2018 Vol. 47, No. 5
2018, 47(5): 641-645.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.001
Abstract:
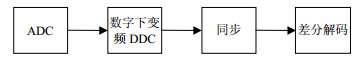
A novel design of multi-channel parallel differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK) receiver based FFT is proposed in this paper. This receiver is capable of processing thousands of time-domain overlapped signals. Traditional receivers allocate digital down converter (DDC) for every channel, pre-existing methods mostly adapt the hardware architecture to enhance the hardware parallel processing capability without ideal resource utilization and implementation complexity. The new method takes advantages of high efficient FFT algorithm to implement multi-channel parallel DDC, and thus achieve ideal performances for DBPSK receiver application.
A novel design of multi-channel parallel differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK) receiver based FFT is proposed in this paper. This receiver is capable of processing thousands of time-domain overlapped signals. Traditional receivers allocate digital down converter (DDC) for every channel, pre-existing methods mostly adapt the hardware architecture to enhance the hardware parallel processing capability without ideal resource utilization and implementation complexity. The new method takes advantages of high efficient FFT algorithm to implement multi-channel parallel DDC, and thus achieve ideal performances for DBPSK receiver application.
A New Blind Signal Extraction Method Based on Cost Reference Particle Filter with Unknown Statistics
2018, 47(5): 646-653.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.002
Abstract:
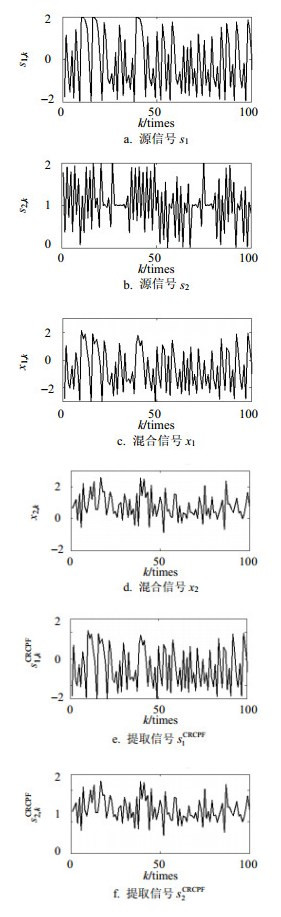
Developing the blind signal processing method in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) often needs to consider several constraints including limited communication bandwidth and energy of sensors. The processing of observed information will import a variety of quantization noise, which is always difficult to be modelled accurately by simple probabilistic models. To study the extraction issue of signal with unknown statistics in WSNs, a signal extracted method based on a cost reference particle filter (CRPF) is proposed in this paper. The method attains the accuracy of prediction particles by cubature-points transformation, and completes particles updating and propagation through cost-risk functions. Simulation results show that the proposed method has comparable performance with the other algorithms for noise of unknown statistics.
Developing the blind signal processing method in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) often needs to consider several constraints including limited communication bandwidth and energy of sensors. The processing of observed information will import a variety of quantization noise, which is always difficult to be modelled accurately by simple probabilistic models. To study the extraction issue of signal with unknown statistics in WSNs, a signal extracted method based on a cost reference particle filter (CRPF) is proposed in this paper. The method attains the accuracy of prediction particles by cubature-points transformation, and completes particles updating and propagation through cost-risk functions. Simulation results show that the proposed method has comparable performance with the other algorithms for noise of unknown statistics.
2018, 47(5): 654-659.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.003
Abstract:
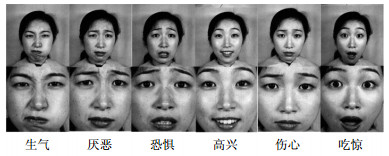
Aiming at the problem that local binary pattern (LBP) cannot describe the change of texture direction, an LBP-gradient direction (LBP-GD) operator which combines gradient direction with LBP is proposed. LBP-GD operator not only keeps the advantages of LBP, but also describes texture direction in detail. Due to the difference of information contained in facial expression organs, an irregular dividing method is designed. The image is divided into 9 non-overlapping sub-blocks with different weighted values, then LBP-GD feature of each sub-block is extracted. Finally, the LBP-GD feature is weightily fused with low-frequency components obtained by lifting wavelet (LW) transform, and the K-nearest neighbor classifier is applied for expression classification. The effectiveness of this approach has been demonstrated on the JAFFE and Cohn-Kanade facial expression databases. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better performance than LW and LBP-GD feature alone.
Aiming at the problem that local binary pattern (LBP) cannot describe the change of texture direction, an LBP-gradient direction (LBP-GD) operator which combines gradient direction with LBP is proposed. LBP-GD operator not only keeps the advantages of LBP, but also describes texture direction in detail. Due to the difference of information contained in facial expression organs, an irregular dividing method is designed. The image is divided into 9 non-overlapping sub-blocks with different weighted values, then LBP-GD feature of each sub-block is extracted. Finally, the LBP-GD feature is weightily fused with low-frequency components obtained by lifting wavelet (LW) transform, and the K-nearest neighbor classifier is applied for expression classification. The effectiveness of this approach has been demonstrated on the JAFFE and Cohn-Kanade facial expression databases. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better performance than LW and LBP-GD feature alone.
