2020 Vol. 49, No. 5
2020, 49(5): 643-651.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020212
Abstract:
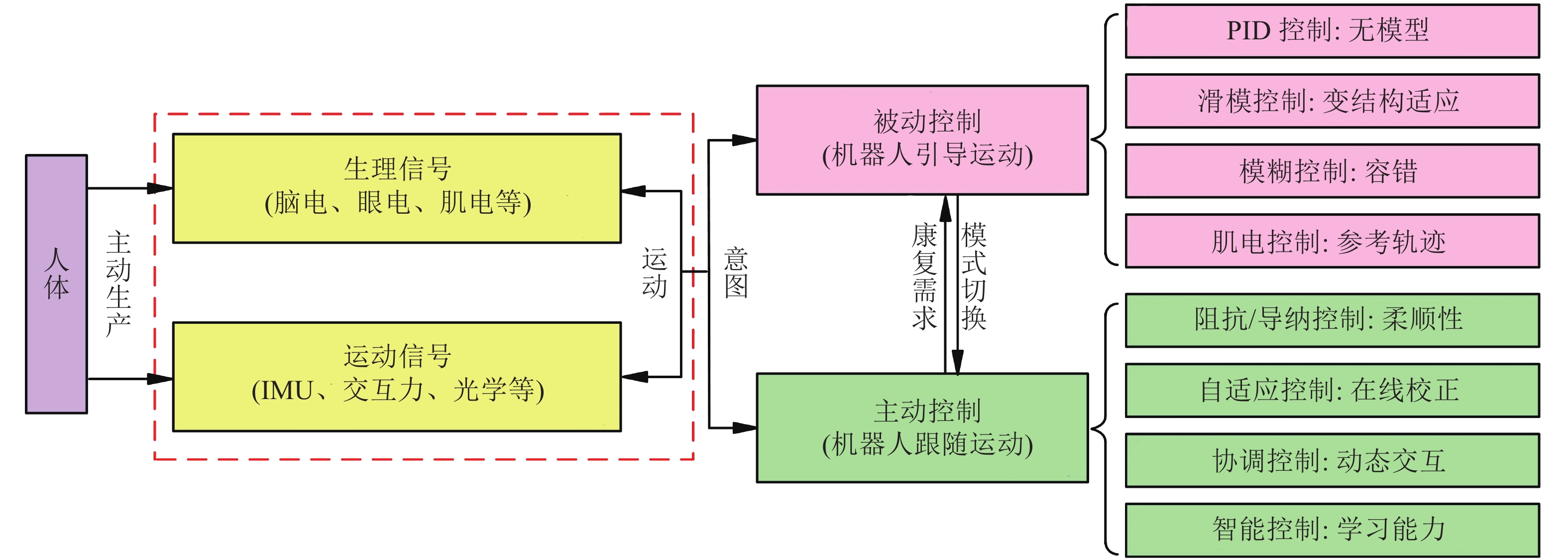
The upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot is mainly used to provide scientific and effective rehabilitation training for the patients with upper limb motor dysfunction. And, the patients could realize the recovery of motor function of the affected limb and to take care of themselves in daily life. This paper reviews the research progress in control strategy of upper limb exoskeleton robots in recent years. Firstly, according to the rehabilitation needs in different periods, the existing control strategies are classified into active and passive control. The different control methods are summarized. The current research status of each control method is pointed out. Finally, some key challenges of the upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot are discussed, and the future research directions are proposed.
The upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot is mainly used to provide scientific and effective rehabilitation training for the patients with upper limb motor dysfunction. And, the patients could realize the recovery of motor function of the affected limb and to take care of themselves in daily life. This paper reviews the research progress in control strategy of upper limb exoskeleton robots in recent years. Firstly, according to the rehabilitation needs in different periods, the existing control strategies are classified into active and passive control. The different control methods are summarized. The current research status of each control method is pointed out. Finally, some key challenges of the upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot are discussed, and the future research directions are proposed.
2020, 49(5): 652-659, 665.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020238
Abstract:
In this paper, a mathematical model is firstly built for economic dispatch of a hybrid resource system consisting of power plants, water plants, and coproduction plants. For this kind of optimization model considering the complex relation of the power and water in production, a continuous-time distributed algorithm is proposed to find the optimal solution of the economic dispatch problem. The convergence analysis shows that the trajectories converge to the optimal solution regardless of the initial allocation, avoiding the consideration of the initial procedure in detail. Moreover, applying the proposed algorithm, the plants no longer need to exchange the gradient information of the cost functions with their neighbors, which can protect the privacy of the plants. Finally, a numerical example is provided to demonstrate the performance and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for the energy-water nexus.
In this paper, a mathematical model is firstly built for economic dispatch of a hybrid resource system consisting of power plants, water plants, and coproduction plants. For this kind of optimization model considering the complex relation of the power and water in production, a continuous-time distributed algorithm is proposed to find the optimal solution of the economic dispatch problem. The convergence analysis shows that the trajectories converge to the optimal solution regardless of the initial allocation, avoiding the consideration of the initial procedure in detail. Moreover, applying the proposed algorithm, the plants no longer need to exchange the gradient information of the cost functions with their neighbors, which can protect the privacy of the plants. Finally, a numerical example is provided to demonstrate the performance and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for the energy-water nexus.
2020, 49(5): 660-665.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020192
Abstract:
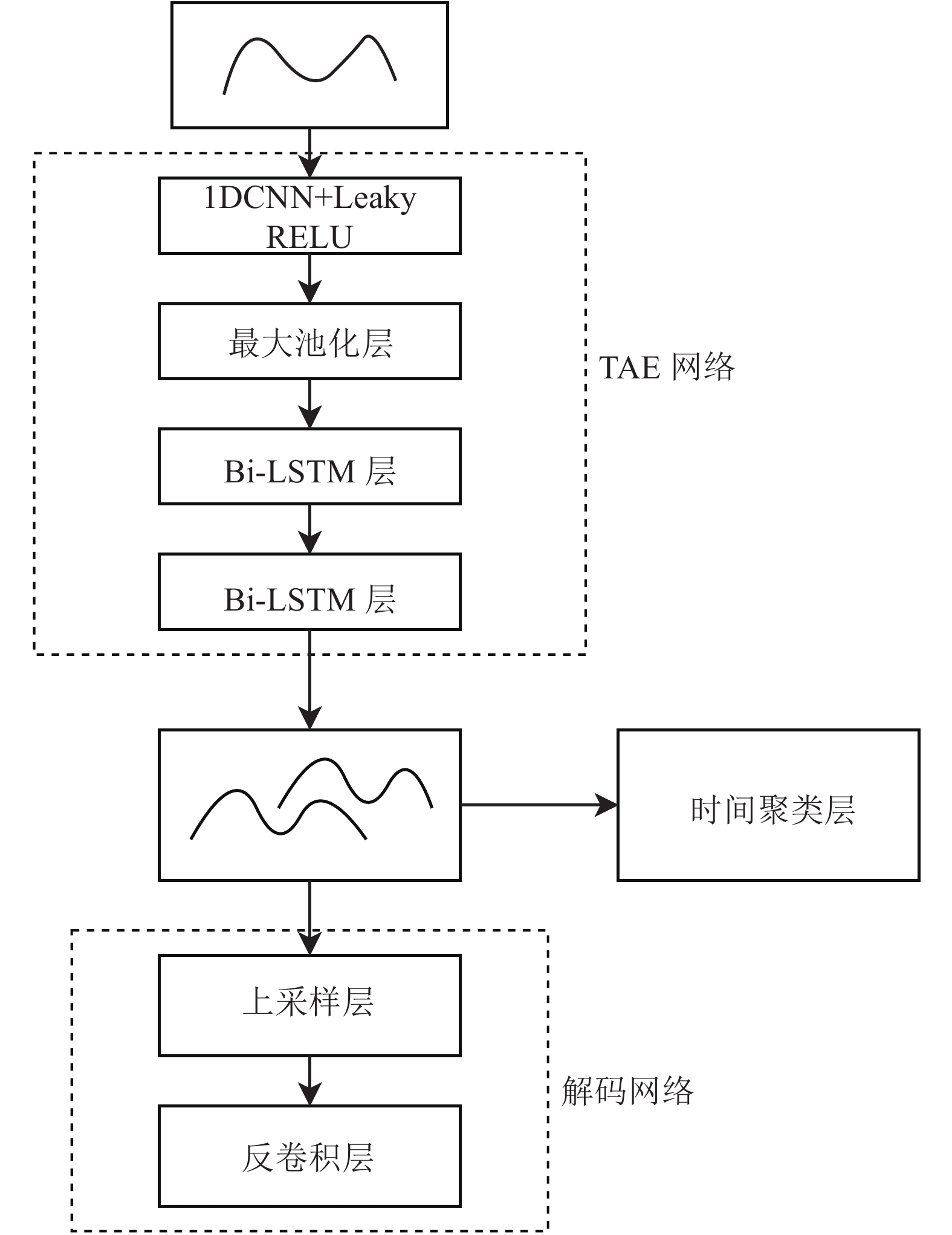
Aiming at the classification problem of the contact state in the robot peg-in-hole task, this paper proposes a clustering method based on the multivariate time series. This method uses a deep temporal clustering network to encode the contact state variables in the assembly process, and then a complexity-invariant distance measure is used to classify the time series fragments. This method avoids the quasi-static analysis of the contact process and thus has a certain generality in practice. And the use of time series is beneficial to extract the time-related characteristics of contact state variables, which can make the clustering results more robust. The experimental results are consistent with expectations, indicating the theoretical correctness and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Aiming at the classification problem of the contact state in the robot peg-in-hole task, this paper proposes a clustering method based on the multivariate time series. This method uses a deep temporal clustering network to encode the contact state variables in the assembly process, and then a complexity-invariant distance measure is used to classify the time series fragments. This method avoids the quasi-static analysis of the contact process and thus has a certain generality in practice. And the use of time series is beneficial to extract the time-related characteristics of contact state variables, which can make the clustering results more robust. The experimental results are consistent with expectations, indicating the theoretical correctness and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
2020, 49(5): 666-673.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020010
Abstract:
To solve the problem of unstable link and low reliability in vehicle ad hoc network (VANET), we propose a relay forwarding scheme based on weighted clustering. In the scheme, we first present the weighted cluster algorithm to improve the stability of the communication link and introduce the relative vehicular confidence distance, relative achievable rate and connectivity as clustering properties and select the optimal cluster head as a relay in the ascending order of their property weight. And then, the bidirectional DF protocol is adopted to enhance the reliability of vehicle to vehicle communication under the NaKagami-m channel. Numerical results show that the stability of the proposed algorithm cloud improve 8 seconds compared with the lane based cluster algorithm. The outage probability of bidirectional DF protocol reduces 6% compared with AF protocol.
