2018 Vol. 47, No. 6
2018, 47(6): 801-805.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.001
Abstract:
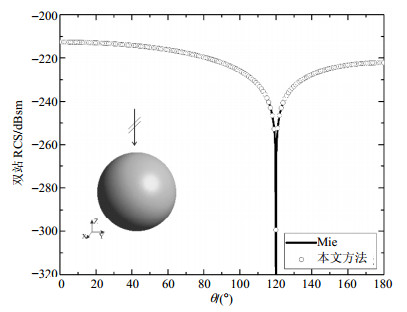
The multilevel complex source point (MLCSP) method is used to solve augmented electric field integral equation (AEFIE) for perfect electric conduct target. As an effective solution of the low-frequency problem, AEFIE separates current and charge to avoid the imbalance between the vector potential and the scalar potential in the conventional electric field integral equation (EFIE). In order to reduce the computational complexity of method of moment (MoM) for AEFIE, the vector potential and scalar potential are expanded by complex source point (CSP). Then, an aggregation operator is introduced to form a multilevel algorithm for acceleration the matrix-vector products. The numerical results showed that, the accuracy of the method is very high when solving low frequency electromagnetic scattering problems and circuit problems, while computational complexity can be reduced to O(N)level.
The multilevel complex source point (MLCSP) method is used to solve augmented electric field integral equation (AEFIE) for perfect electric conduct target. As an effective solution of the low-frequency problem, AEFIE separates current and charge to avoid the imbalance between the vector potential and the scalar potential in the conventional electric field integral equation (EFIE). In order to reduce the computational complexity of method of moment (MoM) for AEFIE, the vector potential and scalar potential are expanded by complex source point (CSP). Then, an aggregation operator is introduced to form a multilevel algorithm for acceleration the matrix-vector products. The numerical results showed that, the accuracy of the method is very high when solving low frequency electromagnetic scattering problems and circuit problems, while computational complexity can be reduced to O(N)level.
2018, 47(6): 806-813.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.002
Abstract:
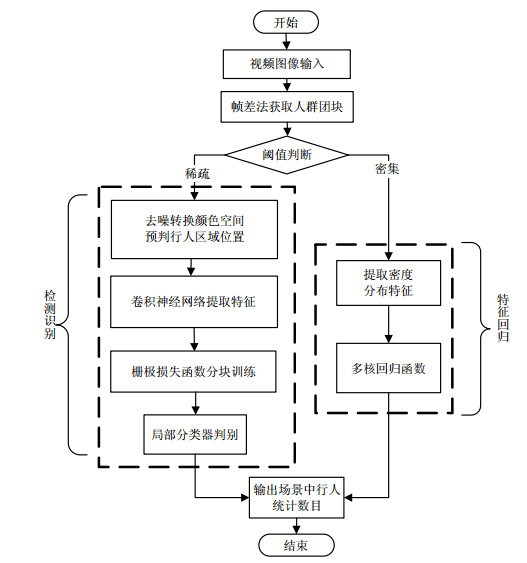
Crowd counting is difficult to get accurate statistics due to shading, shadows and changes in crowd density. This paper presents an approach to combine the convolutional neural networks and density features map legitimately. We segment the crowd scene into many blobs according to the density. For low-density blobs, Retinex algorithm is used to denoise the scene and then the scene is transformed into HSV color space to locate the pedestrian. Convolutional neural networks are used to extract the pedestrian features with grid loss function to avoid the occlusion issue. For high density blobs, crowd density distribution features are extracted to train the multiple kernel regression models to estimate the numbers. Experiments are conducted on datasets PETS2009, UCSD. The experimental results show that the proposed method improves the accuracy to some extent in comparison with other algorithms.
Crowd counting is difficult to get accurate statistics due to shading, shadows and changes in crowd density. This paper presents an approach to combine the convolutional neural networks and density features map legitimately. We segment the crowd scene into many blobs according to the density. For low-density blobs, Retinex algorithm is used to denoise the scene and then the scene is transformed into HSV color space to locate the pedestrian. Convolutional neural networks are used to extract the pedestrian features with grid loss function to avoid the occlusion issue. For high density blobs, crowd density distribution features are extracted to train the multiple kernel regression models to estimate the numbers. Experiments are conducted on datasets PETS2009, UCSD. The experimental results show that the proposed method improves the accuracy to some extent in comparison with other algorithms.
2018, 47(6): 814-818.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.003
Abstract:
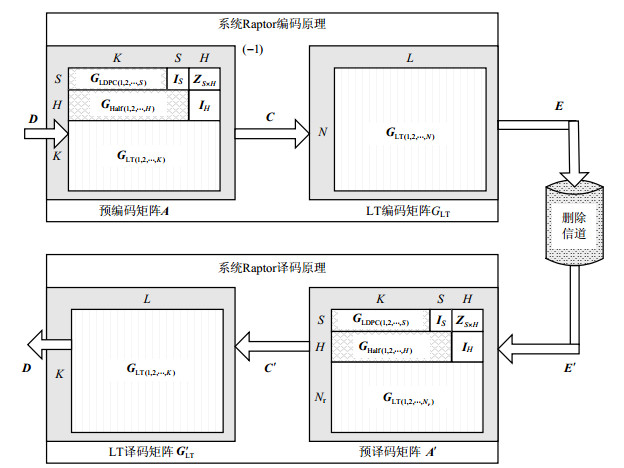
The high complexity Gaussian elimination (GE) algorithm of the systematic raptor decoding results in its high latency and low throughputs. A high efficiency parallel dimensionality-reduction decoding scheme is presented in this paper. The proposed scheme uses low complexity dimensionality-reduction algorithm to decode lost packets to replace the GE algorithm which decodes all source packets. Meanwhile, a full parallel structure for the decoding is proposed to implement the dimensionality-reduction-algorithm. At last, the decoder is implemented on Xilinx FPGA XC7K410T. The test results show that the scheme can achieve a 3.5 Gbps throughput within a 10-2 packet loss probability, which is 80 times better than that of the GE algorithm.
