2020 Vol. 49, No. 2
2020, 49(2): 162-168.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020049
Abstract:
In future mobile networks, such as 5G networks, network slicing will be a promising technology to provide customizing services for different users with different transmission requirements. According to the dynamic network state in slice based mobile networks, users need to make accessing slice handoff periodically for improving the transmission performance. However, in a multi-user networks, the accessing choice of a user changes the amount of available transmission resources in the system, which impacts the accessing choices of other users. Thus, in this paper, we model the multi-user handoff problem in slice based mobile networks as a multi-agent random game. Then, we use multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to solve this game, and propose a multi-user accessing handoff algorithm based on distributed MARL method. The numerical results validate the performance of our proposed multi-user accessing handoff algorithm in slice based mobile networks.
In future mobile networks, such as 5G networks, network slicing will be a promising technology to provide customizing services for different users with different transmission requirements. According to the dynamic network state in slice based mobile networks, users need to make accessing slice handoff periodically for improving the transmission performance. However, in a multi-user networks, the accessing choice of a user changes the amount of available transmission resources in the system, which impacts the accessing choices of other users. Thus, in this paper, we model the multi-user handoff problem in slice based mobile networks as a multi-agent random game. Then, we use multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) to solve this game, and propose a multi-user accessing handoff algorithm based on distributed MARL method. The numerical results validate the performance of our proposed multi-user accessing handoff algorithm in slice based mobile networks.
2020, 49(2): 169-181.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020040
Abstract:
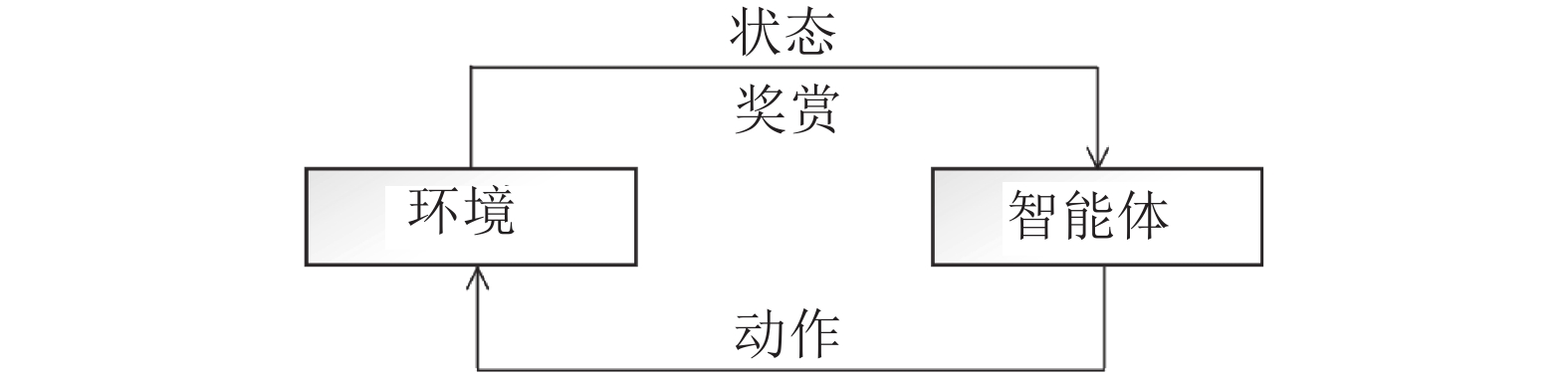
In the era of data explosion, the rapid growth of mobile devices makes the size of wireless networks increase tremendously. Meanwhile, people are having higher demands for wireless communications, which requires the networks to provide precisely on-demand services in order to exploit the limited resource. Due to the above two reasons, the traditional modeling-and-optimizing methods for network management will meet the performance bottleneck in the future. Fortunately, the appearance of artificial intelligence and machine learning provides a new solution to this issue. As a data-driven machine learning technique, deep reinforcement learning can directly learn the pattern of dynamic environments and use it to make optimal decisions. Hence, deep reinforcement learning enables wireless networks to manage and optimize themselves based on their environments, which makes it possible to realize intelligent communications. This paper introduces the application of deep reinforcement learning on wireless communications from the aspects of resource management, access control, and network maintenance, and illustrates that deep reinforcement learning is an effective approach to realizing intelligent communications.
In the era of data explosion, the rapid growth of mobile devices makes the size of wireless networks increase tremendously. Meanwhile, people are having higher demands for wireless communications, which requires the networks to provide precisely on-demand services in order to exploit the limited resource. Due to the above two reasons, the traditional modeling-and-optimizing methods for network management will meet the performance bottleneck in the future. Fortunately, the appearance of artificial intelligence and machine learning provides a new solution to this issue. As a data-driven machine learning technique, deep reinforcement learning can directly learn the pattern of dynamic environments and use it to make optimal decisions. Hence, deep reinforcement learning enables wireless networks to manage and optimize themselves based on their environments, which makes it possible to realize intelligent communications. This paper introduces the application of deep reinforcement learning on wireless communications from the aspects of resource management, access control, and network maintenance, and illustrates that deep reinforcement learning is an effective approach to realizing intelligent communications.
2020, 49(2): 182-186.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018076
Abstract:
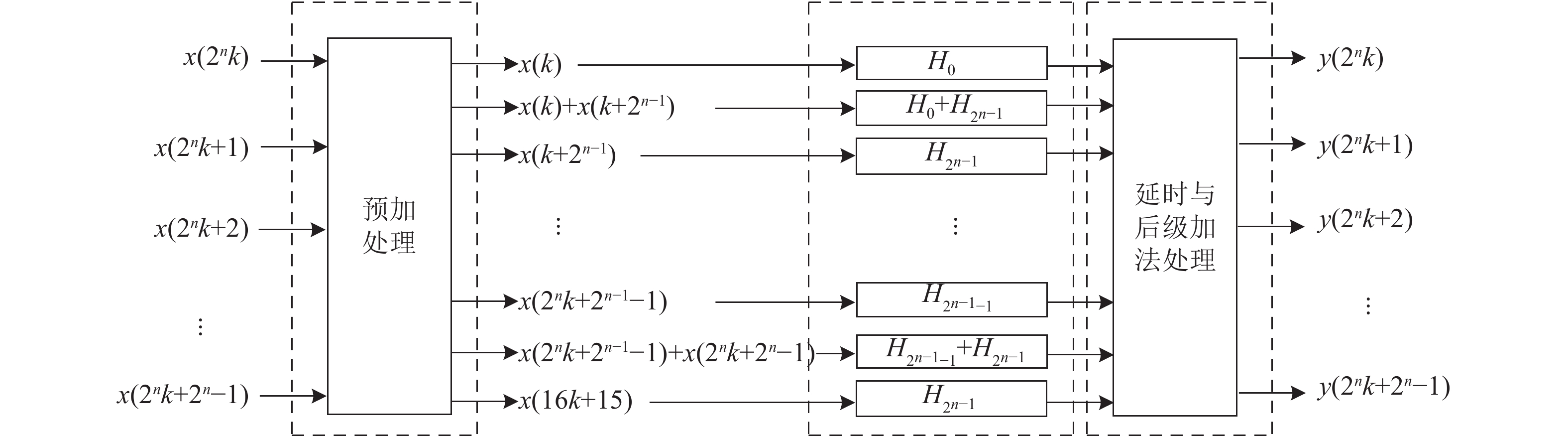
Fast finite impulse response (FIR) algorithm (FFA) can break the limitation that the hardware complexity of traditional parallel algorithm linearly increases with the degree of parallelism, which can improve FIR algorithm efficiency. However, there is few research focusing on the general algorithm and implementation structure for high-parallelism FFA. In this case, we propose high-efficiency 2n-parallel general FFA and its implementation structure. We also provide the high-parallelism FFA structure with non-2n-parallelism. According to the algorithm analysis and hardware efficiency estimation, we know that the efficient 2n-parallel FFA algorithm and structure proposed in this paper can achieve significant advantage over traditional methods, and this advantage is becoming more obvious with the parallelism increasing. Thus, the proposed high-efficiency 2n-parallel FFA can be used for the implementation of high-parallelism FIR filters.
Fast finite impulse response (FIR) algorithm (FFA) can break the limitation that the hardware complexity of traditional parallel algorithm linearly increases with the degree of parallelism, which can improve FIR algorithm efficiency. However, there is few research focusing on the general algorithm and implementation structure for high-parallelism FFA. In this case, we propose high-efficiency 2n-parallel general FFA and its implementation structure. We also provide the high-parallelism FFA structure with non-2n-parallelism. According to the algorithm analysis and hardware efficiency estimation, we know that the efficient 2n-parallel FFA algorithm and structure proposed in this paper can achieve significant advantage over traditional methods, and this advantage is becoming more obvious with the parallelism increasing. Thus, the proposed high-efficiency 2n-parallel FFA can be used for the implementation of high-parallelism FIR filters.