To solve the problem of unstable link and low reliability in vehicle ad hoc network (VANET), we propose a relay forwarding scheme based on weighted clustering. In the scheme, we first present the weighted cluster algorithm to improve the stability of the communication link and introduce the relative vehicular confidence distance, relative achievable rate and connectivity as clustering properties and select the optimal cluster head as a relay in the ascending order of their property weight. And then, the bidirectional DF protocol is adopted to enhance the reliability of vehicle to vehicle communication under the NaKagami-m channel. Numerical results show that the stability of the proposed algorithm cloud improve 8 seconds compared with the lane based cluster algorithm. The outage probability of bidirectional DF protocol reduces 6% compared with AF protocol.
2020, 49(5): 674-679.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020066
Abstract:
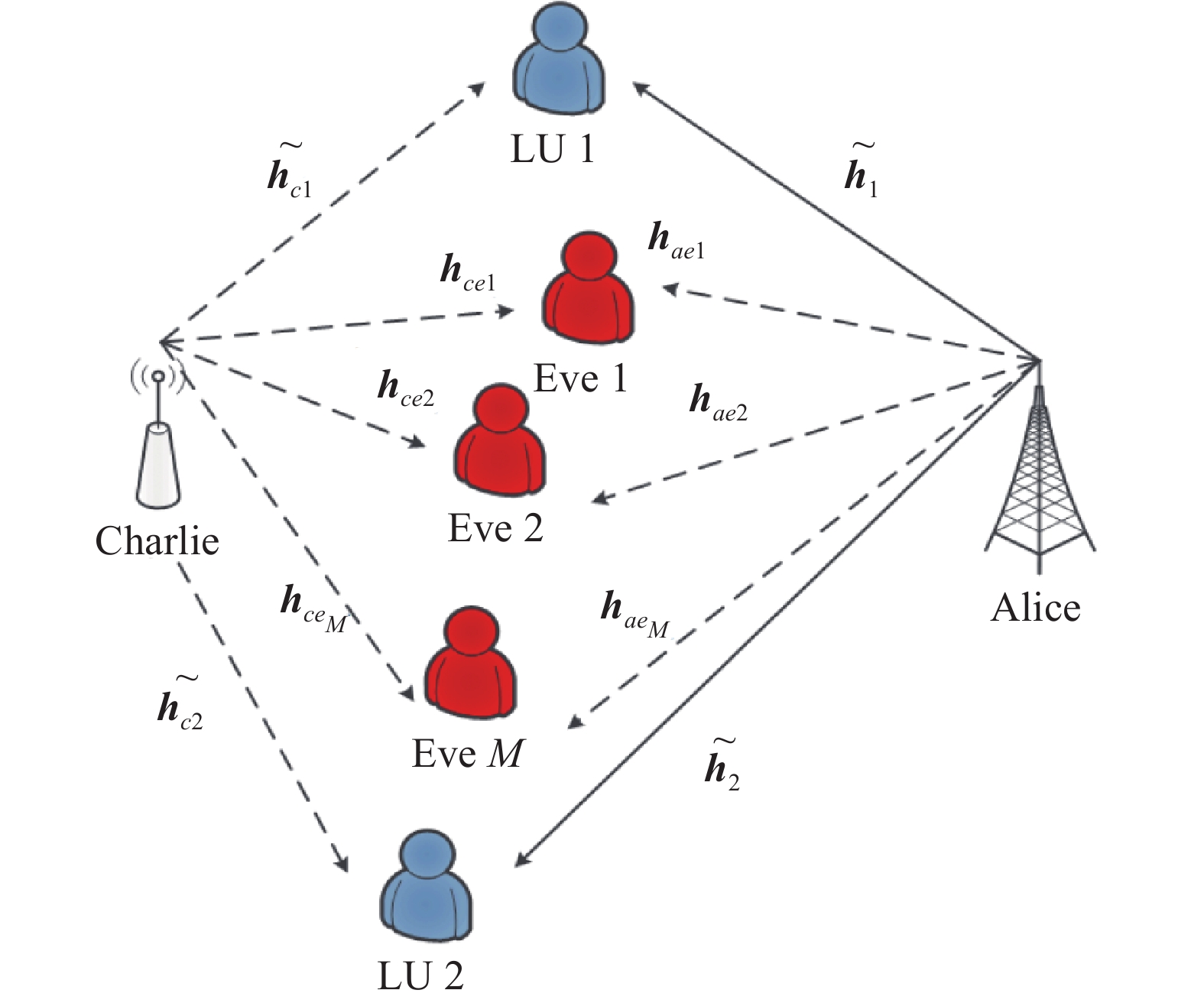
This paper studied secure transmission in cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) networks, where one legitimate user with high-level security requirement (LU1) is overhead by multiple non-colluding eavesdroppers (Eves), and another normal user (LU2) is served by the source (Alice) simultaneously. Aiming to improve the secrecy performance, a cooperative jammer (Charlie) is employed to confound the Eves. In this more practical communication scenario, take both secrecy outage restriction of LU1 and the desired quality of service (QoS) demand of LU2 into consideration, the paper propose an adaptive power allocation strategy for maximizing secrecy rate under imperfect channel state information (CSI). Numerical results are provided to verify the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and show that the system security would be seriously degenerated with channel uncertainty.
This paper studied secure transmission in cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) networks, where one legitimate user with high-level security requirement (LU1) is overhead by multiple non-colluding eavesdroppers (Eves), and another normal user (LU2) is served by the source (Alice) simultaneously. Aiming to improve the secrecy performance, a cooperative jammer (Charlie) is employed to confound the Eves. In this more practical communication scenario, take both secrecy outage restriction of LU1 and the desired quality of service (QoS) demand of LU2 into consideration, the paper propose an adaptive power allocation strategy for maximizing secrecy rate under imperfect channel state information (CSI). Numerical results are provided to verify the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and show that the system security would be seriously degenerated with channel uncertainty.
2020, 49(5): 680-689.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019263
Abstract:
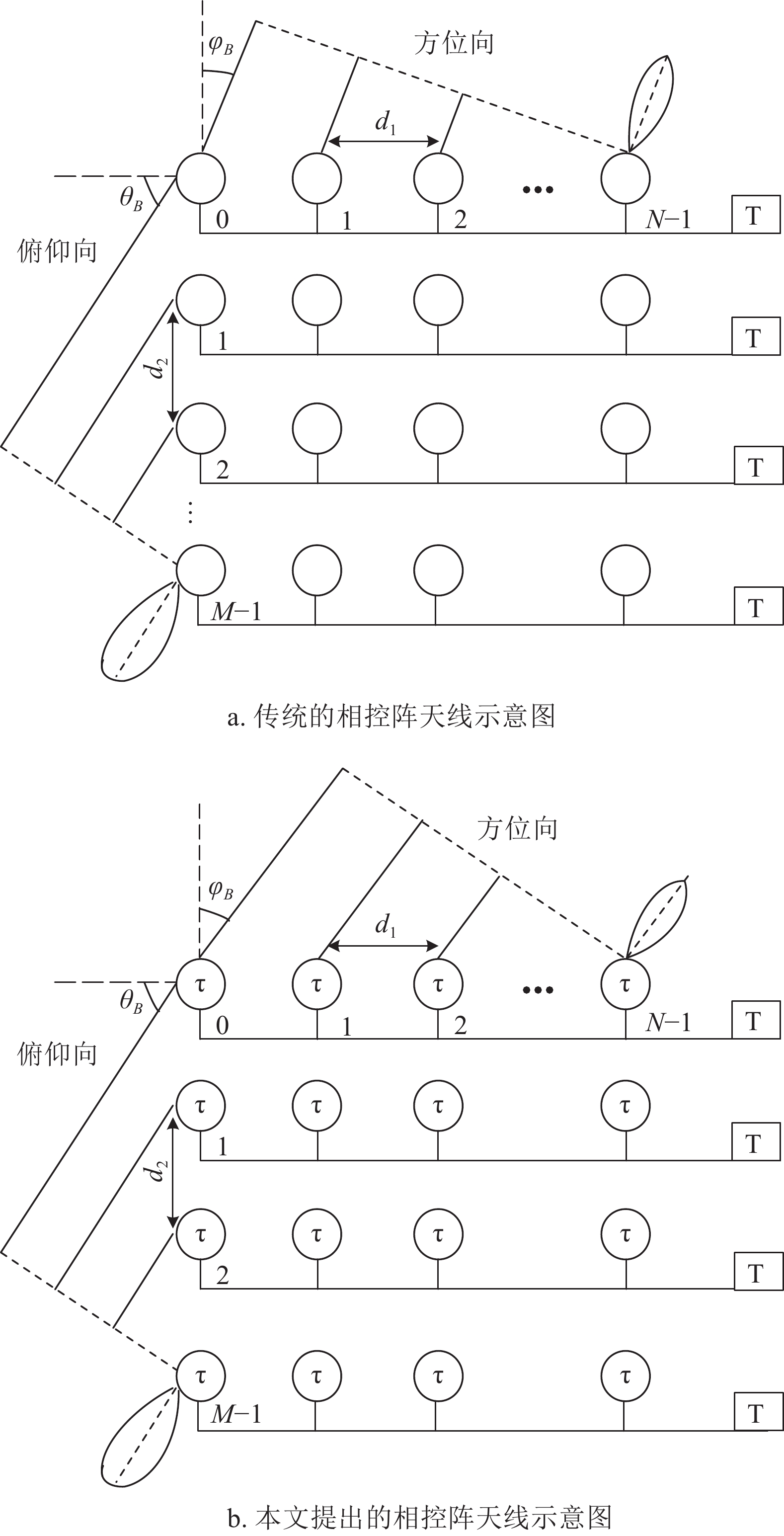
An X-band multi-function chip(MFC) with phase and amplitude control is designed and fabricated in 0.5 μm GaAs pHEMT technology, which can significantly improve the integration of transmit/receive (T/R) radar module. The MFC consists of a 2-bit true time delay(TTD), a 6-bit digital phase shifter, a 6-bit digital attenuator and two drive amplifiers. In terms of architecture design, a 2-bit TTD is introduced at the first time to achieve wideband operation while lowering beam squinting, and realizing the independent control of amplitude, phase and time delay on a single chip. The high-low pass phase shifting network and switch-path-type attenuation topology are employed in order to achieve high-precision phase and amplitude performance. The measurement results show that the RMS phase and amplitude error of 64-state phase shifter is 3.5° and 0.3 dB max, the RMS amplitude and phase error of 64-state attenuator is less than 0.4 dB and 2.5°, and the delay error of 3-state TTD is less than 1.5 ps over the 8 GHz to 12 GHz frequency band. The chip size is 5.0 mm×3.5 mm including the test pads.