The high complexity Gaussian elimination (GE) algorithm of the systematic raptor decoding results in its high latency and low throughputs. A high efficiency parallel dimensionality-reduction decoding scheme is presented in this paper. The proposed scheme uses low complexity dimensionality-reduction algorithm to decode lost packets to replace the GE algorithm which decodes all source packets. Meanwhile, a full parallel structure for the decoding is proposed to implement the dimensionality-reduction-algorithm. At last, the decoder is implemented on Xilinx FPGA XC7K410T. The test results show that the scheme can achieve a 3.5 Gbps throughput within a 10-2 packet loss probability, which is 80 times better than that of the GE algorithm.
2018, 47(6): 819-828.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.004
Abstract:
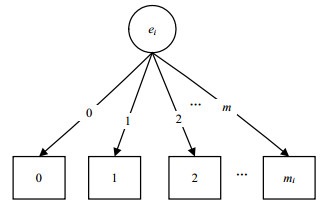
Traditional methods apply system minimum capacity vectors to calculate the reliability of stochastic-flow network with two separate minimal paths (2SMPs), which needs to store the arc of entire network and the process of removing redundant vectors is complex. In view of this, based on multi-valued decision diagram (MDD) for 2SMPs, we propose a reliability analysis algorithm, called MDD_2SMPs. The main idea of this algorithm is using MDD to reflect the relationship between components status and system status, by defining MDD operators, the path capacity can be obtained without the need for flow distribution. Besides, the constraint pruning strategy is introduced in the process of combination to filter many unnecessary combinations. Furthermore, aiming at the problem of path failure, all paths are converted into MDD variables by using the proposed algorithm MDD_BMPs, resulting a great reduction of the computational complexity. Example analysis shows that the proposed algorithm based on MDD has less calculation burden than traditional methods and can select the network backup paths accurately.
Traditional methods apply system minimum capacity vectors to calculate the reliability of stochastic-flow network with two separate minimal paths (2SMPs), which needs to store the arc of entire network and the process of removing redundant vectors is complex. In view of this, based on multi-valued decision diagram (MDD) for 2SMPs, we propose a reliability analysis algorithm, called MDD_2SMPs. The main idea of this algorithm is using MDD to reflect the relationship between components status and system status, by defining MDD operators, the path capacity can be obtained without the need for flow distribution. Besides, the constraint pruning strategy is introduced in the process of combination to filter many unnecessary combinations. Furthermore, aiming at the problem of path failure, all paths are converted into MDD variables by using the proposed algorithm MDD_BMPs, resulting a great reduction of the computational complexity. Example analysis shows that the proposed algorithm based on MDD has less calculation burden than traditional methods and can select the network backup paths accurately.
2018, 47(6): 829-833.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.005
Abstract:
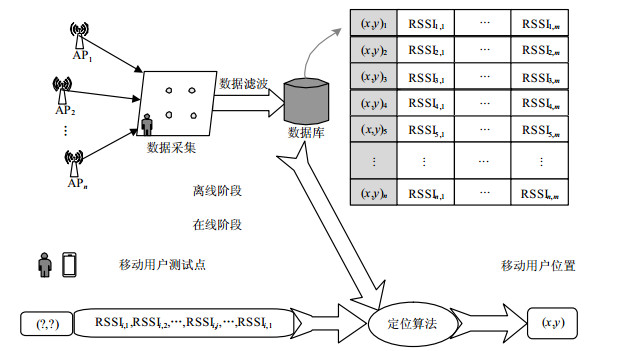
Aiming at the problem of the information jump in WIFI indoor location based on the received signal strength indication (RSSI), which influences the positioning accuracy, an improved adaptive weighted K nearest neighbor (AWKNN) localization method based on Kalman filter is proposed. In this paper, the feasibility of smoothing the RSSI algorithm is compared and analyzed, and the advantages of smoothing the RSSI based on the Kalman filter are verified. Combining with the AWKNN algorithm and taking advantage of the mean square deviation to calculate the matching degree, the size of denominator m in the mean square error can be adjusted automatically through monitoring the number of matching wireless access points in real time to achieve the effective control of positioning error. The experimental results show that the AWKNN algorithm based on Kalman filter is more effective than the traditional WIFI fingerprint algorithm in terms of stability and positioning accuracy.
