2019 Vol. 48, No. 6
2019, 48(6): 802-802.
Abstract:
2019, 48(6): 803-808.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.001
Abstract:
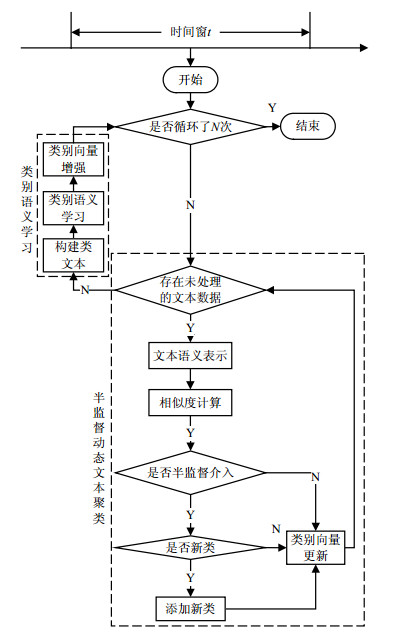
In the traditional dynamic text clustering, the similar texts with different descriptions are divided into different groups; and the difference between the number of cluster categories and the number of real categories is obvious. Aiming at these problems, this paper proposes a semi-supervised semantic dynamic text clustering algorithm (SDCS). The algorithm captures the semantic relationship between texts by semantically representing the text, and dynamically learns the category semantics during the clustering process, so that the text can be accurately clustered according to semantics. At the same time, the algorithm uses the semi-supervised clustering algorithm to supervise the generation of new classes, and produces clustering results that are consistent with the actual situation. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is effective and feasible.
In the traditional dynamic text clustering, the similar texts with different descriptions are divided into different groups; and the difference between the number of cluster categories and the number of real categories is obvious. Aiming at these problems, this paper proposes a semi-supervised semantic dynamic text clustering algorithm (SDCS). The algorithm captures the semantic relationship between texts by semantically representing the text, and dynamically learns the category semantics during the clustering process, so that the text can be accurately clustered according to semantics. At the same time, the algorithm uses the semi-supervised clustering algorithm to supervise the generation of new classes, and produces clustering results that are consistent with the actual situation. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is effective and feasible.
2019, 48(6): 809-814.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.002
Abstract:
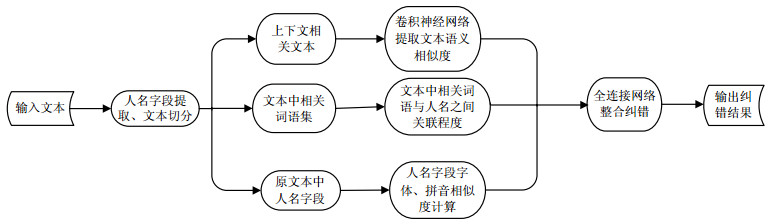
In news texts, incorrect fields in names will affect or even change the semantic expression of the text and the particularity of name fields will generate duplicate name or ambiguity. For solving these problems, this paper proposes a novel news name correction method based on context semantics. This method uses convolutional neural network to extract the semantic information of texts, and adopts word activation model to calculate the degree of association between other words and name fields in texts to capture and use the semantic information of text context. At the same time, aiming at the problem of low recognition caused by errors in the field of human name in texts, the entity boundary recognition algorithm of names is used to improve the recognition and extraction effect of names that are suspected to contain errors in the text. The experimental results show that the method can effectively identify the names in the text and correct the errors.
In news texts, incorrect fields in names will affect or even change the semantic expression of the text and the particularity of name fields will generate duplicate name or ambiguity. For solving these problems, this paper proposes a novel news name correction method based on context semantics. This method uses convolutional neural network to extract the semantic information of texts, and adopts word activation model to calculate the degree of association between other words and name fields in texts to capture and use the semantic information of text context. At the same time, aiming at the problem of low recognition caused by errors in the field of human name in texts, the entity boundary recognition algorithm of names is used to improve the recognition and extraction effect of names that are suspected to contain errors in the text. The experimental results show that the method can effectively identify the names in the text and correct the errors.
2019, 48(6): 802-802.
Abstract:
2019, 48(6): 815-822.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.003
Abstract:
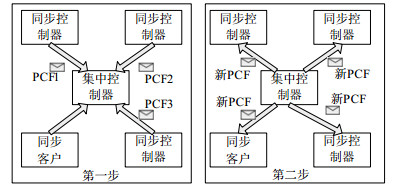
Time triggered deterministic network is a network that can meet the requirements of high reliability, low latency and high real-time. This paper proposes an improved deterministic network suitable for large-scale and concurrent requests. Two improvements are made on the basis of time-triggered Ethernet (TTE). First, a partition strategy containing message security level control is added and the idea of security middleware is presented. Second, in view of the characteristics of off-line scheduling of time-triggered messages, a transmission strategy based on time scheduling matrix is proposed. The analysis of network data test results shows that the proposed TTE network improvement scheme can meet the needs of high concurrent network and change the small scale of deterministic network.