2018, 47(5): 660-664.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.004
Abstract:
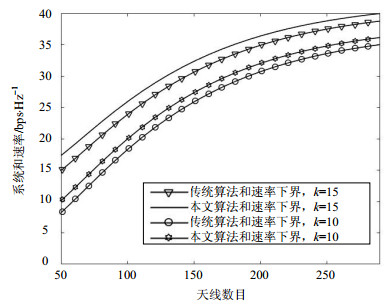
In order to suppress the self-interference and improve spectrum efficiency in full duplex massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) network, an optimal antenna allocation algorithm is proposed. In the full duplex system, the base station exploits zero-forcing linear processing and therefor has imperfect channel estimation. A tight lower bound on the sum-rate for the system with large number of antennas is derived. By resorting to the tight lower bound, a sum-rate maximization problem in terms of antenna ratio is formulated. The analysis and simulation results show that, 1) the ratio of receive antennas and transmit antennas is proportional to the training power of uplink, while it is inverse proportional to the training power of downlink; 2) the optimal antenna ratio converges to 1, when the total number of antenna goes to infinity.
In order to suppress the self-interference and improve spectrum efficiency in full duplex massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) network, an optimal antenna allocation algorithm is proposed. In the full duplex system, the base station exploits zero-forcing linear processing and therefor has imperfect channel estimation. A tight lower bound on the sum-rate for the system with large number of antennas is derived. By resorting to the tight lower bound, a sum-rate maximization problem in terms of antenna ratio is formulated. The analysis and simulation results show that, 1) the ratio of receive antennas and transmit antennas is proportional to the training power of uplink, while it is inverse proportional to the training power of downlink; 2) the optimal antenna ratio converges to 1, when the total number of antenna goes to infinity.
2018, 47(5): 665-671.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.005
Abstract:
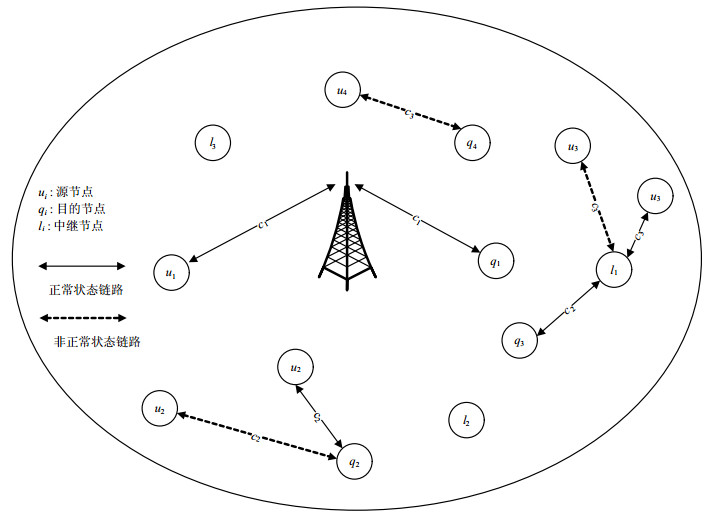
Due to the randomness of device-to-device (D2D) users' mobility, D2D links may suffer from connection loss or co-channel interference. To improve the stability of D2D links, a link state prediction based resource allocation and mode selection algorithm is proposed, which adjusts users' power level, transmission frequency and transmission mode according to the predicted link state. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce the chances of abnormal links and improve the link stability.
Due to the randomness of device-to-device (D2D) users' mobility, D2D links may suffer from connection loss or co-channel interference. To improve the stability of D2D links, a link state prediction based resource allocation and mode selection algorithm is proposed, which adjusts users' power level, transmission frequency and transmission mode according to the predicted link state. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce the chances of abnormal links and improve the link stability.
2018, 47(5): 672-679.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.006
Abstract:
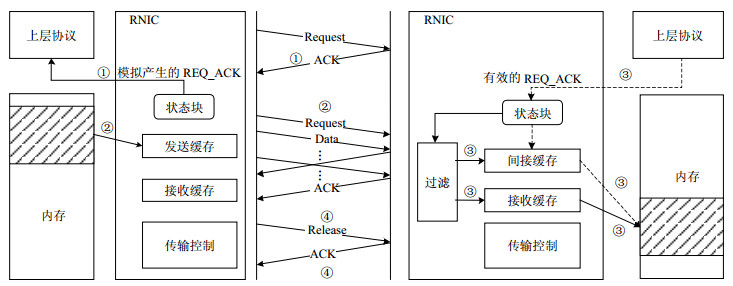
Waiting for connection establishment can be inefficient during remote direct memory access (RDMA) transport for Gigabit Ethernet. Aiming at solving this problem, a hardware accelerated dynamic RDMA method is proposed in this paper. This method allows starting RDMA transport at the same time with connection establishment by sending packages first to indirection buffer in network interface card (NIC) and copying them later to host memory. The terminal models of dynamic RDMA method are built and the simulation platforms for perform experiments are developed. Experimental results show that the dynamic RDMA method not only can solve the long waiting problem of connection establishment with little extra hardware cost, but also can provide higher transport performance compared with traditional RDMA methods.
Waiting for connection establishment can be inefficient during remote direct memory access (RDMA) transport for Gigabit Ethernet. Aiming at solving this problem, a hardware accelerated dynamic RDMA method is proposed in this paper. This method allows starting RDMA transport at the same time with connection establishment by sending packages first to indirection buffer in network interface card (NIC) and copying them later to host memory. The terminal models of dynamic RDMA method are built and the simulation platforms for perform experiments are developed. Experimental results show that the dynamic RDMA method not only can solve the long waiting problem of connection establishment with little extra hardware cost, but also can provide higher transport performance compared with traditional RDMA methods.