Aiming at the problem of the information jump in WIFI indoor location based on the received signal strength indication (RSSI), which influences the positioning accuracy, an improved adaptive weighted K nearest neighbor (AWKNN) localization method based on Kalman filter is proposed. In this paper, the feasibility of smoothing the RSSI algorithm is compared and analyzed, and the advantages of smoothing the RSSI based on the Kalman filter are verified. Combining with the AWKNN algorithm and taking advantage of the mean square deviation to calculate the matching degree, the size of denominator m in the mean square error can be adjusted automatically through monitoring the number of matching wireless access points in real time to achieve the effective control of positioning error. The experimental results show that the AWKNN algorithm based on Kalman filter is more effective than the traditional WIFI fingerprint algorithm in terms of stability and positioning accuracy.
2018, 47(6): 834-839.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.006
Abstract:
A novel dual-mode widebeam planar antenna is proposed to fulfill the requirements of wide-angle scanning phased array application. It consists of two parallel magnetic dipoles and one electric dipole. The magnetic dipole is a microstrip patch with three shorted edges and the electric dipole is a metal strip with fan-shaped loading. With the utilization of two magnetic dipoles, the bandwidth is enhanced compared to one magnetic dipole. The measured 10-dB impedance bandwidth is 5.3% (5.55-5.85GHz) and the 3 dB beamwidth in E-plane is more than 140° within the whole working band. An array composed of eight elements with 0.23 λ0 spacing (λ0 is the free space wavelength of central frequency) is also investigated. The main beam direction of the array can scan from -60° to 60° in E-plane with a gain fluctuation of less than 3 dB and the scanning 3 dB beam can cover a range from -76° to 78°. Good agreement between simulation and measurement is achieved.
A novel dual-mode widebeam planar antenna is proposed to fulfill the requirements of wide-angle scanning phased array application. It consists of two parallel magnetic dipoles and one electric dipole. The magnetic dipole is a microstrip patch with three shorted edges and the electric dipole is a metal strip with fan-shaped loading. With the utilization of two magnetic dipoles, the bandwidth is enhanced compared to one magnetic dipole. The measured 10-dB impedance bandwidth is 5.3% (5.55-5.85GHz) and the 3 dB beamwidth in E-plane is more than 140° within the whole working band. An array composed of eight elements with 0.23 λ0 spacing (λ0 is the free space wavelength of central frequency) is also investigated. The main beam direction of the array can scan from -60° to 60° in E-plane with a gain fluctuation of less than 3 dB and the scanning 3 dB beam can cover a range from -76° to 78°. Good agreement between simulation and measurement is achieved.
2018, 47(6): 840-846.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.007
Abstract:
Theoretical investigation on a highly efficient quasi-optical mode converter for a 0.42THz-TE17, 4 gyrotron is presented in this paper. The converter consists of a dimpled-wall Denisov-type launcher and three mirrors. Based on the coupled-mode theory, the vector diffraction theory, and phase unwrapping technique, a computer code has been developed to evaluate the field distributions, which agrees well with the simulated result. It shows that a well-focused wave beam is achieved with a high Gaussian mode purity (scalar content greater than 99.1%, vector content greater than 97.3%) and high power conversion efficiency of greater than 97.4% at the output window.
Theoretical investigation on a highly efficient quasi-optical mode converter for a 0.42THz-TE17, 4 gyrotron is presented in this paper. The converter consists of a dimpled-wall Denisov-type launcher and three mirrors. Based on the coupled-mode theory, the vector diffraction theory, and phase unwrapping technique, a computer code has been developed to evaluate the field distributions, which agrees well with the simulated result. It shows that a well-focused wave beam is achieved with a high Gaussian mode purity (scalar content greater than 99.1%, vector content greater than 97.3%) and high power conversion efficiency of greater than 97.4% at the output window.
2018, 47(6): 847-852.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.008
Abstract:
Based on the theories of generalized transmission line and electron cyclotron resonance maser, the TE32, 12 mode is selected as the operating mode of a 170 GHz megawatt gyrotron by investigating the mode spectrum and studying the beam-wave coupling coefficient and the start-current of the modes carefully. Through appropriately arranging the parameters of the beam, the transient modes in the high order mode resonator are suppressed effectively. And through designing the gradual sections of a kind of taped cavity, the parasitic modes are suppressed furthest. As a result, an output power of 1.8 MW, corresponding to 50% efficiency, and an oscillation frequency of 170.18 GHz have been achieved with a pitch factor 1.3, radius of guiding center 9.4mm, 80 kV, 45A helical electron beam at a guiding magnetic field of 6.715T. At the same time, we have also set up a velocity-spread model suitable to actual circumstances and discussed the performance impact to the gyrotron.
Based on the theories of generalized transmission line and electron cyclotron resonance maser, the TE32, 12 mode is selected as the operating mode of a 170 GHz megawatt gyrotron by investigating the mode spectrum and studying the beam-wave coupling coefficient and the start-current of the modes carefully. Through appropriately arranging the parameters of the beam, the transient modes in the high order mode resonator are suppressed effectively. And through designing the gradual sections of a kind of taped cavity, the parasitic modes are suppressed furthest. As a result, an output power of 1.8 MW, corresponding to 50% efficiency, and an oscillation frequency of 170.18 GHz have been achieved with a pitch factor 1.3, radius of guiding center 9.4mm, 80 kV, 45A helical electron beam at a guiding magnetic field of 6.715T. At the same time, we have also set up a velocity-spread model suitable to actual circumstances and discussed the performance impact to the gyrotron.
