2020 Vol. 49, No. 1
2020, 49(1): 3-12.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020015
Abstract:
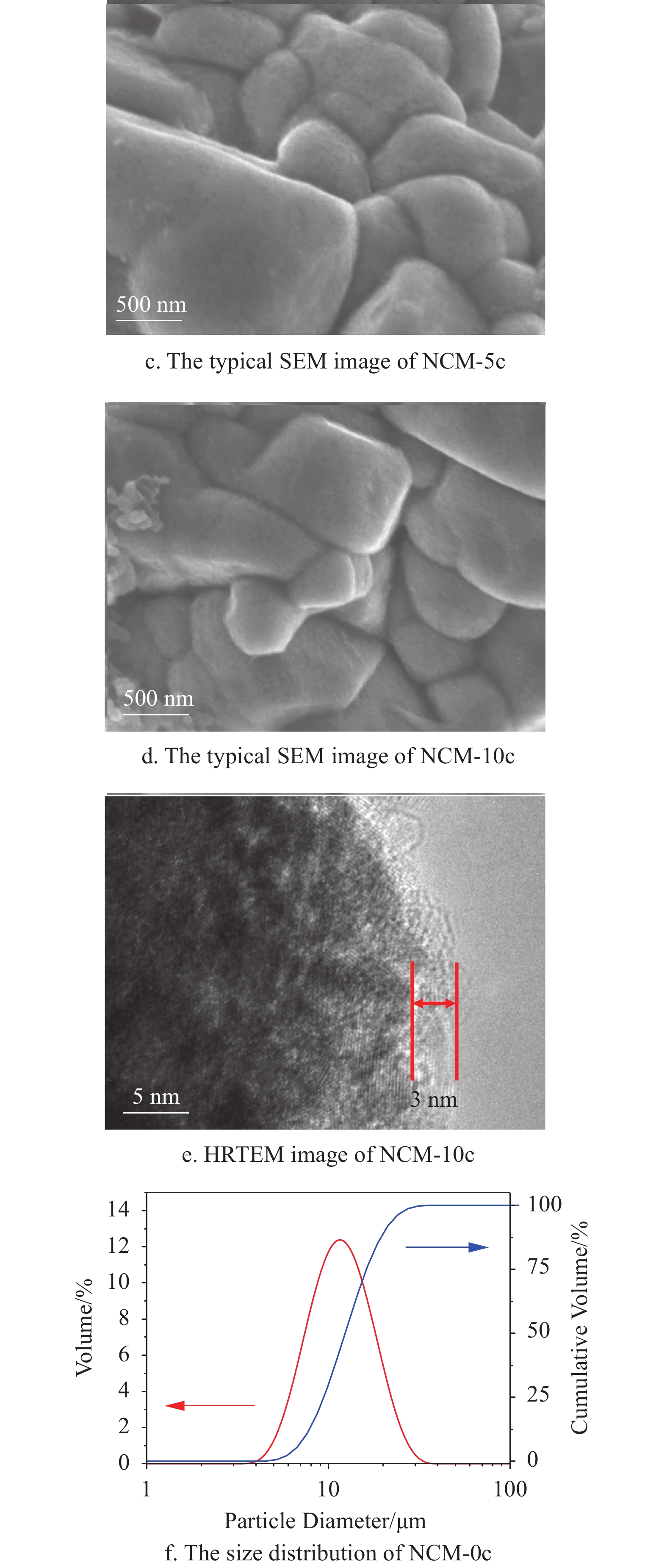
As one of the most promising cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries, LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 with high reversible capacity suffers poor cycling performances, especially at high cutoff potentials. To address this challenge, in this study, an atomic layer deposition is utilized to design controllable MgO coating layers onto LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode material. It is confirmed that the optimized LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode shows an improved electrochemical performance comparing with the pristine material at the cutoff potentials of 4.5 V as well as 4.7 V. After 100 cycles, the LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 with MgO coating displays the reversible capacities of 157 mAh·g−1 and 158 mAh·g−1 at the cutoff potential of 4.5 V and 4.7 V, respectively, which is higher than those of the pristine one (131 mAh·g−1 and 144 mAh·g−1). This study demonstrates that the ALD derived MgO coating layer shows some promising potentials to improve LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 performance for lithium ion batteries. This is mainly due to the effective protection of MgO layer to the material surface, that is, the MgO coating can stabilize the interface and block the metal ion dissolution by reducing the direct connection between LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 and electrolyte.
As one of the most promising cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries, LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 with high reversible capacity suffers poor cycling performances, especially at high cutoff potentials. To address this challenge, in this study, an atomic layer deposition is utilized to design controllable MgO coating layers onto LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode material. It is confirmed that the optimized LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode shows an improved electrochemical performance comparing with the pristine material at the cutoff potentials of 4.5 V as well as 4.7 V. After 100 cycles, the LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 with MgO coating displays the reversible capacities of 157 mAh·g−1 and 158 mAh·g−1 at the cutoff potential of 4.5 V and 4.7 V, respectively, which is higher than those of the pristine one (131 mAh·g−1 and 144 mAh·g−1). This study demonstrates that the ALD derived MgO coating layer shows some promising potentials to improve LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 performance for lithium ion batteries. This is mainly due to the effective protection of MgO layer to the material surface, that is, the MgO coating can stabilize the interface and block the metal ion dissolution by reducing the direct connection between LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 and electrolyte.
2020, 49(1): 13-21.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020016
Abstract:
Natural fatigue crack growth (NFCG) has been investigated extensively for decades due to its significant influence on the overall life of key components and the complex mechanism involved. In this study, a NFCG model based on the phenomenological observations of fatigue crack growth is first invoked, and a computational strategy is developed in the scaled boundary finite element method (SBFEM) context to simulate the NFCG phenomenon and to predict the fatigue life of specimen with different thicknesses under various cyclic loading conditions. The effects ascribed to the loading conditions, specimen thickness and material properties on the NFCG can be investigated in detail with the our elaborated strategy, which provides a helpful tool for practical specimen design, material selection and eddy current testing.
Natural fatigue crack growth (NFCG) has been investigated extensively for decades due to its significant influence on the overall life of key components and the complex mechanism involved. In this study, a NFCG model based on the phenomenological observations of fatigue crack growth is first invoked, and a computational strategy is developed in the scaled boundary finite element method (SBFEM) context to simulate the NFCG phenomenon and to predict the fatigue life of specimen with different thicknesses under various cyclic loading conditions. The effects ascribed to the loading conditions, specimen thickness and material properties on the NFCG can be investigated in detail with the our elaborated strategy, which provides a helpful tool for practical specimen design, material selection and eddy current testing.
2020, 49(1): 22-27.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018214
Abstract:
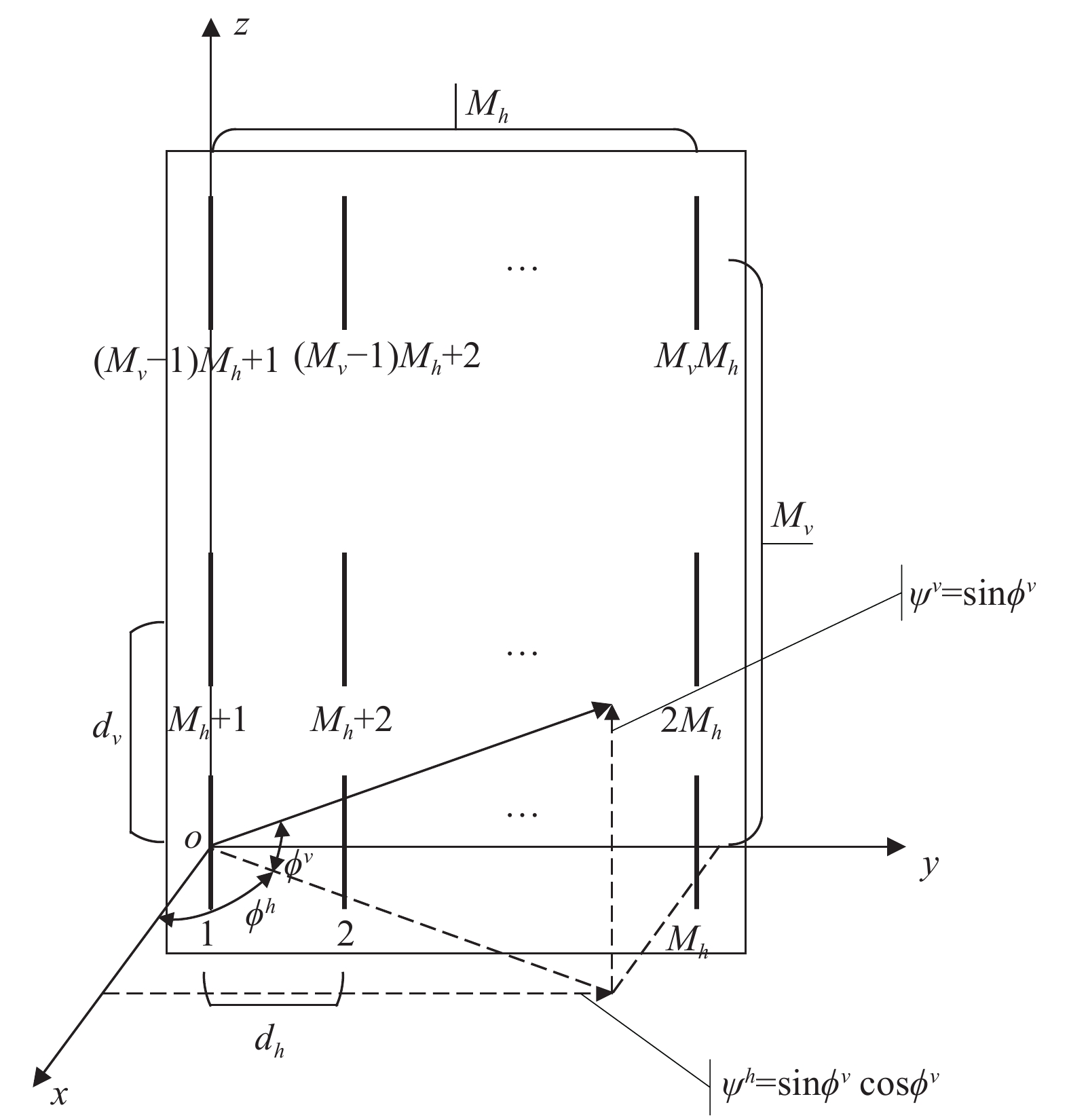
A precoding scheme for the FD-MIMO (full-dimension multiple input multiple output), limited-feedback systems is proposed and a determinant-based criterion of selecting precoding codeword is presented. This scheme can reveal the channel feature information more accurately after channel decomposition, select the codewords in the vertical and horizontal vectors by the presented criterion, and form the codeword structure in the form of Kronecker product. Furthermore, a formula for calculating the efficient number of the feedback is also proposed. The results of simulations show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and the proposed formula.
A precoding scheme for the FD-MIMO (full-dimension multiple input multiple output), limited-feedback systems is proposed and a determinant-based criterion of selecting precoding codeword is presented. This scheme can reveal the channel feature information more accurately after channel decomposition, select the codewords in the vertical and horizontal vectors by the presented criterion, and form the codeword structure in the form of Kronecker product. Furthermore, a formula for calculating the efficient number of the feedback is also proposed. The results of simulations show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and the proposed formula.