2018, 47(5): 680-685.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.007
Abstract:
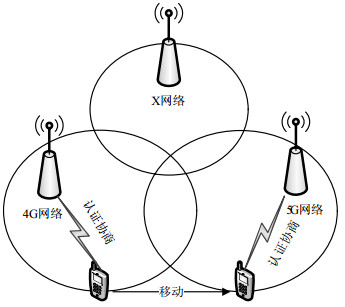
The mobile communication network establishes a trust relationship between the network and the user equipment with authentication and key agreement. 5G network is a convergence network. User equipment can access the network through a variety of ways and it needs to authenticate with the network repeatedly when it is moving between two access networks. In the application environment of Internet of Thing, a group of user equipment with same characteristics and behaviors need to authenticate with the network one by one, which will over-consumes network resource and lowers access efficiency. To solve this problem, an authentication state identification mechanism is designed. If the user equipment successfully accesses the network, the network grants it a status identification. It can access the network with any way, no need access authentication again for a while. It also can transfer such an identification to the other members of the group, thus avoiding the authentication one by one. This mechanism can improve the efficiency of access, avoid the waste of resources and ensure the security network.
The mobile communication network establishes a trust relationship between the network and the user equipment with authentication and key agreement. 5G network is a convergence network. User equipment can access the network through a variety of ways and it needs to authenticate with the network repeatedly when it is moving between two access networks. In the application environment of Internet of Thing, a group of user equipment with same characteristics and behaviors need to authenticate with the network one by one, which will over-consumes network resource and lowers access efficiency. To solve this problem, an authentication state identification mechanism is designed. If the user equipment successfully accesses the network, the network grants it a status identification. It can access the network with any way, no need access authentication again for a while. It also can transfer such an identification to the other members of the group, thus avoiding the authentication one by one. This mechanism can improve the efficiency of access, avoid the waste of resources and ensure the security network.
2018, 47(5): 686-691.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.008
Abstract:
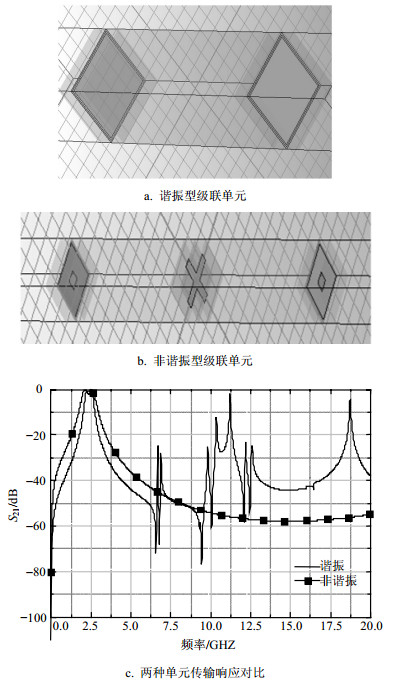
Aiming at the requirement of stealth aircraft antenna, especially the specification for L-band broadband antenna array, it is needed to design a stealth radome with ultra-thin and wideband frequency selectivity surface (FSS) for working in L-band. Due to the low working frequency and wide bandwidth, the traditional design method will make the radome thickness thicker, which is hard to apply in practice. Taking broadband and low profile into consideration, this paper proposes a cascade sub-wavelength structure based on new orthogonal separation metal strip inductance layer, square ring capacitance layer and magnetic materials. At last, a broadband and low profile FSS with 0.035λ thickness of and 28.6% relative bandwidth is designed by means of genetic algorithm.
Aiming at the requirement of stealth aircraft antenna, especially the specification for L-band broadband antenna array, it is needed to design a stealth radome with ultra-thin and wideband frequency selectivity surface (FSS) for working in L-band. Due to the low working frequency and wide bandwidth, the traditional design method will make the radome thickness thicker, which is hard to apply in practice. Taking broadband and low profile into consideration, this paper proposes a cascade sub-wavelength structure based on new orthogonal separation metal strip inductance layer, square ring capacitance layer and magnetic materials. At last, a broadband and low profile FSS with 0.035λ thickness of and 28.6% relative bandwidth is designed by means of genetic algorithm.
2018, 47(5): 692-697.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.009
Abstract:
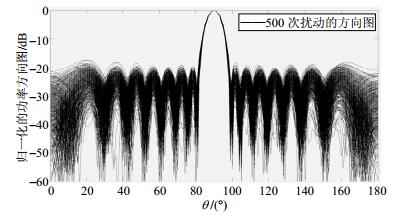
The influence of amplitude, phase and position errors on the performance of an antenna array is analyzed and studied in this paper. On the assumption that each type of these random errors obeys the Gauss distribution, the expectation of the antenna array power pattern is analyzed, and the theoretical formula of variance is derived for the first time. In addition, theoretical upper and lower boundaries on which the power pattern falls on with a given probability are derived by using the Chebyshev's inequality. The effectiveness and accuracy of all the obtained theoretical equations are verified by Monte Carlo simulation. The simulation results show that the influence of the random implementation errors on the power pattern can be accurately predicted by using the proposed technique. Hence, it provides significant guidance for the practical array antenna design.