2020, 49(2): 187-193.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018112
Abstract:
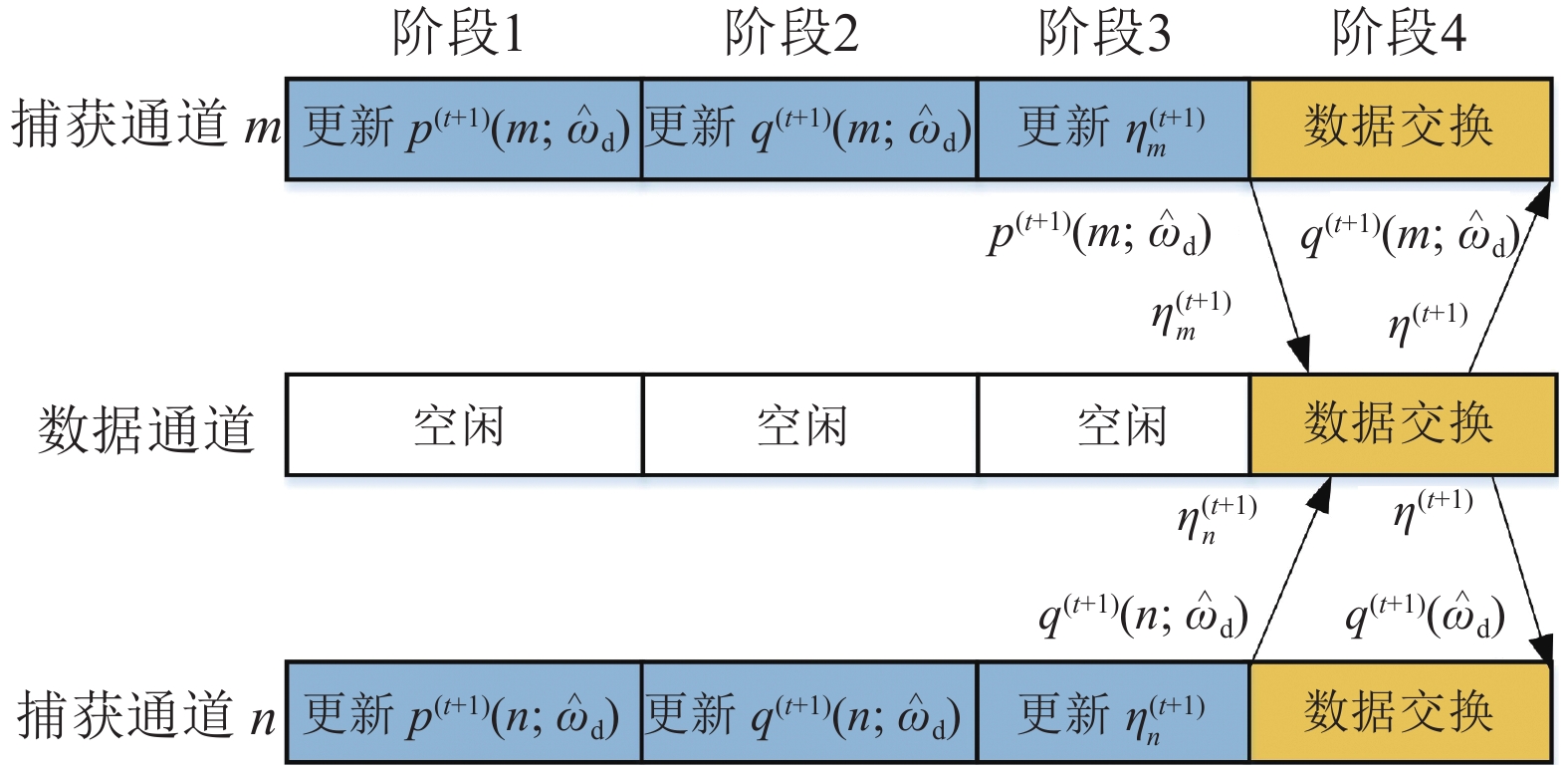
Signal acquisition is one of the key tasks in global position system (GPS) baseband signal processing, which determines the power consumption and the hardware cost of GPS receivers. However, most conventional acquisition algorithms are based on the correlation operations, thus demanding a large amount of data and consuming lots of computational resources. To alleviate this, we propose an efficient parallel GPS signal acquisition algorithm in this paper, utilizing the idea of compressive sensing. Specifically, we first represent the GPS signals in sparse form by projecting the signal onto a base matrix consisting of the orthogonal C/A codes. Based on this sparse representation, a compressive sensing model of GPS signal acquisition is established. Then, we develop an efficient iterative parallel acquisition algorithm for the compressive sensing problem by fitting it into the framework of alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). Each iteration of ADMM can be computed in closed form, thus giving it very low complexity. The efficiency and efficacy of the proposed algorithm are validated by numerical simulations.
Signal acquisition is one of the key tasks in global position system (GPS) baseband signal processing, which determines the power consumption and the hardware cost of GPS receivers. However, most conventional acquisition algorithms are based on the correlation operations, thus demanding a large amount of data and consuming lots of computational resources. To alleviate this, we propose an efficient parallel GPS signal acquisition algorithm in this paper, utilizing the idea of compressive sensing. Specifically, we first represent the GPS signals in sparse form by projecting the signal onto a base matrix consisting of the orthogonal C/A codes. Based on this sparse representation, a compressive sensing model of GPS signal acquisition is established. Then, we develop an efficient iterative parallel acquisition algorithm for the compressive sensing problem by fitting it into the framework of alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). Each iteration of ADMM can be computed in closed form, thus giving it very low complexity. The efficiency and efficacy of the proposed algorithm are validated by numerical simulations.
2020, 49(2): 194-200.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018278
Abstract:
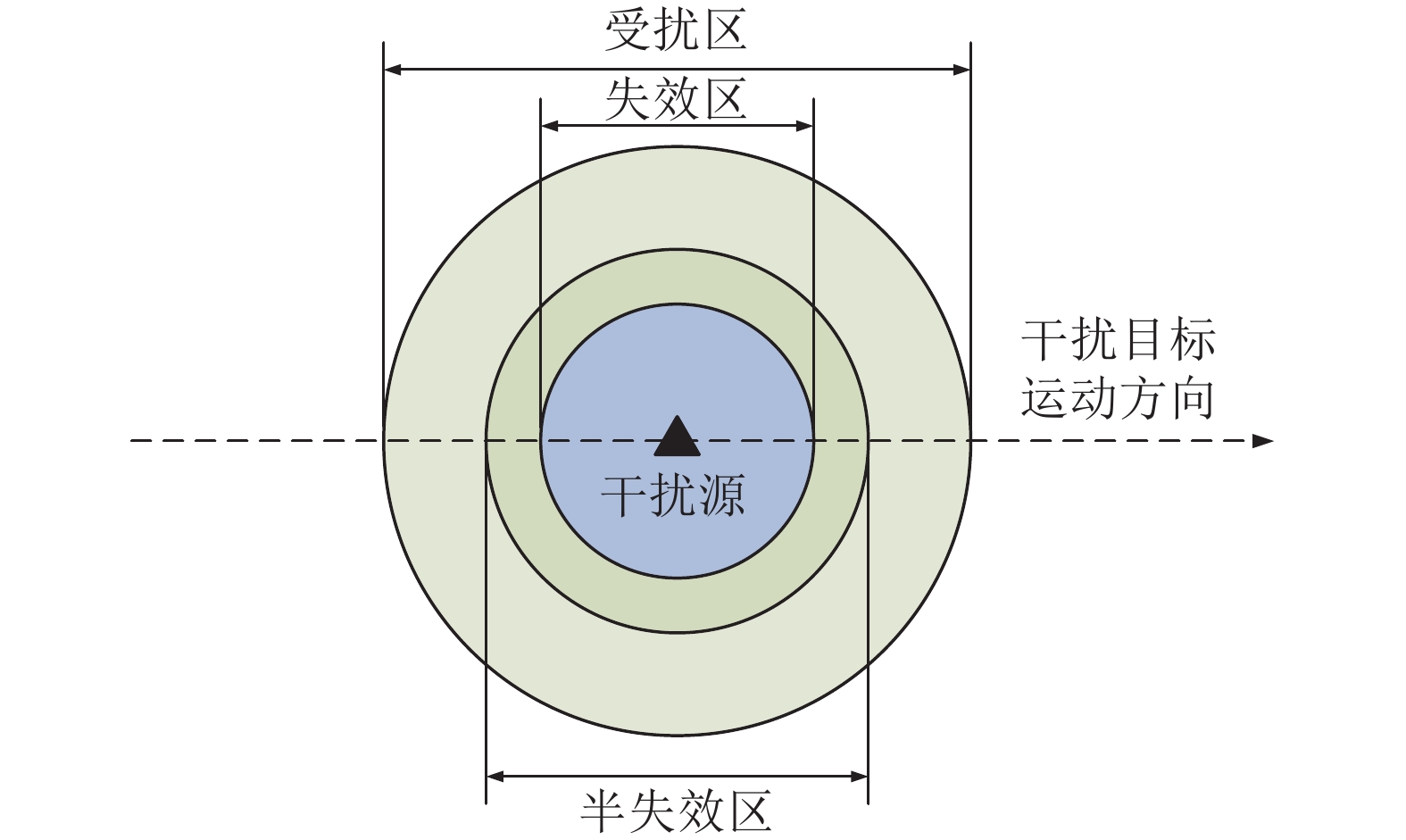
Global positioning system/inertial navigation system (GPS/INS) integrated navigation has been widely used in guiding the precision guidance weapons. With the gradual maturity of GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling technology, the anti-jamming capacity of the entire integrated navigation system is improved significantly. In order to effectively implement navigation countermeasures by adopting GPS/INS super-tight coupled precision-guided weapons, divide the jamming power region into disturbed area, half failure area and failure area according to GPS receiver different link’s performance decline indices, and combine the influence of GPS/INS super-tight coupling on the structure design of receiver tracking loop, this paper derives and analyzes the jamming power required at the receiver’s RF front-end when the capture, tracking and demodulation performance of GPS P(Y) code and M code signal down to division critical value under the matching spectrum jamming. Considering the relationship between the direction of arrival (DOA) of jamming and GPS receiver’s antenna gain, the changes of jamming source transmitting power along with effective jamming range about each jamming power region have been simulated and acquired on different blast-off height. Then, the continuous blanket jamming range to precision guidance weapons of adopting GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling has been analyzed quantitatively. Finally, the problem of setting jamming source number and location is modeled and solved. The conclusion achieved can offer a guidance for the practice of limited load and height blast-off platform jamming source implementing navigation countermeasure to precision guidance weapons of adopting GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling.
Global positioning system/inertial navigation system (GPS/INS) integrated navigation has been widely used in guiding the precision guidance weapons. With the gradual maturity of GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling technology, the anti-jamming capacity of the entire integrated navigation system is improved significantly. In order to effectively implement navigation countermeasures by adopting GPS/INS super-tight coupled precision-guided weapons, divide the jamming power region into disturbed area, half failure area and failure area according to GPS receiver different link’s performance decline indices, and combine the influence of GPS/INS super-tight coupling on the structure design of receiver tracking loop, this paper derives and analyzes the jamming power required at the receiver’s RF front-end when the capture, tracking and demodulation performance of GPS P(Y) code and M code signal down to division critical value under the matching spectrum jamming. Considering the relationship between the direction of arrival (DOA) of jamming and GPS receiver’s antenna gain, the changes of jamming source transmitting power along with effective jamming range about each jamming power region have been simulated and acquired on different blast-off height. Then, the continuous blanket jamming range to precision guidance weapons of adopting GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling has been analyzed quantitatively. Finally, the problem of setting jamming source number and location is modeled and solved. The conclusion achieved can offer a guidance for the practice of limited load and height blast-off platform jamming source implementing navigation countermeasure to precision guidance weapons of adopting GPS/INS ultra-tight coupling.