2020, 49(1): 28-35.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018241
Abstract:
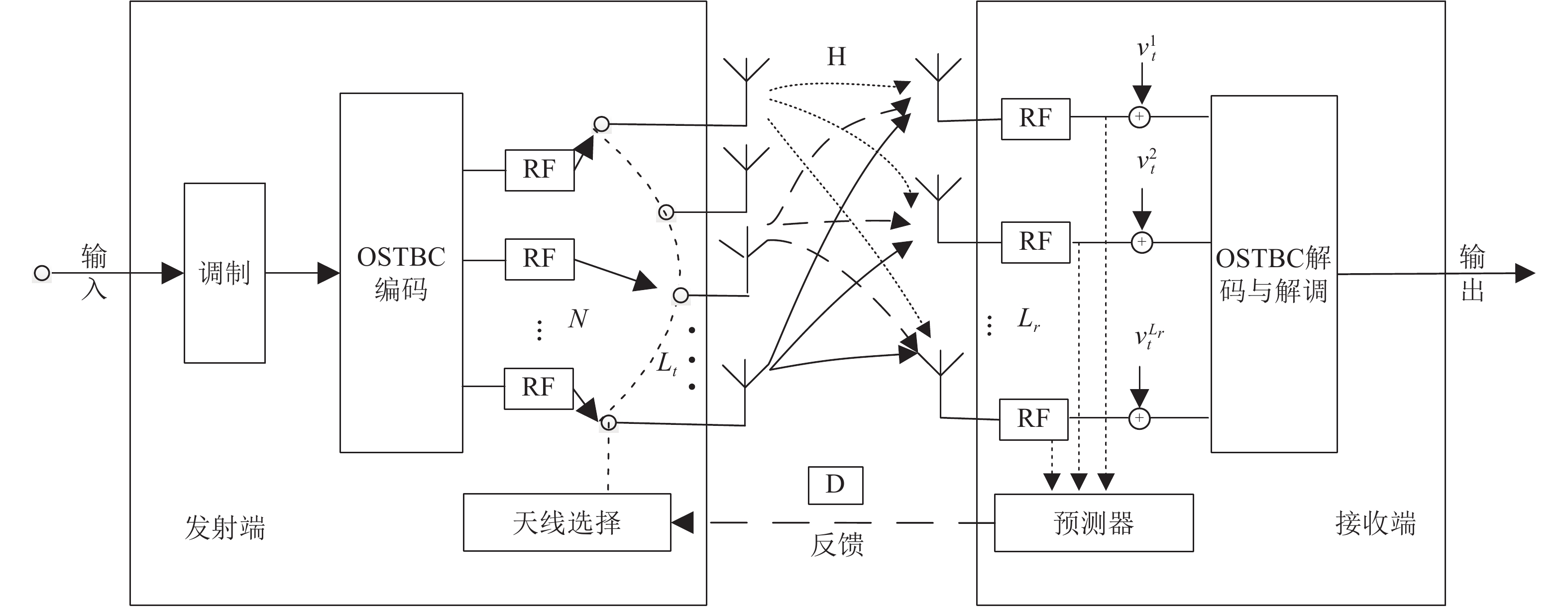
In order to design wireless communication systems with predictive transmit antenna selection (TAS) and orthogonal space-time block code (OSTBC) on Rayleigh block fading channel, the trade-off problem among the number of transmit/receive antennas, the block length, the length of minimum mean square error (MMSE) channel predictor needs to be considered. As a theoretical analysis tool, random coding error exponent (RCEE) can effectively solve the above problems. The closed-form expressions of RCEE of wireless communication systems with TAS/OSTBC on Rayleigh block fading channel are derived by using Meijer-G function and Tricomi hypergeometric function. The closed-form expressions of the relationship among RCEE and ergodic capacity, cut-off rate, expurgated exponent of the above systems are also developed. The numerical calculation and simulation results of the above performance parameters prove the correctness of the above theoretical analysis. The results also show that the RCEE of the TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system with channel prediction is larger than that of TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system under feedback delay. The required code length for the TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system can be calculated by using the expurgated exponent at the low information rate.
In order to design wireless communication systems with predictive transmit antenna selection (TAS) and orthogonal space-time block code (OSTBC) on Rayleigh block fading channel, the trade-off problem among the number of transmit/receive antennas, the block length, the length of minimum mean square error (MMSE) channel predictor needs to be considered. As a theoretical analysis tool, random coding error exponent (RCEE) can effectively solve the above problems. The closed-form expressions of RCEE of wireless communication systems with TAS/OSTBC on Rayleigh block fading channel are derived by using Meijer-G function and Tricomi hypergeometric function. The closed-form expressions of the relationship among RCEE and ergodic capacity, cut-off rate, expurgated exponent of the above systems are also developed. The numerical calculation and simulation results of the above performance parameters prove the correctness of the above theoretical analysis. The results also show that the RCEE of the TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system with channel prediction is larger than that of TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system under feedback delay. The required code length for the TAS/OSTBC wireless communication system can be calculated by using the expurgated exponent at the low information rate.
2020, 49(1): 36-41.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019053
Abstract:
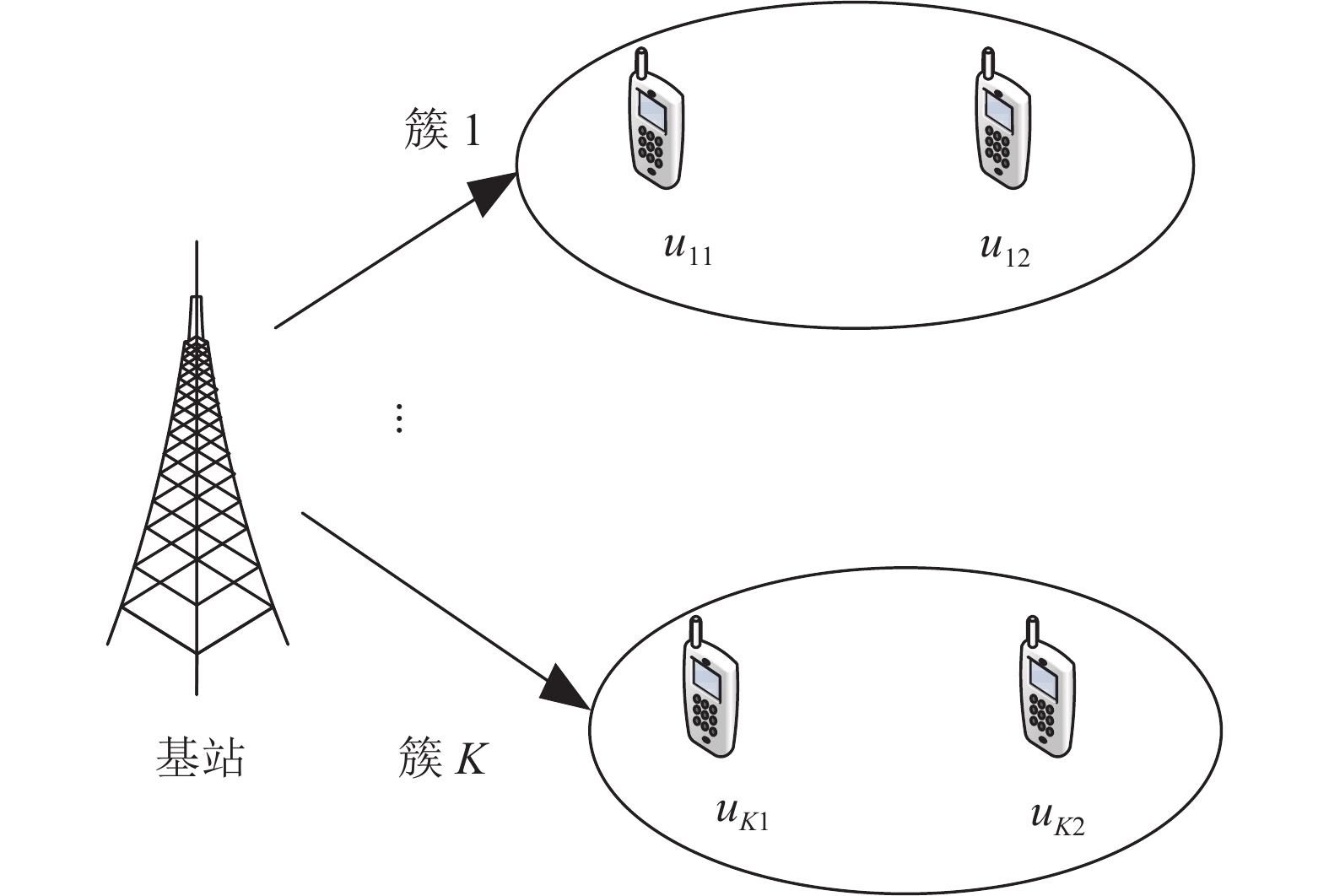
The minimum rate requirements of users are not taken into consideration in the existing power allocation schemes for maximum fairness of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. For this problem, the poa power allocation scheme for fairly improving user rate in NOMA systems is proposed. Firstly, the minimum power required for each cluster is calculated based on channel conditions and rate requirement for each user. Secondly, in the case of meeting the minimum rate requirements of all users, the power allocation optimization problem of improving each user’s rate fairly is established with the constraints of minimum power required by each cluster and the total power required by all clusters. Finally, the power allocation scheme, which satisfies the minimum rate demand of the user and maximizes the user's improved minimum rate, is obtained by adjusting the power of the part clusters. The simulation results show that when the minimum rate requirements of users are different, the increased rates of users and the outage probabilities of the proposed scheme both outperform these of the existing schemes in the same scenario.
The minimum rate requirements of users are not taken into consideration in the existing power allocation schemes for maximum fairness of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. For this problem, the poa power allocation scheme for fairly improving user rate in NOMA systems is proposed. Firstly, the minimum power required for each cluster is calculated based on channel conditions and rate requirement for each user. Secondly, in the case of meeting the minimum rate requirements of all users, the power allocation optimization problem of improving each user’s rate fairly is established with the constraints of minimum power required by each cluster and the total power required by all clusters. Finally, the power allocation scheme, which satisfies the minimum rate demand of the user and maximizes the user's improved minimum rate, is obtained by adjusting the power of the part clusters. The simulation results show that when the minimum rate requirements of users are different, the increased rates of users and the outage probabilities of the proposed scheme both outperform these of the existing schemes in the same scenario.