The influence of amplitude, phase and position errors on the performance of an antenna array is analyzed and studied in this paper. On the assumption that each type of these random errors obeys the Gauss distribution, the expectation of the antenna array power pattern is analyzed, and the theoretical formula of variance is derived for the first time. In addition, theoretical upper and lower boundaries on which the power pattern falls on with a given probability are derived by using the Chebyshev's inequality. The effectiveness and accuracy of all the obtained theoretical equations are verified by Monte Carlo simulation. The simulation results show that the influence of the random implementation errors on the power pattern can be accurately predicted by using the proposed technique. Hence, it provides significant guidance for the practical array antenna design.
2018, 47(5): 698-704.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.010
Abstract:
In order to study the terminal response characteristics of abruptly non-uniform line on a lossy ground exposed in radiation field, the terminal response formula of abruptly non-uniform transmission line above a lossy ground is derived based on transmission line model and microwave network parameters transition matrix. The terminal response of the abruptly non-uniform line can be calculated accurately based on the derived formula. To confirm the validity of the theory, the abruptly non-uniform transmission line with a converter is analyzed and calculated theoretically. The terminal response of transmission line structure with different conductivity is analyzed and calculated theoretically:the influence of different conductivities on the terminal conducted current is less than 3dB. Based on practice, the terminal response of non-uniform transmission line with a converter above a lossy ground, whose conductivity is 0.01S/m, is measured. It is shown that the theoretical results are in agreement with the measured results. This proves that the method of microwave network transition matrix in this paper is especially suitable for the calculation of the response of the response of the abruptly non-uniform lines.
In order to study the terminal response characteristics of abruptly non-uniform line on a lossy ground exposed in radiation field, the terminal response formula of abruptly non-uniform transmission line above a lossy ground is derived based on transmission line model and microwave network parameters transition matrix. The terminal response of the abruptly non-uniform line can be calculated accurately based on the derived formula. To confirm the validity of the theory, the abruptly non-uniform transmission line with a converter is analyzed and calculated theoretically. The terminal response of transmission line structure with different conductivity is analyzed and calculated theoretically:the influence of different conductivities on the terminal conducted current is less than 3dB. Based on practice, the terminal response of non-uniform transmission line with a converter above a lossy ground, whose conductivity is 0.01S/m, is measured. It is shown that the theoretical results are in agreement with the measured results. This proves that the method of microwave network transition matrix in this paper is especially suitable for the calculation of the response of the response of the abruptly non-uniform lines.
2018, 47(5): 705-713.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.011
Abstract:
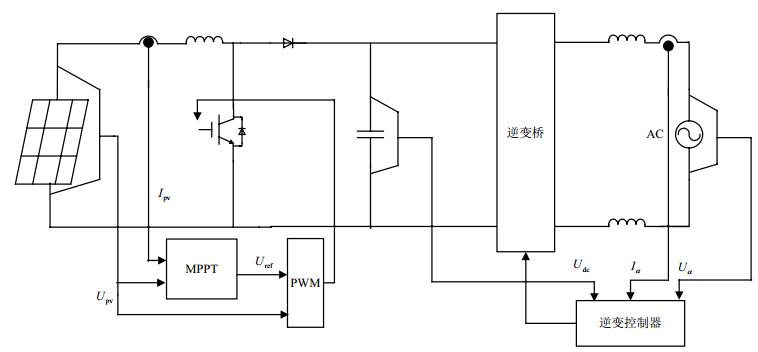
In order to solve the current distortion phenomenon, which is caused by the dead-time effect and DC voltage fluctuation in the single-phase solar grid-connected inverter, this paper presents a selective characteristic harmonic elimination strategy to design a current controller for grid-connect inverter for optimizing current waveform and improving current tracking performance. The double loop proportional integral (PI) control of voltage and current is realized by adopting Park transformation. PWM is reconstructed to compensate harmonics by the harmonic compensation with dynamic gain. Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm is used to improve back propagation (BP) neural network, so as to increase the accuracy of feed-forward compensation and enhance the adaptability of voltage distortion. Finally, MATLAB simulation and experimental results verify the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed method.
In order to solve the current distortion phenomenon, which is caused by the dead-time effect and DC voltage fluctuation in the single-phase solar grid-connected inverter, this paper presents a selective characteristic harmonic elimination strategy to design a current controller for grid-connect inverter for optimizing current waveform and improving current tracking performance. The double loop proportional integral (PI) control of voltage and current is realized by adopting Park transformation. PWM is reconstructed to compensate harmonics by the harmonic compensation with dynamic gain. Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm is used to improve back propagation (BP) neural network, so as to increase the accuracy of feed-forward compensation and enhance the adaptability of voltage distortion. Finally, MATLAB simulation and experimental results verify the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed method.
2018, 47(5): 714-719.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.012
Abstract:
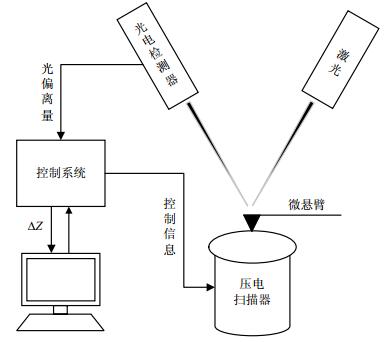
This paper presents a novel controller design based on iterative learning control (ILC) for atomic force microscopy (AFM) nanopositioning. The controller focuses on eliminating the adverse effects brought by nonlinear of piezoelectric actuator and external environmental interference. Specifically, scanning in the horizontal plane of AFM is regarded as a path tracking control problem and the error information of the previous iteration periods is used to modify the control input, to ensure the fast convergence of the output along the iterative axis. The tracking simulation and AFM imaging experimental results are presented and show that the proposed controller can effectively eliminate the adverse effects and significantly improve the imaging accuracy of AFM.