An X-band multi-function chip(MFC) with phase and amplitude control is designed and fabricated in 0.5 μm GaAs pHEMT technology, which can significantly improve the integration of transmit/receive (T/R) radar module. The MFC consists of a 2-bit true time delay(TTD), a 6-bit digital phase shifter, a 6-bit digital attenuator and two drive amplifiers. In terms of architecture design, a 2-bit TTD is introduced at the first time to achieve wideband operation while lowering beam squinting, and realizing the independent control of amplitude, phase and time delay on a single chip. The high-low pass phase shifting network and switch-path-type attenuation topology are employed in order to achieve high-precision phase and amplitude performance. The measurement results show that the RMS phase and amplitude error of 64-state phase shifter is 3.5° and 0.3 dB max, the RMS amplitude and phase error of 64-state attenuator is less than 0.4 dB and 2.5°, and the delay error of 3-state TTD is less than 1.5 ps over the 8 GHz to 12 GHz frequency band. The chip size is 5.0 mm×3.5 mm including the test pads.
2020, 49(5): 690-694.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019296
Abstract:
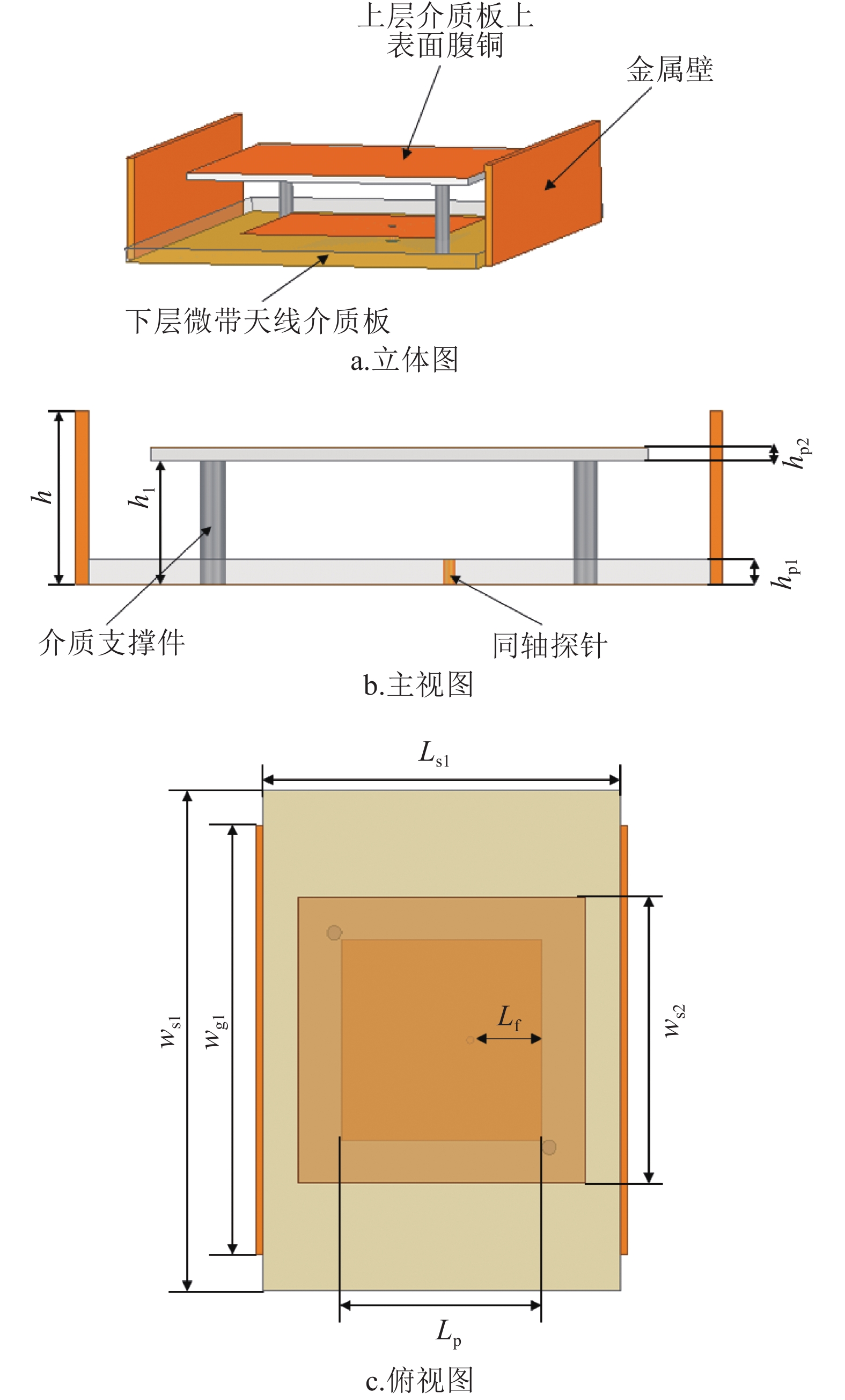
This paper introduces a novel idea for designing a phase array microstrip antenna element with low coupling and wide beam scan capabilities. Consisted of two-layers patches separated by an air gap and fold grounds, the proposed antenna element has a simple structure. In order to minimize the array gain drop due to the limited antenna beam width, the proposed antenna is designed to expand the half-power beam width as far as possible with fold grounds structure. At the same time, in order to reduce the distortion of antenna element pattern caused by mutual coupling, some methods are proposed for reducing the mutual coupling to make sure satisfy the product theorem of antenna pattern as much as possible. Moreover, a prototype of the proposed antenna and a linear array are fabricated and measured. The measured results show that the wide angle scanning array is capable of scanning up to ± 70° along with stable gain characteristics. Meanwhile, the proposed antenna is a classical antenna which can be used for 5G applications ranging from infotainment solutions to consumer devices.
This paper introduces a novel idea for designing a phase array microstrip antenna element with low coupling and wide beam scan capabilities. Consisted of two-layers patches separated by an air gap and fold grounds, the proposed antenna element has a simple structure. In order to minimize the array gain drop due to the limited antenna beam width, the proposed antenna is designed to expand the half-power beam width as far as possible with fold grounds structure. At the same time, in order to reduce the distortion of antenna element pattern caused by mutual coupling, some methods are proposed for reducing the mutual coupling to make sure satisfy the product theorem of antenna pattern as much as possible. Moreover, a prototype of the proposed antenna and a linear array are fabricated and measured. The measured results show that the wide angle scanning array is capable of scanning up to ± 70° along with stable gain characteristics. Meanwhile, the proposed antenna is a classical antenna which can be used for 5G applications ranging from infotainment solutions to consumer devices.
2020, 49(5): 695-699.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019245
Abstract:
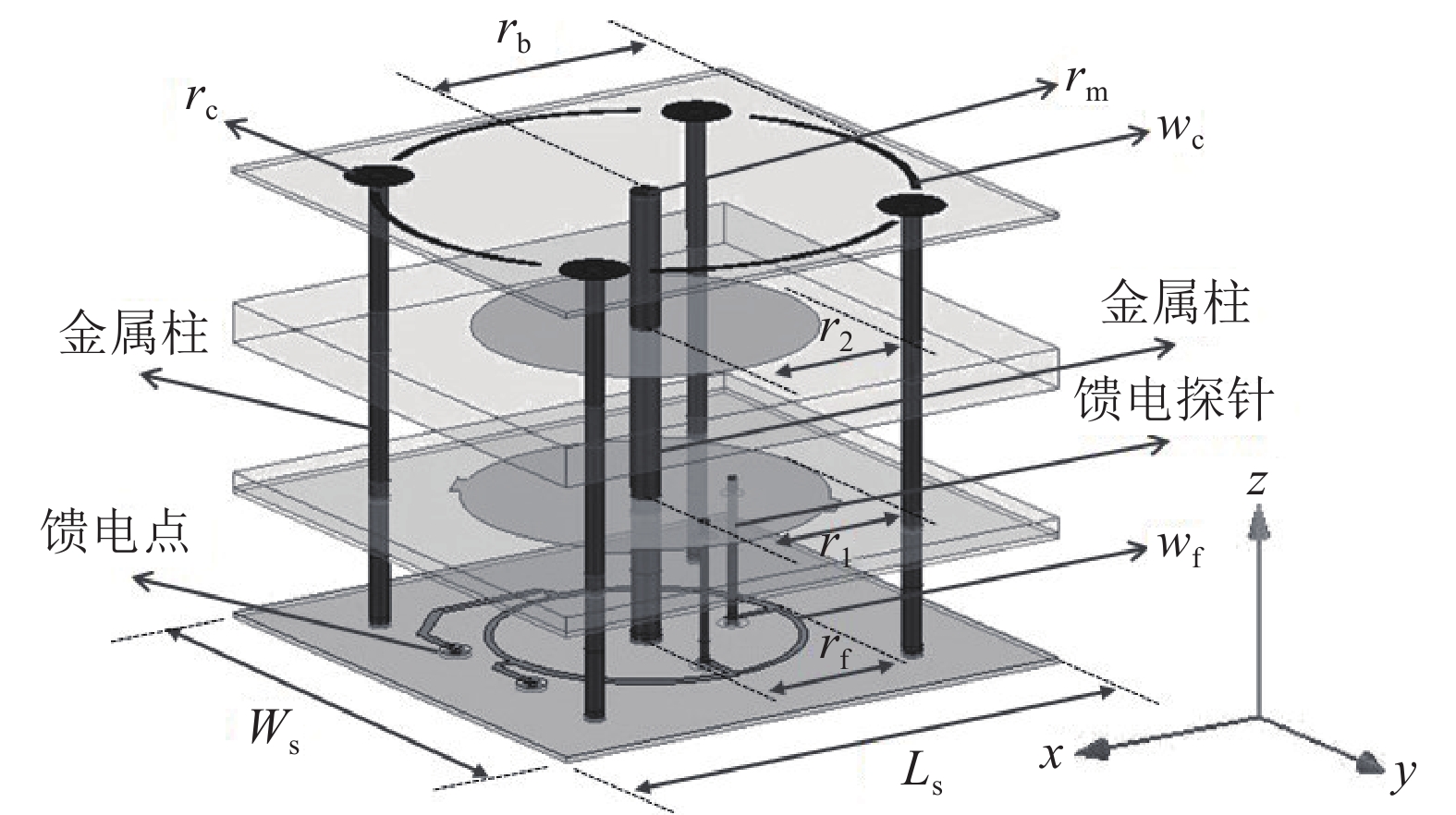
A double circular polarization broadband antenna is designed, and a small array is realized on this basis. The element antenna is a stacked microstrip antenna with a ring of metal bands and metal columns around the radiation patch to expand the beam width. In addition, in order to meet the requirements of double circular polarization and to expand the antenna bandwidth, the antenna is fed by a ring bridge. The 10 dB impedance bandwidth is 26.9% (1.8 GHz~2.36 GHz), the 3 dB axial ratio bandwidth is 19.3% (1.92~2.33 GHz), and the 3 dB beam width is greater than 110°. A non-regular five elements array is investigated. The test results show that the synthetic gain is higher than 11.5dBi, and the ±55° scanning gain is higher than 9dBi. The simulation and experimental results are consistent, which is the foundation of broadband satellite communication application.