Time triggered deterministic network is a network that can meet the requirements of high reliability, low latency and high real-time. This paper proposes an improved deterministic network suitable for large-scale and concurrent requests. Two improvements are made on the basis of time-triggered Ethernet (TTE). First, a partition strategy containing message security level control is added and the idea of security middleware is presented. Second, in view of the characteristics of off-line scheduling of time-triggered messages, a transmission strategy based on time scheduling matrix is proposed. The analysis of network data test results shows that the proposed TTE network improvement scheme can meet the needs of high concurrent network and change the small scale of deterministic network.
2019, 48(6): 823-830.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.004
Abstract:
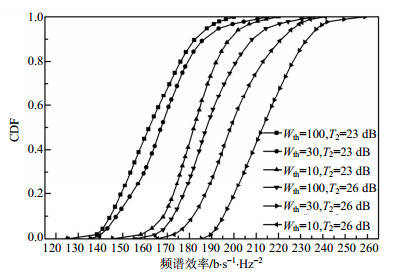
To reduce the co-tier interference among femtocell base stations (FBSs) in ultra-dense networks (UDN), an interference-limited clustering and resource allocation (ILCRA) scheme is proposed, in which preset threshold is used to limit the number of FBS in each FBS cluster. Firstly, FBSs are divided into clusters, and the sum weights of interference in each FBS cluster can not exceed the preset threshold. Secondly, user equipment (UE) is clustered by exhaustive graph coloring algorithm in each FBS cluster. Then, the resources are allocated independently within each FBS cluster. Sub-channels are assigned according to the throughput of UE clusters on each sub-channel. Finally, the water-filling algorithm is performed to allocate power to UEs in each FBS cluster. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme effectively limits the number of FBS in each FBS cluster and improves system throughput and spectrum efficiency.
To reduce the co-tier interference among femtocell base stations (FBSs) in ultra-dense networks (UDN), an interference-limited clustering and resource allocation (ILCRA) scheme is proposed, in which preset threshold is used to limit the number of FBS in each FBS cluster. Firstly, FBSs are divided into clusters, and the sum weights of interference in each FBS cluster can not exceed the preset threshold. Secondly, user equipment (UE) is clustered by exhaustive graph coloring algorithm in each FBS cluster. Then, the resources are allocated independently within each FBS cluster. Sub-channels are assigned according to the throughput of UE clusters on each sub-channel. Finally, the water-filling algorithm is performed to allocate power to UEs in each FBS cluster. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme effectively limits the number of FBS in each FBS cluster and improves system throughput and spectrum efficiency.
2019, 48(6): 831-837.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.005
Abstract:
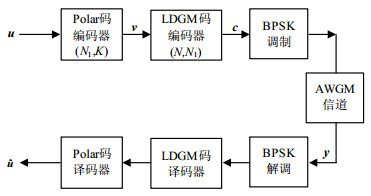
In order to satisfy the requirements of low complexity, capacity approaching performance and no error floor for the error correcting codes used in the optical transport network (OTN), a high-rate concatenated codes based on polar codes and low density generator matrix (LDGM) is proposed. The polar-LDGM coding scheme for the concatenated model is first described and the encoding complexity of the scheme is analyzed. And then, the concatenated decoding algorithm based on belief propagation (BP) algorithm is detailed according to the decoding structure of both codes. By reasonably using Gaussian approximation (GA) method, we derive the mean of message passed in the decoding structure, which results in the accurate prediction of the error probability for the Polar-LDGM codes. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves the demands of the optical transport network (OTN).
In order to satisfy the requirements of low complexity, capacity approaching performance and no error floor for the error correcting codes used in the optical transport network (OTN), a high-rate concatenated codes based on polar codes and low density generator matrix (LDGM) is proposed. The polar-LDGM coding scheme for the concatenated model is first described and the encoding complexity of the scheme is analyzed. And then, the concatenated decoding algorithm based on belief propagation (BP) algorithm is detailed according to the decoding structure of both codes. By reasonably using Gaussian approximation (GA) method, we derive the mean of message passed in the decoding structure, which results in the accurate prediction of the error probability for the Polar-LDGM codes. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves the demands of the optical transport network (OTN).
2019, 48(6): 838-844, 857.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.006
Abstract:
Medium-orbit SAR (MEO SAR) is an important complement to low-orbit SAR and geosynchronous orbit SAR because of its advantages of wide swath and short revisit time. However, compared with low-orbit SAR, MEO SAR has the characteristics of long synthetic aperture time, complex orbital characteristics. Conventional echo model is not suitable for the imaging of moving targets in MEO SAR. In this paper, the slant-range models of MEO SAR are quantitatively analyzed. It is concluded that the fourth-order slant-range model can meet the imaging requirements when the ship is in the case of static, uniform motion and acceleration. But it will be invalid when the ship is affected by ocean waves. Finally, the accurate echo model of medium-orbit SAR is realized.