This paper presents a novel controller design based on iterative learning control (ILC) for atomic force microscopy (AFM) nanopositioning. The controller focuses on eliminating the adverse effects brought by nonlinear of piezoelectric actuator and external environmental interference. Specifically, scanning in the horizontal plane of AFM is regarded as a path tracking control problem and the error information of the previous iteration periods is used to modify the control input, to ensure the fast convergence of the output along the iterative axis. The tracking simulation and AFM imaging experimental results are presented and show that the proposed controller can effectively eliminate the adverse effects and significantly improve the imaging accuracy of AFM.
2018, 47(5): 720-725.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.013
Abstract:
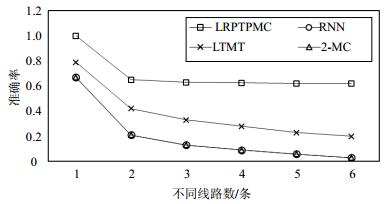
By utilizing the smart card data from Chongqing light rail system, the travel characteristics of light rail passengers are analyzed and a trajectory prediction algorithm based on Markov chain is proposed. In the algorithm, the next travel trajectory of a passenger is classified by Bayesian classification and then predicted according to the relationship between the passenger's last travel trajectory and her/his residence. Experimental results based on real datasets show that the algorithm outperforms LTMT, RNN and 2-MC on predicting passenger's next travel trajectory. Meanwhile, the algorithm is coded on Spark, a big data processing framework, which reduces its runtime.
By utilizing the smart card data from Chongqing light rail system, the travel characteristics of light rail passengers are analyzed and a trajectory prediction algorithm based on Markov chain is proposed. In the algorithm, the next travel trajectory of a passenger is classified by Bayesian classification and then predicted according to the relationship between the passenger's last travel trajectory and her/his residence. Experimental results based on real datasets show that the algorithm outperforms LTMT, RNN and 2-MC on predicting passenger's next travel trajectory. Meanwhile, the algorithm is coded on Spark, a big data processing framework, which reduces its runtime.
2018, 47(5): 726-732.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.014
Abstract:
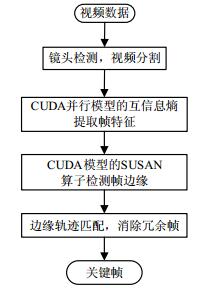
The video key frame extraction involves feature extraction and matching, it easily leads to high computation complexity. The paper proposes mutual information entropy multi-level extraction algorithm with compute unified device architecture (CUDA). Under CPU scheduling and GPU partition thread, three-channel mutual information entropy among the frames is designed to divide the video clips into the static and the dynamic fragment coarsely. By minimum value method for inter-frame mutual information, the dynamic fragments are categorized into multiple subclasses further, from which pre-key frames are selected. Furthermore, in order to filter out the redundancy of the pre-key frames, the SUSAN operator based on block computing is used to complete the edge matching among the inter-frames, and the final key frame sequence can be obtained by the threshold setting. The experiment results show that, compared with the other algorithms, the precision and the recall ratio of the algorithm in the paper are at least 91%, and the amount of the key frames extracted is reduced by 42.82%. It greatly cut down the video data and saves storage space. Besides it, compared with the CPU serial method, the extraction time by CUDA is shorted by about 50% and it improves the efficiency.
The video key frame extraction involves feature extraction and matching, it easily leads to high computation complexity. The paper proposes mutual information entropy multi-level extraction algorithm with compute unified device architecture (CUDA). Under CPU scheduling and GPU partition thread, three-channel mutual information entropy among the frames is designed to divide the video clips into the static and the dynamic fragment coarsely. By minimum value method for inter-frame mutual information, the dynamic fragments are categorized into multiple subclasses further, from which pre-key frames are selected. Furthermore, in order to filter out the redundancy of the pre-key frames, the SUSAN operator based on block computing is used to complete the edge matching among the inter-frames, and the final key frame sequence can be obtained by the threshold setting. The experiment results show that, compared with the other algorithms, the precision and the recall ratio of the algorithm in the paper are at least 91%, and the amount of the key frames extracted is reduced by 42.82%. It greatly cut down the video data and saves storage space. Besides it, compared with the CPU serial method, the extraction time by CUDA is shorted by about 50% and it improves the efficiency.
2018, 47(5): 733-739.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.015
Abstract:
Due to disadvantage of the affinity propagation algorithm of which the number of clusters can not be pre-specified, an improved method including three phases is proposed in this paper. The proposed method uses affinity propagation algorithm to obtain the representation center points of the dataset. Then K-means is applied to the clustering of the center points and produces the initial training set. Moreover, the modified K nearest neighbor algorithm is applied to the procedure of clustering analysis. Artificial data and UCI datasets are used in experiment to compare the new algorithm with other clustering menthes. The results demonstrate that the new clustering algorithm is outperforms the affinity propagation algorithm and traditional clustering algorithms.