2020, 49(1): 42-48.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018060
Abstract:
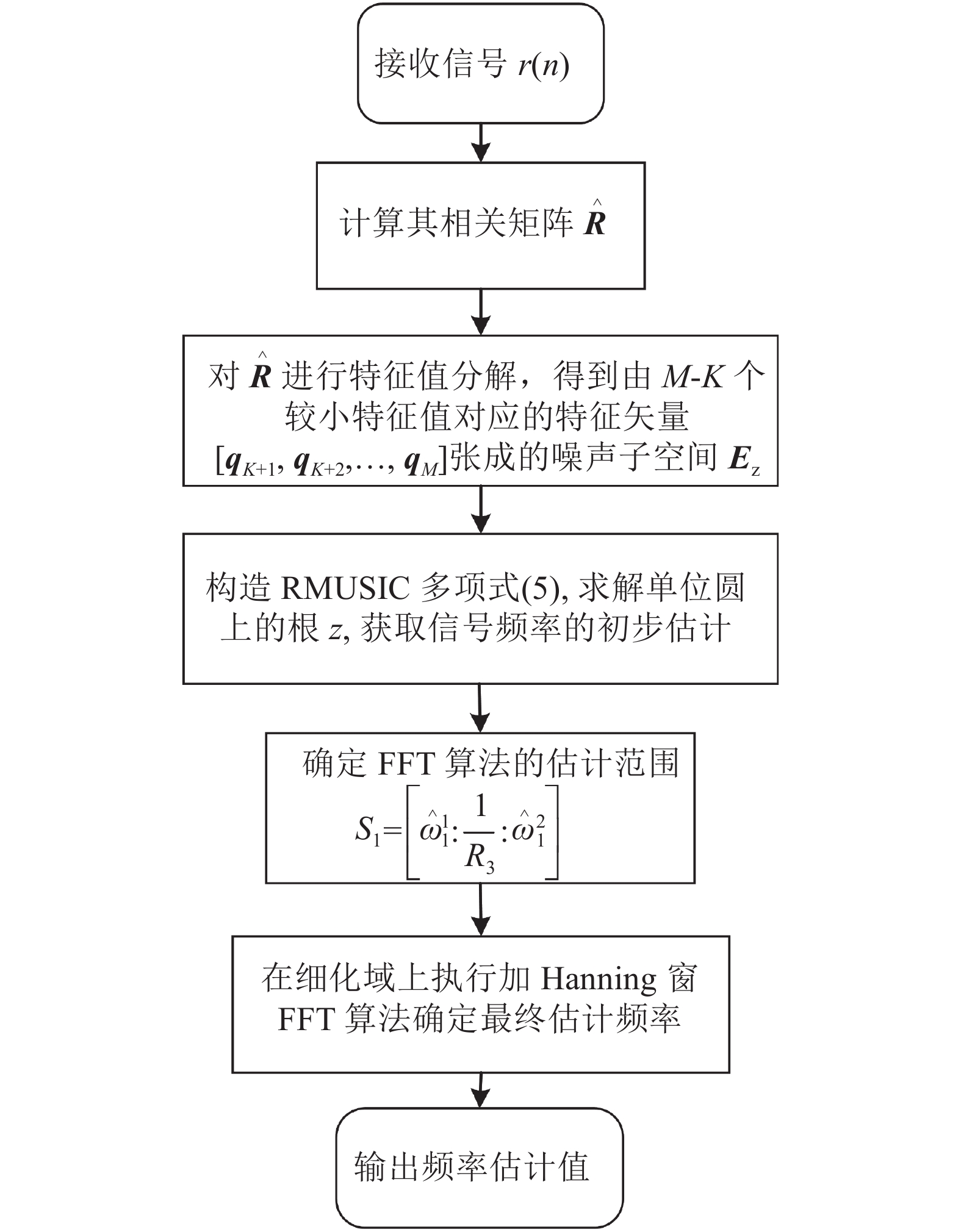
To meet the requirements of high-accuracy and real-time frequency estimation in high-speed digital demodulators, this paper analyzes the characteristics of subspace decomposition algorithms and proposes a novel high-accuracy frequency estimation algorithm that the root multiple signal classification ( root-MUSIC) algorithm and the estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques (ESPRIT) combined with fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm, respectively. Firstly, the root-MUSIC or the ESPRIT algorithm is applied to pre-estimate the signal frequency; then, the narrowband spectrum interested is determined; finally, the Hanning window with FFT algorithm is used to complete the accurate frequency search by the method of frequency refinement. In addition, in order to satisfy the conditions of different signal to noise ratios (SNRs) for high-accuracy frequency estimation, a new algorithm based on the optional construction is proposed. Simulation results show that not only is the estimation accuracy greatly improved compared to pre-existing algorithms because of notable anti-noise performance but also the processing time of the demodulator is reduced.
To meet the requirements of high-accuracy and real-time frequency estimation in high-speed digital demodulators, this paper analyzes the characteristics of subspace decomposition algorithms and proposes a novel high-accuracy frequency estimation algorithm that the root multiple signal classification ( root-MUSIC) algorithm and the estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques (ESPRIT) combined with fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm, respectively. Firstly, the root-MUSIC or the ESPRIT algorithm is applied to pre-estimate the signal frequency; then, the narrowband spectrum interested is determined; finally, the Hanning window with FFT algorithm is used to complete the accurate frequency search by the method of frequency refinement. In addition, in order to satisfy the conditions of different signal to noise ratios (SNRs) for high-accuracy frequency estimation, a new algorithm based on the optional construction is proposed. Simulation results show that not only is the estimation accuracy greatly improved compared to pre-existing algorithms because of notable anti-noise performance but also the processing time of the demodulator is reduced.
2020, 49(1): 49-55.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018109
Abstract:
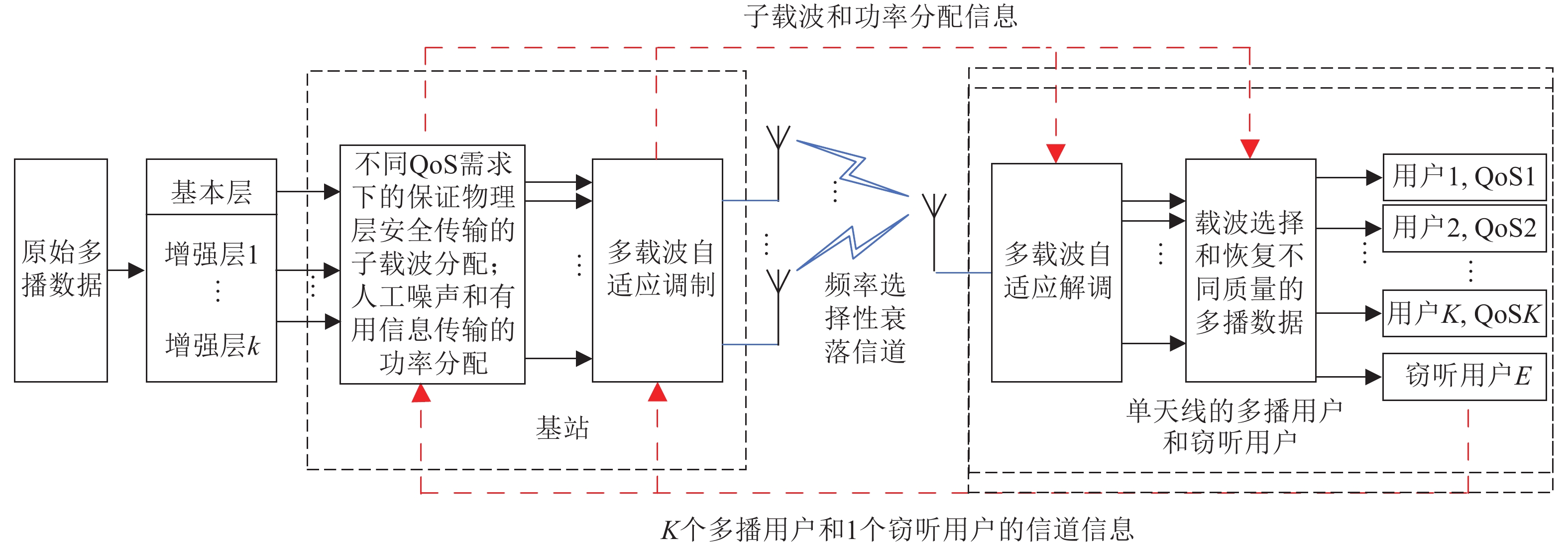
The total security throughput of multicast group is limited by the users with the worst channel quality. Moreover, traditional the artificial noise of physical layer security techniques for unicast transmission, do not apply well to multicast transmission. To solve this problem, we consider a layered coding based physical layer secure multicast algorithm. The algorithm can max security throughput of the entire multicast group, while ensuring the security of all users' quality of service (QoS) requirements. The simulation results show that the performance gap between the optimal algorithm and the suboptimal algorithm is very small. Moreover, the computational complexity of suboptimal algorithm is obviously reduced. The proposed algorithm is much better than the conventional multicast security scheme (CMSS). In addition, it achieves more throughput than another algorithm.
The total security throughput of multicast group is limited by the users with the worst channel quality. Moreover, traditional the artificial noise of physical layer security techniques for unicast transmission, do not apply well to multicast transmission. To solve this problem, we consider a layered coding based physical layer secure multicast algorithm. The algorithm can max security throughput of the entire multicast group, while ensuring the security of all users' quality of service (QoS) requirements. The simulation results show that the performance gap between the optimal algorithm and the suboptimal algorithm is very small. Moreover, the computational complexity of suboptimal algorithm is obviously reduced. The proposed algorithm is much better than the conventional multicast security scheme (CMSS). In addition, it achieves more throughput than another algorithm.
2020, 49(1): 56-63.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019084
Abstract:
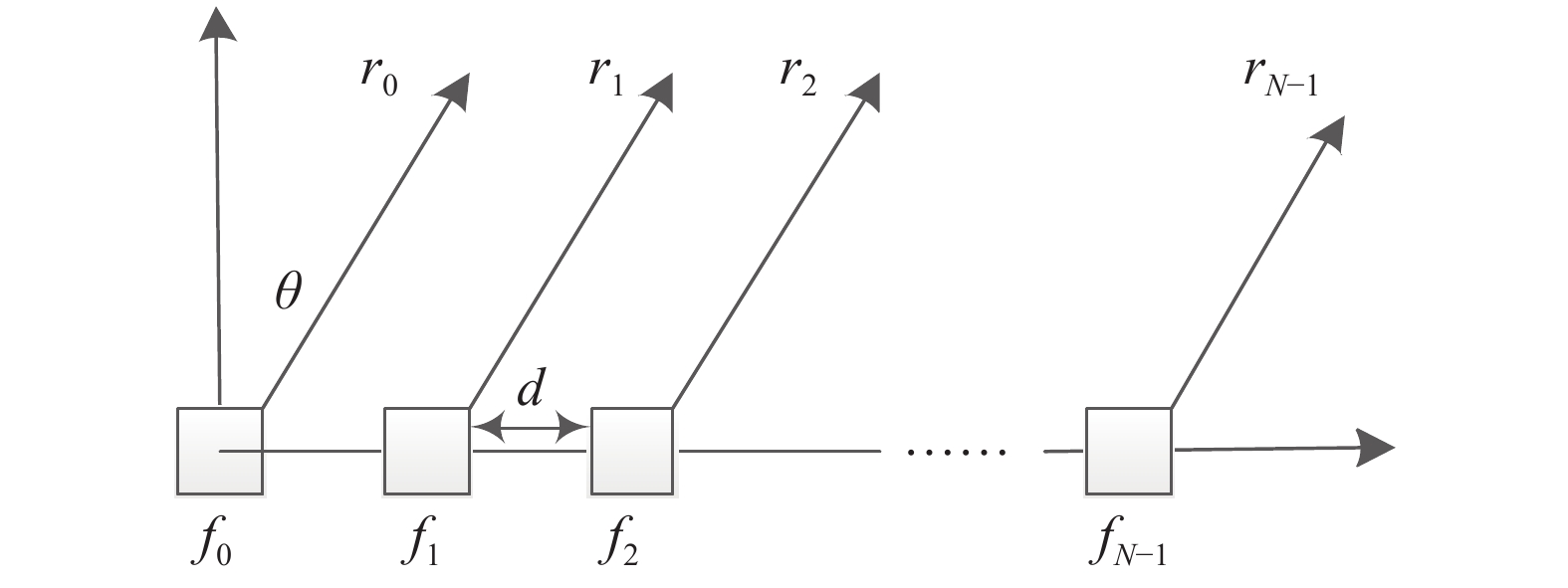
The research of frequency diverse array (FDA) in existing literature is mostly based on the hypothesis of simple pulse under narrowband conditions, but less on other pulse compression signals. Therefore, based on the establishment of the FDA array data model, this paper systematically derives the negative ambiguity function and its characteristics under the FDA-MIMO transmit/receive model. Then, based on the full-band coherent processing of the FDA radar architecture, the ambiguity function characteristics of rectangular pulses, linear frequency modulate (LFM), coherent pulse trains, and phase-encoded signals are simulated and analyzed. The adaptability of the above-mentioned typical pulse compression radar signals to the architecture is verified, which lays an important foundation for the follow-up FDA radar transmission waveform design and reactance characteristics optimization based on ambiguity function optimization.