2020, 49(2): 201-205.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018306
Abstract:
As the transmission rate and bandwidth efficiency of tradition direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) system are relatively low. Based on the basic characteristics of spread sequences, DSSS modulated signals and the theories of Hilbert transformation, a novel DSSS baseband modulation method is proposed. Theoretical analysis and simulation experiments are carried out on the characteristics of inter branch and intersymbol interference of modulated signal. Results show that under additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel, compared with tradition DSSS system based on a single pseudo-random code, the novel method doubled the transmission rate without decreasing the BER performance or increasing the transmission bandwidth or increasing the signal power per bit.
As the transmission rate and bandwidth efficiency of tradition direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) system are relatively low. Based on the basic characteristics of spread sequences, DSSS modulated signals and the theories of Hilbert transformation, a novel DSSS baseband modulation method is proposed. Theoretical analysis and simulation experiments are carried out on the characteristics of inter branch and intersymbol interference of modulated signal. Results show that under additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel, compared with tradition DSSS system based on a single pseudo-random code, the novel method doubled the transmission rate without decreasing the BER performance or increasing the transmission bandwidth or increasing the signal power per bit.
2020, 49(2): 206-212.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018314
Abstract:
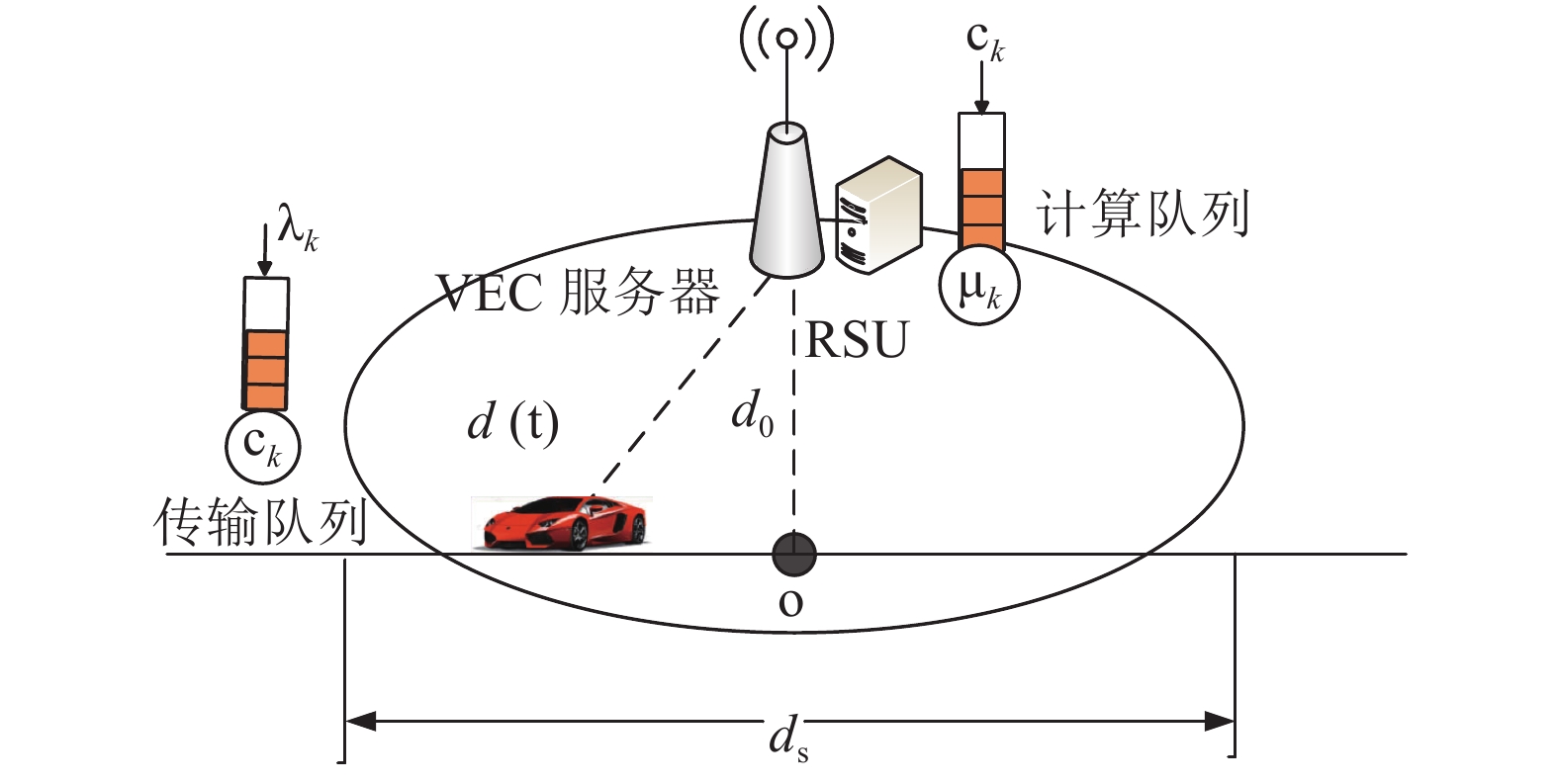
Considering the effect of time-varying channel on the resource allocation scheme, a vehicle user power minimization problem with task QoS requirement constraints is formulated. By utilizing the vehicle channel predictability and Lyapunov theory, the original problem is reformulated as two sub-problems of a single variable, which can be solved easily. Thus an algorithm is proposed to solve these two sub-problems of resource allocation and then a joint radio and computation resource allocation scheme is formed according to the two sub-problems solutions. The simulation results show that the power consumption of the proposed algorithm is decreased by 48.85% compared with traditional greedy algorithm when the data average arrival rate grows from 20 packets/slot to 40 packets/slot.
Considering the effect of time-varying channel on the resource allocation scheme, a vehicle user power minimization problem with task QoS requirement constraints is formulated. By utilizing the vehicle channel predictability and Lyapunov theory, the original problem is reformulated as two sub-problems of a single variable, which can be solved easily. Thus an algorithm is proposed to solve these two sub-problems of resource allocation and then a joint radio and computation resource allocation scheme is formed according to the two sub-problems solutions. The simulation results show that the power consumption of the proposed algorithm is decreased by 48.85% compared with traditional greedy algorithm when the data average arrival rate grows from 20 packets/slot to 40 packets/slot.
2020, 49(2): 213-218.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019041
Abstract:
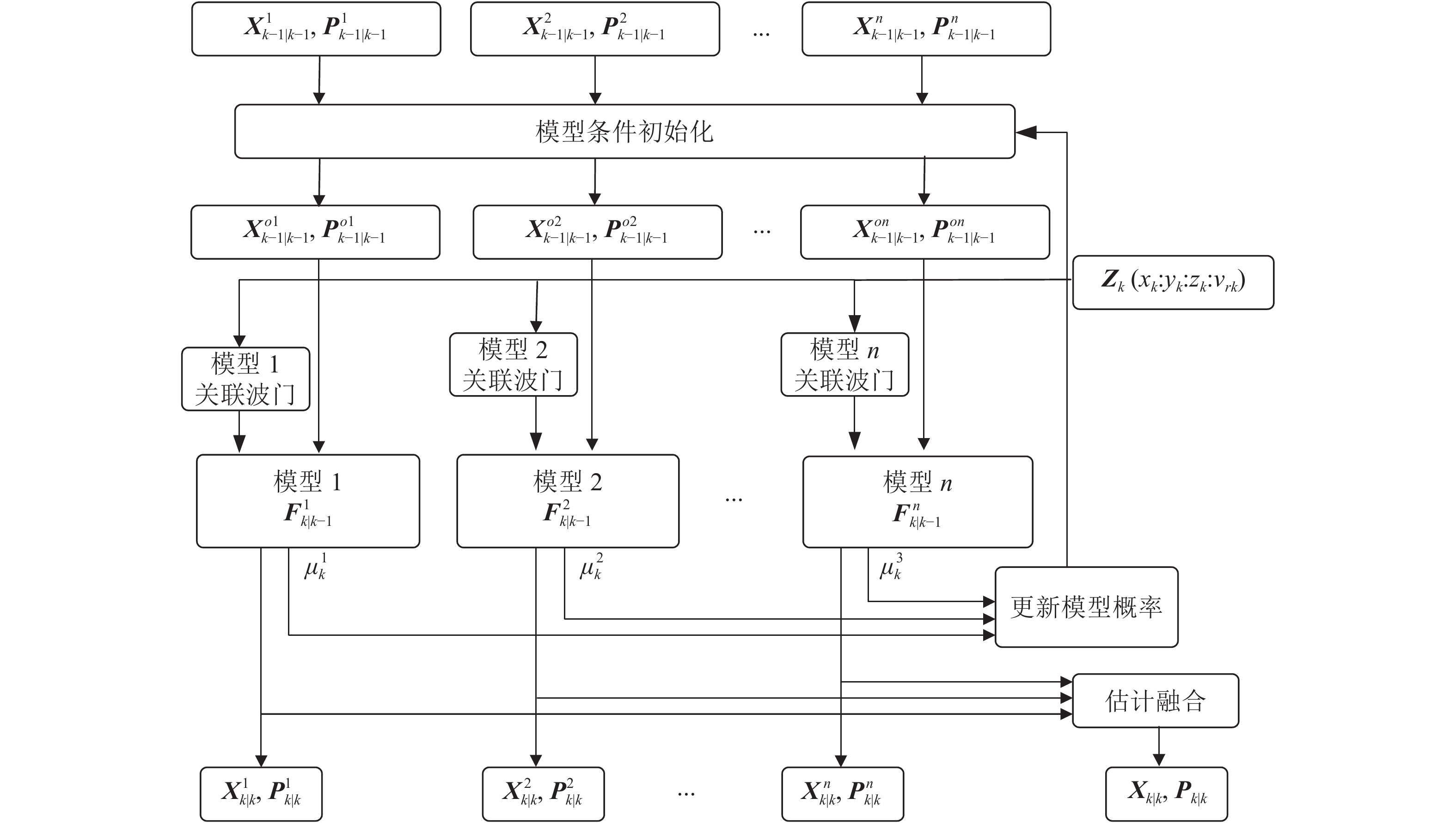
Aiming at the problem of maneuvering target tracking under the clutter environments, we propose a method for the maneuvering target tracking using the Doppler measurement. In our method, the radial velocity, which was estimated with the Doppler measurement, is first introduced to the measurement equation of the target, and then it is linearized after omitting the high-order terms in the Taylor series expansion. The radial velocity gate is added to the radar targets in the association to filter out clutter points. The radial velocity of the target observed is updated with the radial velocity calculated by the Doppler measurement. The simulated results demonstrate that the target location accuracy, velocity accuracy, and the convergence speed of proposed algorithm are all improved compared with those of traditional algorithms. In addition, the influence of the Doppler measurement error on the target tracking performance is also analyzed and the result indicates that the smaller the Doppler measurement error, the better the target tracking performance.