2018, 47(6): 853-863.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.009
Abstract:
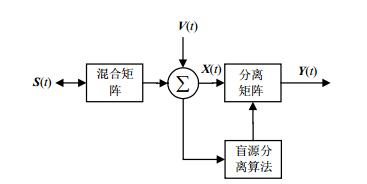
Traditional composite faults diagnosis approaches applied in isolating rolling bearing mixed faults are not effectively.To overcome this defect, this paper proposes a hybrid collaborative diagnosis method for rolling bearing composite faults.Firstly, by using second order blind identification method, we calculate the whiten matrix of fault signals.Then, by minimizing the degree of diagonalization function, we can realize joint diagonalization on whiten fault matrix.Finally, we use singular value decomposition for the orthogonal matrix, further we can estimate the signal matrix of fault sources from the compound fault signals.But through the above procedure, we can only get the out-of-order signals.If there are some similar signals, it is hard to recognize them by our intuitions.So we next apply the short-term Fourier transform to solve this problem, by comparing the time-frequency spectrograms trends between isolated and original signals, we can clearly identify the fault types.At last, to validate its effectiveness, we put the fault data from the Key Laboratory of Fault Diagnosis of Petrochemical Equipment in Guangdong Province into this proposed method, the results show its practical value in mechanical engineering.
Traditional composite faults diagnosis approaches applied in isolating rolling bearing mixed faults are not effectively.To overcome this defect, this paper proposes a hybrid collaborative diagnosis method for rolling bearing composite faults.Firstly, by using second order blind identification method, we calculate the whiten matrix of fault signals.Then, by minimizing the degree of diagonalization function, we can realize joint diagonalization on whiten fault matrix.Finally, we use singular value decomposition for the orthogonal matrix, further we can estimate the signal matrix of fault sources from the compound fault signals.But through the above procedure, we can only get the out-of-order signals.If there are some similar signals, it is hard to recognize them by our intuitions.So we next apply the short-term Fourier transform to solve this problem, by comparing the time-frequency spectrograms trends between isolated and original signals, we can clearly identify the fault types.At last, to validate its effectiveness, we put the fault data from the Key Laboratory of Fault Diagnosis of Petrochemical Equipment in Guangdong Province into this proposed method, the results show its practical value in mechanical engineering.
2018, 47(6): 864-868.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.010
Abstract:
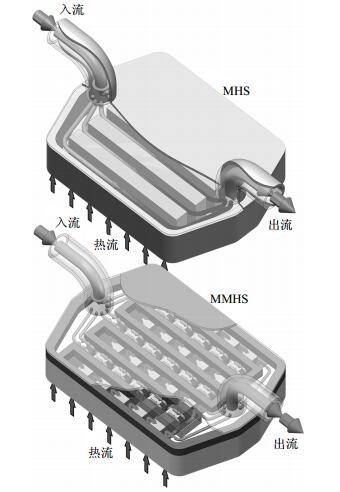
Manifold micro-channel heat sink (MMHS) has a better heat transfer capacity and uniformity compared with the conventional micro-channel heat sink (MHS), showing a great potential in cooling equipments with high heat generation rate like electronic chips.A numerical simulation work was carried out on heat transfer process in a single unit of MHS and MMHS.For the mass flow rate covering 0.57~2.87 kg/h, averaged heat transfer coefficient of the MMHS is enhanced over 100% and the heat dissipation uniformity is increased 52% compared with the MHS.The multiple inlets and outlets in the MMHS contribute a lot to the improvement of heat transfer performance.
Manifold micro-channel heat sink (MMHS) has a better heat transfer capacity and uniformity compared with the conventional micro-channel heat sink (MHS), showing a great potential in cooling equipments with high heat generation rate like electronic chips.A numerical simulation work was carried out on heat transfer process in a single unit of MHS and MMHS.For the mass flow rate covering 0.57~2.87 kg/h, averaged heat transfer coefficient of the MMHS is enhanced over 100% and the heat dissipation uniformity is increased 52% compared with the MHS.The multiple inlets and outlets in the MMHS contribute a lot to the improvement of heat transfer performance.
2018, 47(6): 869-875.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.011
Abstract:
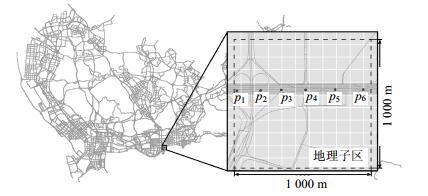
To take the capacity variations of road segments into consideration, and to avoid the fake traffic anomaly detections caused by the normal fluctuation of road segment capacity, a new traffic anomaly detection method based on travel time of path is proposed. Shenzhen road network as sub spatial regions is divided into grids, and then ST-matching algorithm is applied to match Shenzhen taxi GPS coordinate to corresponding road segments, after that the DBSCAN algorithm is adopted to compute the time-varying threshold of path travel time, the travel time above threshold is recognized as anomaly. While maintaining high accuracy and sensitivity of detecting traffic network anomaly, this method is cost efficient and easy to implement.