The research of frequency diverse array (FDA) in existing literature is mostly based on the hypothesis of simple pulse under narrowband conditions, but less on other pulse compression signals. Therefore, based on the establishment of the FDA array data model, this paper systematically derives the negative ambiguity function and its characteristics under the FDA-MIMO transmit/receive model. Then, based on the full-band coherent processing of the FDA radar architecture, the ambiguity function characteristics of rectangular pulses, linear frequency modulate (LFM), coherent pulse trains, and phase-encoded signals are simulated and analyzed. The adaptability of the above-mentioned typical pulse compression radar signals to the architecture is verified, which lays an important foundation for the follow-up FDA radar transmission waveform design and reactance characteristics optimization based on ambiguity function optimization.
2020, 49(1): 64-70.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019107
Abstract:
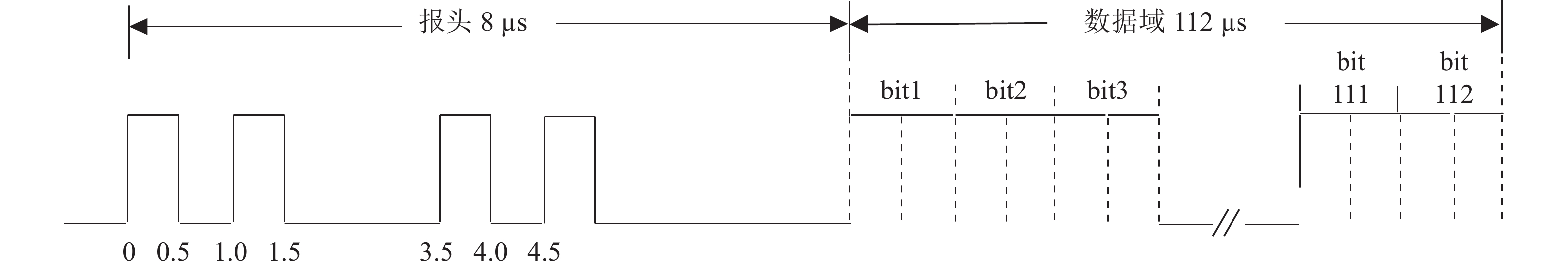
To solve the problem of low accuracy of space-based automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) signal decoding under low signal-to-noise ratio, the paper proposes a new inversion decoding method. It supposed that the ADS-B signal transmission space is a stable linear system during the transmission period, and the received signal is convoluted by the space system and transmitted ADS-B signal. According to this idea, the inversion decoding includes signal preamble detection, space system parameters estimation, signal inversion, pulse waveform correction. A simulation experiment was conducted. In the experiment, the accuracy ADS-B decoding pulse sequence was extracted and the decoding correctness rate was much higher than the mono-pulse detection method. The results verified the validity of the proposed inversion decoding method.
To solve the problem of low accuracy of space-based automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) signal decoding under low signal-to-noise ratio, the paper proposes a new inversion decoding method. It supposed that the ADS-B signal transmission space is a stable linear system during the transmission period, and the received signal is convoluted by the space system and transmitted ADS-B signal. According to this idea, the inversion decoding includes signal preamble detection, space system parameters estimation, signal inversion, pulse waveform correction. A simulation experiment was conducted. In the experiment, the accuracy ADS-B decoding pulse sequence was extracted and the decoding correctness rate was much higher than the mono-pulse detection method. The results verified the validity of the proposed inversion decoding method.
2020, 49(1): 71-80.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018102
Abstract:
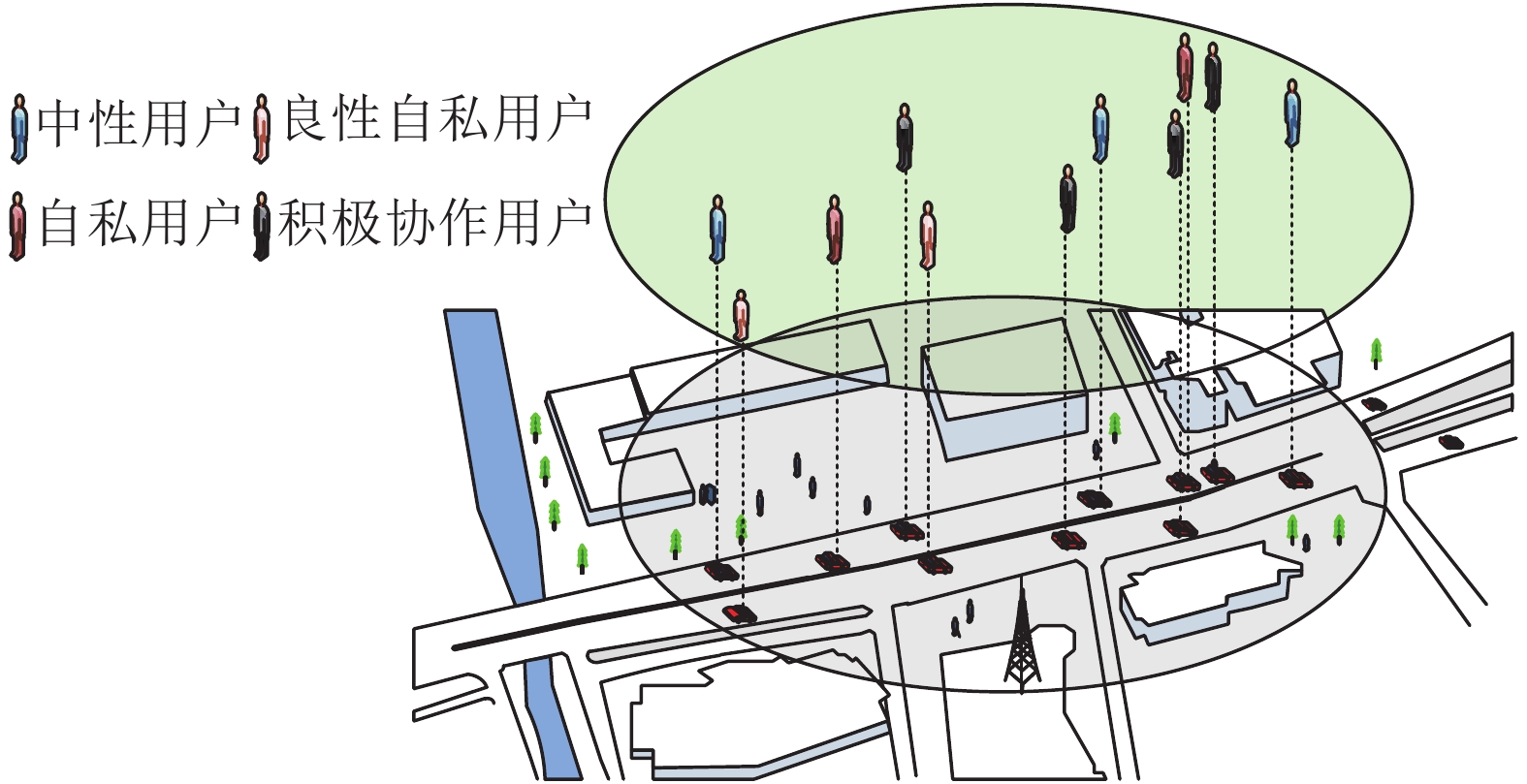
To solve the problem of the low data transmission rate due to the selfish behavior of relay users in vehicular cooperative communication, an optimal relay selection algorithm based on credit card risk assessment is proposed. At the first, a D2D relay cooperative two-layer (social network and physical layer) model is set up to describe the human behavior characteristics of the vehicle nodes. And then, the relay’s trust is evaluated by applying the credit risk assessment mechanism from business requirements perspective, relay’s credit levels are rated by the decision theory. On the other hand, the relays with good credit are compensated and motivated from the relay’s perspective. Finally, the optimal relay with high trust and reasonable price is selected. The numerical simulation results show that the data transmission rate of the proposed algorithm is increased about 10% compared with those that only the active relays are selected.
To solve the problem of the low data transmission rate due to the selfish behavior of relay users in vehicular cooperative communication, an optimal relay selection algorithm based on credit card risk assessment is proposed. At the first, a D2D relay cooperative two-layer (social network and physical layer) model is set up to describe the human behavior characteristics of the vehicle nodes. And then, the relay’s trust is evaluated by applying the credit risk assessment mechanism from business requirements perspective, relay’s credit levels are rated by the decision theory. On the other hand, the relays with good credit are compensated and motivated from the relay’s perspective. Finally, the optimal relay with high trust and reasonable price is selected. The numerical simulation results show that the data transmission rate of the proposed algorithm is increased about 10% compared with those that only the active relays are selected.
2020, 49(1): 81-86.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018106
Abstract:
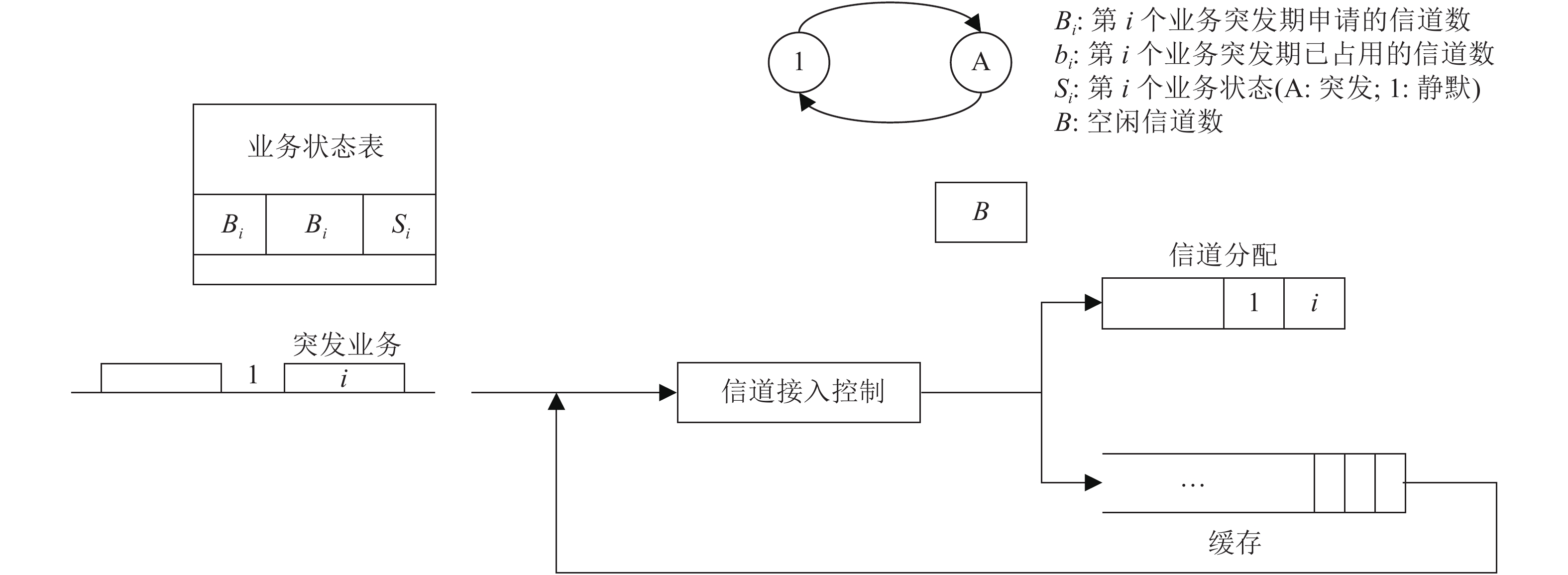
Wireless traffic channel access control algorithm based on statistical multiplexing is very important for improving the capacity of wireless communication network, link utilization and system stability. According to the one-time-discriminate used on existing iteration traffic access control algorithm, which may cause the shortage of the traffic channel been accepted by system acceptance, the improved scheme been analyzed and simulated by flow model is put forward by repeatedly discrimination in silent period with setting the cache. The simulation results show that the improved algorithm obviously reduces the loss probability of data caused by multi-service simultaneous burst.
