2022 Vol. 51, No. 2
column
- Special Section on Quantum Information
- Special Section on Bioinformatics
- Special Section for UESTC Youth: Information and Communication Engineering
- Communication and Information Engineering
- Automation Techniques
- Computer Engineering and Applications
- Complexity Sciences
- Bioelectronics
- Physical Electronics
2022, 51(2): 161-161.
Abstract:
2022, 51(2): 162-169.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021374
Abstract:
Blockchain is a new decentralized infrastructure emerging with digital cryptocurrencies. The application scope of blockchain as the underlying technology has already gone beyond digital cryptocurrencies, extending to various fields such as finance, economy, technology and politics. At the same time, quantum technology with great scientific significance and strategic value is developing rapidly. In the coming quantum era, blockchain will face unprecedented opportunities and challenges brought by quantum technology. It is mainly reflected in the following aspects: firstly, powerful quantum computing poses a great threat to the blockchain cryptosystem; secondly, the application of quantum technology in blockchain can effectively improve the security of the system. This paper mainly analyzes the different ways of quantum computing to attack blockchain in the coming quantum era. We also point out the development status and trend of quantum technology enabling blockchain. "Blockchain + Quantum Computing" cross fusion research has great realistic significance and quantum blockchain will become the focus in the future high-tech industries.
Blockchain is a new decentralized infrastructure emerging with digital cryptocurrencies. The application scope of blockchain as the underlying technology has already gone beyond digital cryptocurrencies, extending to various fields such as finance, economy, technology and politics. At the same time, quantum technology with great scientific significance and strategic value is developing rapidly. In the coming quantum era, blockchain will face unprecedented opportunities and challenges brought by quantum technology. It is mainly reflected in the following aspects: firstly, powerful quantum computing poses a great threat to the blockchain cryptosystem; secondly, the application of quantum technology in blockchain can effectively improve the security of the system. This paper mainly analyzes the different ways of quantum computing to attack blockchain in the coming quantum era. We also point out the development status and trend of quantum technology enabling blockchain. "Blockchain + Quantum Computing" cross fusion research has great realistic significance and quantum blockchain will become the focus in the future high-tech industries.