Medium-orbit SAR (MEO SAR) is an important complement to low-orbit SAR and geosynchronous orbit SAR because of its advantages of wide swath and short revisit time. However, compared with low-orbit SAR, MEO SAR has the characteristics of long synthetic aperture time, complex orbital characteristics. Conventional echo model is not suitable for the imaging of moving targets in MEO SAR. In this paper, the slant-range models of MEO SAR are quantitatively analyzed. It is concluded that the fourth-order slant-range model can meet the imaging requirements when the ship is in the case of static, uniform motion and acceleration. But it will be invalid when the ship is affected by ocean waves. Finally, the accurate echo model of medium-orbit SAR is realized.
2019, 48(6): 845-849.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.007
Abstract:
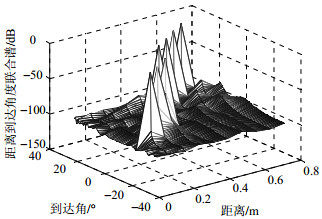
Aiming at the problem of near-field sound source localization estimation under the condition of less array elements than sources, the method of sparse reconstruction based on Khatri-Rao (KR) product is proposed. The source signals are wide-sense quasi-stationary in this method. A virtual array structure is acquired by KR product and the degree of freedom is increased. In the virtual array structure the spectra of the sound sources are acquired band on sparse reconstruction, which is solved by l1 norm method. Simulations demonstrate the proposed method can realized underdeterminded estimation of sound source and the performance is better than the subspace method.
Aiming at the problem of near-field sound source localization estimation under the condition of less array elements than sources, the method of sparse reconstruction based on Khatri-Rao (KR) product is proposed. The source signals are wide-sense quasi-stationary in this method. A virtual array structure is acquired by KR product and the degree of freedom is increased. In the virtual array structure the spectra of the sound sources are acquired band on sparse reconstruction, which is solved by l1 norm method. Simulations demonstrate the proposed method can realized underdeterminded estimation of sound source and the performance is better than the subspace method.
2019, 48(6): 850-857.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.008
Abstract:
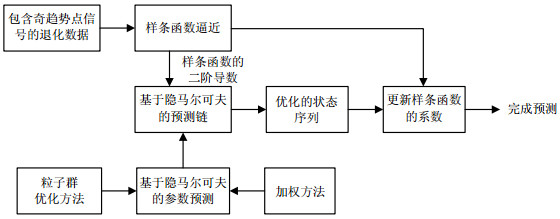
Current model for remaining useful life prognostic is usually based on the historical data, which can provide evidence for maintenance. However, singularity arising in the degradation data frequently give rise to a bad decline in prediction accuracy, this phenomenon is a great challenge for the time series prediction. To address this issue, we develop a new surrogate modeling prognostic approach based on cubic non-polynomial spline model in this paper. Meanwhile, due to the singularity perturbation in degradation tendency, the spline model's second derivative can be adopted and calculated to form a series of observation frames, and then a weighted hidden Markov model (HMM) method combined with particle swarm optimization (PSO) is used to forecast the observation sequence, then rebuild the spline function. A simulation example and a practical application involving typical singularities verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Current model for remaining useful life prognostic is usually based on the historical data, which can provide evidence for maintenance. However, singularity arising in the degradation data frequently give rise to a bad decline in prediction accuracy, this phenomenon is a great challenge for the time series prediction. To address this issue, we develop a new surrogate modeling prognostic approach based on cubic non-polynomial spline model in this paper. Meanwhile, due to the singularity perturbation in degradation tendency, the spline model's second derivative can be adopted and calculated to form a series of observation frames, and then a weighted hidden Markov model (HMM) method combined with particle swarm optimization (PSO) is used to forecast the observation sequence, then rebuild the spline function. A simulation example and a practical application involving typical singularities verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2019, 48(6): 858-864.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.009
Abstract:
Multichannel sampling upon the frequency dimension is an important method to improve the overall sampling rate, where each channel needs to design an independent analog sampling filter and a digital reconfiguration filter to achieve the separation and undistorted recovery of the signal, resulting in high complexity of the structure and algorithm. In this paper, a method of frequency-interleaved sampling and reconstruction based on orthogonal frequency conversion is proposed. The sampling process divides the input signal into several sub-channels, where the radio frequency/intermediate frequency (RF/IF) channels are moved to the baseband by orthogonal mixing and sampling filter, and the quantization conversion is executed. The reconstruction process adopts digital up-conversion to move each channel back to its original carrier and obtain the output after frequency synthesis. The proposed method only needs one analog sampling filter and one digital reconstruction filter based on perfect reconstruction, which is more convenient for realization. Finally, the validity of the frequency-interleaved sampling and reconstruction method based on orthogonal frequency conversion is illustrated.