Due to disadvantage of the affinity propagation algorithm of which the number of clusters can not be pre-specified, an improved method including three phases is proposed in this paper. The proposed method uses affinity propagation algorithm to obtain the representation center points of the dataset. Then K-means is applied to the clustering of the center points and produces the initial training set. Moreover, the modified K nearest neighbor algorithm is applied to the procedure of clustering analysis. Artificial data and UCI datasets are used in experiment to compare the new algorithm with other clustering menthes. The results demonstrate that the new clustering algorithm is outperforms the affinity propagation algorithm and traditional clustering algorithms.
2018, 47(5): 740-744.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.016
Abstract:
A thermal monitoring system for machine tool by using motion tracking technique is presented in the paper. First, a motion tracking algorithm is developed to track moving targets. Second, an infrared temperature sensor with built-in laser is deployed for non-contact temperature measurement of the moving target. Third, a predictive motion control system carries the thermal sensor and follows the moving target to realize continuous temperature monitoring. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme.
A thermal monitoring system for machine tool by using motion tracking technique is presented in the paper. First, a motion tracking algorithm is developed to track moving targets. Second, an infrared temperature sensor with built-in laser is deployed for non-contact temperature measurement of the moving target. Third, a predictive motion control system carries the thermal sensor and follows the moving target to realize continuous temperature monitoring. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme.
2018, 47(5): 745-752.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.017
Abstract:
Designing a discriminative speed function plays a vital role in conducting contour evolution in level set-based tracking framework. In this work, we propose a superpixel-driven speed function modeling method by fusion of two supplementary cues:appearance and motion. Based on kernel density estimation, a discriminative model separating the object from the background is constructed in appearance space. Meanwhile, by making use of the statistical characteristics of the optical flow field, the relative motion between the object and the background can be distinguished and enhanced by an adaptively chosen threshold. Finally, these two cues are combined in decision level under the Semi-Naive Bayes framework. Experimental results on a number of challenging video sequences demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed tracking methods.
Designing a discriminative speed function plays a vital role in conducting contour evolution in level set-based tracking framework. In this work, we propose a superpixel-driven speed function modeling method by fusion of two supplementary cues:appearance and motion. Based on kernel density estimation, a discriminative model separating the object from the background is constructed in appearance space. Meanwhile, by making use of the statistical characteristics of the optical flow field, the relative motion between the object and the background can be distinguished and enhanced by an adaptively chosen threshold. Finally, these two cues are combined in decision level under the Semi-Naive Bayes framework. Experimental results on a number of challenging video sequences demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed tracking methods.
2018, 47(5): 753-760.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.018
Abstract:
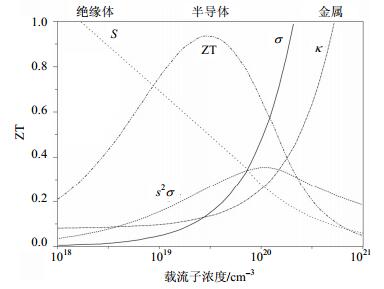
The important mid-temperature thermoelectric materials Mg2Si-based semiconducting compounds have attracted considerable interest due to their abundance, low cost and nontoxic constituents, as well as optimizable electric properties caused by tunable effective mass and mobility of carriers. This paper reviews the latest progress of Mg2Si-based solid solutions. The methods to improve thermoelectric performance are discussed. The comparison of the advantages and drawbacks of various fabrication techniques is proposed. It is shown that, the present researches are focused on the n-type materials, and it is urgent to optimize the p-type materials properties. Doping is an effective method, and combining doping and nanostructuring through the process optimizing can further enhance thermoelectric properties.
The important mid-temperature thermoelectric materials Mg2Si-based semiconducting compounds have attracted considerable interest due to their abundance, low cost and nontoxic constituents, as well as optimizable electric properties caused by tunable effective mass and mobility of carriers. This paper reviews the latest progress of Mg2Si-based solid solutions. The methods to improve thermoelectric performance are discussed. The comparison of the advantages and drawbacks of various fabrication techniques is proposed. It is shown that, the present researches are focused on the n-type materials, and it is urgent to optimize the p-type materials properties. Doping is an effective method, and combining doping and nanostructuring through the process optimizing can further enhance thermoelectric properties.
2018, 47(5): 761-765.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.019
Abstract:
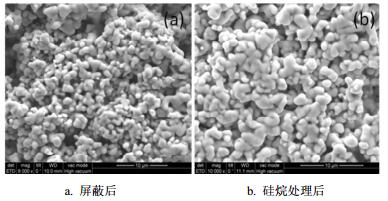
The high temperature characteristics of high voltage organic chip tantalum capacitors are the bottlenecks to limit the wide applications of capacitors. At present, the temperature limit of 105℃ is widely used in the world, but cannot meet the special requirements of 125℃ environment. By the "shielding" and pretreatment of the dielectrics, the post treatment of the organic solid electrolyte, and the improvement of encapsulation layer, the high temperature characteristics of high voltage organic chip tantalum capacitors are significantly improved, and therefore the life tests of 105℃, 2 000 h and 125℃, 2 000 h have passed safely. This study will provide a technical support for the applications of organic chip tantalum capacitors in the special environment.