2022, 51(2): 170-175.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022043
Abstract:
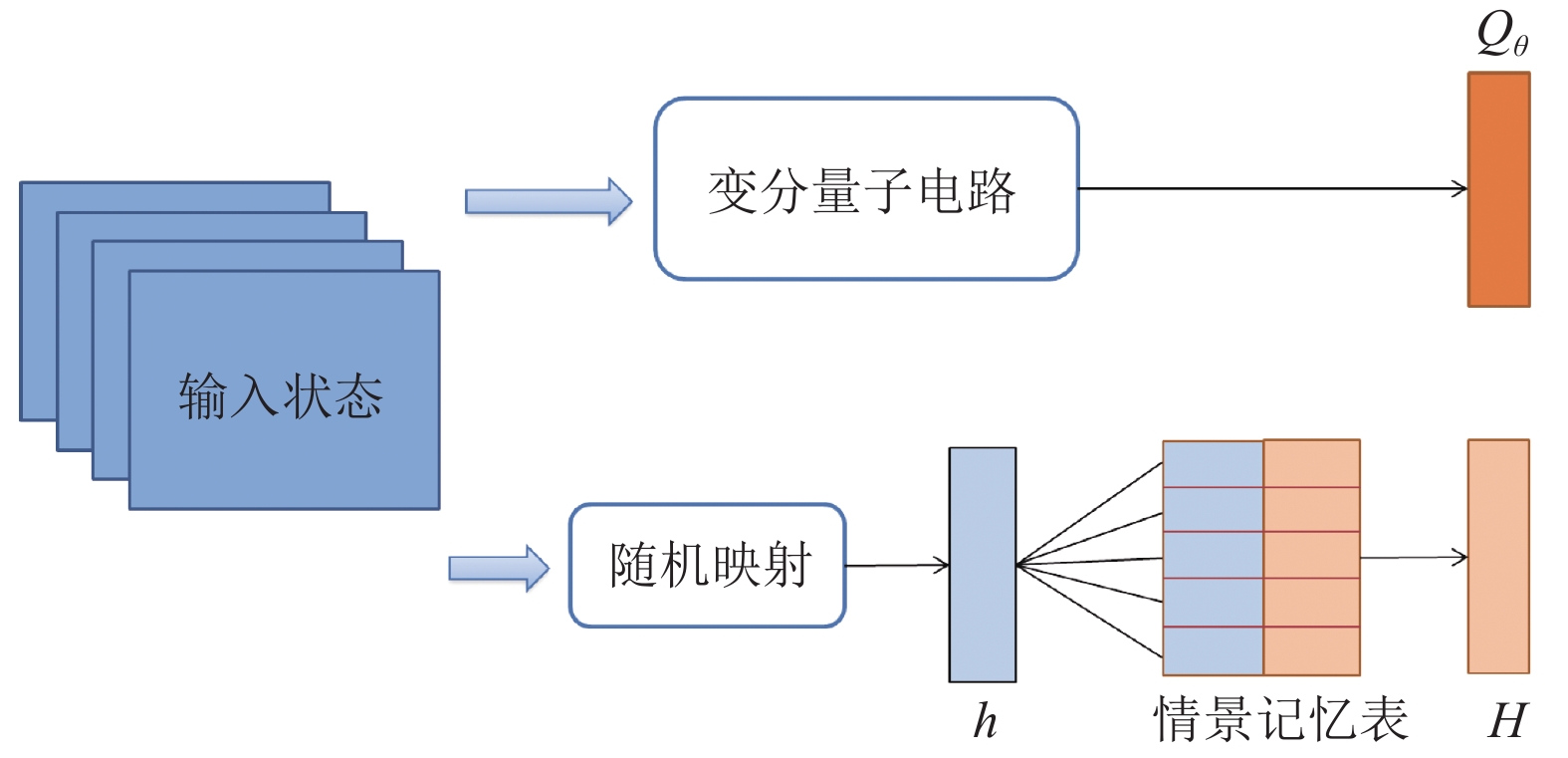
As an emerging subfield of quantum machine learning, quantum deep reinforcement learning (QDRL) utilizes quantum neural networks (QNNs) to construct a quantum agent and trains QNNs through multiple interactions with an environment to maximize the expected cumulative return. However, existing QDRL methods require the quantum agent to interact with a classical environment many times, requiring a huge number of executions of the QNN circuit. To address this problem, this work proposes a QDRL model, a quantum episodic memory deep Q-network, which utilizes episodic memory to accelerate the training process. Specifically, the proposed model stores experiences with high rewards in history into the episodic memory, which then helps the quantum agent to obtain the desired action with significantly fewer iterations when the environment state is similar to one of those stored in the episodic memory. Numerical simulations on five typical Atari games show that the proposed method can significantly reduce the number of training iterations and can achieve a higher score compared to other conventional QDRL methods.
As an emerging subfield of quantum machine learning, quantum deep reinforcement learning (QDRL) utilizes quantum neural networks (QNNs) to construct a quantum agent and trains QNNs through multiple interactions with an environment to maximize the expected cumulative return. However, existing QDRL methods require the quantum agent to interact with a classical environment many times, requiring a huge number of executions of the QNN circuit. To address this problem, this work proposes a QDRL model, a quantum episodic memory deep Q-network, which utilizes episodic memory to accelerate the training process. Specifically, the proposed model stores experiences with high rewards in history into the episodic memory, which then helps the quantum agent to obtain the desired action with significantly fewer iterations when the environment state is similar to one of those stored in the episodic memory. Numerical simulations on five typical Atari games show that the proposed method can significantly reduce the number of training iterations and can achieve a higher score compared to other conventional QDRL methods.
2022, 51(2): 176-176.