Multichannel sampling upon the frequency dimension is an important method to improve the overall sampling rate, where each channel needs to design an independent analog sampling filter and a digital reconfiguration filter to achieve the separation and undistorted recovery of the signal, resulting in high complexity of the structure and algorithm. In this paper, a method of frequency-interleaved sampling and reconstruction based on orthogonal frequency conversion is proposed. The sampling process divides the input signal into several sub-channels, where the radio frequency/intermediate frequency (RF/IF) channels are moved to the baseband by orthogonal mixing and sampling filter, and the quantization conversion is executed. The reconstruction process adopts digital up-conversion to move each channel back to its original carrier and obtain the output after frequency synthesis. The proposed method only needs one analog sampling filter and one digital reconstruction filter based on perfect reconstruction, which is more convenient for realization. Finally, the validity of the frequency-interleaved sampling and reconstruction method based on orthogonal frequency conversion is illustrated.
2019, 48(6): 865-869.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.010
Abstract:
Aiming at the differential fault attack of PRESENT cipher algorithm, the differential fault propagation characteristics of PRESENT algorithm are analyzed and the import fault locations are optimized in this paper. On this base, different attack models for quickly obtaining the original cipher are established by using combination exhaustive search. The encryption process and attack process of PRESENT algorithm are implemented by using C++. The results reveal that there are two factors that affect the differential fault attack of PRESENT, the number of attack and the number of fault ciphertext. In the last second round attack, an average of 30 pieces of fault ciphertext are required to restore 64bit round key, while an average of only 9 pieces of fault ciphertexts are necessary to restore all keys in preceding rounds. Meanwhile, the attack complexity of this attack method of single fault cipher is 226, while the key search complexity is 231.
Aiming at the differential fault attack of PRESENT cipher algorithm, the differential fault propagation characteristics of PRESENT algorithm are analyzed and the import fault locations are optimized in this paper. On this base, different attack models for quickly obtaining the original cipher are established by using combination exhaustive search. The encryption process and attack process of PRESENT algorithm are implemented by using C++. The results reveal that there are two factors that affect the differential fault attack of PRESENT, the number of attack and the number of fault ciphertext. In the last second round attack, an average of 30 pieces of fault ciphertext are required to restore 64bit round key, while an average of only 9 pieces of fault ciphertexts are necessary to restore all keys in preceding rounds. Meanwhile, the attack complexity of this attack method of single fault cipher is 226, while the key search complexity is 231.
2019, 48(6): 870-879.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.011
Abstract:
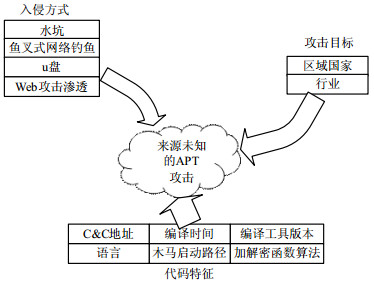
Advanced persistent threat (APT) is a new kind of cyber-attack as a growth security events. This paper analysis more than 150 typical APT cases happened during last decade, and constructs the analytical model of APT attack, indicates 4 major problems of APT attack detection and countering:the fragile penetration protection problem, the low detection accuracy, the difficulty of determining the attack forensic, and the slow response to the unknown attack problem. In the meanwhile, this paper analyzes typical APT attacks in recent years, mines the association based on attacking tools. According to the experiments, there are similarity patterns between the tools used by the same organization. In summary, the integral APT defense scheme in this paper includes the latest achievements of four types of defense schemes, plays an academic supporting role in building a unified attack detection and traceability countermeasure platform.
Advanced persistent threat (APT) is a new kind of cyber-attack as a growth security events. This paper analysis more than 150 typical APT cases happened during last decade, and constructs the analytical model of APT attack, indicates 4 major problems of APT attack detection and countering:the fragile penetration protection problem, the low detection accuracy, the difficulty of determining the attack forensic, and the slow response to the unknown attack problem. In the meanwhile, this paper analyzes typical APT attacks in recent years, mines the association based on attacking tools. According to the experiments, there are similarity patterns between the tools used by the same organization. In summary, the integral APT defense scheme in this paper includes the latest achievements of four types of defense schemes, plays an academic supporting role in building a unified attack detection and traceability countermeasure platform.
2019, 48(6): 880-885.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.012
Abstract:
The temporal constraints decomposition model (TCD), which guarantees the global temporal, can decompose the temporal service composition into two relatively independent processes:constraints decomposition and local optimization. However, the model may lose the feasible combination scheme, which may lead to no solution when the user constraints strength is strong. This paper proposes a constraints strength-aware temporal constraints decomposition model (CIA-TCD), which introduces a relaxation factor into the existing TCD model. When the user constraint strength is weak, the global constraint can be guaranteed; and when the constraint strength is strong, a certain amount of combination scheme can be reserved, thereby increasing the probability that a feasible solution can be found. The experimental analysis shows that the CIA-TCD model has a significantly better probability of finding a feasible combination scheme than the TCD model when the constraint strength is strong.
The temporal constraints decomposition model (TCD), which guarantees the global temporal, can decompose the temporal service composition into two relatively independent processes:constraints decomposition and local optimization. However, the model may lose the feasible combination scheme, which may lead to no solution when the user constraints strength is strong. This paper proposes a constraints strength-aware temporal constraints decomposition model (CIA-TCD), which introduces a relaxation factor into the existing TCD model. When the user constraint strength is weak, the global constraint can be guaranteed; and when the constraint strength is strong, a certain amount of combination scheme can be reserved, thereby increasing the probability that a feasible solution can be found. The experimental analysis shows that the CIA-TCD model has a significantly better probability of finding a feasible combination scheme than the TCD model when the constraint strength is strong.