Aiming at the problem of maneuvering target tracking under the clutter environments, we propose a method for the maneuvering target tracking using the Doppler measurement. In our method, the radial velocity, which was estimated with the Doppler measurement, is first introduced to the measurement equation of the target, and then it is linearized after omitting the high-order terms in the Taylor series expansion. The radial velocity gate is added to the radar targets in the association to filter out clutter points. The radial velocity of the target observed is updated with the radial velocity calculated by the Doppler measurement. The simulated results demonstrate that the target location accuracy, velocity accuracy, and the convergence speed of proposed algorithm are all improved compared with those of traditional algorithms. In addition, the influence of the Doppler measurement error on the target tracking performance is also analyzed and the result indicates that the smaller the Doppler measurement error, the better the target tracking performance.
2020, 49(2): 219-227.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018319
Abstract:
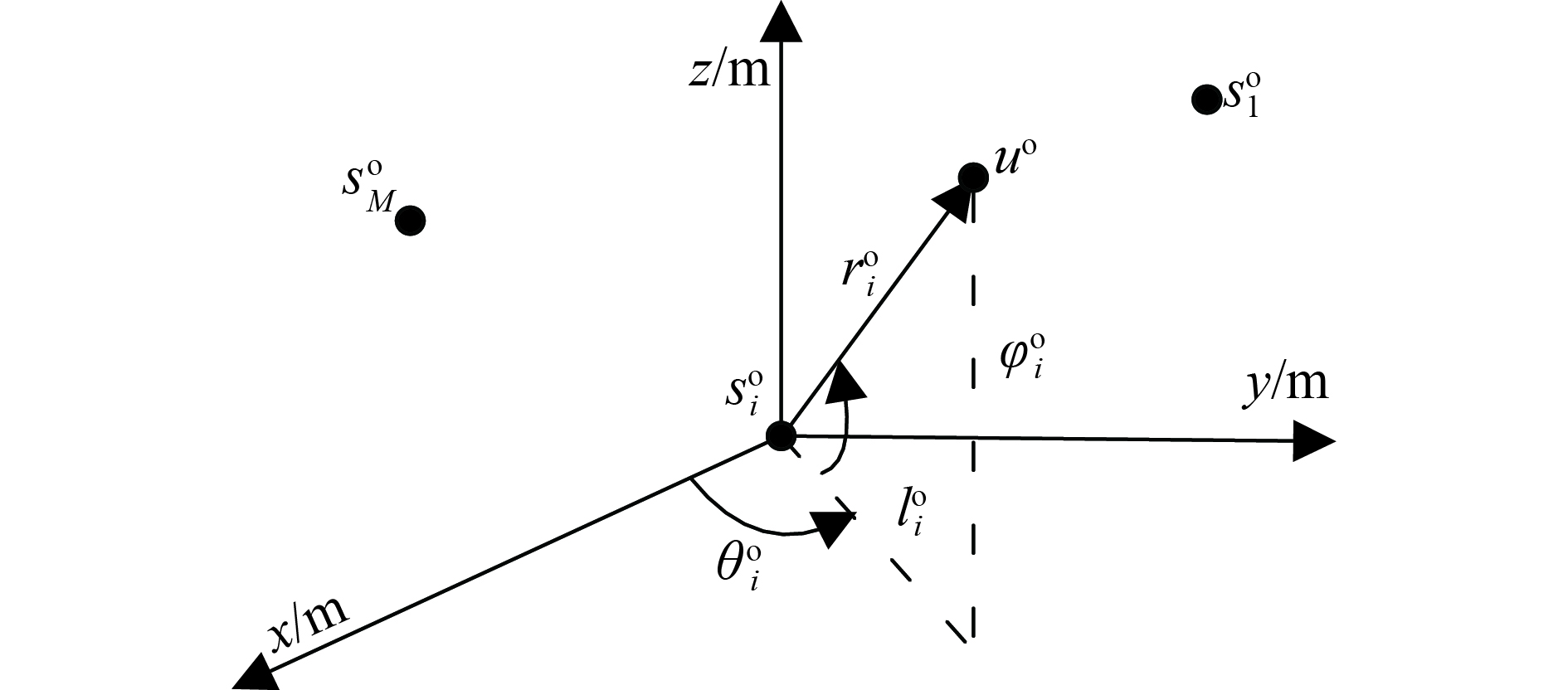
The location of a moving emitting source is a key problem in the field of electronic countermeasures. One of the effective solutions to solve this problem is the passive location closed-form algorithm based on the time difference of arrival (TDOA) and frequency difference of arrival (FDOA) measurements. However, in order to satisfy the requirement of the above algorithm, at least 5 nodes need to collaborate to complete a location task. Given the closed-form frame of passive location algorithm, by combining the angle of arrival (AOA), TDOA and FDOA measurements, a novel location algorithm is proposed to reduce the number of collaborative platforms. The approximate algebraic relationships are derived between the moving source position and the measurements with platform positions. According to the aforementioned conditions, the closed formed expressions can be calculated by joint AOA-TDOA-FDOA mechanism. The theoretical analysis demonstrates that solution accuracy of the proposed location algorithm can achieve the Cramér–Rao lower bound (CRLB), some numerical simulation results coincide with the theoretical results.
The location of a moving emitting source is a key problem in the field of electronic countermeasures. One of the effective solutions to solve this problem is the passive location closed-form algorithm based on the time difference of arrival (TDOA) and frequency difference of arrival (FDOA) measurements. However, in order to satisfy the requirement of the above algorithm, at least 5 nodes need to collaborate to complete a location task. Given the closed-form frame of passive location algorithm, by combining the angle of arrival (AOA), TDOA and FDOA measurements, a novel location algorithm is proposed to reduce the number of collaborative platforms. The approximate algebraic relationships are derived between the moving source position and the measurements with platform positions. According to the aforementioned conditions, the closed formed expressions can be calculated by joint AOA-TDOA-FDOA mechanism. The theoretical analysis demonstrates that solution accuracy of the proposed location algorithm can achieve the Cramér–Rao lower bound (CRLB), some numerical simulation results coincide with the theoretical results.
2020, 49(2): 228-234.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019210
Abstract:
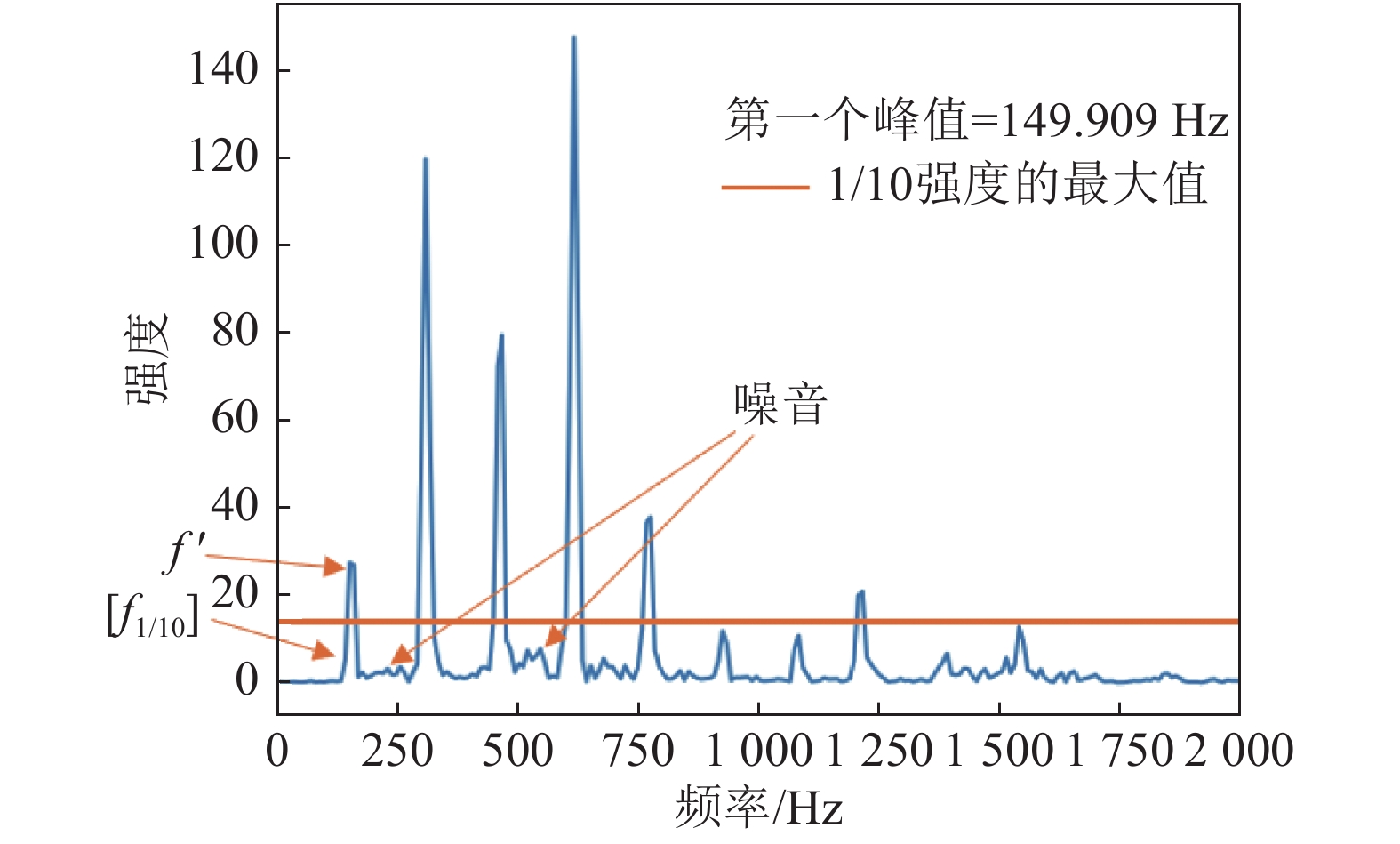
Humming notation is an important method and process of composing music. Considering the complexity of humming audio and the influence of various environmental factors, this paper analyzes the basic characteristics of humming audio. On the basis of windowed Fourier Transform, the humming audio is regionally divided, defined and extracted according to the notes. A method of fast extraction of fundamental frequency is proposed based on relative amplitude of humming audio. And further a variable-region Fourier Transform iteration algorithm is designed and implemented programmatically by Python 3.6. This iteration algorithm can recognize humming melody more accurately, obtain the pitch and length of each note of humming, and automatically form a digital music score. The accuracy of the experimental test reached 84.3%. The achieved results show that the algorithm can identify humming tunes more accurately, thus it would be a feasible recognition and notation algorithm for developing composing-assisting software with good application prospects.