Wireless traffic channel access control algorithm based on statistical multiplexing is very important for improving the capacity of wireless communication network, link utilization and system stability. According to the one-time-discriminate used on existing iteration traffic access control algorithm, which may cause the shortage of the traffic channel been accepted by system acceptance, the improved scheme been analyzed and simulated by flow model is put forward by repeatedly discrimination in silent period with setting the cache. The simulation results show that the improved algorithm obviously reduces the loss probability of data caused by multi-service simultaneous burst.
2020, 49(1): 87-91.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018004
Abstract:
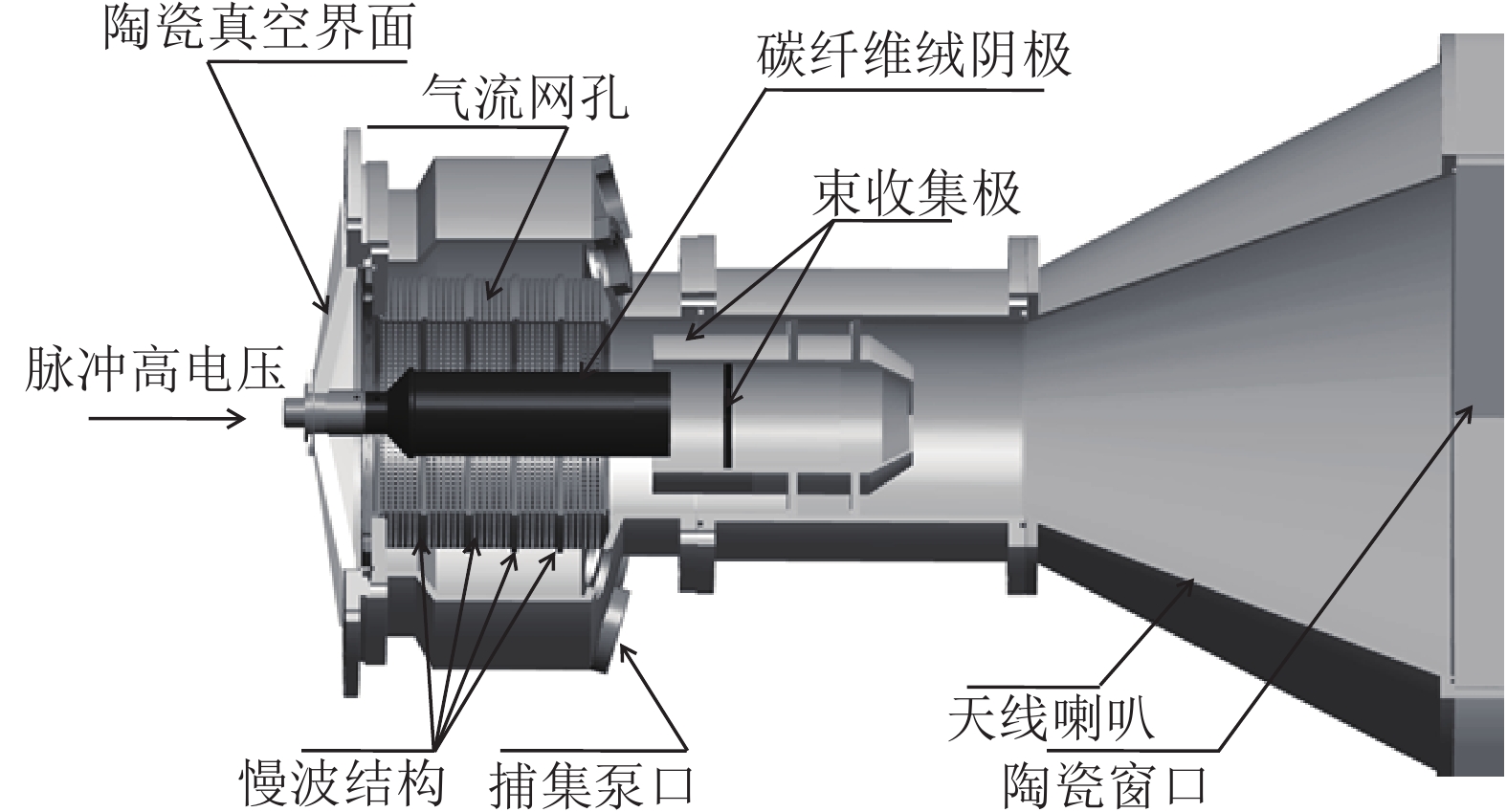
A compact L-band sealed-tube magnetically insulated transmission line oscillator (MILO) has been developed that does not require bulky external vacuum pump for repetitive operations. A special designed ceramic insulated vacuum interface was designed and the flashover was well controlled. A dynamic 3-D Monte-Carlo (MC) model for the molecular flow movement and collision was setup for the MILO chamber. The pulse desorption, gas evolution and pressure distribution were exactly simulated. In the 5 Hz repetition rate experiments, using a ~30 GW pulse modulator, the average radiated microwave power for 25 shots is about 3 GW in 40 ns pulse duration and the maximum equilibrium pressure is below 4.0×10−2 Pa. This sealed-tube MILO device is useful for compact and portable high-power microwave applications.
A compact L-band sealed-tube magnetically insulated transmission line oscillator (MILO) has been developed that does not require bulky external vacuum pump for repetitive operations. A special designed ceramic insulated vacuum interface was designed and the flashover was well controlled. A dynamic 3-D Monte-Carlo (MC) model for the molecular flow movement and collision was setup for the MILO chamber. The pulse desorption, gas evolution and pressure distribution were exactly simulated. In the 5 Hz repetition rate experiments, using a ~30 GW pulse modulator, the average radiated microwave power for 25 shots is about 3 GW in 40 ns pulse duration and the maximum equilibrium pressure is below 4.0×10−2 Pa. This sealed-tube MILO device is useful for compact and portable high-power microwave applications.
2020, 49(1): 92-97.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018250
Abstract:
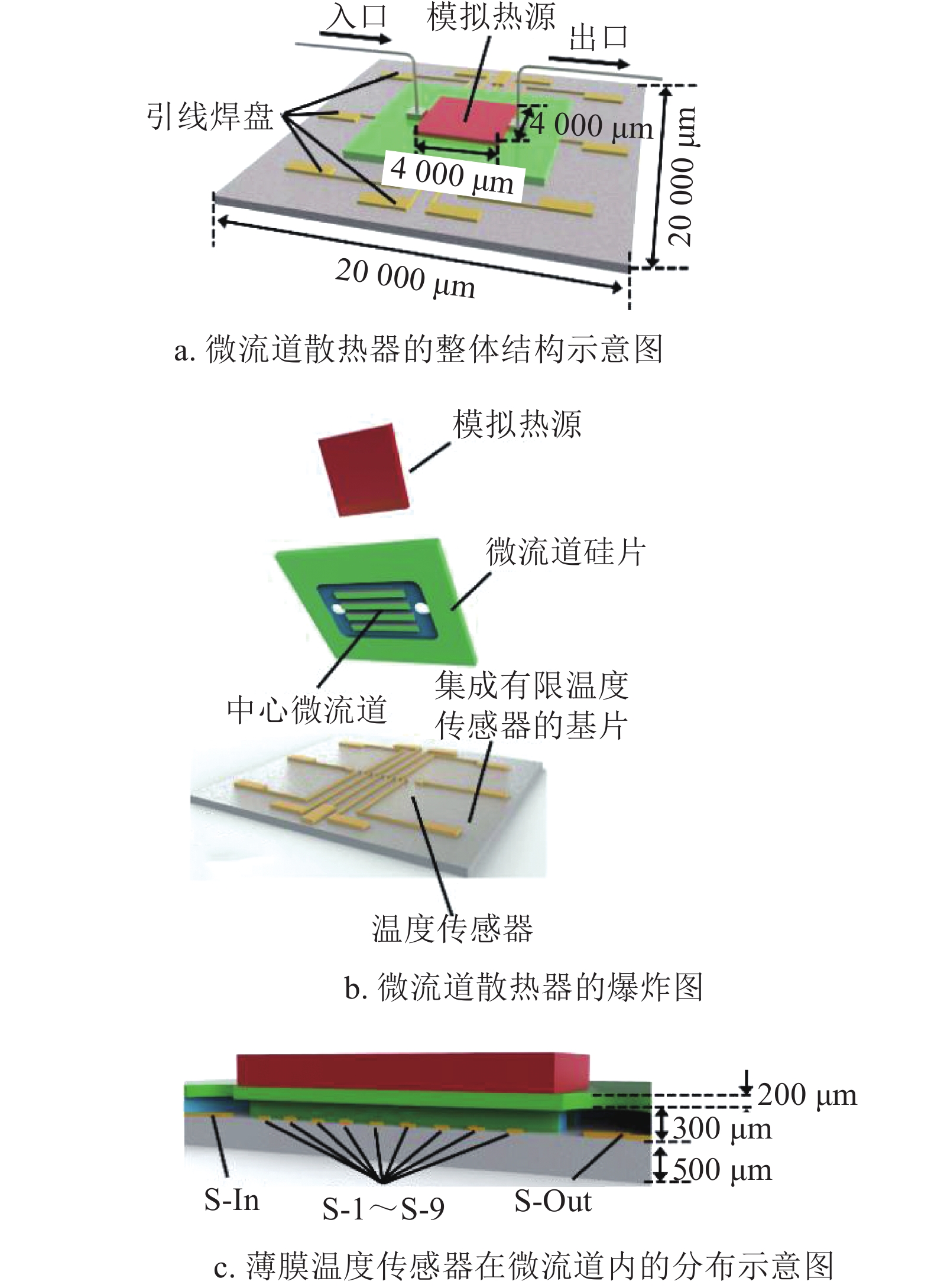
The silicon microchannel in this paper is fabricated by laser process. The thin-film temperature sensors are integrated in the internal surface of microchannel by micro-machined technique. The heat dissipation performances of microchannel fabricated by laser process and deep reactive iron etching (DRIE) are experimentally tested respectively in different flow rates and heat fluxes. The experiment results represent that the rough internal surface of microchannel can effectively decrease the thermal resistance. Under the same condition, the thermal resistance can reduce by almost 50% when compared with the microchannel heat sink fabricated by DRIE. The temperature sensors integrated in microchannel can accurately capture temperature change in real time and reflect the temperature distribution in microchannel. It provides a new method to optimize the design of microchannel.