The high temperature characteristics of high voltage organic chip tantalum capacitors are the bottlenecks to limit the wide applications of capacitors. At present, the temperature limit of 105℃ is widely used in the world, but cannot meet the special requirements of 125℃ environment. By the "shielding" and pretreatment of the dielectrics, the post treatment of the organic solid electrolyte, and the improvement of encapsulation layer, the high temperature characteristics of high voltage organic chip tantalum capacitors are significantly improved, and therefore the life tests of 105℃, 2 000 h and 125℃, 2 000 h have passed safely. This study will provide a technical support for the applications of organic chip tantalum capacitors in the special environment.
2018, 47(5): 766-769.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.020
Abstract:
The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) parameters for K2Zn(SO4)2·6H2O:Cu2+, i.e. g factors (gx, gy, gz) and hyperfine structure constants (Ax, Ay, Az), are theoretically investigated by using the high-order perturbation formulas of these parameters for Cu2+ in orthorhombically elongated octahedra. Based on the calculation, the Cu2+-H2O bond-lengths of the[Cu(H2O)6]2+ cluster in K2Zn(SO4)2·6H2O crystal are found to be Rx ≈ 0.197 nm, Ry ≈ 0.213 nm, Rz ≈ 0.224 nm, and the mixing coefficients of the ground state wave function parameters areα ≈ 0.978 and β ≈ 0.209, respectively. The calculated EPR parameters show a good agreement with the experimental data.
The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) parameters for K2Zn(SO4)2·6H2O:Cu2+, i.e. g factors (gx, gy, gz) and hyperfine structure constants (Ax, Ay, Az), are theoretically investigated by using the high-order perturbation formulas of these parameters for Cu2+ in orthorhombically elongated octahedra. Based on the calculation, the Cu2+-H2O bond-lengths of the[Cu(H2O)6]2+ cluster in K2Zn(SO4)2·6H2O crystal are found to be Rx ≈ 0.197 nm, Ry ≈ 0.213 nm, Rz ≈ 0.224 nm, and the mixing coefficients of the ground state wave function parameters areα ≈ 0.978 and β ≈ 0.209, respectively. The calculated EPR parameters show a good agreement with the experimental data.
2018, 47(5): 770-774.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.021
Abstract:
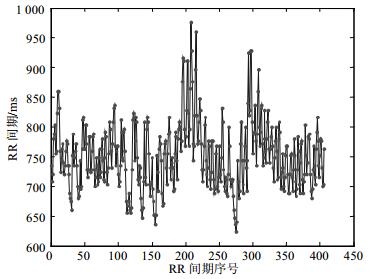
Mental activities can increase the incidence of malignant arrhythmia. Two different mental task projects, i.e. mathematical task and control of heart rate task, are designed to study the changes of cardiac function. The spectral coherence is used to analyze the coupling of electroencephalogram (EEG) and electrocardiograph (ECG). The results demonstrated that pre-central and post-central areas were participated in the information exchange of the heart during the mathematic task, while the information coupling between heart and brain for controlling heart rate task mainly concentrated in the central and pre-central areas.
Mental activities can increase the incidence of malignant arrhythmia. Two different mental task projects, i.e. mathematical task and control of heart rate task, are designed to study the changes of cardiac function. The spectral coherence is used to analyze the coupling of electroencephalogram (EEG) and electrocardiograph (ECG). The results demonstrated that pre-central and post-central areas were participated in the information exchange of the heart during the mathematic task, while the information coupling between heart and brain for controlling heart rate task mainly concentrated in the central and pre-central areas.
2018, 47(5): 775-780.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.022
Abstract:
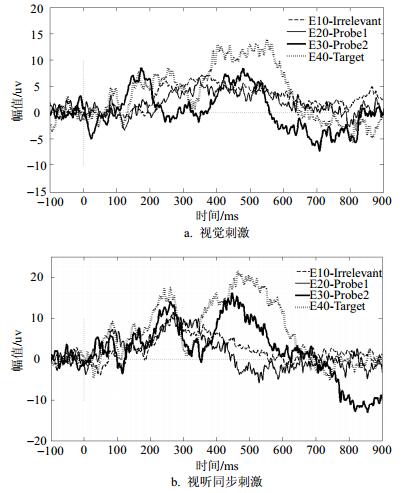
Brain has different cognition responses to the concealed information under visual and auditory stimuli, and this process involves the coordination and information flow between different regions. In this paper, based on the traditional visual stimuli for concealed information, we designed the video-audio synchronization test for comparison. For the defect in current research that mainly focus on the electrodes in central of the brain, we recorded the signals from the whole brain to reflect the neural activity of the brain. Firstly, we constructed the brain functional network using the visual and video-audio stimuli related potentials, then calculated the clustering coefficient and path length as the features of the signals, lastly, we build a quantum gated neural network as the classification for the features. The experimental results show that combining the characteristics of brain network with quantum neural network classifier, the concealed information can be indentified accurately, and the video-audio stimuli is better than visual stimuli.
Brain has different cognition responses to the concealed information under visual and auditory stimuli, and this process involves the coordination and information flow between different regions. In this paper, based on the traditional visual stimuli for concealed information, we designed the video-audio synchronization test for comparison. For the defect in current research that mainly focus on the electrodes in central of the brain, we recorded the signals from the whole brain to reflect the neural activity of the brain. Firstly, we constructed the brain functional network using the visual and video-audio stimuli related potentials, then calculated the clustering coefficient and path length as the features of the signals, lastly, we build a quantum gated neural network as the classification for the features. The experimental results show that combining the characteristics of brain network with quantum neural network classifier, the concealed information can be indentified accurately, and the video-audio stimuli is better than visual stimuli.