Humming notation is an important method and process of composing music. Considering the complexity of humming audio and the influence of various environmental factors, this paper analyzes the basic characteristics of humming audio. On the basis of windowed Fourier Transform, the humming audio is regionally divided, defined and extracted according to the notes. A method of fast extraction of fundamental frequency is proposed based on relative amplitude of humming audio. And further a variable-region Fourier Transform iteration algorithm is designed and implemented programmatically by Python 3.6. This iteration algorithm can recognize humming melody more accurately, obtain the pitch and length of each note of humming, and automatically form a digital music score. The accuracy of the experimental test reached 84.3%. The achieved results show that the algorithm can identify humming tunes more accurately, thus it would be a feasible recognition and notation algorithm for developing composing-assisting software with good application prospects.
2020, 49(2): 235-239.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018269
Abstract:
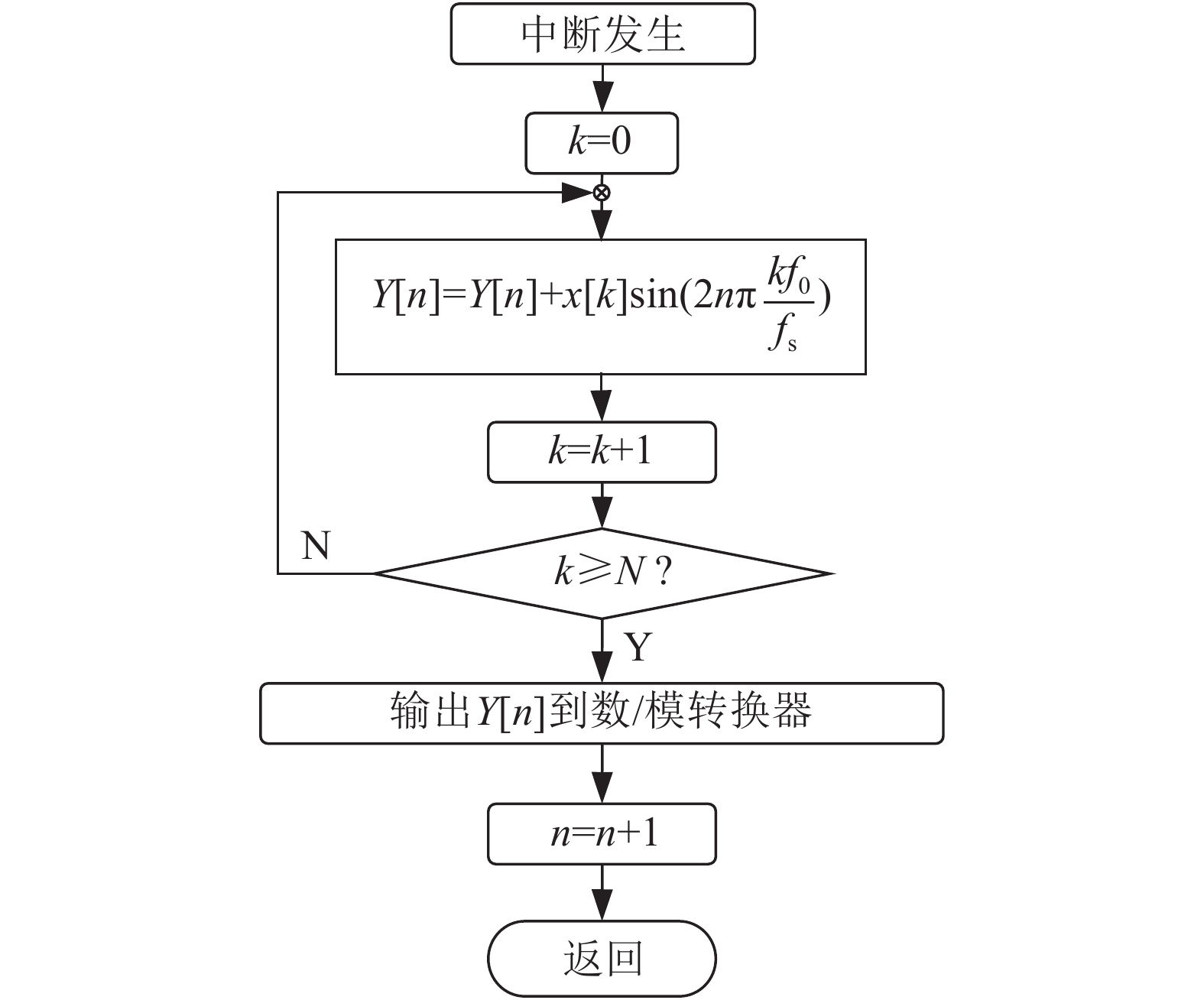
An acoustical audible alarm is generally requested in the medical electronics devices to posit where an alarm happen. At present, the medical audio alarm signals are mainly generated by voice recording or pulse-based signals. With those methods, many shrill voices and sharp noises are easily produced to affect the quality of an alarm. Therefore, aim at a qualified medical audible alarm, the traditional Goertzel algorithm was simplified into the real number field from the complex number field. Based on this simplified Goertzel algorithm, a recursive algorithm was proposed to generate a serial of sinusoidal fundamental and its harmonic signals. The algorithm was programmed and tested with an audio processing circuit. The audio circuit was designed based on microcomputer LM3S9B92. According to the tested signal waveforms and the frequency spectrum, a group of low-noise and multi-overtone audible alarm signals were produced.
An acoustical audible alarm is generally requested in the medical electronics devices to posit where an alarm happen. At present, the medical audio alarm signals are mainly generated by voice recording or pulse-based signals. With those methods, many shrill voices and sharp noises are easily produced to affect the quality of an alarm. Therefore, aim at a qualified medical audible alarm, the traditional Goertzel algorithm was simplified into the real number field from the complex number field. Based on this simplified Goertzel algorithm, a recursive algorithm was proposed to generate a serial of sinusoidal fundamental and its harmonic signals. The algorithm was programmed and tested with an audio processing circuit. The audio circuit was designed based on microcomputer LM3S9B92. According to the tested signal waveforms and the frequency spectrum, a group of low-noise and multi-overtone audible alarm signals were produced.
2020, 49(2): 248-254.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018249
Abstract:
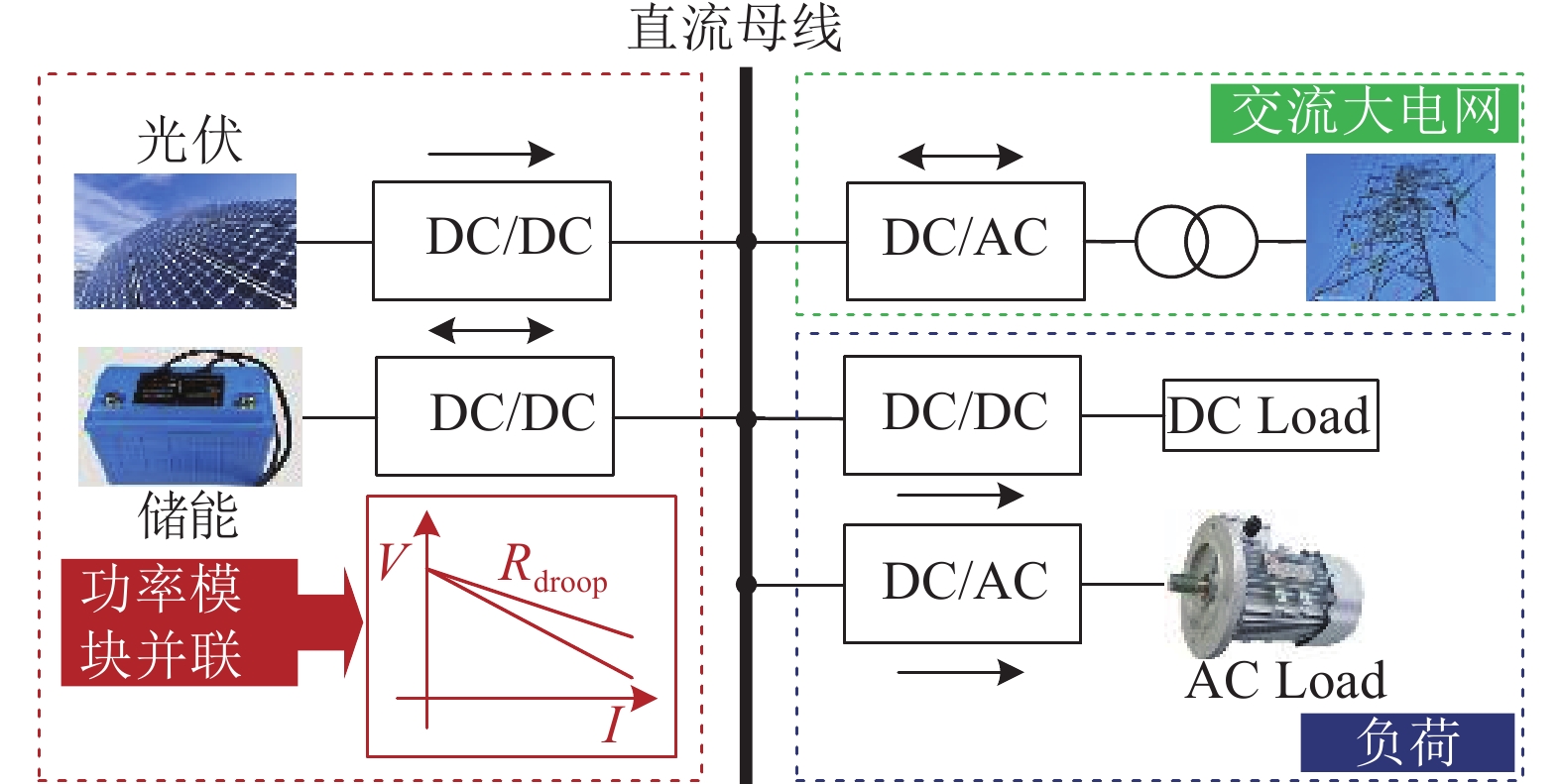
DC microgrids deploy hierarchical control to achieve decoupling design in different time scales for different control objectives, where the droop strategy is widely used in the primary control for autonomous current sharing of voltage modules in parallel. While the improvement of current sharing relies on the increase of the droop coefficient, this will also produce large voltage drop. In this paper, a piecewise linear droop control (PWLDC) with multi-level feedforward compensation of bus voltage for DC microgrid is proposed, where the droop coefficient can be flexibly configured according to partition of load range and bus voltage deviation be compensated by multi-level feedforward of reference. In the primary level, the current sharing performance of parallel module and voltage regulation can be solved at the same time. Finally, a laboratory prototype is designed and the control strategy is validated by experimental results.