The silicon microchannel in this paper is fabricated by laser process. The thin-film temperature sensors are integrated in the internal surface of microchannel by micro-machined technique. The heat dissipation performances of microchannel fabricated by laser process and deep reactive iron etching (DRIE) are experimentally tested respectively in different flow rates and heat fluxes. The experiment results represent that the rough internal surface of microchannel can effectively decrease the thermal resistance. Under the same condition, the thermal resistance can reduce by almost 50% when compared with the microchannel heat sink fabricated by DRIE. The temperature sensors integrated in microchannel can accurately capture temperature change in real time and reflect the temperature distribution in microchannel. It provides a new method to optimize the design of microchannel.
2020, 49(1): 98-101.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019044
Abstract:
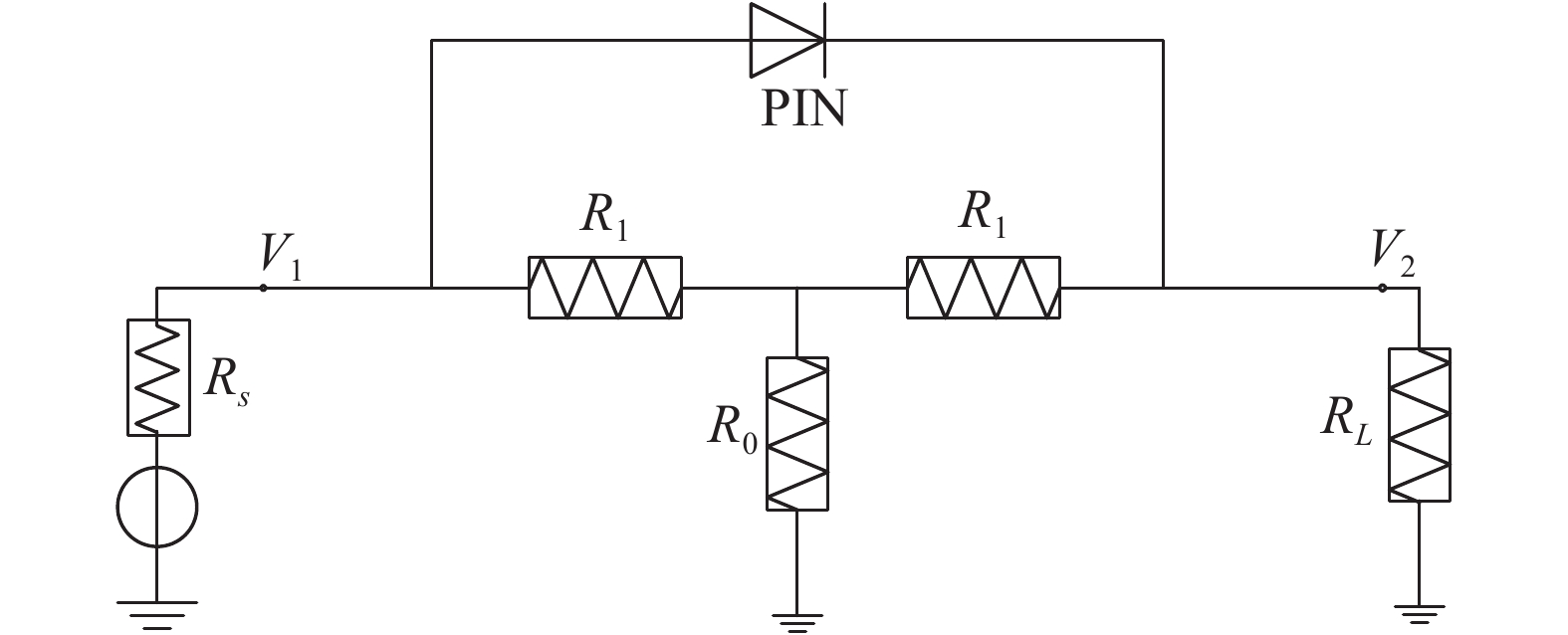
This paper presents the design of an ultra-broadband T-type analog linearizer with detailed analysis and simulation. The proposed structure, which is mainly composed of tee-attenuator and PIN diode, can achieve the amplitude expansion and phase compression. Featuring a simple bias circuit and good return loss of both two ports, the designed linearizer operates in the 0.8 GHz to 2 GHz frequency range. The test results confirm that 5 dB amplitude expansion and 18°phase compression can be achieved respectively in this way.
This paper presents the design of an ultra-broadband T-type analog linearizer with detailed analysis and simulation. The proposed structure, which is mainly composed of tee-attenuator and PIN diode, can achieve the amplitude expansion and phase compression. Featuring a simple bias circuit and good return loss of both two ports, the designed linearizer operates in the 0.8 GHz to 2 GHz frequency range. The test results confirm that 5 dB amplitude expansion and 18°phase compression can be achieved respectively in this way.
2020, 49(1): 102-109.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018199
Abstract:
In order to solve the problem of complex insulation fault type recognition and redundancy of feature selection of cable accessories insulation defects, a method to recognize the fault of insulation defects by directly using the partial discharge signal containing the noise is proposed in this paper. The signals in three power frequency cycles are selected as a sample. The discharge pulse is firstly extracted by using mathematical morphological filtering technology to obtain two statistical characteristics of average discharge and discharge times. At the same time, the Hurst exponent is used to judge the fractality of partial discharge signals. If the condition is satisfied, the box dimension is directly obtained as a fractal feature. Finally, three features are imported into the extension neural network for pattern recognition to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the method. The results show that the three features of box dimension, average discharge, and discharge times have strong separability, which can solve the problem of redundancy of feature selection, and the extension neural network can identify different types of insulation defects, and the recognition rate is better than that of similar methods based on support vector machine and BP neural network.
In order to solve the problem of complex insulation fault type recognition and redundancy of feature selection of cable accessories insulation defects, a method to recognize the fault of insulation defects by directly using the partial discharge signal containing the noise is proposed in this paper. The signals in three power frequency cycles are selected as a sample. The discharge pulse is firstly extracted by using mathematical morphological filtering technology to obtain two statistical characteristics of average discharge and discharge times. At the same time, the Hurst exponent is used to judge the fractality of partial discharge signals. If the condition is satisfied, the box dimension is directly obtained as a fractal feature. Finally, three features are imported into the extension neural network for pattern recognition to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the method. The results show that the three features of box dimension, average discharge, and discharge times have strong separability, which can solve the problem of redundancy of feature selection, and the extension neural network can identify different types of insulation defects, and the recognition rate is better than that of similar methods based on support vector machine and BP neural network.
2020, 49(1): 110-116.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019109
Abstract:
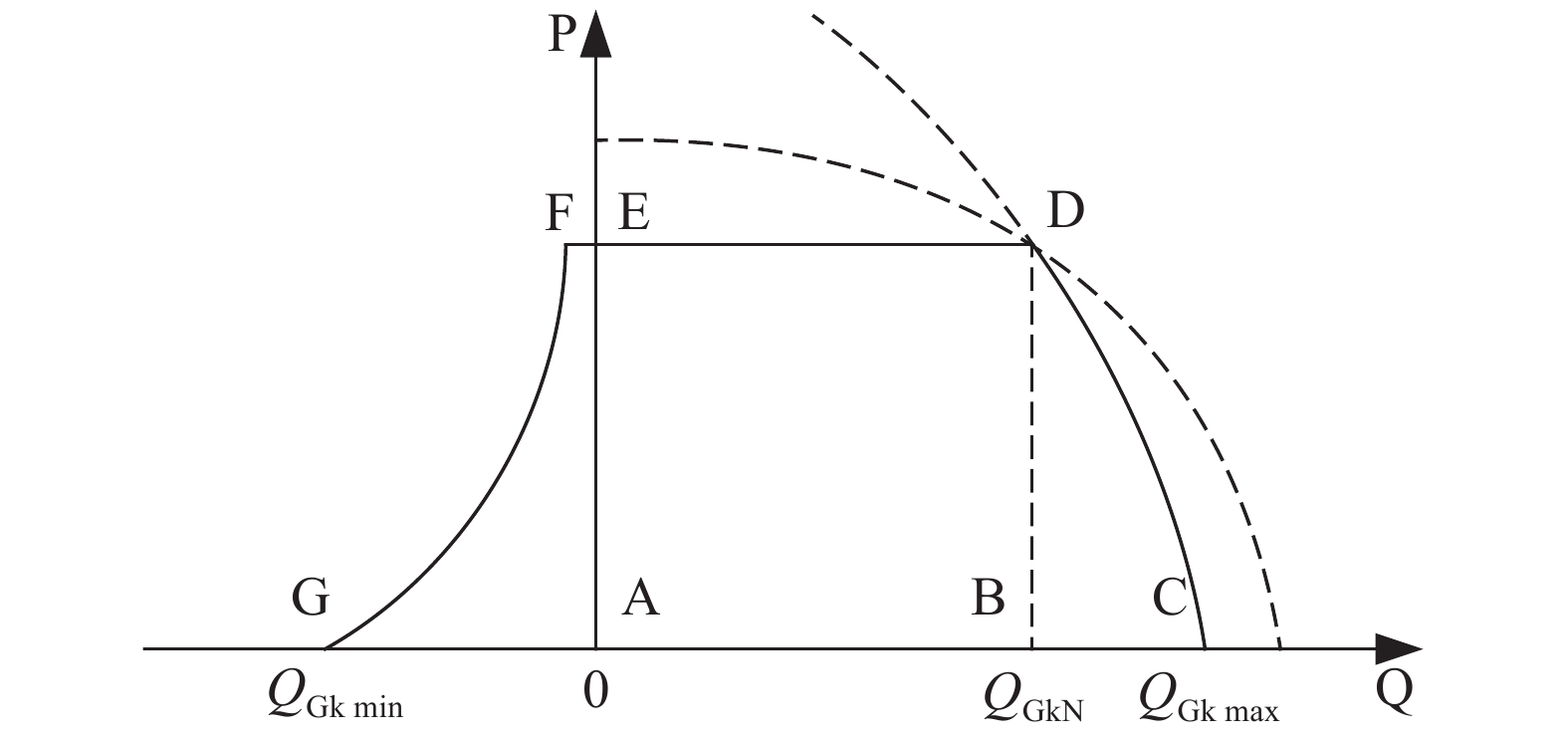
In the context of the gradual improvement of the electricity market, formulating pricing principle for reactive voltage regulating equipment can balance the profits of power generation enterprise and power supply companies and reduce the cost of reactive power. By considering the P-Q characteristics of DFIG and synchronous motor, a generator reactive power pricing model is established, and a DFIG reactive power segment pricing strategy in case of wind speed fluctuation is proposed. A dynamic reactive power optimization model for power system with wind farm is established, whose objective function are generator reactive power cost, discrete variable action depreciation price, active power network loss combined cost and total node voltage deviation. A new improved HPSO algorithm is proposed to solve the dynamic reactive power optimization model, which improves the global optimization ability and convergence speed. Finally, the IEEE30 node is taken as an example to analyze the effectiveness of the proposed model, strategy and algorithm is verified with simulation on MATLAB.