2018, 47(5): 781-787.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.023
Abstract:
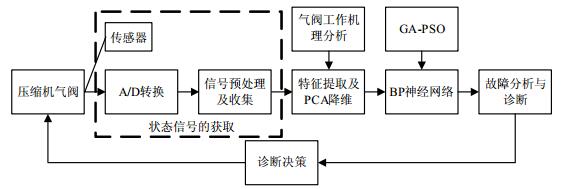
Aiming at the characteristics of faults signals of the gas valve:strong non-stationary and aperiodic, a fault diagnosis method of reciprocating compressor valve is proposed based on principal component analysis (PCA) and back-propagation (BP) neural network of a genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization (GA-PSO). First of all, the features of valve faults are extracted by wavelet packet decomposition; then fault feature vectors are dimensionally reduced by using PCA for reducing the scale and computing time of the network. Since the traditional BP algorithm has slow convergence speed and is easy to fall into local minimum, a GA-PSO is employed to optimize the parameters of BP neural network. Finally, using the vibration signal of valve cover of reciprocating compressor as research object, the simulation tests show that PCA and BP neural network of the GA-PSO is feasible and effective for the reciprocating compressor valve fault diagnosis.
Aiming at the characteristics of faults signals of the gas valve:strong non-stationary and aperiodic, a fault diagnosis method of reciprocating compressor valve is proposed based on principal component analysis (PCA) and back-propagation (BP) neural network of a genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization (GA-PSO). First of all, the features of valve faults are extracted by wavelet packet decomposition; then fault feature vectors are dimensionally reduced by using PCA for reducing the scale and computing time of the network. Since the traditional BP algorithm has slow convergence speed and is easy to fall into local minimum, a GA-PSO is employed to optimize the parameters of BP neural network. Finally, using the vibration signal of valve cover of reciprocating compressor as research object, the simulation tests show that PCA and BP neural network of the GA-PSO is feasible and effective for the reciprocating compressor valve fault diagnosis.
2018, 47(5): 788-792.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.024
Abstract:
Components or systems fails are usually caused by multiple failure models in practical engineering. Copula functions are used to model complicated nonlinear corrections between variables and failure modes. To avoid error from subjective hypothesis at utmost, maximum entropy approach is employed for approximating probability density functions of extreme value responses, and the lower and upper bounds of probability of failure can be determined according to the approximated probability density functions. Finally, both simulation and maximum likelihood estimation approaches are used for determining the lower and upper bounds of parameters in selected Copula functions. An optimization model is presented to calculate the lower and upper bounds of system probability of failure. Numerical example has demonstrated that the proposed method is available for structural systems with multiple failure modes under mixed uncertainties.
Components or systems fails are usually caused by multiple failure models in practical engineering. Copula functions are used to model complicated nonlinear corrections between variables and failure modes. To avoid error from subjective hypothesis at utmost, maximum entropy approach is employed for approximating probability density functions of extreme value responses, and the lower and upper bounds of probability of failure can be determined according to the approximated probability density functions. Finally, both simulation and maximum likelihood estimation approaches are used for determining the lower and upper bounds of parameters in selected Copula functions. An optimization model is presented to calculate the lower and upper bounds of system probability of failure. Numerical example has demonstrated that the proposed method is available for structural systems with multiple failure modes under mixed uncertainties.
2018, 47(5): 793-800.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.05.025
Abstract:
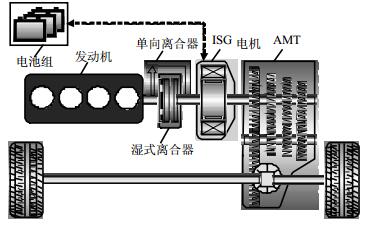
The longitudinal drivability is degraded seriously when the full hybrid electric drivetrain with single motor switches from the pure electric drive mode to the hybrid drive mode. To address this problem, a phased coordination control strategy of power source and clutch is proposed in this paper. Firstly, a control-oriented dynamic model is established. And then, according to the operating status of engine and clutch, the whole mode transition process is divided into four stages. Based on the feed forward and feedback control method, the pashed coordination control strategy is designed to adjust the speed or torque of power source and clutch in each phase. Finally, the effectiveness of the control strategy is verified by simulation comparison and bench test. The proposed coordinated control strategy can effectively improve the longitudinal drivability of the full hybrid electric drivetrain with single motor during mode transition, and also can reduce the wear of the clutch.
The longitudinal drivability is degraded seriously when the full hybrid electric drivetrain with single motor switches from the pure electric drive mode to the hybrid drive mode. To address this problem, a phased coordination control strategy of power source and clutch is proposed in this paper. Firstly, a control-oriented dynamic model is established. And then, according to the operating status of engine and clutch, the whole mode transition process is divided into four stages. Based on the feed forward and feedback control method, the pashed coordination control strategy is designed to adjust the speed or torque of power source and clutch in each phase. Finally, the effectiveness of the control strategy is verified by simulation comparison and bench test. The proposed coordinated control strategy can effectively improve the longitudinal drivability of the full hybrid electric drivetrain with single motor during mode transition, and also can reduce the wear of the clutch.

 ISSN
ISSN