A double circular polarization broadband antenna is designed, and a small array is realized on this basis. The element antenna is a stacked microstrip antenna with a ring of metal bands and metal columns around the radiation patch to expand the beam width. In addition, in order to meet the requirements of double circular polarization and to expand the antenna bandwidth, the antenna is fed by a ring bridge. The 10 dB impedance bandwidth is 26.9% (1.8 GHz~2.36 GHz), the 3 dB axial ratio bandwidth is 19.3% (1.92~2.33 GHz), and the 3 dB beam width is greater than 110°. A non-regular five elements array is investigated. The test results show that the synthetic gain is higher than 11.5dBi, and the ±55° scanning gain is higher than 9dBi. The simulation and experimental results are consistent, which is the foundation of broadband satellite communication application.
2020, 49(5): 700-708.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019291
Abstract:
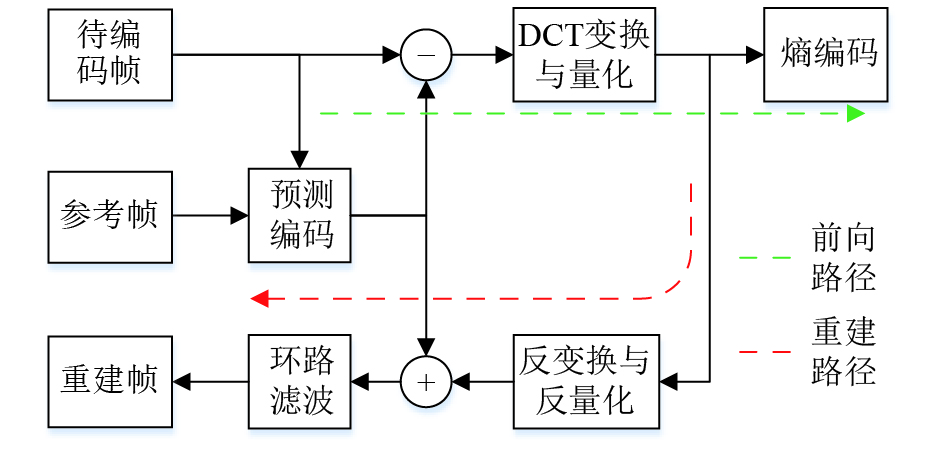
Aiming at the problem of high complexity of existing video encryption algorithms, a low complexity texture-adaptive video encryption algorithm is proposed. Firstly, the quantized residual DCT coefficients and motion vectors obtained in the video encoding process are used to build the threshold-adaptive texture estimation model, which is used to detect texture region for video encryption. Then, considering the video encoding efficiency and format compatibility, the signs of quantized non-zero DCT coefficient and non-zero MVD are selected for encryption in the texture region, respectively. The algorithm takes the H.264/AVC video codec as a verification example, the experimental results show that, the proposed encryption algorithm ensures the security of video content and the efficiency of compression encoding, while reducing the complexity of the encryption algorithm and the amount of data to be encrypted greatly. Meanwhile, compared with existing texture detection methods, the complexity of the proposed texture detection algorithm is extremely low, and it can be applied to real-time video encryption application scenarios.
Aiming at the problem of high complexity of existing video encryption algorithms, a low complexity texture-adaptive video encryption algorithm is proposed. Firstly, the quantized residual DCT coefficients and motion vectors obtained in the video encoding process are used to build the threshold-adaptive texture estimation model, which is used to detect texture region for video encryption. Then, considering the video encoding efficiency and format compatibility, the signs of quantized non-zero DCT coefficient and non-zero MVD are selected for encryption in the texture region, respectively. The algorithm takes the H.264/AVC video codec as a verification example, the experimental results show that, the proposed encryption algorithm ensures the security of video content and the efficiency of compression encoding, while reducing the complexity of the encryption algorithm and the amount of data to be encrypted greatly. Meanwhile, compared with existing texture detection methods, the complexity of the proposed texture detection algorithm is extremely low, and it can be applied to real-time video encryption application scenarios.
2020, 49(5): 709-717.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019122
Abstract:
In order to improve the accuracy of anthropometric feature point localization in complex background and arbitrary dress cases, the stacked hourglass network (SHN) is introduced into the localization of anthropometric feature points in body images. However, the resolution of the SHN model’s output feature map is too low to obtain high accurate feature points. So, a Deconv-SHN model is proposed to address this problem. On the one hand, the output layer of the initial model is replaced by several deconvolution layers to improve the resolution of the output feature map. On the other hand, the objective function is optimized based on Smooth L1 and local response. According to the experimental results on the self-built dataset consisting of 6 700 human body images, the localization precision of the Deconv-SHN model in complex background and arbitrary dress cases is significantly higher than that of the traditional algorithm, which is also obviously superior to the SHN model, and basically meets the requirements of anthropometric applications.
In order to improve the accuracy of anthropometric feature point localization in complex background and arbitrary dress cases, the stacked hourglass network (SHN) is introduced into the localization of anthropometric feature points in body images. However, the resolution of the SHN model’s output feature map is too low to obtain high accurate feature points. So, a Deconv-SHN model is proposed to address this problem. On the one hand, the output layer of the initial model is replaced by several deconvolution layers to improve the resolution of the output feature map. On the other hand, the objective function is optimized based on Smooth L1 and local response. According to the experimental results on the self-built dataset consisting of 6 700 human body images, the localization precision of the Deconv-SHN model in complex background and arbitrary dress cases is significantly higher than that of the traditional algorithm, which is also obviously superior to the SHN model, and basically meets the requirements of anthropometric applications.
2020, 49(5): 718-731.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019088
Abstract:
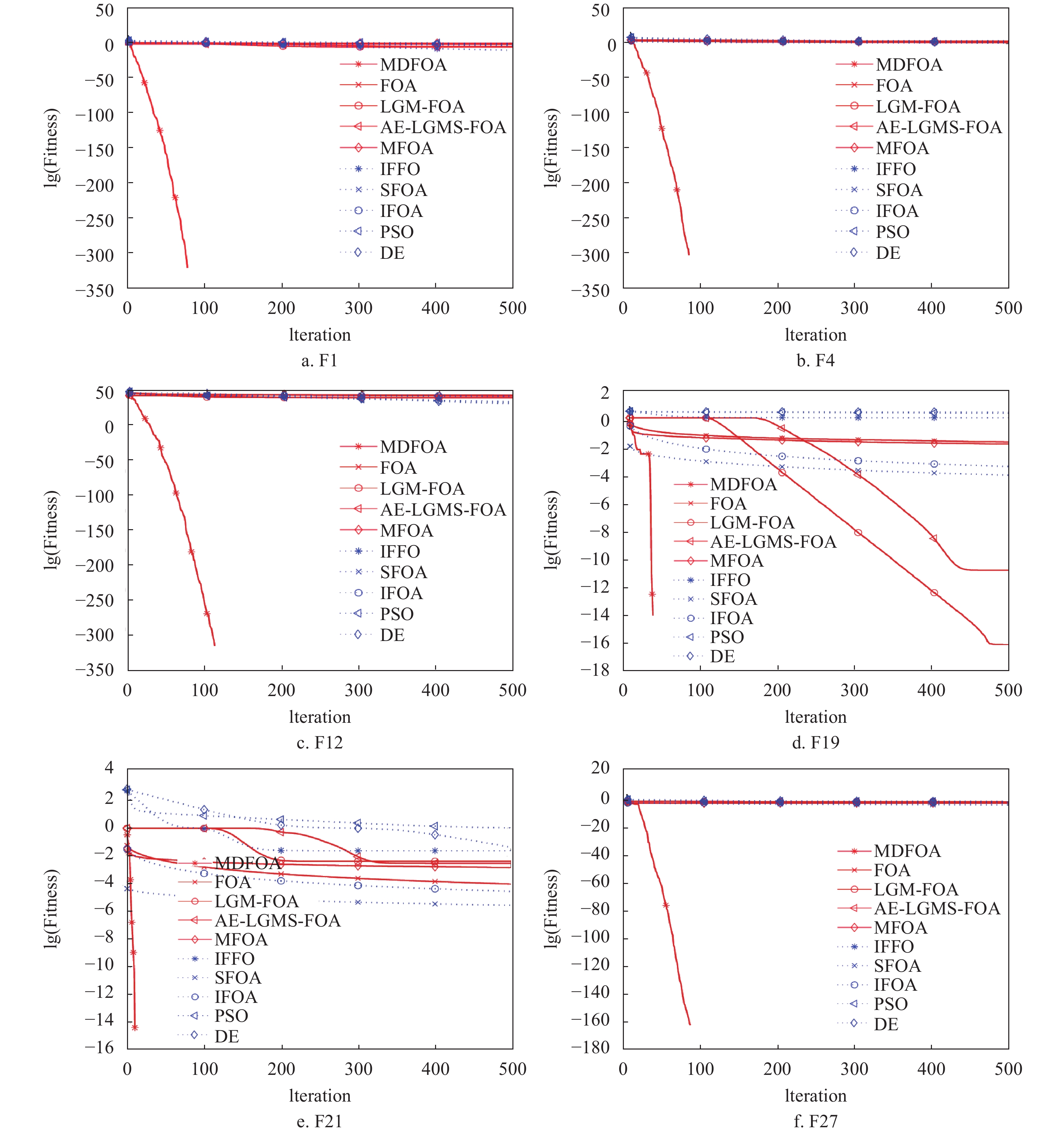
Fruit fly optimization algorithm (FOA) is a new global optimization algorithm inspired by the osphresis and vision behaviors of the fruit flies, which has been shown to have a strong capacity for solving continuous optimization problems. However, the candidate solutions of FOA could not take values those are negative, and the basic FOA is also faced with the challenges of poor diversity of the swarm and weak local search ability. To overcome these limitations synthetically, this study presents an improved FOA based on multi-strategy evolution and dynamic updating of swarm optimal information (MDFOA), aiming at well balancing the global search and local search abilities. In the proposed MDFOA, an effective candidate solution generating method and a new control parameter are introduced to improve the convergence performance. Moreover, a real-time update mechanism of the global optimal information is designed to further improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. 29 complex continuous benchmark functions are used to test the effectiveness of the proposed method. Numerical results show that the proposed MDFOA is superior to several other algorithms, such as the basic FOA, six variants of FOA, and two state-of-the-art intelligent optimization algorithms.