DC microgrids deploy hierarchical control to achieve decoupling design in different time scales for different control objectives, where the droop strategy is widely used in the primary control for autonomous current sharing of voltage modules in parallel. While the improvement of current sharing relies on the increase of the droop coefficient, this will also produce large voltage drop. In this paper, a piecewise linear droop control (PWLDC) with multi-level feedforward compensation of bus voltage for DC microgrid is proposed, where the droop coefficient can be flexibly configured according to partition of load range and bus voltage deviation be compensated by multi-level feedforward of reference. In the primary level, the current sharing performance of parallel module and voltage regulation can be solved at the same time. Finally, a laboratory prototype is designed and the control strategy is validated by experimental results.
2020, 49(2): 255-261.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018279
Abstract:
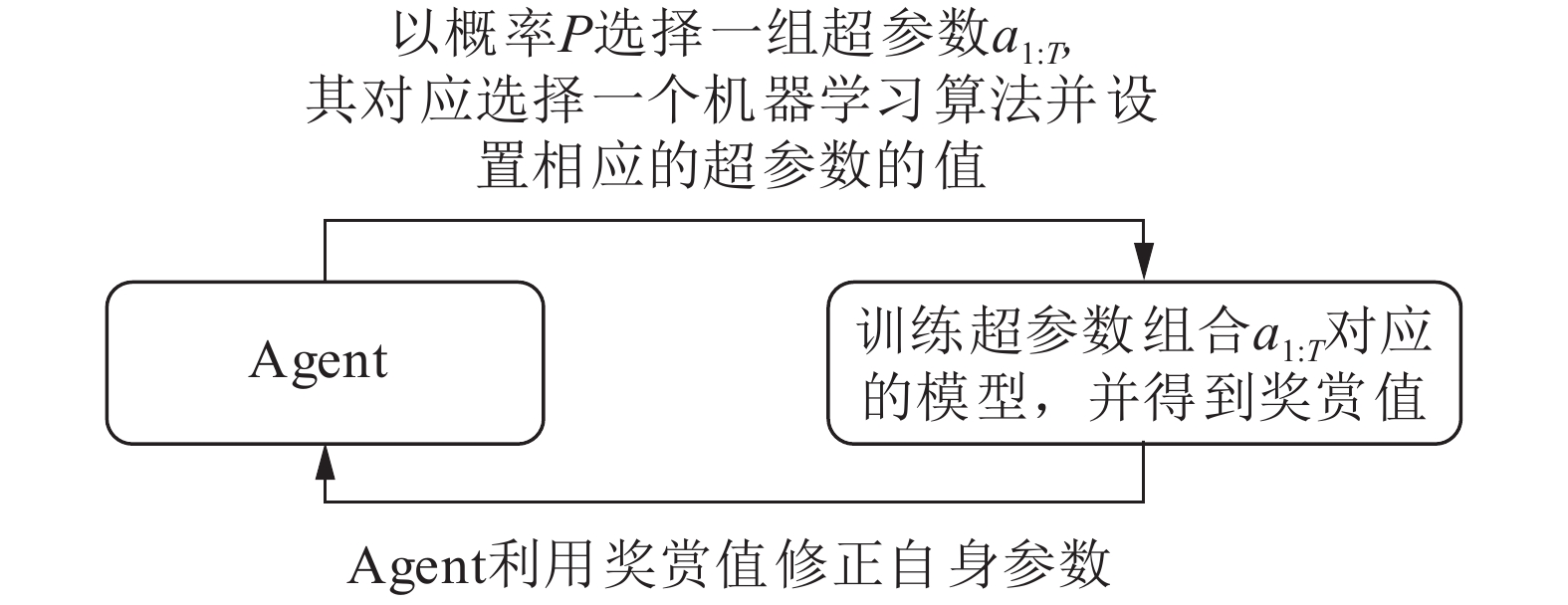
With the development of machine learning technology, the number of machine learning algorithms grows rapidly and the models become more and more complex. That causes two major problems in practice: the selection of machine learning models and the hyperparameter optimization. In order to tackle these issues, this paper proposes a new method based on deep reinforcement learning. Long short-term memory (LSTM) network is used to build an agent which automatically selects the machine learning model and optimizes hyperparameters for a given dataset. The agent aims to maximize the accuracy of the selected machine learning model on the validation dataset. At each iteration, it utilizes the accuracy of the selected model on the validation dataset as a reward signal to improve its decision for the next time. The reinforcement learning algorithm is used to guide the learning process for the agent. To verify the idea, the proposed method is compared with two widely optimization methods, tree-structured Parzen estimator and random search on UCI datasets. The results show that the proposed method outperforms other methods in terms of stability, time efficiency and accuracy.
With the development of machine learning technology, the number of machine learning algorithms grows rapidly and the models become more and more complex. That causes two major problems in practice: the selection of machine learning models and the hyperparameter optimization. In order to tackle these issues, this paper proposes a new method based on deep reinforcement learning. Long short-term memory (LSTM) network is used to build an agent which automatically selects the machine learning model and optimizes hyperparameters for a given dataset. The agent aims to maximize the accuracy of the selected machine learning model on the validation dataset. At each iteration, it utilizes the accuracy of the selected model on the validation dataset as a reward signal to improve its decision for the next time. The reinforcement learning algorithm is used to guide the learning process for the agent. To verify the idea, the proposed method is compared with two widely optimization methods, tree-structured Parzen estimator and random search on UCI datasets. The results show that the proposed method outperforms other methods in terms of stability, time efficiency and accuracy.
2020, 49(2): 262-268.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019076
Abstract:
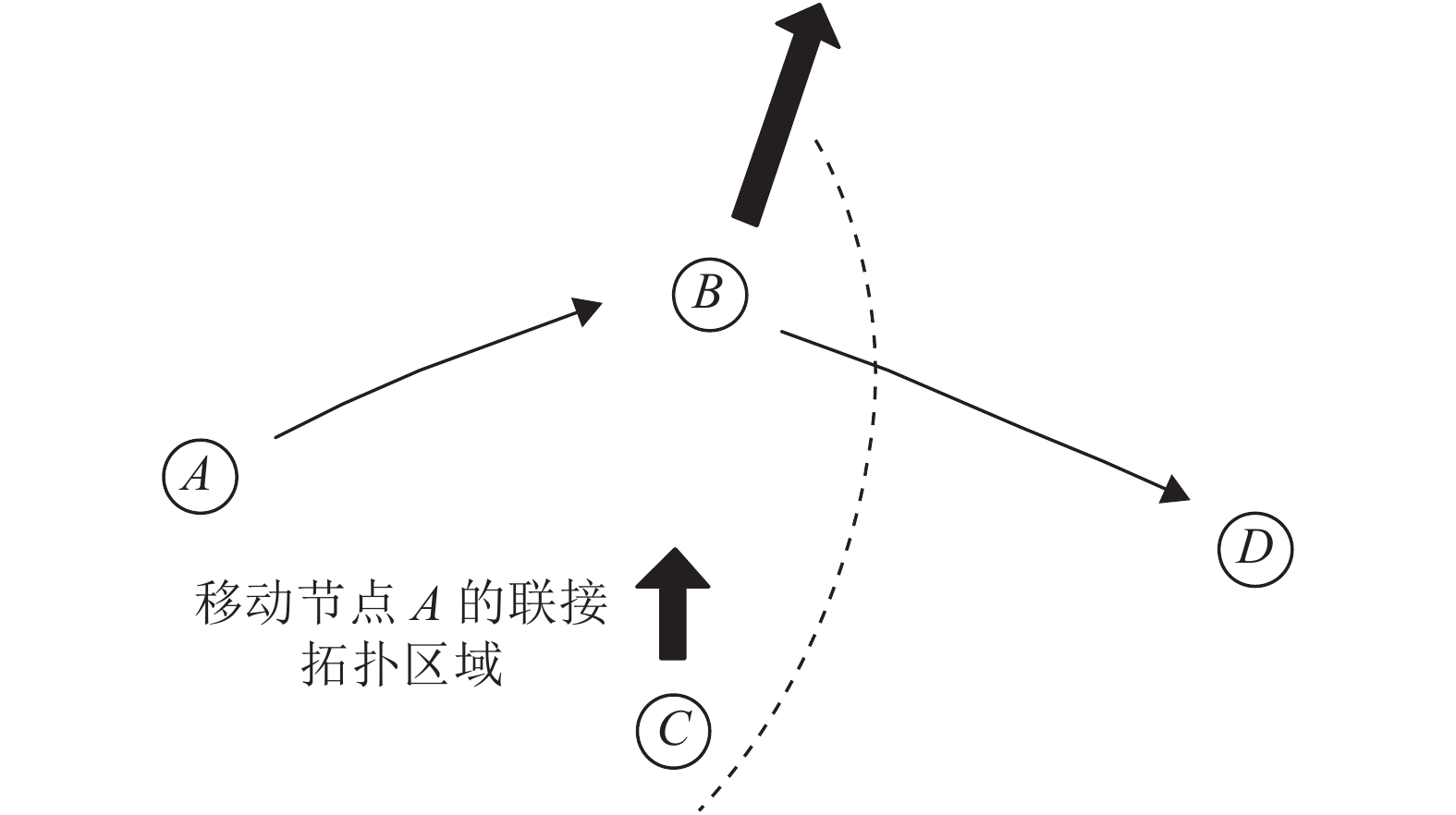
Aiming at the influence of mobile nodes on network topological stability, an adaptive distributed reinforcement learning algorithm is proposed to predict the stable connection of adjacent nodes. Each node uses the method of combining reinforcement learning with adaptive division of learning intervals, uses the received signal strength information between adjacent nodes to determine the connection state between adjacent nodes, and finally predicts the set of neighbor nodes that can maintain stable connection. The simulation results of random walk model under various conditions show that the prediction accuracy is about 95%, which verifies the effectiveness and stability of the algorithm.