To take the capacity variations of road segments into consideration, and to avoid the fake traffic anomaly detections caused by the normal fluctuation of road segment capacity, a new traffic anomaly detection method based on travel time of path is proposed. Shenzhen road network as sub spatial regions is divided into grids, and then ST-matching algorithm is applied to match Shenzhen taxi GPS coordinate to corresponding road segments, after that the DBSCAN algorithm is adopted to compute the time-varying threshold of path travel time, the travel time above threshold is recognized as anomaly. While maintaining high accuracy and sensitivity of detecting traffic network anomaly, this method is cost efficient and easy to implement.
2018, 47(6): 876-881.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.012
Abstract:
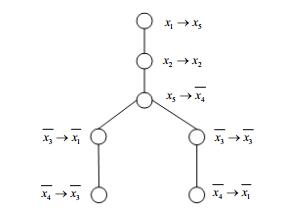
The paper proposes a pairwise NPN (Input Negation and/or Input Permutation and/or Output Negation) Boolean matching algorithm based on symmetry and signature.The algorithm utilizes variable symmetry, the first order signature vector and Shannon decomposition to design and implement NPN Boolean matching.The candidate NP transformations between two functions are searched and verified through two necessary conditions:1) two NP equivalent Boolean functions must have the same the first order signature vector and 2) two variables having a mapping relation must have the same the first order signature.The use of symmetry and signature reduces the search space of the candidate NP transformations and speeds up NPN Boolean matching process.
The paper proposes a pairwise NPN (Input Negation and/or Input Permutation and/or Output Negation) Boolean matching algorithm based on symmetry and signature.The algorithm utilizes variable symmetry, the first order signature vector and Shannon decomposition to design and implement NPN Boolean matching.The candidate NP transformations between two functions are searched and verified through two necessary conditions:1) two NP equivalent Boolean functions must have the same the first order signature vector and 2) two variables having a mapping relation must have the same the first order signature.The use of symmetry and signature reduces the search space of the candidate NP transformations and speeds up NPN Boolean matching process.
2018, 47(6): 882-887.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.013
Abstract:
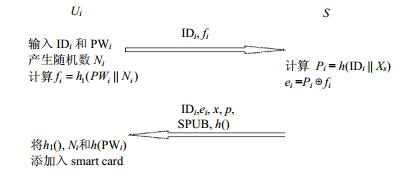
In this paper, we propose a novel three-party authentication and key exchange protocol without using a timestamp based on chaotic maps. The proposed protocol requires neither symmetric nor asymmetric cryptosystems. Therefore, the computation complexity of the protocol is reduced and the efficiency of the protocol is improved. In addition, a convenient mechanism for updating user keys is provided, which improves the security of the protocol. Furthermore, the security analysis and performance evaluation are presented in the paper. In comparison with the related protocols, the proposed scheme is secure under certain types of attacks. It also has fewer transmissions and lower computational cost. Accordingly, it is feasible for real world applications.
In this paper, we propose a novel three-party authentication and key exchange protocol without using a timestamp based on chaotic maps. The proposed protocol requires neither symmetric nor asymmetric cryptosystems. Therefore, the computation complexity of the protocol is reduced and the efficiency of the protocol is improved. In addition, a convenient mechanism for updating user keys is provided, which improves the security of the protocol. Furthermore, the security analysis and performance evaluation are presented in the paper. In comparison with the related protocols, the proposed scheme is secure under certain types of attacks. It also has fewer transmissions and lower computational cost. Accordingly, it is feasible for real world applications.
2018, 47(6): 888-894.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.014
Abstract:
As an important sort of cyberspace security threats, computer viruses have been a hotspot in cyberspace security research. Inspired by the gene theory and the artificial life theory, we present a gene-based model of computer viruses evolution. The form definition of the computer virus is given and the mathematical models of computer viruses evolution in the three levels of gene, DNA, and chromosome are constructed. And then the computer viruses evolution process in natural selection is simulated. Experimental results show that, even in face of harsh external environment, computer viruses which have characteristics of both algorithm and life still have strong ability of adaptation and evolution.
As an important sort of cyberspace security threats, computer viruses have been a hotspot in cyberspace security research. Inspired by the gene theory and the artificial life theory, we present a gene-based model of computer viruses evolution. The form definition of the computer virus is given and the mathematical models of computer viruses evolution in the three levels of gene, DNA, and chromosome are constructed. And then the computer viruses evolution process in natural selection is simulated. Experimental results show that, even in face of harsh external environment, computer viruses which have characteristics of both algorithm and life still have strong ability of adaptation and evolution.
2018, 47(6): 895-900.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.015
Abstract:
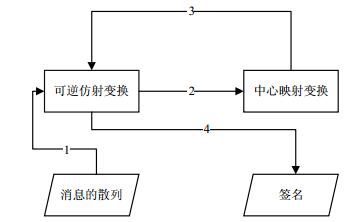
Rainbow is a digital signature scheme. It is based on multivariate polynomials, which belongs to multivariate public key cryptography. Compared with the existing signature schemes, e.g. rivest-shamir-adleman (RSA) and ellipse curve cryptography (ECC), Rainbow can resist quantum computer attacks, which is a candidate of the signature schemes of the next generation. According to the importance of Rainbow, in this paper, we present techniques to exploit differential power analysis (DPA) and fault analysis attacks for analyzing the effectiveness of side channel attacks on Rainbow signature. We implement a naive Rainbow scheme on hardware and propose a successful side channel attack on the implementation. Experimental results show that our attack successfully obtains all the pieces from the private keys of the Rainbow scheme and they clearly demonstrate that we need to protect Rainbow against side channel attacks.
