new algorithm can obtain better results.
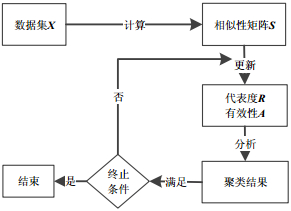
Due to the different effects of different features on multidimensional data during the clustering, this paper proposes an affinity propagation clustering algorithm based on adaptive feature weight. This method introduces a feature weight similarity measure to affinity propagation by considering different importance of different features. During the clustering the new method evaluates the objective function according to current data partition, and calculates the contribution of each features made to current clustering. Then the feature weights will be self-adaptive updated according to the contribution, and the two messages passing between data points in affinity propagation will be recalculated on the basis of feature weight similarity matrix to enhance the clustering results. The experimental results show that feature updating works well on the new algorithm, and compared to the affinity propagation and other traditional clustering algorithm the new algorithm can obtain better results.
2018, 47(2): 279-285.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.019
Abstract:
The multi-attribute ranking method based on Euclidean distance (TOPSIS-ED) can evaluate researcher academic influence through taking into account the different attributes of researchers. However, the method also has a problem that the points on the vertical line cannot be sorted. In this paper, we propose a multi-attribute ranking method based on relative entropy (TOPSIS-RE) by considering five indicators including the total number of papers, the total number of citations, citations per papers, I10-index and H-index. By calculating the relative entropy of the five indicators to the positive-ideal solution and the negative-ideal solution, this method ranks the authors according to the measurement that the results are close to the positive-ideal solution and far away from the negative-ideal solution. We select the American Physical Society data set as the training set and the authors who have won the Nobel Prize in the American Physical Society data set as the testing set. The area under curve (AUC) value is used to illustrate the accuracy of the algorithm. The results show that the AUC value calculated by TOPSIS-RE is 0.9321, and increases by 2.047% and 0.833% respectively compared with the total number of citations and TOPSIS-ED. Our work may shed some lights for quantifying the influence of scientists from the multi-attribute perspective.
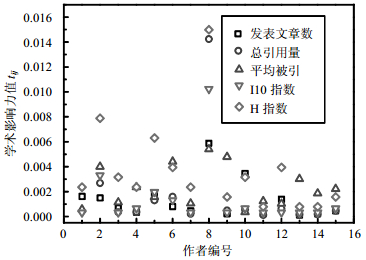
The multi-attribute ranking method based on Euclidean distance (TOPSIS-ED) can evaluate researcher academic influence through taking into account the different attributes of researchers. However, the method also has a problem that the points on the vertical line cannot be sorted. In this paper, we propose a multi-attribute ranking method based on relative entropy (TOPSIS-RE) by considering five indicators including the total number of papers, the total number of citations, citations per papers, I10-index and H-index. By calculating the relative entropy of the five indicators to the positive-ideal solution and the negative-ideal solution, this method ranks the authors according to the measurement that the results are close to the positive-ideal solution and far away from the negative-ideal solution. We select the American Physical Society data set as the training set and the authors who have won the Nobel Prize in the American Physical Society data set as the testing set. The area under curve (AUC) value is used to illustrate the accuracy of the algorithm. The results show that the AUC value calculated by TOPSIS-RE is 0.9321, and increases by 2.047% and 0.833% respectively compared with the total number of citations and TOPSIS-ED. Our work may shed some lights for quantifying the influence of scientists from the multi-attribute perspective.
2018, 47(2): 286-291.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.020
Abstract:
To integrate information of several weighted genes associated networks (WGAN), this paper proposes a network data integration method based on information entropy. This method uses information entropy to depict uncertain degree of gene-gene links, and thus realizes the integration of four existing human weighted genes associated network to construct a larger WGAN network which includes richer biology information. This new WGAN network contains more edges than each of the original network, and the edge weights have higher biological relevance than in the original networks. It also exhibits more satisfactory performance in disease genes prediction.
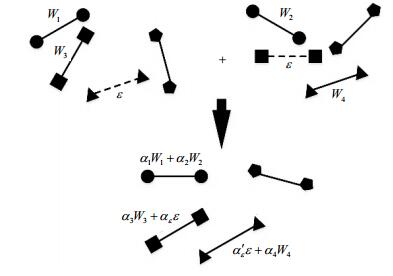
To integrate information of several weighted genes associated networks (WGAN), this paper proposes a network data integration method based on information entropy. This method uses information entropy to depict uncertain degree of gene-gene links, and thus realizes the integration of four existing human weighted genes associated network to construct a larger WGAN network which includes richer biology information. This new WGAN network contains more edges than each of the original network, and the edge weights have higher biological relevance than in the original networks. It also exhibits more satisfactory performance in disease genes prediction.
2018, 47(2): 292-297.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.021
Abstract:
Identification of critical nodes in a network is one of key issues in complex network analysis. The input-output (IO) model in economics can be used to evaluate the node centrality in open flow networks, but it cannot be directly applied to closed flow networks which lack of external inflow and outflow. This paper introduces a virtual external node to convert the closed flow network into an open flow network, which makes the standard IO analysis method can be used to identify critical nodes in closed flow networks. This virtual external IO analysis method is then applied to the identification of critical nodes in Chinese Railway Network and the World Food and Agriculture Trade Network. The proposed analysis method provides an alternative approach for evaluating node centrality in closed flow networks.