2019, 48(6): 886-892.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.013
Abstract:
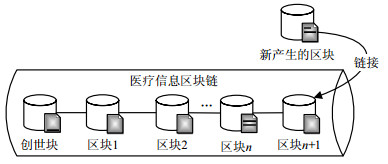
With the progress of information development of medical industry, the medical field has got into the era of big data. However, it still faces many challenges in data heterogeneity, interoperability, and privacy protection. In response to the above problems, a decentralized medical big data sharing model based on ring signature is constructed. The model maintains a reliable medical ledger database based on the decoupling of blockchain, ensuring that the privacy data cannot be tampered. It constructs a private data storage protocol based on ring signature, which guarantees medical data and patient identity privacy with its full anonymity. We proposed a medical information strict access control management mechanism based on smart contract automation execution of preset instructions. The authority and confidentiality of medical privacy data are guaranteed by clearly dividing the access rights of medical privacy information. The safety test results show that the model has better real-time and robustness than the traditional medical big data sharing model.
With the progress of information development of medical industry, the medical field has got into the era of big data. However, it still faces many challenges in data heterogeneity, interoperability, and privacy protection. In response to the above problems, a decentralized medical big data sharing model based on ring signature is constructed. The model maintains a reliable medical ledger database based on the decoupling of blockchain, ensuring that the privacy data cannot be tampered. It constructs a private data storage protocol based on ring signature, which guarantees medical data and patient identity privacy with its full anonymity. We proposed a medical information strict access control management mechanism based on smart contract automation execution of preset instructions. The authority and confidentiality of medical privacy data are guaranteed by clearly dividing the access rights of medical privacy information. The safety test results show that the model has better real-time and robustness than the traditional medical big data sharing model.
2019, 48(6): 893-903.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.014
Abstract:
With the development of infrared monitoring and early warning system, more and more attention has been paid to the research of infrared small target detection technology. How to continuously and effectively detect the target position in a complex background has always been a major challenge for researchers. Based on the study of the characteristics of infrared point moving targets, this paper proposes a small target detection algorithm for multi-scale local gradient strength measurement. Firstly, a multi-scale image pyramid is constructed, and a fast and coarse small target detection method is proposed at multiple scales. Then, the difference between the target itself and the surrounding background is used to measure the intensity of grayscale changes in various directions in the local window. Then the most appropriate response based on these measurements is obtained. The experimental results show that the proposed method has better robustness under the background of complex and variable, and it has more effective detection performance under lower signal-to-noise ratio.
With the development of infrared monitoring and early warning system, more and more attention has been paid to the research of infrared small target detection technology. How to continuously and effectively detect the target position in a complex background has always been a major challenge for researchers. Based on the study of the characteristics of infrared point moving targets, this paper proposes a small target detection algorithm for multi-scale local gradient strength measurement. Firstly, a multi-scale image pyramid is constructed, and a fast and coarse small target detection method is proposed at multiple scales. Then, the difference between the target itself and the surrounding background is used to measure the intensity of grayscale changes in various directions in the local window. Then the most appropriate response based on these measurements is obtained. The experimental results show that the proposed method has better robustness under the background of complex and variable, and it has more effective detection performance under lower signal-to-noise ratio.
2019, 48(6): 904-909, 924.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.015
Abstract:
In order to better deal with the problem of small sample size, and to overcome the defect of two-dimensional locality preserving projection (2DLPP) algorithm which can only keep the local nature of the data, an improved bi-directional two dimensional locality preserving projection algorithm for face recognition is proposed, by combining the characteristics of Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) and Two-Dimensional Linear Discriminate Analysis (2DLDA). First, it introduced the sample class information to improve the weight matrix, and enhances the robustness of the 2DLPP algorithm to samples' changes. Second, two fusion algorithms of 2DLPP+2DPCA and 2DLPP+2DLDA were improved to the feature extraction of row and column direction of the input sample image data. After the feature selection, the optimal projection in row and column direction was obtained. Finally, by performing row and column direction projection on the sample data, the nearest neighbor classification was used to classify the sample data and obtain the recognition results on the given datasets. Experimental results on the face datasets ORL, YALE and AR show that the proposed algorithm is generally superior to the algorithms such as 2DPCA, 2DLDA, 2DLPP, (2D)2PCA, (2D)2LDA, (2D)2PCALDA, and (2D)2LPP-PCA in face recognition performance.