Fruit fly optimization algorithm (FOA) is a new global optimization algorithm inspired by the osphresis and vision behaviors of the fruit flies, which has been shown to have a strong capacity for solving continuous optimization problems. However, the candidate solutions of FOA could not take values those are negative, and the basic FOA is also faced with the challenges of poor diversity of the swarm and weak local search ability. To overcome these limitations synthetically, this study presents an improved FOA based on multi-strategy evolution and dynamic updating of swarm optimal information (MDFOA), aiming at well balancing the global search and local search abilities. In the proposed MDFOA, an effective candidate solution generating method and a new control parameter are introduced to improve the convergence performance. Moreover, a real-time update mechanism of the global optimal information is designed to further improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. 29 complex continuous benchmark functions are used to test the effectiveness of the proposed method. Numerical results show that the proposed MDFOA is superior to several other algorithms, such as the basic FOA, six variants of FOA, and two state-of-the-art intelligent optimization algorithms.
2020, 49(5): 732-738.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019294
Abstract:
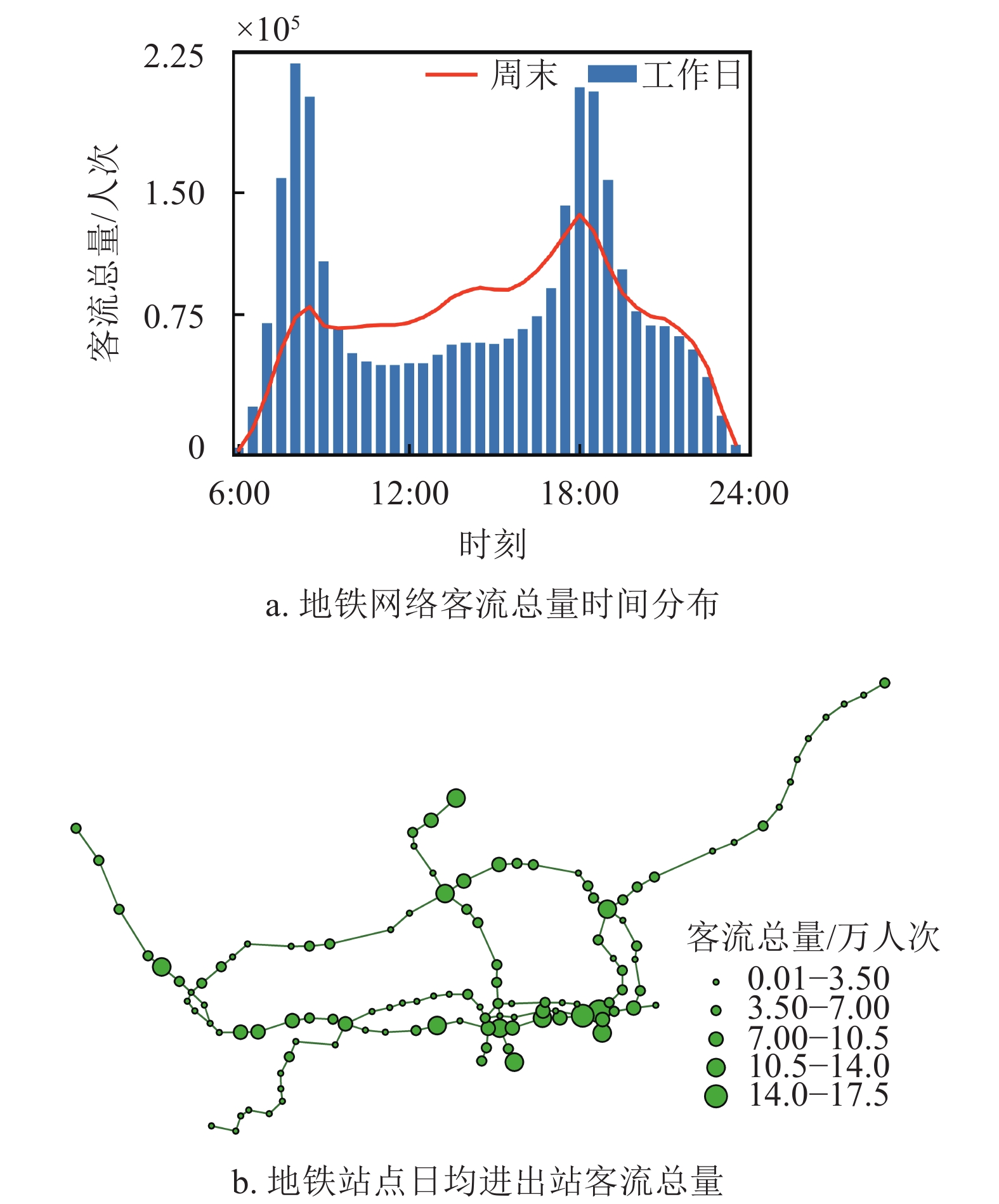
In order to reveal the evolutionary mechanism of large passenger flow in urban metro, this paper introduces the concept of anomalous mobility network. Complex network analysis is used to study the structural complexity and dynamic evolution of anomalous mobility networks under ordinary and large passenger flow situations in Shenzhen metro. In addition, this paper proposes an indicator to identify the key nodes of anomalous mobility network. Results show that the anomalous mobility network evolves from long-tailed indegree to long-tailed outdegree with the aggregation and the evacuation of passenger flows. There is a transition process between the scale-free network and the random network. This research can provide a reference for early warning of large passenger flow, passenger flow organization and management in urban metro.
In order to reveal the evolutionary mechanism of large passenger flow in urban metro, this paper introduces the concept of anomalous mobility network. Complex network analysis is used to study the structural complexity and dynamic evolution of anomalous mobility networks under ordinary and large passenger flow situations in Shenzhen metro. In addition, this paper proposes an indicator to identify the key nodes of anomalous mobility network. Results show that the anomalous mobility network evolves from long-tailed indegree to long-tailed outdegree with the aggregation and the evacuation of passenger flows. There is a transition process between the scale-free network and the random network. This research can provide a reference for early warning of large passenger flow, passenger flow organization and management in urban metro.
2020, 49(5): 739-744.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020152
Abstract:
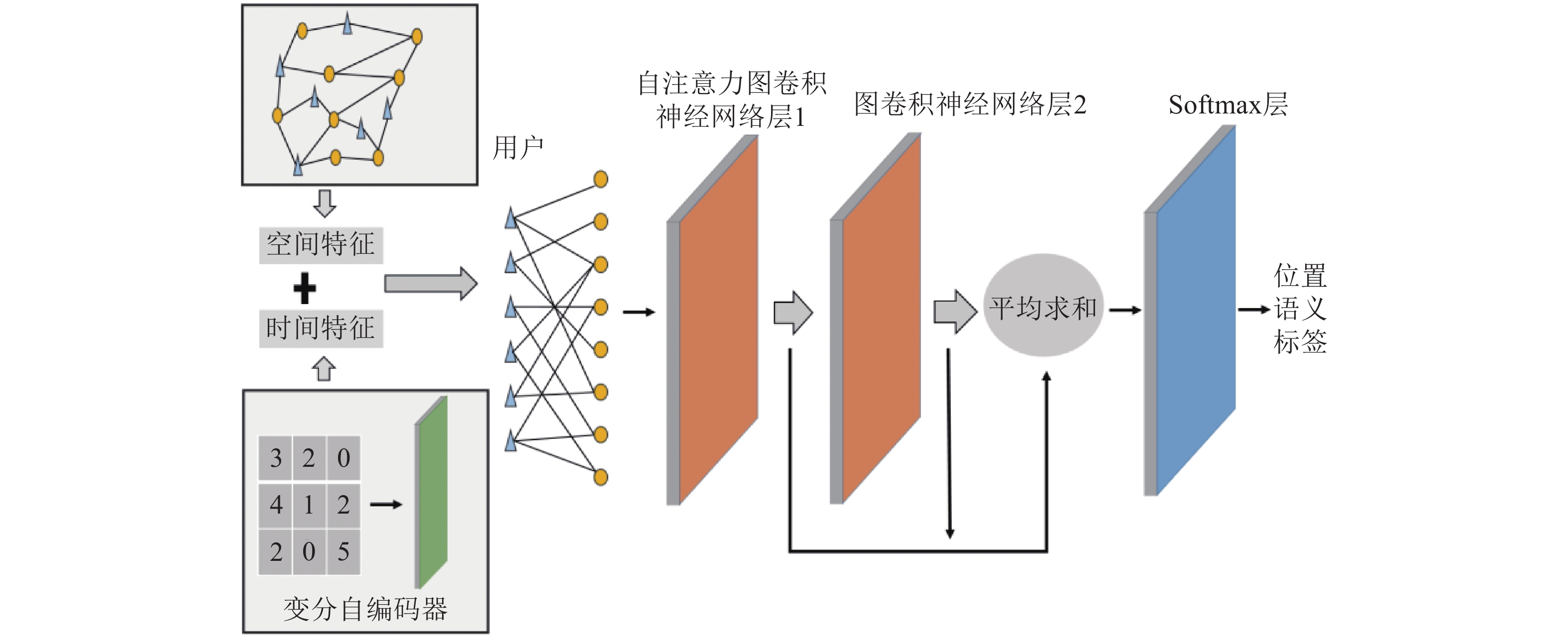
Data mining on check-in data inlocation based social networks (LBSNs) is an important research direction of urban computing and smart city, and a critical task is to infer location semantic. The study of location semantics has attracted increasing attention in diverse fields due to its wide applications such as location retrieval, location recommendation, data preprocessing and so on. Established inference approaches tend to manually discover the spatiotemporal pattern of unique location as features for training classifiers. However, extracting valuable spatiotemporal patterns or features is a non-trivial task. In this paper, we propose a novel location semantic inference with graph convolutional networks (SI-GCN). We introduce node2vec and variational autoencoder to learn spatial and temporal features of location, respectively. Furthermore, we leverage graph convolutional networks to capture high order relations in user’s check-in activity with building a user-location bipartite network. And leveraging self-attention mechanism is allowed to distinguish contributions of the different nodes. Extensive experiments on several real-world check-in data sets show that our proposed framework outperforms than three state-of-art algorithms.
Data mining on check-in data inlocation based social networks (LBSNs) is an important research direction of urban computing and smart city, and a critical task is to infer location semantic. The study of location semantics has attracted increasing attention in diverse fields due to its wide applications such as location retrieval, location recommendation, data preprocessing and so on. Established inference approaches tend to manually discover the spatiotemporal pattern of unique location as features for training classifiers. However, extracting valuable spatiotemporal patterns or features is a non-trivial task. In this paper, we propose a novel location semantic inference with graph convolutional networks (SI-GCN). We introduce node2vec and variational autoencoder to learn spatial and temporal features of location, respectively. Furthermore, we leverage graph convolutional networks to capture high order relations in user’s check-in activity with building a user-location bipartite network. And leveraging self-attention mechanism is allowed to distinguish contributions of the different nodes. Extensive experiments on several real-world check-in data sets show that our proposed framework outperforms than three state-of-art algorithms.