Aiming at the influence of mobile nodes on network topological stability, an adaptive distributed reinforcement learning algorithm is proposed to predict the stable connection of adjacent nodes. Each node uses the method of combining reinforcement learning with adaptive division of learning intervals, uses the received signal strength information between adjacent nodes to determine the connection state between adjacent nodes, and finally predicts the set of neighbor nodes that can maintain stable connection. The simulation results of random walk model under various conditions show that the prediction accuracy is about 95%, which verifies the effectiveness and stability of the algorithm.
2020, 49(2): 269-275.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019017
Abstract:
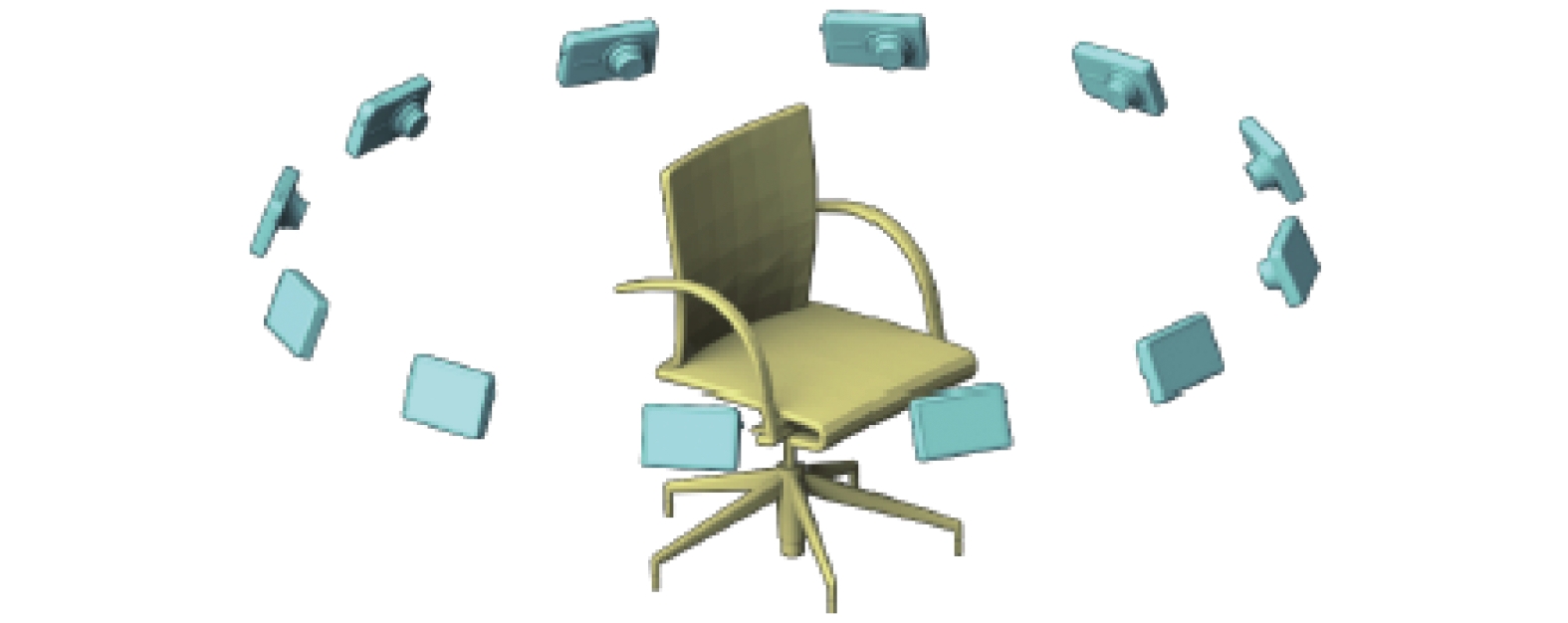
Multi-view convolutional neural networks (MVCNN) is more accurate and faster than those methods based on state-of-the-art 3D shape descriptors in 3D object recognition tasks. However, the input of MVCNN are views rendered from cameras at fixed positions, which is not the case of most applications. Furthermore, MVCNN uses max-pooling operation to fuse multi-view features and the information of original features may be lost. To address those two problems, a new recognition method of 3D objects based on multi-view recurrent neural networks (MVRNN) is proposed based on MVCNN with improvements on three aspects. First, a new item which is defined as the measure of discrimination is introduced into the cross-entropy loss function to enhance the discrimination of features from different objects. Second, a recurrent neural networks (RNN) is used to fuse multi-view features from free positions into a compact one, instead of the max-pooling operation in MVCNN. RNN can keep the completeness of information about appearance feature. At last, single view feature from free positon is matched with fused features via a bi-classification network to attain fine-grained recognition of 3D objects. Experiments are conducted on the open dataset ModelNet and the private dataset MV3D separately to validate the performance of MVRNN. The results show that MVRNN can exact multi-view features with higher degree of discrimination, and achieve higher accuracy than MVCNN on both datasets.
Multi-view convolutional neural networks (MVCNN) is more accurate and faster than those methods based on state-of-the-art 3D shape descriptors in 3D object recognition tasks. However, the input of MVCNN are views rendered from cameras at fixed positions, which is not the case of most applications. Furthermore, MVCNN uses max-pooling operation to fuse multi-view features and the information of original features may be lost. To address those two problems, a new recognition method of 3D objects based on multi-view recurrent neural networks (MVRNN) is proposed based on MVCNN with improvements on three aspects. First, a new item which is defined as the measure of discrimination is introduced into the cross-entropy loss function to enhance the discrimination of features from different objects. Second, a recurrent neural networks (RNN) is used to fuse multi-view features from free positions into a compact one, instead of the max-pooling operation in MVCNN. RNN can keep the completeness of information about appearance feature. At last, single view feature from free positon is matched with fused features via a bi-classification network to attain fine-grained recognition of 3D objects. Experiments are conducted on the open dataset ModelNet and the private dataset MV3D separately to validate the performance of MVRNN. The results show that MVRNN can exact multi-view features with higher degree of discrimination, and achieve higher accuracy than MVCNN on both datasets.
2020, 49(2): 276-282.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019143
Abstract:
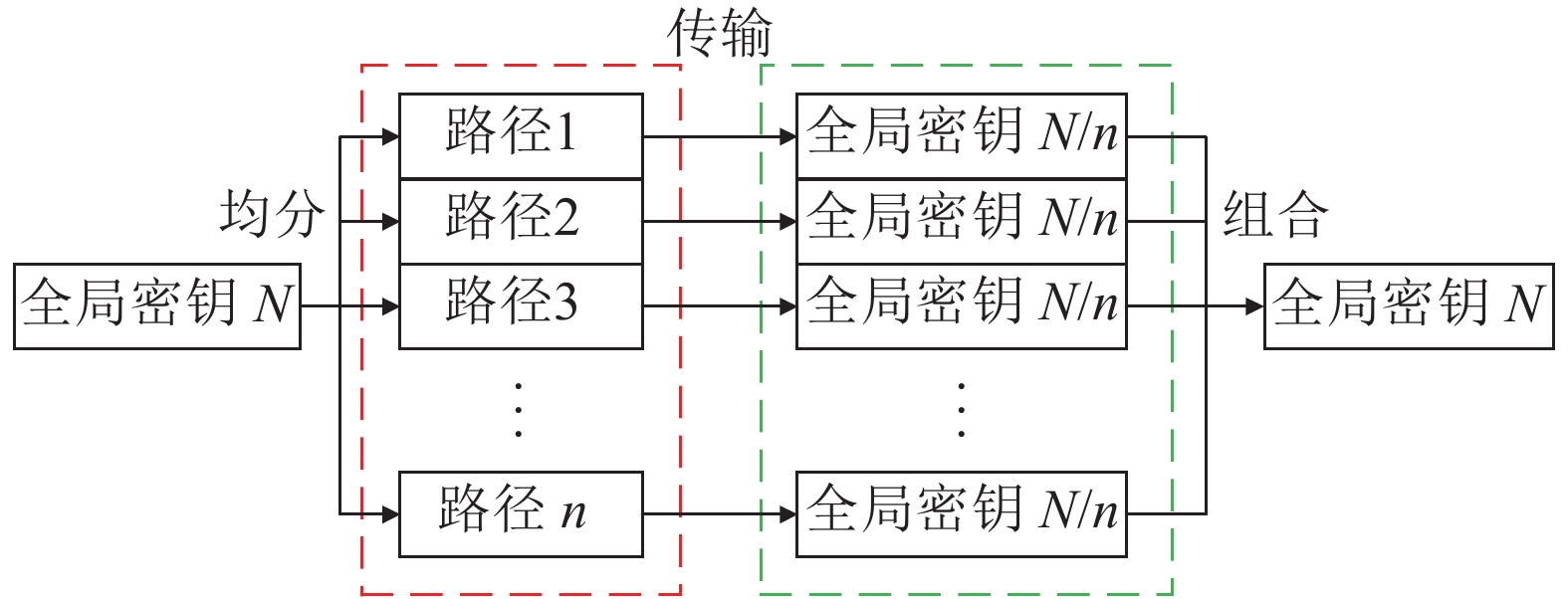
In order to improve the security and efficiency of secure communication in quantum key distribution (QKD) networks, this paper proposes a multipath key transmission method. Firstly, the link cost function is calculated according to the contribution rate of the node to the link and the freshness of the key. Secondly, the multipath selection algorithm based on minimum heap optimization is used to select the optimal paths. Finally, the key block transmission is applied to realize the simultaneous transmission of the key on multiple optimal paths. The experimental results show that the proposed multipath key transmission method is more secure and efficient.
In order to improve the security and efficiency of secure communication in quantum key distribution (QKD) networks, this paper proposes a multipath key transmission method. Firstly, the link cost function is calculated according to the contribution rate of the node to the link and the freshness of the key. Secondly, the multipath selection algorithm based on minimum heap optimization is used to select the optimal paths. Finally, the key block transmission is applied to realize the simultaneous transmission of the key on multiple optimal paths. The experimental results show that the proposed multipath key transmission method is more secure and efficient.