Rainbow is a digital signature scheme. It is based on multivariate polynomials, which belongs to multivariate public key cryptography. Compared with the existing signature schemes, e.g. rivest-shamir-adleman (RSA) and ellipse curve cryptography (ECC), Rainbow can resist quantum computer attacks, which is a candidate of the signature schemes of the next generation. According to the importance of Rainbow, in this paper, we present techniques to exploit differential power analysis (DPA) and fault analysis attacks for analyzing the effectiveness of side channel attacks on Rainbow signature. We implement a naive Rainbow scheme on hardware and propose a successful side channel attack on the implementation. Experimental results show that our attack successfully obtains all the pieces from the private keys of the Rainbow scheme and they clearly demonstrate that we need to protect Rainbow against side channel attacks.
2018, 47(6): 901-905.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.016
Abstract:
UEFI-based BOOTKIT compromise the integrity of both UEFI firmware and OS, posing a fatal threat on the security of computer. In response, a new bootkit defense system based on UEFI, named UDS, is proposed in this paper. The proposed UDS is implemented as a UEFI device driver, which is booted before the OS. By adopting a strategy that combines integrity checking and file restoring, UDS protects firmware and OS kernels. And the methods of code obfuscation and file hiding are introduced to prevent UDS itself from being attacked by BOOTKIT. Finally, several experiments had been conducted to prove that UDS can protect itself from the attack of BOOTKIT, while effectively protecting integrity of both OS and firmware.
UEFI-based BOOTKIT compromise the integrity of both UEFI firmware and OS, posing a fatal threat on the security of computer. In response, a new bootkit defense system based on UEFI, named UDS, is proposed in this paper. The proposed UDS is implemented as a UEFI device driver, which is booted before the OS. By adopting a strategy that combines integrity checking and file restoring, UDS protects firmware and OS kernels. And the methods of code obfuscation and file hiding are introduced to prevent UDS itself from being attacked by BOOTKIT. Finally, several experiments had been conducted to prove that UDS can protect itself from the attack of BOOTKIT, while effectively protecting integrity of both OS and firmware.
2018, 47(6): 906-912.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.017
Abstract:
For the transmission security of digital image, a novel bit-level image encryption algorithm is proposed by using a four dimensional (4D) hyper-chaotic system. Firstly, a pseudo-random binary sequence with good performance is obtained by classifying the chaotic sequences generated from the hyper-chaotic system. Then, the plain-image is decomposed into 8 bit-planes, the higher 3 and lower 5 bit-planes are shuffled separately by using circular shift of their rows and columns, and the resulting bit-planes are further embedded into four carrier matrices generated from the pseudo-random sequences. The preliminary cipher-image is obtained by performing exclusive-OR operation on the four carrier matrices. Finally, a linear pixel diffusion in two directions is performed on the preliminary cipher-image by using the diffusion matrix also generated from the binary sequence, after which the final encrypted image is obtained. Experiments and result analysis demonstrate that the algorithm has a high security with large key space and can resist common attacks including brute-force, statistical and differential analysis, etc. Furthermore, it also has a good efficiency.
For the transmission security of digital image, a novel bit-level image encryption algorithm is proposed by using a four dimensional (4D) hyper-chaotic system. Firstly, a pseudo-random binary sequence with good performance is obtained by classifying the chaotic sequences generated from the hyper-chaotic system. Then, the plain-image is decomposed into 8 bit-planes, the higher 3 and lower 5 bit-planes are shuffled separately by using circular shift of their rows and columns, and the resulting bit-planes are further embedded into four carrier matrices generated from the pseudo-random sequences. The preliminary cipher-image is obtained by performing exclusive-OR operation on the four carrier matrices. Finally, a linear pixel diffusion in two directions is performed on the preliminary cipher-image by using the diffusion matrix also generated from the binary sequence, after which the final encrypted image is obtained. Experiments and result analysis demonstrate that the algorithm has a high security with large key space and can resist common attacks including brute-force, statistical and differential analysis, etc. Furthermore, it also has a good efficiency.
2018, 47(6): 913-920.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.018
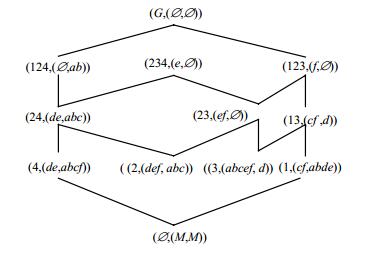
Abstract:
As one of the research focuses in the field of formal concept analysis, three-way concept lattice can make more effective decision analysis. Firstly, the rule extraction based on object-induced three-way concept are investigated and compared compared with those of the classical concept lattice and attribute-induced three-way concept lattice. Then, by merging the object-induced three-way concept lattice and the attribute-induced three-way concept lattice, a new three-way concept lattice, i.e. object-attribute-induced three-way concept lattice, and its rule extraction[0] algorithm are proposed. Theoretical analyses and results show that the merging of object-induced three-way concept lattice and attribute-induced three-way concept lattice can improve the quality of rules.