2020, 49(5): 745-750.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019233
Abstract:
AFL-CGI-wrapper (ACW) is designed for detecting vulnerabilities in desktop CGI programs, the core idea is fuzzing CGI via executing the targeted program in the QEMU environment. However, there are two challenges when applying ACW on discovering vulnerabilities of embedded CGIs: 1) the diversity of devices makes fuzzing via fixed input-model is inefficient; 2) only tracing the main module of CGI cannot utilize coverage information to guide fuzzing to explore those code paths that are dependent on functions hosted in extern module. To overcome these two challenges, a lazy input-model based on feedback and a selective extern function tracing are presented and implemented in the prototyping system named BCFuzzer. Finally, several experiments had been conducted based on a set of embedded CGIs from some real-word devices. The result shows that the techniques of BCFuzzer can help to explore more code paths and detect more vulnerabilities as soon as possible.
AFL-CGI-wrapper (ACW) is designed for detecting vulnerabilities in desktop CGI programs, the core idea is fuzzing CGI via executing the targeted program in the QEMU environment. However, there are two challenges when applying ACW on discovering vulnerabilities of embedded CGIs: 1) the diversity of devices makes fuzzing via fixed input-model is inefficient; 2) only tracing the main module of CGI cannot utilize coverage information to guide fuzzing to explore those code paths that are dependent on functions hosted in extern module. To overcome these two challenges, a lazy input-model based on feedback and a selective extern function tracing are presented and implemented in the prototyping system named BCFuzzer. Finally, several experiments had been conducted based on a set of embedded CGIs from some real-word devices. The result shows that the techniques of BCFuzzer can help to explore more code paths and detect more vulnerabilities as soon as possible.
2020, 49(5): 751-757.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019205
Abstract:
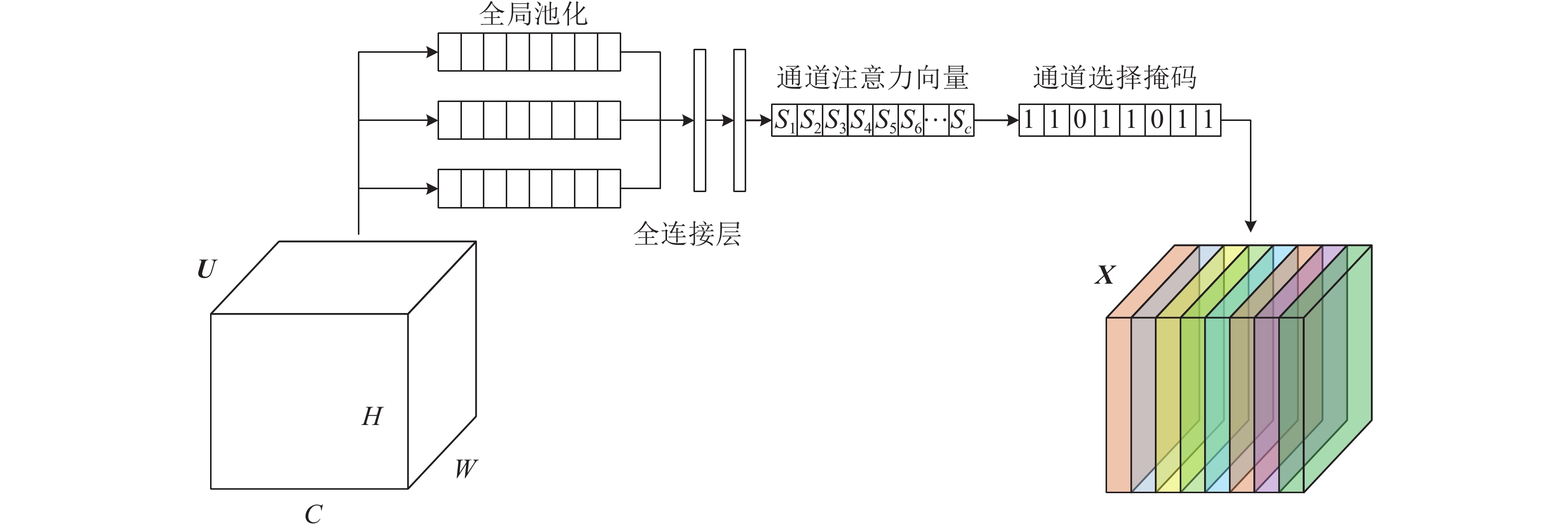
To improve the fault diagnosis accuracy of pumping unit and reduce the storage memory of diagnosis model, a novel fault diagnosis method based on a lightweight attention convolutional neural network is designed to recognize the dynamometer card in this paper. The shape outline composed by the displacement and load of dynamometer card is transformed into the image. Regarding the model architecture, we leverage the depthwise separable convolution and propose a regularization attention module which can be embedded to the consecutive convolution layers. Each channel of the depthwise separable convolution layer is compressed and filtered by the mechanism provided by the model. It constructs the attention feature map, in which the feature is suppressed or enhanced. Regarding the model training, the attention-based loss function is presented to suppress the contribution of easy samples to the training loss. It makes the training to pay more attention to hard samples than easy ones. Finally, the proposed method is evaluated by the experiment. The experimental results show that the size of the model is only 5.4 Mb, while the diagnosis accuracy is 95.1%, which meet the requirements of fault diagnosis of the pumping unit.
To improve the fault diagnosis accuracy of pumping unit and reduce the storage memory of diagnosis model, a novel fault diagnosis method based on a lightweight attention convolutional neural network is designed to recognize the dynamometer card in this paper. The shape outline composed by the displacement and load of dynamometer card is transformed into the image. Regarding the model architecture, we leverage the depthwise separable convolution and propose a regularization attention module which can be embedded to the consecutive convolution layers. Each channel of the depthwise separable convolution layer is compressed and filtered by the mechanism provided by the model. It constructs the attention feature map, in which the feature is suppressed or enhanced. Regarding the model training, the attention-based loss function is presented to suppress the contribution of easy samples to the training loss. It makes the training to pay more attention to hard samples than easy ones. Finally, the proposed method is evaluated by the experiment. The experimental results show that the size of the model is only 5.4 Mb, while the diagnosis accuracy is 95.1%, which meet the requirements of fault diagnosis of the pumping unit.
2020, 49(5): 758-765.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019297
Abstract:
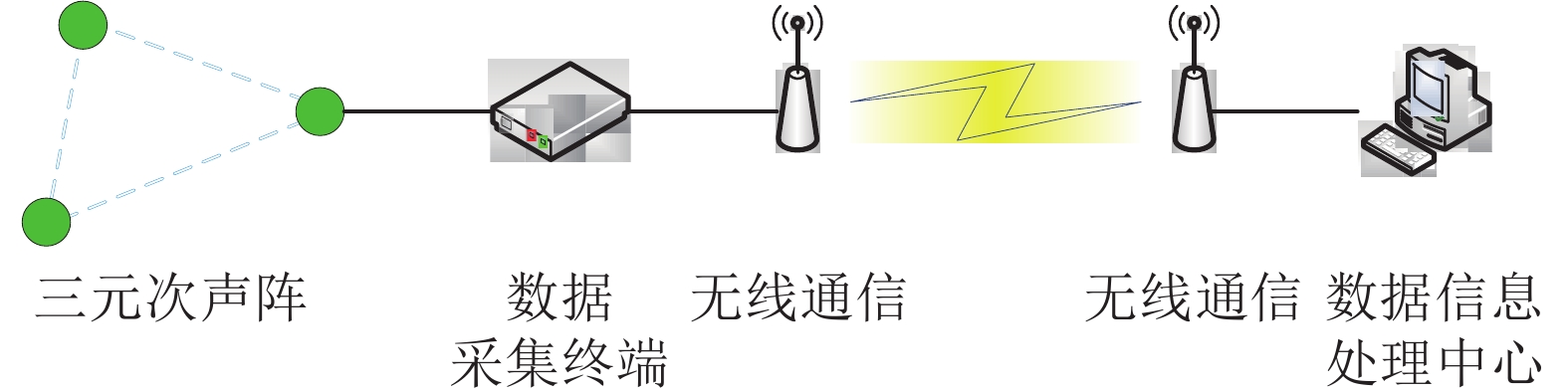
To solve the problem of effective recognition of atmospheric low-frequency acoustic signal in the low-frequency acoustic monitoring of the total nuclear test, a method of using convolution neural network is proposed. It converts low-frequency acoustic signal into images, then puts images into convolution neural network. The method is compared with SVM method based on artificial design features. The experimental results show that, when the training data set is not large, the convolution neural network with improved learning process can mine the potential features of signals, it has the same recognition ability as SVM.
To solve the problem of effective recognition of atmospheric low-frequency acoustic signal in the low-frequency acoustic monitoring of the total nuclear test, a method of using convolution neural network is proposed. It converts low-frequency acoustic signal into images, then puts images into convolution neural network. The method is compared with SVM method based on artificial design features. The experimental results show that, when the training data set is not large, the convolution neural network with improved learning process can mine the potential features of signals, it has the same recognition ability as SVM.