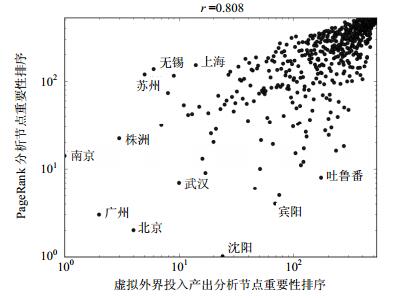
Identification of critical nodes in a network is one of key issues in complex network analysis. The input-output (IO) model in economics can be used to evaluate the node centrality in open flow networks, but it cannot be directly applied to closed flow networks which lack of external inflow and outflow. This paper introduces a virtual external node to convert the closed flow network into an open flow network, which makes the standard IO analysis method can be used to identify critical nodes in closed flow networks. This virtual external IO analysis method is then applied to the identification of critical nodes in Chinese Railway Network and the World Food and Agriculture Trade Network. The proposed analysis method provides an alternative approach for evaluating node centrality in closed flow networks.
2018, 47(2): 298-302.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.022
Abstract:
Social networks based on binary relationships are very important for understanding people's sociality. People's social relationships largely determine the stability of social networks among which mobile communication is one of the typical way reflecting people's emotional connection. In this paper, we used a large mobile phone dataset from an area of China to study that how people build and maintain social relationships. To measure the uniformity of human emotional behavior, an entropy-based index is proposed and used to analyze the mobile phone data. The results reveals that there are obvious sex and age differences that people invest and assign their resources in social networks.
Social networks based on binary relationships are very important for understanding people's sociality. People's social relationships largely determine the stability of social networks among which mobile communication is one of the typical way reflecting people's emotional connection. In this paper, we used a large mobile phone dataset from an area of China to study that how people build and maintain social relationships. To measure the uniformity of human emotional behavior, an entropy-based index is proposed and used to analyze the mobile phone data. The results reveals that there are obvious sex and age differences that people invest and assign their resources in social networks.
2018, 47(2): 303-306.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.023
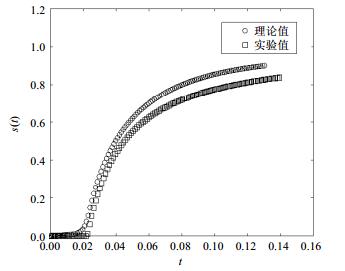
Abstract:
Recently, the extensive researches have done on percolation characteristics of different rules. Nevertheless, the impact of initial size distributions on percolation transition is rare in concern. In this paper, we investigate a modified ER (Eröds-Rényi) percolation process, in which the initial size distributions is set to exponential distribution. Through the analysis of Smoluchowski equation, it is found that although percolation transition is continuous compared to classical ER percolation process, the distributions of cluster size do not comply with the power-of distributions near the critical point, and both analytical and simulation results reveal that susceptibility does not satisfy the Curie-Weiss law.
Recently, the extensive researches have done on percolation characteristics of different rules. Nevertheless, the impact of initial size distributions on percolation transition is rare in concern. In this paper, we investigate a modified ER (Eröds-Rényi) percolation process, in which the initial size distributions is set to exponential distribution. Through the analysis of Smoluchowski equation, it is found that although percolation transition is continuous compared to classical ER percolation process, the distributions of cluster size do not comply with the power-of distributions near the critical point, and both analytical and simulation results reveal that susceptibility does not satisfy the Curie-Weiss law.
2018, 47(2): 307-310.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.024
Abstract:
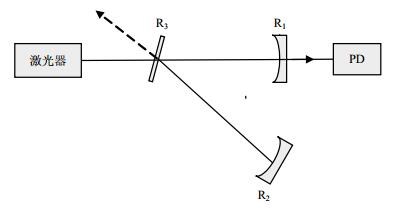
An optical feedback cavity ring down (OF-CRD) technique for simultaneously measuring the S-(perpendicular to the plane of incidence) and P-(in the plane of incidence) polarization reflectivity of highly reflective coatings is developed. Polarized light with a certain ratio of S-and P-polarization power and with square-wave modulated intensity is coupled into a ring-down cavity. The ring-down signal that leaks out from a cavity mirror is recorded at the negative edge of the modulation and fitted to a bi-exponential function to determine simultaneously the ring-down time for S and P polarizations. The reflection coefficients of highly reflective coatings for the S and P polarizations are therefore calculated from the determined ring-down time. Compared to the results obtained with purely S or P polarization, the differences for both S and P polarizations are respectively 1 ppm and 15 ppm, indicating the correctness of the simultaneous measurements. Compared to the conventional CRD approach, this simultaneous measurement method has the advantages of simpler configuration, easier operation, and higher speed.