As one of the research focuses in the field of formal concept analysis, three-way concept lattice can make more effective decision analysis. Firstly, the rule extraction based on object-induced three-way concept are investigated and compared compared with those of the classical concept lattice and attribute-induced three-way concept lattice. Then, by merging the object-induced three-way concept lattice and the attribute-induced three-way concept lattice, a new three-way concept lattice, i.e. object-attribute-induced three-way concept lattice, and its rule extraction[0] algorithm are proposed. Theoretical analyses and results show that the merging of object-induced three-way concept lattice and attribute-induced three-way concept lattice can improve the quality of rules.
2018, 47(6): 921-926.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.019
Abstract:
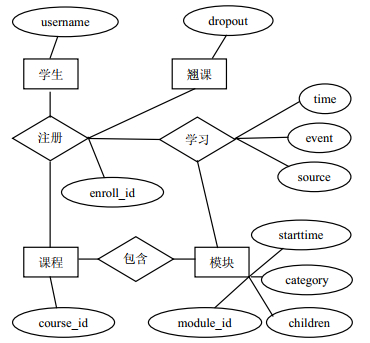
Dropout of classes reflects the quality of MOOCs, which is the key issue of online education. In order to predict the dropout rate in advance, this paper presents an efficient prediction framework based on the analysis on real online education data and the prior knowledge of online education. This presented framework combines the feature importance learning and the selection by the classification algorithm of XGBoost, and establishes a Drop-Out-Index (DOI) for online courses. Experiments analysis on massive features extracted from the online-data of XueTang website shows that the feature selection method based on XGBoost achieves better results than other feature selection methods. The validity of DOI has also been verified by testing on different time points in the data set.
Dropout of classes reflects the quality of MOOCs, which is the key issue of online education. In order to predict the dropout rate in advance, this paper presents an efficient prediction framework based on the analysis on real online education data and the prior knowledge of online education. This presented framework combines the feature importance learning and the selection by the classification algorithm of XGBoost, and establishes a Drop-Out-Index (DOI) for online courses. Experiments analysis on massive features extracted from the online-data of XueTang website shows that the feature selection method based on XGBoost achieves better results than other feature selection methods. The validity of DOI has also been verified by testing on different time points in the data set.
2018, 47(6): 927-931.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.020
Abstract:
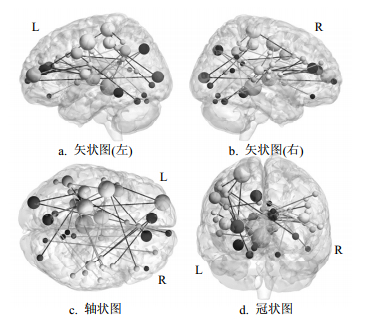
In order to investigate the brain network characteristics of the health-risk behavior, we collected fMRI data of 49 subjects under rest state. The fluctuation amplitude of dynamic functional connectivity is used as the features of support vector regression (SVR) to predict the health-risk behavior. The results show a good correlation between spontaneous fluctuation of rest state and the health-risk behavior. Some informational functional connectivities could be used to predict the health-risk behavior and they mainly locate among the connections of networks:mainly cingulo-opercular network, frontoparietal network, sensorimotor network, etc..
In order to investigate the brain network characteristics of the health-risk behavior, we collected fMRI data of 49 subjects under rest state. The fluctuation amplitude of dynamic functional connectivity is used as the features of support vector regression (SVR) to predict the health-risk behavior. The results show a good correlation between spontaneous fluctuation of rest state and the health-risk behavior. Some informational functional connectivities could be used to predict the health-risk behavior and they mainly locate among the connections of networks:mainly cingulo-opercular network, frontoparietal network, sensorimotor network, etc..
2018, 47(6): 932-936.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.021
Abstract:
Zn- and Sn-doped MgO powder preparing via a chemical coprecipitation method was spin-coated on alternating current plasma display panel (AC PDP) front panel as a functional layer to improve the discharging performance of AC PDP. The new products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectrom spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer. The results showed that zinc and tin atoms had been successfully incorporated into the crystal lattice of MgO, which made the transmission only decrease by 4%~7%. Within 7% Xe-Ne pressure range of 200~450 torr, the new functional layer consistently showed lower firing and sustain maximum voltages than that of the conventional MgO layer. Therefore, this functional layer was important for improving the discharge efficiency of AC PDP and reducing its power consumption.
Zn- and Sn-doped MgO powder preparing via a chemical coprecipitation method was spin-coated on alternating current plasma display panel (AC PDP) front panel as a functional layer to improve the discharging performance of AC PDP. The new products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectrom spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer. The results showed that zinc and tin atoms had been successfully incorporated into the crystal lattice of MgO, which made the transmission only decrease by 4%~7%. Within 7% Xe-Ne pressure range of 200~450 torr, the new functional layer consistently showed lower firing and sustain maximum voltages than that of the conventional MgO layer. Therefore, this functional layer was important for improving the discharge efficiency of AC PDP and reducing its power consumption.