2020, 49(5): 766-773.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019173
Abstract:
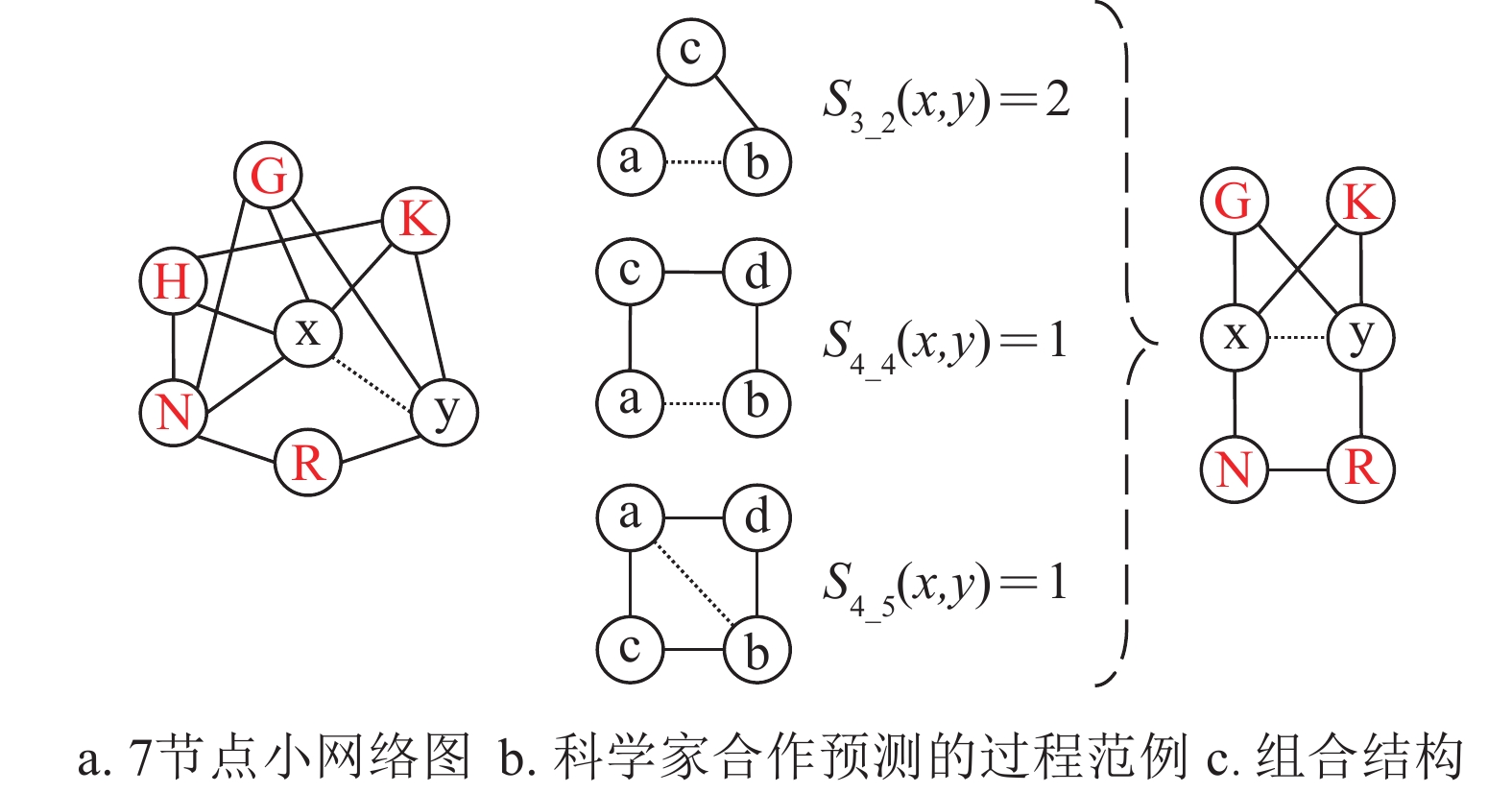
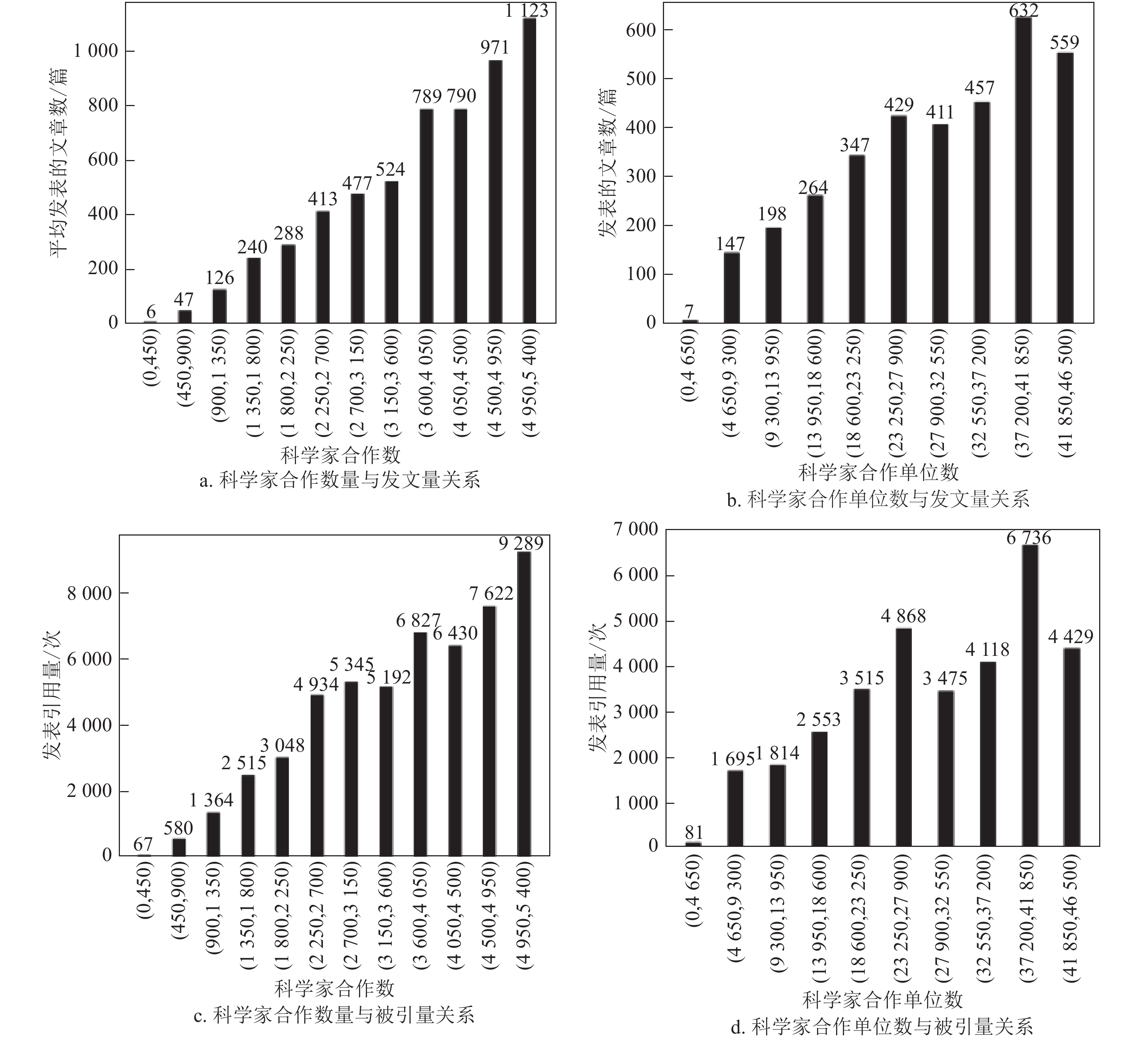
With the development of science itself, science of science has become research in recent years. The scientific cooperation network which is an important structural foundation of scientific research organizations and knowledge dissemination has attracted wide attention from scholars. Under this circumstance, the formation of cooperation and the weight of cooperation in the scientific cooperation network have become very meaningful research issues. This paper proposes a link prediction and weight prediction methods based on multiple motif features and machine learning framework, and compares the experimental results with several classical methods. It is found that the proposed methods can effectively improve the accuracy prediction: up to 8.9% in the link prediction and 59.6% in the weight prediction. This paper helps to predict the possibility of scientist collaboration in the scientific research network and their cooperation weight, and then to explore the profound impact of the structural characteristics of the scientific cooperation network on the scientific research output and teamwork of scholars.
With the development of science itself, science of science has become research in recent years. The scientific cooperation network which is an important structural foundation of scientific research organizations and knowledge dissemination has attracted wide attention from scholars. Under this circumstance, the formation of cooperation and the weight of cooperation in the scientific cooperation network have become very meaningful research issues. This paper proposes a link prediction and weight prediction methods based on multiple motif features and machine learning framework, and compares the experimental results with several classical methods. It is found that the proposed methods can effectively improve the accuracy prediction: up to 8.9% in the link prediction and 59.6% in the weight prediction. This paper helps to predict the possibility of scientist collaboration in the scientific research network and their cooperation weight, and then to explore the profound impact of the structural characteristics of the scientific cooperation network on the scientific research output and teamwork of scholars.
2020, 49(5): 774-779.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2018236
Abstract:
This paper presents a model to evaluate input-output performance of scientists. With consideration of the input cost of scientists' communication and time, this model takes the number of co-authors and the number of institutions of target scientists in scientific papers as input variables, and the number of co-published articles and their cited number as output variables. The experiments results show the scientists who won Nobel Price are ranked higher than the sciences who did not win Nobel Price. The experimental results also show that the AUC values of input-output performance model could reach 0.7957 for the APS data set, which is better than the results generated by h-index, i10-index, total number of papers, and total number of citations. Furthermore, The experimental results indicate that most input-output performances of scientists before winning award is higher than the input-output performances of scientists after winning award for the APS data set and the web of science data set. The proposed model also provides an effective tool for policy makers to quantify the input-output performances of sciences.
This paper presents a model to evaluate input-output performance of scientists. With consideration of the input cost of scientists' communication and time, this model takes the number of co-authors and the number of institutions of target scientists in scientific papers as input variables, and the number of co-published articles and their cited number as output variables. The experiments results show the scientists who won Nobel Price are ranked higher than the sciences who did not win Nobel Price. The experimental results also show that the AUC values of input-output performance model could reach 0.7957 for the APS data set, which is better than the results generated by h-index, i10-index, total number of papers, and total number of citations. Furthermore, The experimental results indicate that most input-output performances of scientists before winning award is higher than the input-output performances of scientists after winning award for the APS data set and the web of science data set. The proposed model also provides an effective tool for policy makers to quantify the input-output performances of sciences.