In the context of the gradual improvement of the electricity market, formulating pricing principle for reactive voltage regulating equipment can balance the profits of power generation enterprise and power supply companies and reduce the cost of reactive power. By considering the P-Q characteristics of DFIG and synchronous motor, a generator reactive power pricing model is established, and a DFIG reactive power segment pricing strategy in case of wind speed fluctuation is proposed. A dynamic reactive power optimization model for power system with wind farm is established, whose objective function are generator reactive power cost, discrete variable action depreciation price, active power network loss combined cost and total node voltage deviation. A new improved HPSO algorithm is proposed to solve the dynamic reactive power optimization model, which improves the global optimization ability and convergence speed. Finally, the IEEE30 node is taken as an example to analyze the effectiveness of the proposed model, strategy and algorithm is verified with simulation on MATLAB.
2020, 49(1): 117-122.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019156
Abstract:
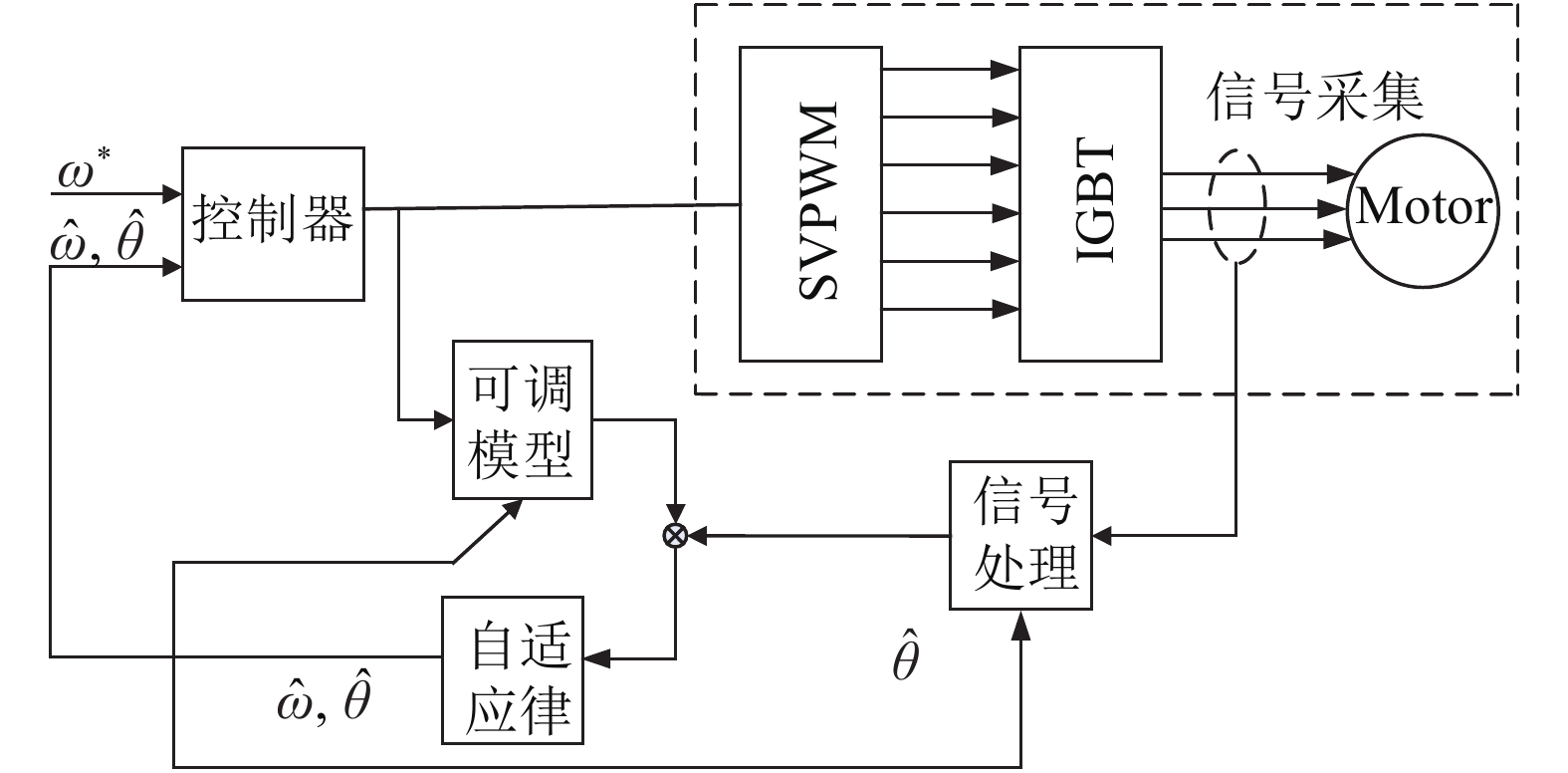
The common speed sensor-less motor control methods are introduced and classified according to parameter robustness and system anti-interference ability. Completely dependent on the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms have poor robustness and weak anti-noise ability. Partially dependent on the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms are divided into four methods. The model reference adaptation system (MRAS) is introduced, and the model reference adaptive system and sliding mode observer are simulated. Two high-frequency signal algorithms and some artificial intelligence algorithms independent of the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms are described. The advantages, disadvantages and applicability of each algorithm are summarized.
The common speed sensor-less motor control methods are introduced and classified according to parameter robustness and system anti-interference ability. Completely dependent on the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms have poor robustness and weak anti-noise ability. Partially dependent on the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms are divided into four methods. The model reference adaptation system (MRAS) is introduced, and the model reference adaptive system and sliding mode observer are simulated. Two high-frequency signal algorithms and some artificial intelligence algorithms independent of the physical parameters of the motor and the electromagnetic equation speed estimation algorithms are described. The advantages, disadvantages and applicability of each algorithm are summarized.
2020, 49(1): 123-130.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019131
Abstract:
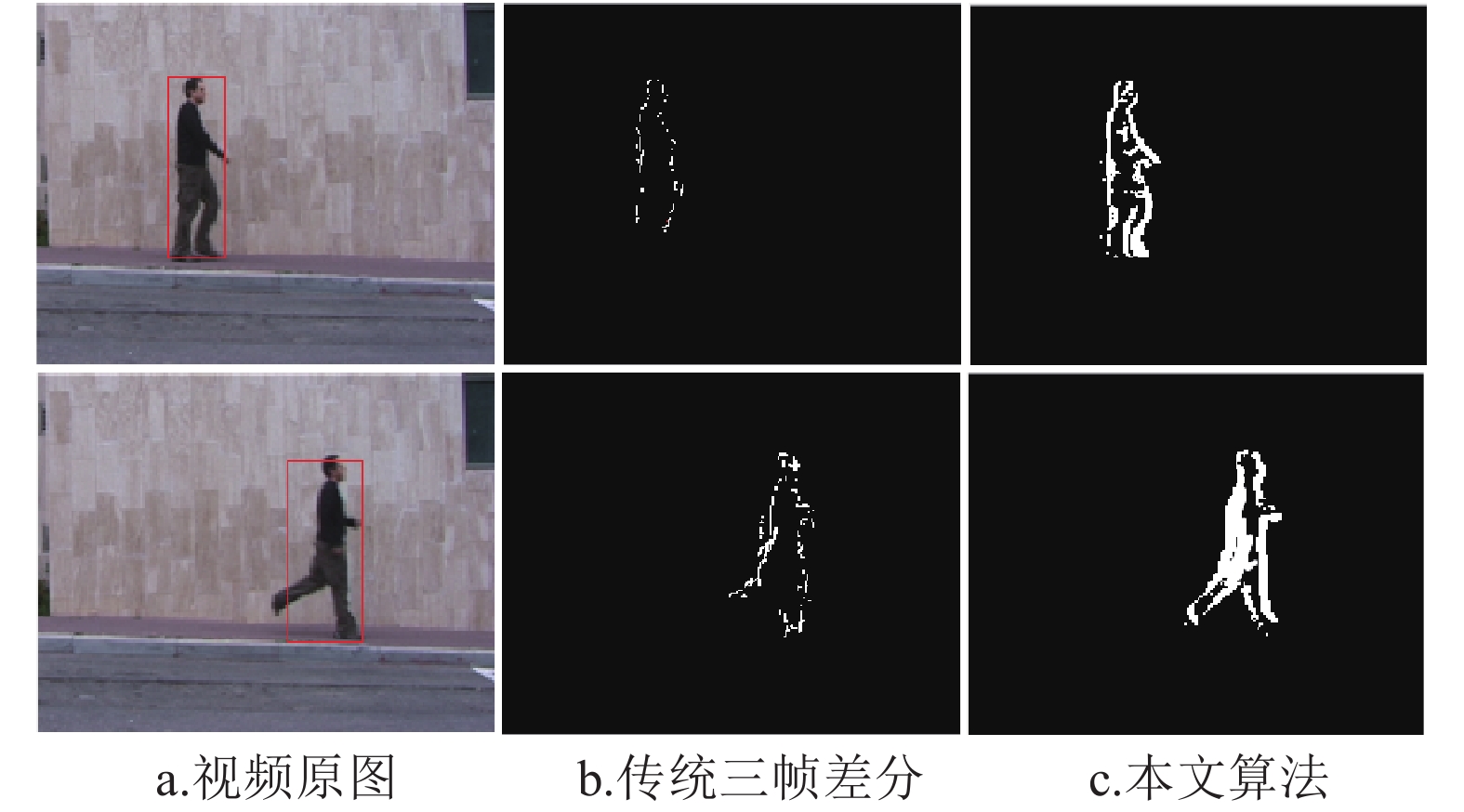
This paper proposes a three-frame difference method based on adaptive learning rate Gaussian mixture modeling. Through the Gaussian mixture background modeling based on adaptive learning rate, the adaptive correction of the background model is realized, and the algorithm can completely extract the internal information of the target in the dynamic environment. Then, the three-frame difference improvement algorithm based on edge extraction is used to extract the target contour rapidly and use it as the edge complement. The experimental results show that the algorithm can completely extract moving targets and ensure the continuity and smoothness of the target edges. At the same time, the speed of target detection is increased, and it can be widely used in intelligent video surveillance, medical treatment and other fields.
This paper proposes a three-frame difference method based on adaptive learning rate Gaussian mixture modeling. Through the Gaussian mixture background modeling based on adaptive learning rate, the adaptive correction of the background model is realized, and the algorithm can completely extract the internal information of the target in the dynamic environment. Then, the three-frame difference improvement algorithm based on edge extraction is used to extract the target contour rapidly and use it as the edge complement. The experimental results show that the algorithm can completely extract moving targets and ensure the continuity and smoothness of the target edges. At the same time, the speed of target detection is increased, and it can be widely used in intelligent video surveillance, medical treatment and other fields.