In order to better deal with the problem of small sample size, and to overcome the defect of two-dimensional locality preserving projection (2DLPP) algorithm which can only keep the local nature of the data, an improved bi-directional two dimensional locality preserving projection algorithm for face recognition is proposed, by combining the characteristics of Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) and Two-Dimensional Linear Discriminate Analysis (2DLDA). First, it introduced the sample class information to improve the weight matrix, and enhances the robustness of the 2DLPP algorithm to samples' changes. Second, two fusion algorithms of 2DLPP+2DPCA and 2DLPP+2DLDA were improved to the feature extraction of row and column direction of the input sample image data. After the feature selection, the optimal projection in row and column direction was obtained. Finally, by performing row and column direction projection on the sample data, the nearest neighbor classification was used to classify the sample data and obtain the recognition results on the given datasets. Experimental results on the face datasets ORL, YALE and AR show that the proposed algorithm is generally superior to the algorithms such as 2DPCA, 2DLDA, 2DLPP, (2D)2PCA, (2D)2LDA, (2D)2PCALDA, and (2D)2LPP-PCA in face recognition performance.
2019, 48(6): 910-917.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.016
Abstract:
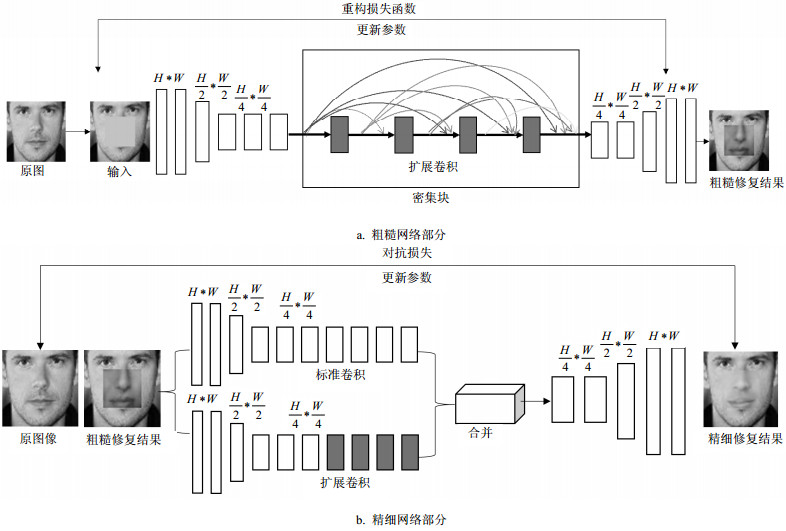
Face image inpainting is a hot topic of image processing research in recent years. This paper proposes a face image restoration method based on cascade generative adversarial network. In this method, the generator employs a cascading structure consisting of a coarse network and a refinement network and adopts dense connections to recover more details of the missing face area; the discriminator uses a dual discriminant model combining local and global features to improve the discriminant accuracy; the loss function consists of reconstruction loss and generative adversarial loss for better training performance. Experiments on CelebA dataset show that the proposed method can restore facial image with more than 50% missing area. The objective evaluation index PSNR and SSIM are 1.1 dB to 7.5 dB and 0.02 to 0.15 higher respectively compared with state of the arts. For subjective evaluation, the restored face images look more detailed and natural.
Face image inpainting is a hot topic of image processing research in recent years. This paper proposes a face image restoration method based on cascade generative adversarial network. In this method, the generator employs a cascading structure consisting of a coarse network and a refinement network and adopts dense connections to recover more details of the missing face area; the discriminator uses a dual discriminant model combining local and global features to improve the discriminant accuracy; the loss function consists of reconstruction loss and generative adversarial loss for better training performance. Experiments on CelebA dataset show that the proposed method can restore facial image with more than 50% missing area. The objective evaluation index PSNR and SSIM are 1.1 dB to 7.5 dB and 0.02 to 0.15 higher respectively compared with state of the arts. For subjective evaluation, the restored face images look more detailed and natural.
2019, 48(6): 918-924.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.017
Abstract:
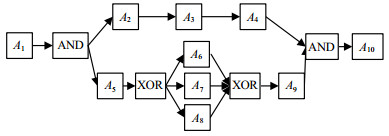
To improve the performance of genetic process mining algorithm for handling large scale event log, a GPU-based parallel genetic process mining algorithm is proposed. Since traditional binary chromosome coding method can not represent the AND-Split/AND-Join and the OR-Split/OR-Join structures in causal matrix, a new coding method of chromosome is proposed. The proposed method can effectively solve the problem of genetic representation of causal matrix on graphics processing units (GPU) by three arrays, which are content, labels and position. Meanwhile, the efficient genetic crossover/mutation operators and a parallel method of fitness value computation are designed and implemented. Simulation experiments show that the proposed algorithm, compared with the CPU-based genetic process mining algorithm, has obvious advantages in precision and convergence rate, and moreover it obtains speedup of 36.4 and 47.2 on two data sets respectively.