2020, 49(5): 780-787.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2019221
Abstract:
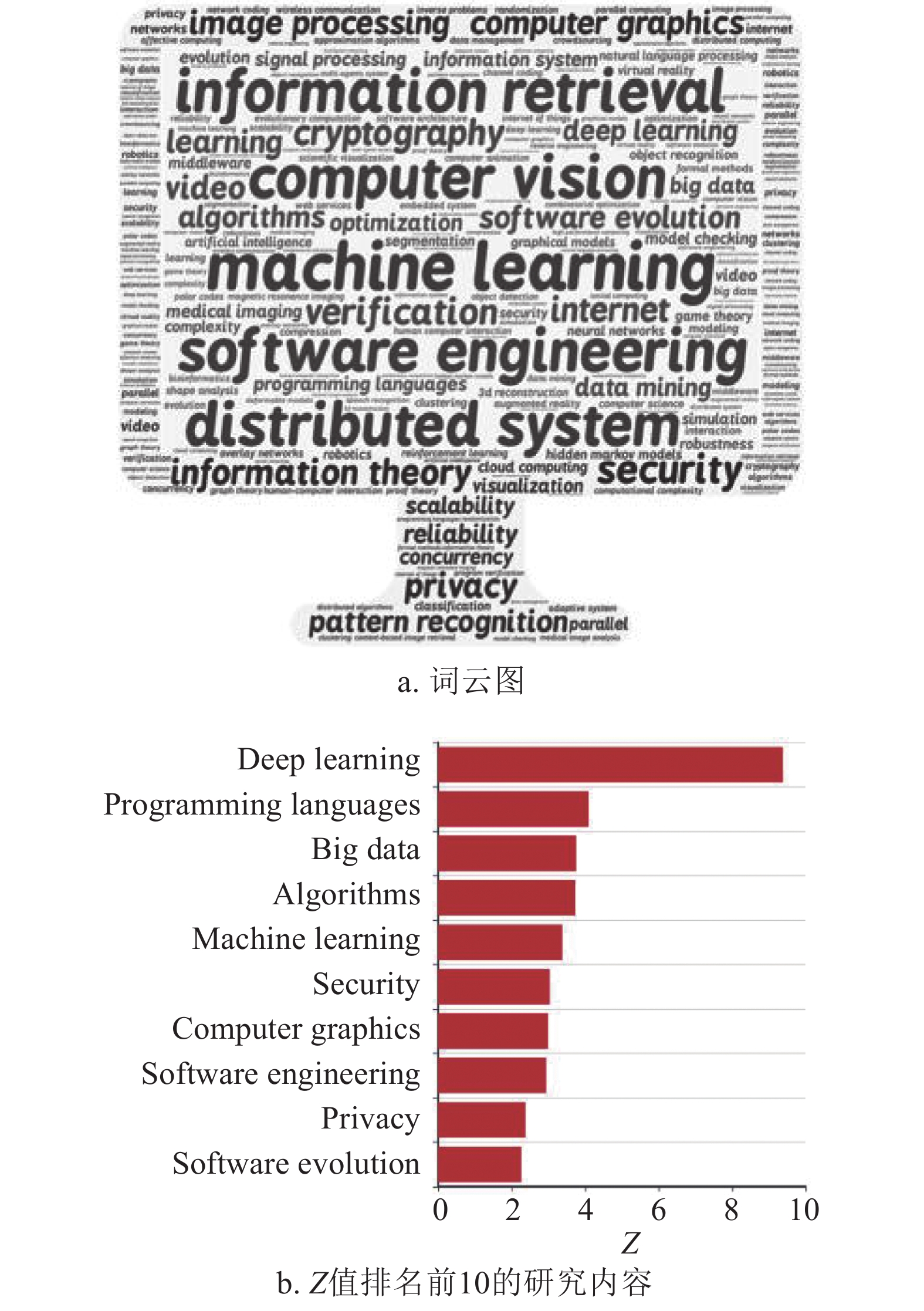
The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) is the leading supporter of research funding in Switzerland and is primarily responsible for promoting the development of Swiss scientific and technological innovations. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the research status and research trends of the innovations according to SNSF data, which could inspire forward thinking of Chinese researchers and managers. We collected the data of research projects from the SNSF database in 1999−2018. In this study, the evolution of keywords in the information technology discipline is analyzed and it is found that information technology evolved from software development research, such as distributed systems to artificial intelligence research like machine learning and deep learning and hierarchical structure distribution maps, to visualize information technology and mathematical keyword distribution. It is worth noting that cryptography and algorithms are the most obvious cross-disciplinary research content in information technology and mathematics. The results show that research content of cross-disciplinary research is relatively better. Then, by interpreting the intersection of information technology and mathematics by Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence analysis of keyword distribution in different time periods, the cross-research experience of these two disciplines is found that after rapid development, it entered a more stable and mature state.
The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) is the leading supporter of research funding in Switzerland and is primarily responsible for promoting the development of Swiss scientific and technological innovations. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the research status and research trends of the innovations according to SNSF data, which could inspire forward thinking of Chinese researchers and managers. We collected the data of research projects from the SNSF database in 1999−2018. In this study, the evolution of keywords in the information technology discipline is analyzed and it is found that information technology evolved from software development research, such as distributed systems to artificial intelligence research like machine learning and deep learning and hierarchical structure distribution maps, to visualize information technology and mathematical keyword distribution. It is worth noting that cryptography and algorithms are the most obvious cross-disciplinary research content in information technology and mathematics. The results show that research content of cross-disciplinary research is relatively better. Then, by interpreting the intersection of information technology and mathematics by Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence analysis of keyword distribution in different time periods, the cross-research experience of these two disciplines is found that after rapid development, it entered a more stable and mature state.
2020, 49(5): 788-794.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020263
Abstract:
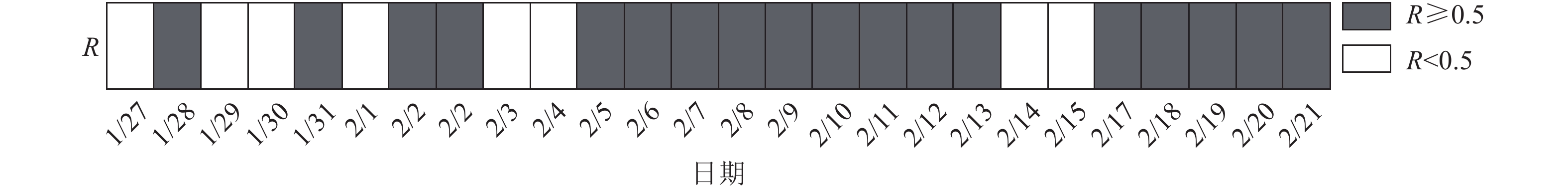
Close contacts with high-risk exposure to COVID-19 cases are more robust in statistics for inferring future development of COVID-19 epidemic. In Beijing, the proportion of close contact cases in newly confirmed cases had increased from about 50% at the end of January to nearly 100% in mid-February, indicating that contact tracing and quarantine measures are effective non-pharmaceutical interventions for containing the epidemic. In addition, we show at the national level that the cumulative number of close contacts was stabilized at about eight times as much as infected individuals, and the growth rate of daily close contacts was consistent with that of daily confirmed cases 5~6 days later. Consequently, tracking the daily change of close contacts is beneficial to predict the trend of the epidemic, based on which advanced medical supplies scheduling and effective epidemic prevention can be achieved.
Close contacts with high-risk exposure to COVID-19 cases are more robust in statistics for inferring future development of COVID-19 epidemic. In Beijing, the proportion of close contact cases in newly confirmed cases had increased from about 50% at the end of January to nearly 100% in mid-February, indicating that contact tracing and quarantine measures are effective non-pharmaceutical interventions for containing the epidemic. In addition, we show at the national level that the cumulative number of close contacts was stabilized at about eight times as much as infected individuals, and the growth rate of daily close contacts was consistent with that of daily confirmed cases 5~6 days later. Consequently, tracking the daily change of close contacts is beneficial to predict the trend of the epidemic, based on which advanced medical supplies scheduling and effective epidemic prevention can be achieved.
2020, 49(5): 795-800.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020139
Abstract:
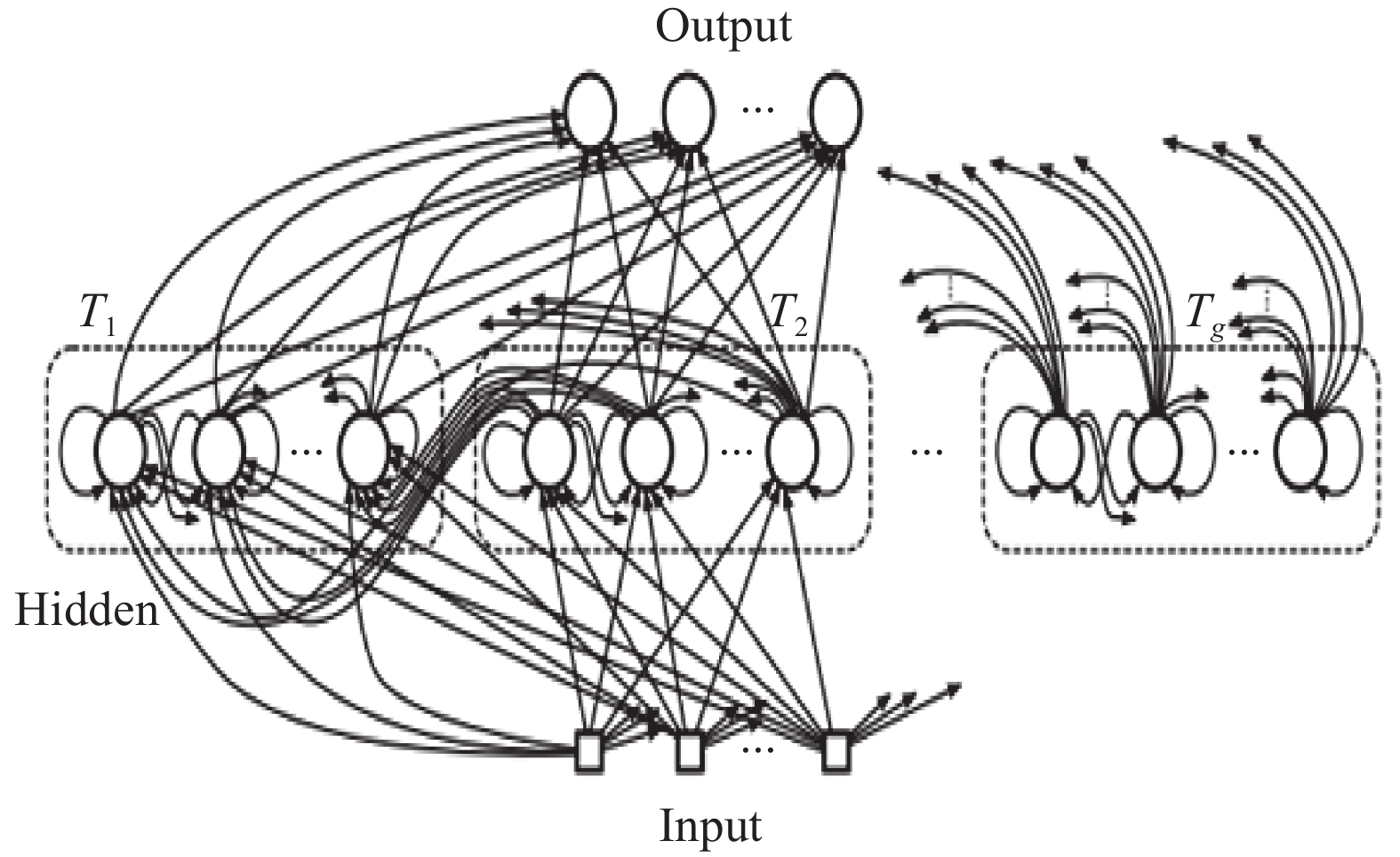
The poverty alleviation work for college students has always been the focus of attention in education. How to use effective big data analysis methods to reduce the workload of review and fair review process and achieve the goal of targeted poverty alleviation in colleges and universities is a question worthy of further study. Based on the behavioral data of college students, this paper combines the time-series characteristics of college data, extracts the basic information and multi-dimensional features of behavioral data, and proposes a clockwork long short-term memory (CW-LSTM) algorithm based on deep learning theory for prediction. Finally, the model is verified using real data, and the results show that our method is better than the Naive Bayes algorithm and decision tree algorithm.
The poverty alleviation work for college students has always been the focus of attention in education. How to use effective big data analysis methods to reduce the workload of review and fair review process and achieve the goal of targeted poverty alleviation in colleges and universities is a question worthy of further study. Based on the behavioral data of college students, this paper combines the time-series characteristics of college data, extracts the basic information and multi-dimensional features of behavioral data, and proposes a clockwork long short-term memory (CW-LSTM) algorithm based on deep learning theory for prediction. Finally, the model is verified using real data, and the results show that our method is better than the Naive Bayes algorithm and decision tree algorithm.

 ISSN
ISSN