An optical feedback cavity ring down (OF-CRD) technique for simultaneously measuring the S-(perpendicular to the plane of incidence) and P-(in the plane of incidence) polarization reflectivity of highly reflective coatings is developed. Polarized light with a certain ratio of S-and P-polarization power and with square-wave modulated intensity is coupled into a ring-down cavity. The ring-down signal that leaks out from a cavity mirror is recorded at the negative edge of the modulation and fitted to a bi-exponential function to determine simultaneously the ring-down time for S and P polarizations. The reflection coefficients of highly reflective coatings for the S and P polarizations are therefore calculated from the determined ring-down time. Compared to the results obtained with purely S or P polarization, the differences for both S and P polarizations are respectively 1 ppm and 15 ppm, indicating the correctness of the simultaneous measurements. Compared to the conventional CRD approach, this simultaneous measurement method has the advantages of simpler configuration, easier operation, and higher speed.
2018, 47(2): 311-316.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.025
Abstract:
In order to improve the operation stability of traditional Spindt field emission array cathode, a novel structure of lanthanum hexaboride (LaB6) composite field emission array cathode is proposed, which includes an amorphous silicon resistance layer, a molybdenum transition layer, and a lanthanum hexaboride emitter layer. The influences of the thickness of the resistive layer, the transition layer, and the emitter layer on the thermal stress field distribution of the cathode are simulated by ANSYS and the results of simulation are verified by experiments. Simulation results show that the thickness of the resistive layer does not affect the distribution of the thermal stress field, but only changes the value of the thermal stress. The maximum thermal stress of the cathode decreases as the thickness of the resistive layer increases. The transition layer can effectively alleviate the thermal stress of the emission layer, and its thickness affects the field distribution of thermal stress. As a result, the optimum parameters are as follows:a-Si layer thickness is 72 nm, Mo layer thickness is 200 nm, and LaB6 layer thickness is 728 nm. The thermal stress test results of the films are consistent with the simulation results, which proves the feasibility of reducing the thermal stress by introducing the transition layer and the resistive layer.
In order to improve the operation stability of traditional Spindt field emission array cathode, a novel structure of lanthanum hexaboride (LaB6) composite field emission array cathode is proposed, which includes an amorphous silicon resistance layer, a molybdenum transition layer, and a lanthanum hexaboride emitter layer. The influences of the thickness of the resistive layer, the transition layer, and the emitter layer on the thermal stress field distribution of the cathode are simulated by ANSYS and the results of simulation are verified by experiments. Simulation results show that the thickness of the resistive layer does not affect the distribution of the thermal stress field, but only changes the value of the thermal stress. The maximum thermal stress of the cathode decreases as the thickness of the resistive layer increases. The transition layer can effectively alleviate the thermal stress of the emission layer, and its thickness affects the field distribution of thermal stress. As a result, the optimum parameters are as follows:a-Si layer thickness is 72 nm, Mo layer thickness is 200 nm, and LaB6 layer thickness is 728 nm. The thermal stress test results of the films are consistent with the simulation results, which proves the feasibility of reducing the thermal stress by introducing the transition layer and the resistive layer.
2018, 47(2): 317-320.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.02.026
Abstract:
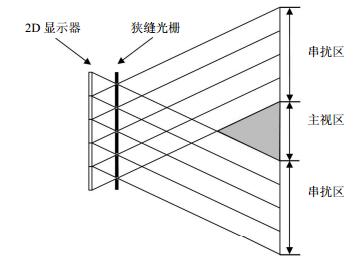
Dual-view integral imaging (DVⅡ) three-dimensional (3D) display presents two different 3D images in the left and right viewing directions, respectively. However, the low resolution limits the applications of the DVⅡ 3D display. This paper proposes a one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display based on a parallax barrier. The element image array is composed of two sets of alternating elemental images. The two sets of elemental images are captured from two different 3D scenes, respectively. The mathematical relation between the pitches of elemental image and slit is deduced through geometrical optics. According to the width of the 3D viewing zone, the calculation formula of the viewing angle is obtained. The mathematical relation between the optimal viewing distance and the parameters of the one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display is also analyzed. A prototype of the one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display based on the parallax barrier is developed to verify the principle. The 3D scene "CS" is obtained between 18° and 2° to the left, while the 3D scene 'SC' is seen between 2° and 18° to the right.
Dual-view integral imaging (DVⅡ) three-dimensional (3D) display presents two different 3D images in the left and right viewing directions, respectively. However, the low resolution limits the applications of the DVⅡ 3D display. This paper proposes a one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display based on a parallax barrier. The element image array is composed of two sets of alternating elemental images. The two sets of elemental images are captured from two different 3D scenes, respectively. The mathematical relation between the pitches of elemental image and slit is deduced through geometrical optics. According to the width of the 3D viewing zone, the calculation formula of the viewing angle is obtained. The mathematical relation between the optimal viewing distance and the parameters of the one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display is also analyzed. A prototype of the one-dimensional DVⅡ 3D display based on the parallax barrier is developed to verify the principle. The 3D scene "CS" is obtained between 18° and 2° to the left, while the 3D scene 'SC' is seen between 2° and 18° to the right.

 ISSN
ISSN