2020, 49(1): 131-138.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019164
Abstract:
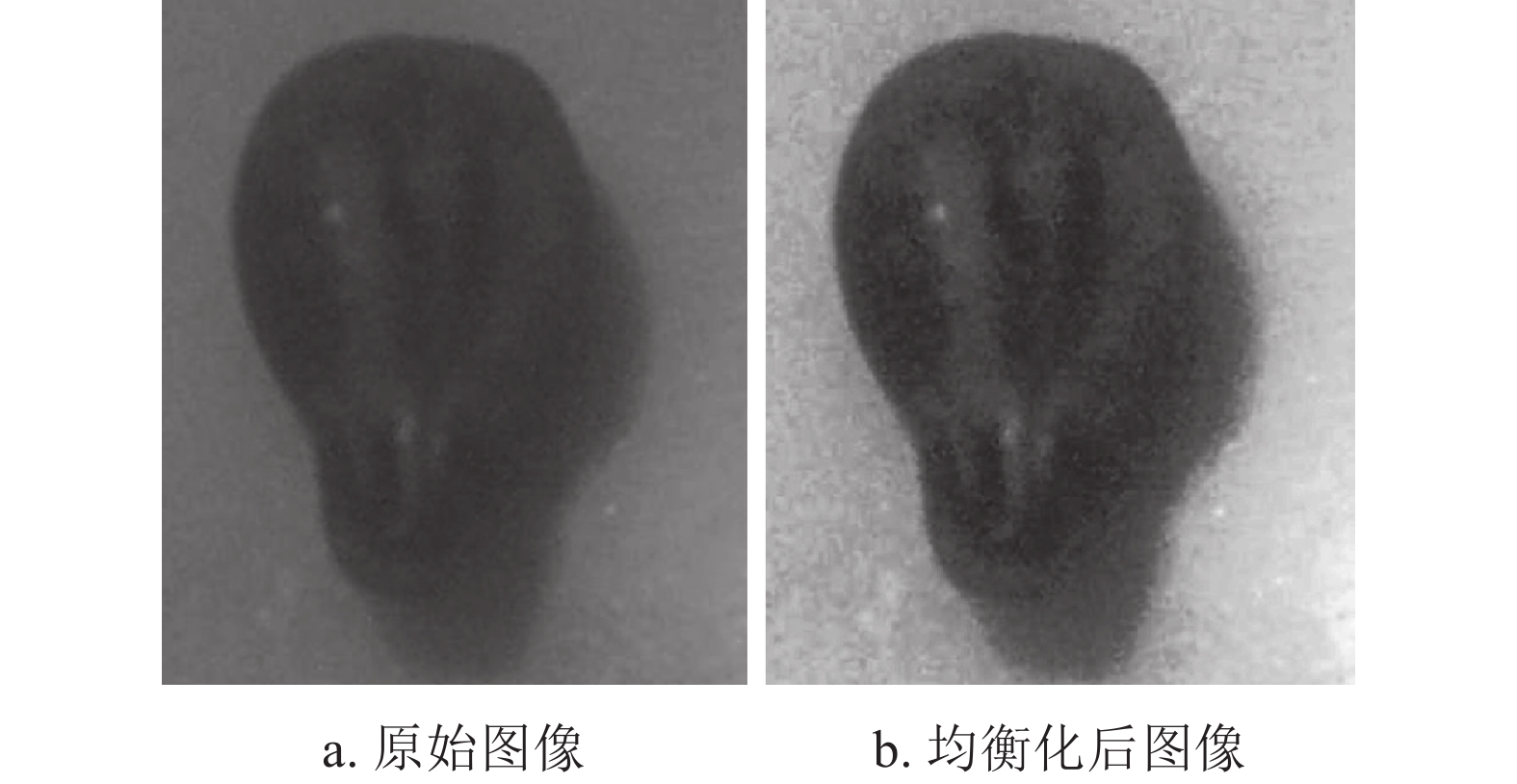
Seed maturity has a great influence on the quality of wine, and it needs to be observed and judged by the naked eye by experts who have been trained for a long time. In order to change the way of traditional artificial experience judgment, a grape seed image classification and recognition algorithm based on Gabor wavelet feature extraction and deep neural network is proposed to achieve efficient and accurate classification and recognition. First, the background difference method is used to segment the interest target in the background image, thereby completing the image preprocessing. Then, the improved Gabor wavelet feature extraction makes the Gabor filtered image have more detailed texture information. Finally, the deep convolutional neural network and the extracted texture feature information are combined to classify. The experimental results show that the recognition of grape seed maturity based on machine learning is feasible. The proposed image classification accuracy exhibits a certain improvement compared with other similar classification algorithms.
Seed maturity has a great influence on the quality of wine, and it needs to be observed and judged by the naked eye by experts who have been trained for a long time. In order to change the way of traditional artificial experience judgment, a grape seed image classification and recognition algorithm based on Gabor wavelet feature extraction and deep neural network is proposed to achieve efficient and accurate classification and recognition. First, the background difference method is used to segment the interest target in the background image, thereby completing the image preprocessing. Then, the improved Gabor wavelet feature extraction makes the Gabor filtered image have more detailed texture information. Finally, the deep convolutional neural network and the extracted texture feature information are combined to classify. The experimental results show that the recognition of grape seed maturity based on machine learning is feasible. The proposed image classification accuracy exhibits a certain improvement compared with other similar classification algorithms.
2020, 49(1): 139-154.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019187
Abstract:
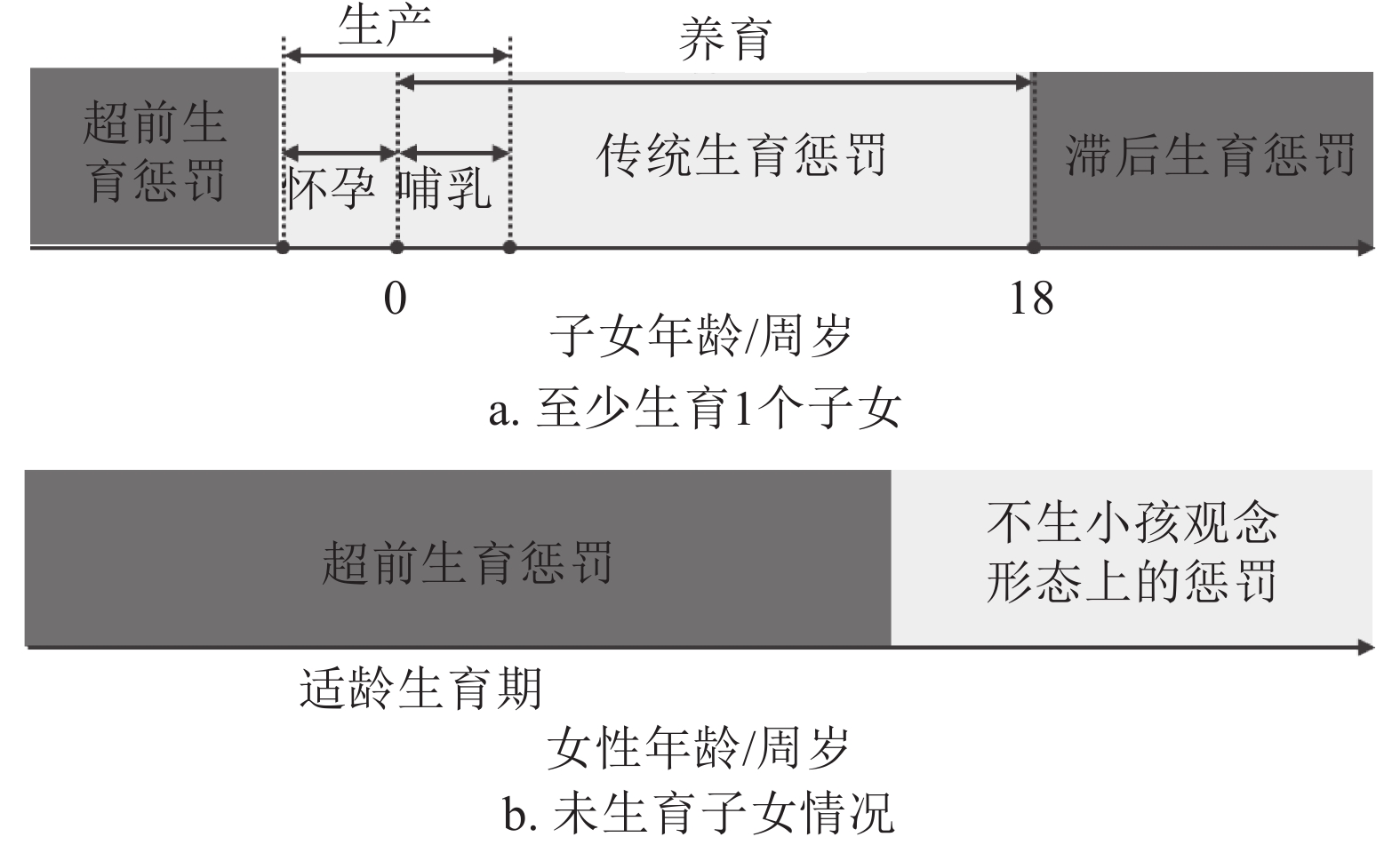
The gender gap in labor market is an important issue in gender inequality. It will also enlarge gender differences in other fields. Among them, motherhood penalty refers to the negative impacts of the birth event on women career development, which could explain a considerable part of the gender gap within labor market. Although extensive studies have been accomplished, a comprehensive landscape of this domain has not yet been built. In this survey, the related progresses, including the quantification and comparison of motherhood penalty in different times and regions are presented and the main factors affecting the strength of motherhood penalty from the individual, family and political perspectives are discussed, where the emphasis is put on Chinese situations. Concentrating on the contradiction between labor and labor, this survey summarizes the known explanations into three different yet related theories: family restriction theory, human capital theory and employer discrimination theory. From the supply and demand sides of the labor market, we suggest two ways, namely empowering women and creating opportunities, to help women balance their family and working duties. Lastly, we propose political recommendations and outline a number of open issues for future researches.
The gender gap in labor market is an important issue in gender inequality. It will also enlarge gender differences in other fields. Among them, motherhood penalty refers to the negative impacts of the birth event on women career development, which could explain a considerable part of the gender gap within labor market. Although extensive studies have been accomplished, a comprehensive landscape of this domain has not yet been built. In this survey, the related progresses, including the quantification and comparison of motherhood penalty in different times and regions are presented and the main factors affecting the strength of motherhood penalty from the individual, family and political perspectives are discussed, where the emphasis is put on Chinese situations. Concentrating on the contradiction between labor and labor, this survey summarizes the known explanations into three different yet related theories: family restriction theory, human capital theory and employer discrimination theory. From the supply and demand sides of the labor market, we suggest two ways, namely empowering women and creating opportunities, to help women balance their family and working duties. Lastly, we propose political recommendations and outline a number of open issues for future researches.
2020, 49(1): 155-160.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018320
Abstract:
Due to the rapid growth of Internet, consumers obtain information about products and experiences from online rating platforms, which further influences their purchase decisions. The popularity, individuation, diversification, and heterogeneity of consumers contribute to the diversity of online review. This study examines the evolution process of opinions on the online review platform. Specifically, the network structure and confidence thresholds of traditional models are optimized based on the ground truth of Dianping via the combination of simulation and actual data. The proposed method can deepen the understanding for the evolution process of online opinion.
Due to the rapid growth of Internet, consumers obtain information about products and experiences from online rating platforms, which further influences their purchase decisions. The popularity, individuation, diversification, and heterogeneity of consumers contribute to the diversity of online review. This study examines the evolution process of opinions on the online review platform. Specifically, the network structure and confidence thresholds of traditional models are optimized based on the ground truth of Dianping via the combination of simulation and actual data. The proposed method can deepen the understanding for the evolution process of online opinion.

 ISSN
ISSN