To improve the performance of genetic process mining algorithm for handling large scale event log, a GPU-based parallel genetic process mining algorithm is proposed. Since traditional binary chromosome coding method can not represent the AND-Split/AND-Join and the OR-Split/OR-Join structures in causal matrix, a new coding method of chromosome is proposed. The proposed method can effectively solve the problem of genetic representation of causal matrix on graphics processing units (GPU) by three arrays, which are content, labels and position. Meanwhile, the efficient genetic crossover/mutation operators and a parallel method of fitness value computation are designed and implemented. Simulation experiments show that the proposed algorithm, compared with the CPU-based genetic process mining algorithm, has obvious advantages in precision and convergence rate, and moreover it obtains speedup of 36.4 and 47.2 on two data sets respectively.
2019, 48(6): 925-930.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.018
Abstract:
Trajectory clustering algorithm can be widely used in traffic management. Finding the vehicle trajectory hotspots by using trajectory clustering algorithm has important guiding significance for traffic planning and management of traffic travel. Current trajectory clustering algorithms are mostly measured by spatial similarity, which cannot reflect the division of trajectory hotspots in different time periods. In response to the above problems, this paper proposes a hotspot region extraction algorithm for spatio-temporal trajectory, combined with the factor of time. Firstly, the traditional density peak clustering algorithm and the density calculation method are improved by considering the linear and nonlinear parts of the calculated density. At the same time, the method of choosing cluster center is modified to enable it to automatically select the cluster center. On the basis of the above, we propose a clustering fusion algorithm to filter inappropriate clusters and redundant clusters and use the DB index to detect the division results. The experimental results show that our algorithm can extract the hot spots of spatio-temporal trajectories more effectively than the traditional clustering algorithms.
Trajectory clustering algorithm can be widely used in traffic management. Finding the vehicle trajectory hotspots by using trajectory clustering algorithm has important guiding significance for traffic planning and management of traffic travel. Current trajectory clustering algorithms are mostly measured by spatial similarity, which cannot reflect the division of trajectory hotspots in different time periods. In response to the above problems, this paper proposes a hotspot region extraction algorithm for spatio-temporal trajectory, combined with the factor of time. Firstly, the traditional density peak clustering algorithm and the density calculation method are improved by considering the linear and nonlinear parts of the calculated density. At the same time, the method of choosing cluster center is modified to enable it to automatically select the cluster center. On the basis of the above, we propose a clustering fusion algorithm to filter inappropriate clusters and redundant clusters and use the DB index to detect the division results. The experimental results show that our algorithm can extract the hot spots of spatio-temporal trajectories more effectively than the traditional clustering algorithms.
2019, 48(6): 931-938.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.019
Abstract:
The research of complex networks has been developing rapidly, which has had a profound impact on such disciplines as automatic control, statistical physics, computers, and management. However, there has been a lack of systematic and intuitive analysis of the development of topics in China. Taking the abstracts of the 13th National Complex Network Conference in 2017 as research object, we investigate the topic trend of the domestic complex network researches. Firstly, the text information of the abstracts are preprocessed and segmented by adding a custom dictionary and a stop word dictionary to obtain a document-word matrix. Then the LDA model is used to mine topics of the abstracts and SVD decomposition is applied to obtain the number of topics. As a result, ten topics of the conference are found through agglomerative hierarchical clustering according to the JS distance among the abstracts and four research communities involved in the conference are identified through community detection according to the JS distance among institutions. This work not only makes insight on the research trends and the popularity of different research directions in complex networks, but also provides reference institutions for new researchers to find corresponding research directions based on the results.
The research of complex networks has been developing rapidly, which has had a profound impact on such disciplines as automatic control, statistical physics, computers, and management. However, there has been a lack of systematic and intuitive analysis of the development of topics in China. Taking the abstracts of the 13th National Complex Network Conference in 2017 as research object, we investigate the topic trend of the domestic complex network researches. Firstly, the text information of the abstracts are preprocessed and segmented by adding a custom dictionary and a stop word dictionary to obtain a document-word matrix. Then the LDA model is used to mine topics of the abstracts and SVD decomposition is applied to obtain the number of topics. As a result, ten topics of the conference are found through agglomerative hierarchical clustering according to the JS distance among the abstracts and four research communities involved in the conference are identified through community detection according to the JS distance among institutions. This work not only makes insight on the research trends and the popularity of different research directions in complex networks, but also provides reference institutions for new researchers to find corresponding research directions based on the results.
2019, 48(6): 939-946.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.020
Abstract:
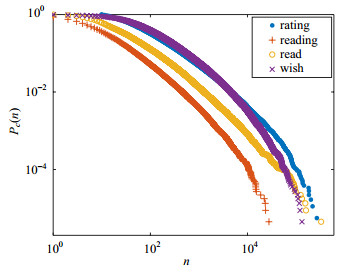
To reveal the subject preference of reading and the diversity of reading interest of users in online reading communities, this paper crawls the data of Douban reading, uses the common reading relationship to construct the book networks, and combines the complex network theory and machine learning methods to study the book networks. We find that in the book networks, the two-way weights between disciplines are nearly equal. Users who read philosophy, political science, and other humanities and social sciences have the most extensive interest in reading, while users who read engineering technology disciplines such as mining engineering and nuclear science and technology have the narrowest interest in reading. The network constructed by the secondary disciplines has three distinct communities, corresponding to the three major areas of humanities and social sciences, engineering technology, and basic sciences. For the suitability of interdisciplinary research, the basic sciences are the highest, the humanities and social sciences are the second, and the engineering technology is the lowest. Research results are of great significance to interdisciplinary cross recommendation of books.