2020, 49(2): 283-286.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019098
Abstract:
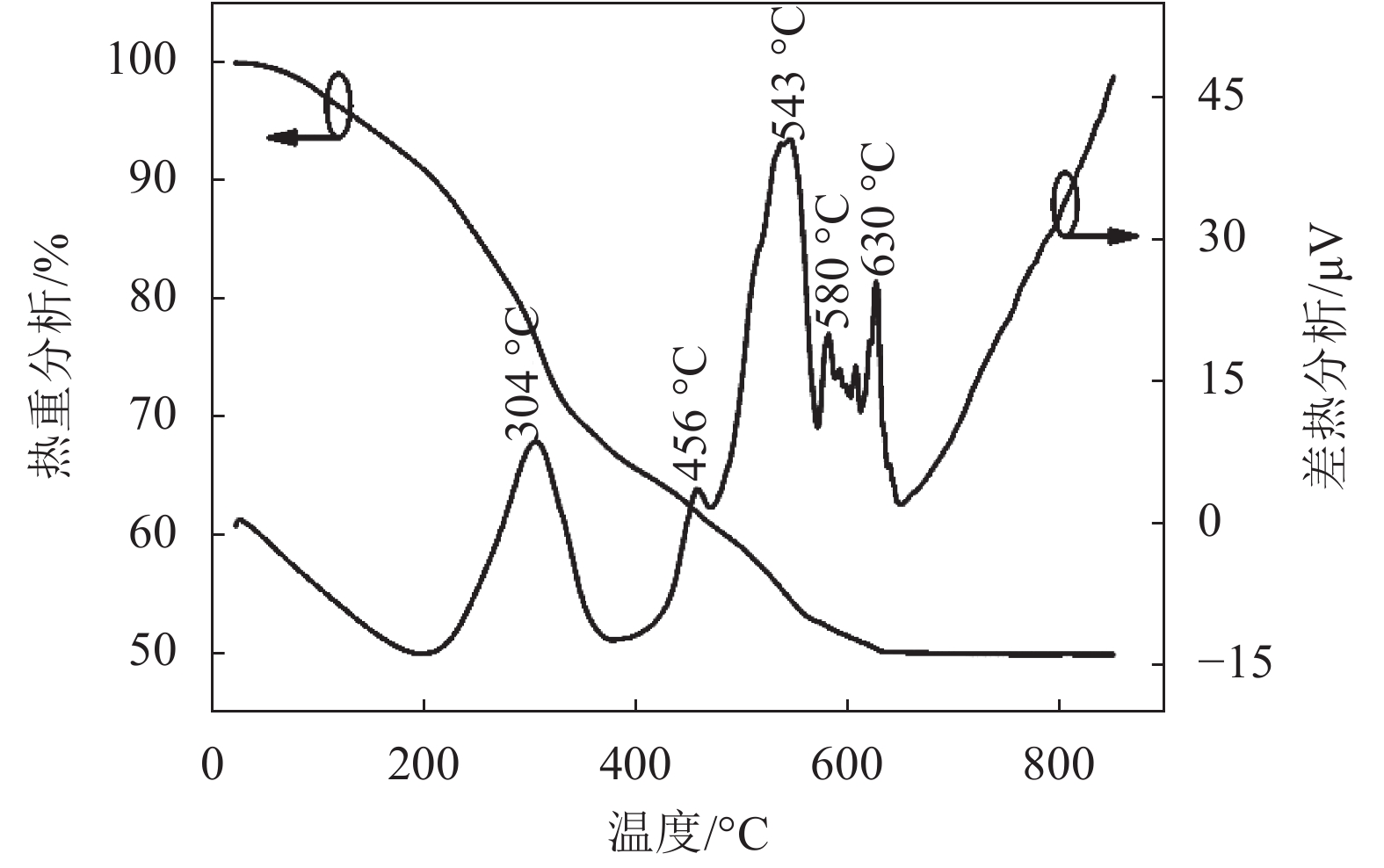
LiTaO3 thin films were deposited on FTO conductive glass substrates by sol-gel method. The surface morphology, crystallization and optical properties of the films were analyzed by TG-DTA, SEM, XRD and UV-Vis spectroscopy. The results show that the films annealed at 650 °C have strong preferred orientation in (006) direction, uniform surface morphology and less cracks. The half-peak width of LiTa3O8 impurity peak and optical band gap Eg are obviously affected by the crystallization properties of LiTaO3 thin films. Optical band gap Eg increases with the decrease of half peak width of impurity LiTa3O8 peak. The blue shift of the optical band gap Eg increases from 3.87 eV to 3.91 eV.
LiTaO3 thin films were deposited on FTO conductive glass substrates by sol-gel method. The surface morphology, crystallization and optical properties of the films were analyzed by TG-DTA, SEM, XRD and UV-Vis spectroscopy. The results show that the films annealed at 650 °C have strong preferred orientation in (006) direction, uniform surface morphology and less cracks. The half-peak width of LiTa3O8 impurity peak and optical band gap Eg are obviously affected by the crystallization properties of LiTaO3 thin films. Optical band gap Eg increases with the decrease of half peak width of impurity LiTa3O8 peak. The blue shift of the optical band gap Eg increases from 3.87 eV to 3.91 eV.
2020, 49(2): 287-290.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019220
Abstract:
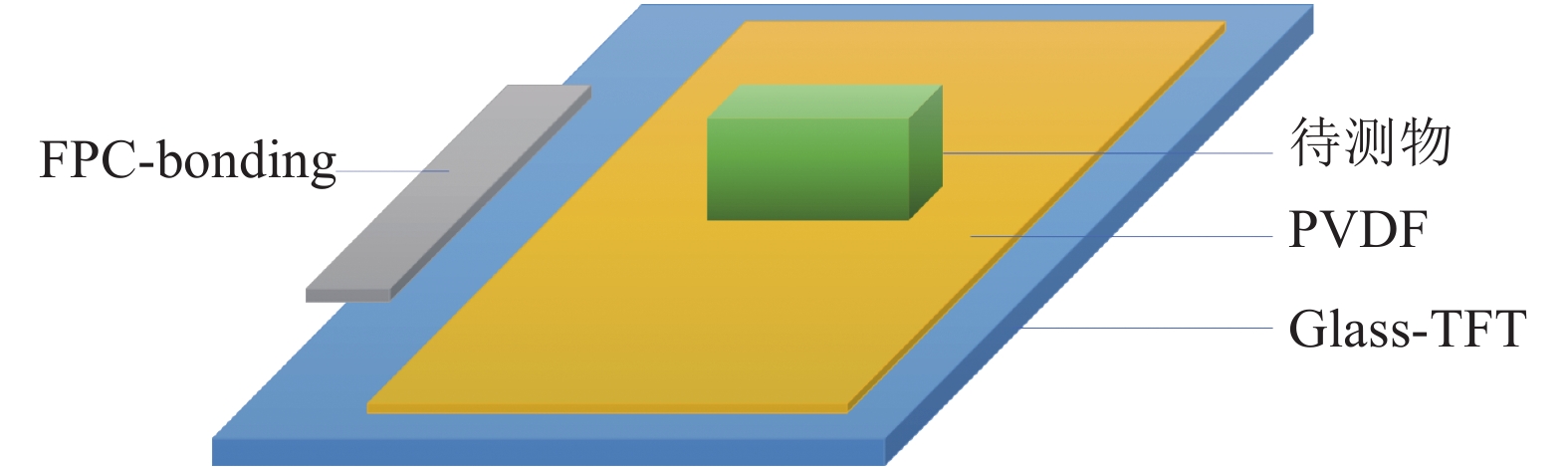
Aiming at nondestructive detection of the surface morphology of objects, a method based on large-area thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays and poly(vinglidene) fluoride (PVDF) films was developed, which can cover a large area and different shapes while is also portable and highly accurate. This method applies the TFT array, which has been widely used in the semiconductor display field, to the sensor applications. The sensor combined with TFT arrays utilizes the principle of capacitive sensor to accurately detect the surface topography, which can accurately locate micron-level surface defects with a resolution of 50 μm.
Aiming at nondestructive detection of the surface morphology of objects, a method based on large-area thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays and poly(vinglidene) fluoride (PVDF) films was developed, which can cover a large area and different shapes while is also portable and highly accurate. This method applies the TFT array, which has been widely used in the semiconductor display field, to the sensor applications. The sensor combined with TFT arrays utilizes the principle of capacitive sensor to accurately detect the surface topography, which can accurately locate micron-level surface defects with a resolution of 50 μm.
2020, 49(2): 291-314.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019054
Abstract:
Comparing with static network, temporal network is more suitable to characterize the dynamic evolution of real systems. It is of great importance to identify vital nodes and evaluate the node influence based on the models of temporal network. From the perspective of the topology and dynamics of temporal networks, we aim to review the recent research progress of identifying vital nodes, summarize and classify relevant identification methods, analyze their advantages and disadvantages, and point out the forefront as well as critical challenges of the field.
Comparing with static network, temporal network is more suitable to characterize the dynamic evolution of real systems. It is of great importance to identify vital nodes and evaluate the node influence based on the models of temporal network. From the perspective of the topology and dynamics of temporal networks, we aim to review the recent research progress of identifying vital nodes, summarize and classify relevant identification methods, analyze their advantages and disadvantages, and point out the forefront as well as critical challenges of the field.
2020, 49(2): 315-320.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018212
Abstract:
Clustering analysis is an important technology in data mining. By clustering analysis of multi-dimensional user behavior, it can help managers get more accurate and effective user evaluation information from the user level. In this paper, multi-dimensional user behavior features are extracted from user behavior data, and then unsupervised feature selection based on mutual information (UFS-MI) is used to sort, filter and confirm the features of the extracted features, and the weighted feature vectors of each user's behavior are obtained. The network is constructed according to the similarity between user behaviors, and then the user behavior network is clustered and analyzed by Blondel community partition algorithm. The experimental results on an empirical data set of a bus line show that the accuracy of the method is 92%, which is significantly higher than the accuracy rate of the traditional clustering algorithm K-means. The results can provide a reference for the management and training of the public transport management. This paper expands the application scope of network science in multi-dimensional user behavior data clustering analysis, enriches the idea of multi-dimensional driving behavior data clustering analysis, and provides reference for managers.
Clustering analysis is an important technology in data mining. By clustering analysis of multi-dimensional user behavior, it can help managers get more accurate and effective user evaluation information from the user level. In this paper, multi-dimensional user behavior features are extracted from user behavior data, and then unsupervised feature selection based on mutual information (UFS-MI) is used to sort, filter and confirm the features of the extracted features, and the weighted feature vectors of each user's behavior are obtained. The network is constructed according to the similarity between user behaviors, and then the user behavior network is clustered and analyzed by Blondel community partition algorithm. The experimental results on an empirical data set of a bus line show that the accuracy of the method is 92%, which is significantly higher than the accuracy rate of the traditional clustering algorithm K-means. The results can provide a reference for the management and training of the public transport management. This paper expands the application scope of network science in multi-dimensional user behavior data clustering analysis, enriches the idea of multi-dimensional driving behavior data clustering analysis, and provides reference for managers.

 ISSN
ISSN