2018, 47(6): 937-942.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.022
Abstract:
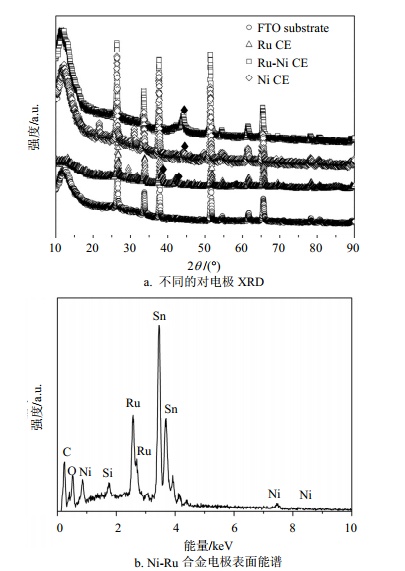
We develop a hydrothermal in situ growth of Nickel-Ruthenium alloy nanoelectrode for quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) applications. QDSC based on Ni-Ru alloy electrode delivers a much higher power conversion efficiency 1.96% than its counterparts, i.e., either pure Ni or Ru metal electrodes. In detail, Ni-Ru alloy electrode exhibits high specific area, excellent electrical behavior, intimate interface contact, and good stability, thus leading to notable improved device performances. The impressive robust function of Ni-Ru alloy with simple manufacturing procedure highlights its potential applications in robust QDSCs.
We develop a hydrothermal in situ growth of Nickel-Ruthenium alloy nanoelectrode for quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) applications. QDSC based on Ni-Ru alloy electrode delivers a much higher power conversion efficiency 1.96% than its counterparts, i.e., either pure Ni or Ru metal electrodes. In detail, Ni-Ru alloy electrode exhibits high specific area, excellent electrical behavior, intimate interface contact, and good stability, thus leading to notable improved device performances. The impressive robust function of Ni-Ru alloy with simple manufacturing procedure highlights its potential applications in robust QDSCs.
2018, 47(6): 943-952.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.023
Abstract:
According to the community structure in complex social networks, we propose an evolutionary game model on community network generated by the double-degree preference mechanism under social dilemma, based on traditional Prisoner's Dilemma Game and accumulated payoff update rule. Then, we systematically analyze the effect of external connectivity density in static community networks, co-evolution time scale of strategy and structure in dynamic community network, and the noise in updating process on the emergence of cooperation and the corresponding mechanism. The results of simulation indicate that:the density of connections between communities has a negative impact on the emergence of cooperation. Although the level of cooperation in static community networks is higher than dynamic community networks, there are significant differences between static and dynamic community networks for the strategy composition, strategy stability and dynamics of cooperative evolution. In dynamic community networks, the effect of co-evolution time scale of strategy and structure on cooperation emergence shows reciprocal trend of change between pros and cons, which represents that it has a smaller cooperation level with smaller time scale under low value of temptation while it is more beneficial for cooperation with smaller time scale under high value of temptation. The effect of noise in strategy updating process on the cooperation emergence in static and dynamic community networks is monotonous, and it can significantly increases the cooperation level by introducing moderate noise.
According to the community structure in complex social networks, we propose an evolutionary game model on community network generated by the double-degree preference mechanism under social dilemma, based on traditional Prisoner's Dilemma Game and accumulated payoff update rule. Then, we systematically analyze the effect of external connectivity density in static community networks, co-evolution time scale of strategy and structure in dynamic community network, and the noise in updating process on the emergence of cooperation and the corresponding mechanism. The results of simulation indicate that:the density of connections between communities has a negative impact on the emergence of cooperation. Although the level of cooperation in static community networks is higher than dynamic community networks, there are significant differences between static and dynamic community networks for the strategy composition, strategy stability and dynamics of cooperative evolution. In dynamic community networks, the effect of co-evolution time scale of strategy and structure on cooperation emergence shows reciprocal trend of change between pros and cons, which represents that it has a smaller cooperation level with smaller time scale under low value of temptation while it is more beneficial for cooperation with smaller time scale under high value of temptation. The effect of noise in strategy updating process on the cooperation emergence in static and dynamic community networks is monotonous, and it can significantly increases the cooperation level by introducing moderate noise.
2018, 47(6): 953-960.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.06.024
Abstract:
In the real world, networks often have "scale-free", "high clustering" and "interconnection" features. In order to model these characteristics, we proposes an algorithm for constructing the interdependent Holme-Kim network and use tools of complex networks and evolutionary game theory to research the emergence of cooperation in our network model, where a Prisoner's Dilemma game is played. Through simulation experiments, the effects of the connection degree, the connection probability mentioned in the algorithm and the temptation to defect in the payoff matrix of the Prisoner's Dilemma game are studied. Our results show that the lower the connection degree and the connection probability on the same scale of the network, the easier the formation of cooperative behavior on the network. When the parameter of the temptation to defect is more than a certain threshold, a great number of defectors will be on the networks.
In the real world, networks often have "scale-free", "high clustering" and "interconnection" features. In order to model these characteristics, we proposes an algorithm for constructing the interdependent Holme-Kim network and use tools of complex networks and evolutionary game theory to research the emergence of cooperation in our network model, where a Prisoner's Dilemma game is played. Through simulation experiments, the effects of the connection degree, the connection probability mentioned in the algorithm and the temptation to defect in the payoff matrix of the Prisoner's Dilemma game are studied. Our results show that the lower the connection degree and the connection probability on the same scale of the network, the easier the formation of cooperative behavior on the network. When the parameter of the temptation to defect is more than a certain threshold, a great number of defectors will be on the networks.

 ISSN
ISSN