To reveal the subject preference of reading and the diversity of reading interest of users in online reading communities, this paper crawls the data of Douban reading, uses the common reading relationship to construct the book networks, and combines the complex network theory and machine learning methods to study the book networks. We find that in the book networks, the two-way weights between disciplines are nearly equal. Users who read philosophy, political science, and other humanities and social sciences have the most extensive interest in reading, while users who read engineering technology disciplines such as mining engineering and nuclear science and technology have the narrowest interest in reading. The network constructed by the secondary disciplines has three distinct communities, corresponding to the three major areas of humanities and social sciences, engineering technology, and basic sciences. For the suitability of interdisciplinary research, the basic sciences are the highest, the humanities and social sciences are the second, and the engineering technology is the lowest. Research results are of great significance to interdisciplinary cross recommendation of books.
2019, 48(6): 947-953.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.021
Abstract:
The decrease in the trapped charges at SiC/SiO2 interface is helpful to lower the on-state resistance and switching loss of SiC MOSFET, however, the lift of channel current brings higher current stress to SiC MOSFET during short-circuit case. On the basis of the traditional equivalent circuit model for SiC MOSFET, a short-circuit failure model of SiC MOSFET has been developed. The model introduces the leakage current across the PN junction between N-drift region and P base region of SiC MOSFET, and employs an advance carrier mobility model with the trapped charges at the SiC/SiO2 interface. By the developed failure model, the influence brought by the interface trapped charges on the short-circuit performances has been exploited, and the result shows that the reduction of interface trapped charge shortens the time of SiC MOSFET withstanding short-circuit stress. Further, the mechanism of interface trapped charges affecting the short-circuit withstanding time has been discussed by separating the leakage current components from the failure current.
The decrease in the trapped charges at SiC/SiO2 interface is helpful to lower the on-state resistance and switching loss of SiC MOSFET, however, the lift of channel current brings higher current stress to SiC MOSFET during short-circuit case. On the basis of the traditional equivalent circuit model for SiC MOSFET, a short-circuit failure model of SiC MOSFET has been developed. The model introduces the leakage current across the PN junction between N-drift region and P base region of SiC MOSFET, and employs an advance carrier mobility model with the trapped charges at the SiC/SiO2 interface. By the developed failure model, the influence brought by the interface trapped charges on the short-circuit performances has been exploited, and the result shows that the reduction of interface trapped charge shortens the time of SiC MOSFET withstanding short-circuit stress. Further, the mechanism of interface trapped charges affecting the short-circuit withstanding time has been discussed by separating the leakage current components from the failure current.
2019, 48(6): 954-960.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.06.022
Abstract:
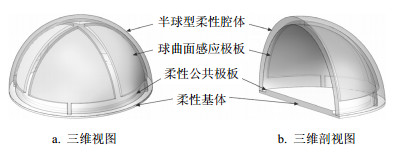
To improve the sensing sensitivity of electronic skin (e-skin), a capacitive flexible tactile sensor based on spherical surface plate is proposed in this paper. The structural characteristics and fabrication process of the sensor was illustrated, meanwhile, the tactile sensing mechanism is also presented based on the combine of theoretical calculation and ANSYS finite element simulation. The sensitivity of the capacitive flexible tactile can be cooperatively improved based on the spatial arrangement of spherical surface plate and differential structure. Furthermore, the signal acquisition and processing system of the capacitive tactile sensor is constructed based on the high performance capacitive digital converter AD7147-1 and STM32 microprocessor, and the characteristic test and the application of the proposed device are also conducted. The experiment results show that the high sensitivity tactile sensing of normal force and tangential force and high stability can be obtained by using the capacitive tactile sensor with the spherical surface plate with a fast response time of 70 ms, and the feasibility of the capacitive tactile sensor used as electric skin is further demonstrated.
To improve the sensing sensitivity of electronic skin (e-skin), a capacitive flexible tactile sensor based on spherical surface plate is proposed in this paper. The structural characteristics and fabrication process of the sensor was illustrated, meanwhile, the tactile sensing mechanism is also presented based on the combine of theoretical calculation and ANSYS finite element simulation. The sensitivity of the capacitive flexible tactile can be cooperatively improved based on the spatial arrangement of spherical surface plate and differential structure. Furthermore, the signal acquisition and processing system of the capacitive tactile sensor is constructed based on the high performance capacitive digital converter AD7147-1 and STM32 microprocessor, and the characteristic test and the application of the proposed device are also conducted. The experiment results show that the high sensitivity tactile sensing of normal force and tangential force and high stability can be obtained by using the capacitive tactile sensor with the spherical surface plate with a fast response time of 70 ms, and the feasibility of the capacitive tactile sensor used as electric skin is further demonstrated.

 ISSN
ISSN