Abstract:
2022, 51(2): 177-183.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021372
Abstract:
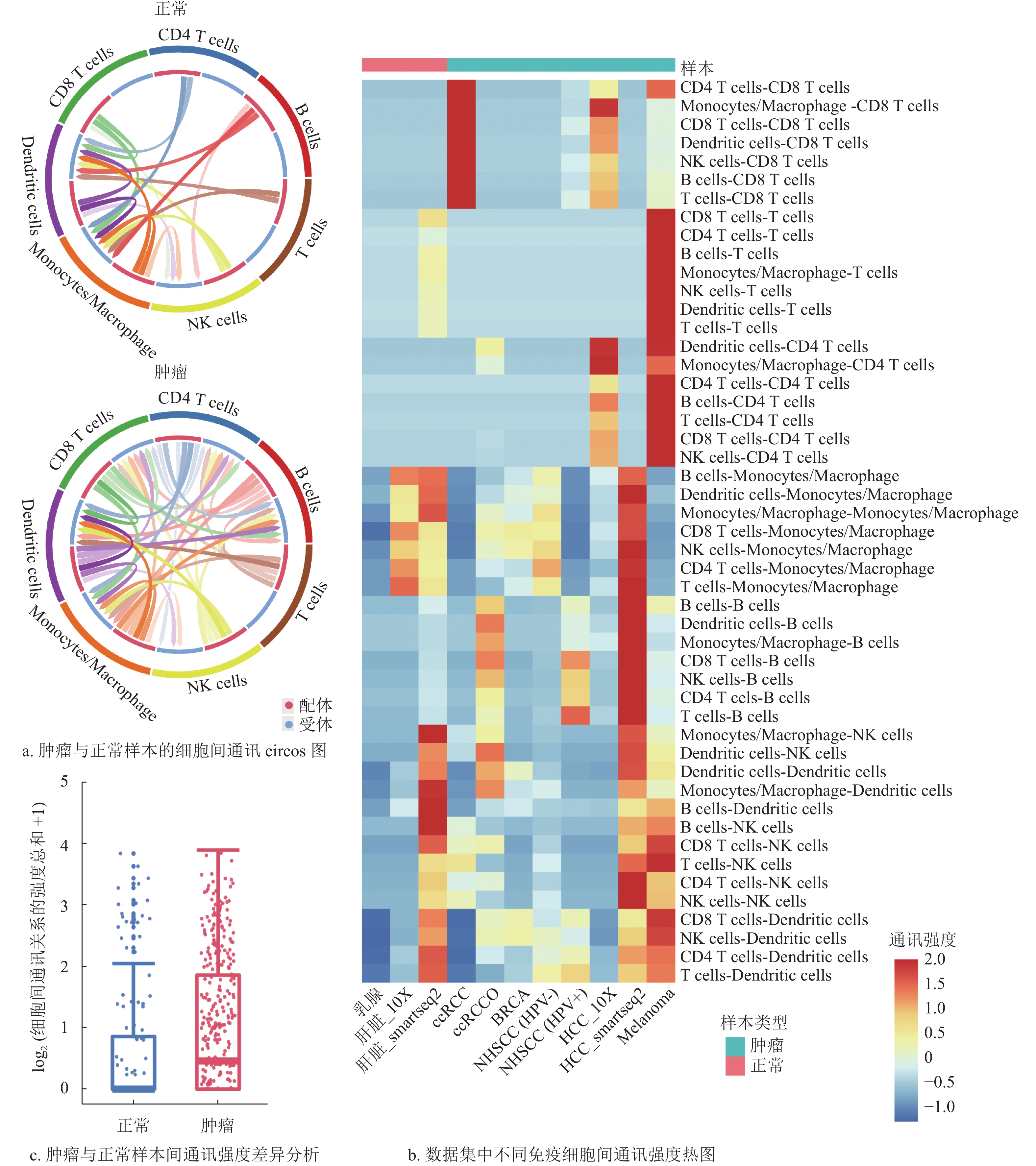
The intercellular communication in tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) provides an important niche for tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Most of single cell level studies focus on the crosstalk between tumor cells and immune cells, lacking of research on the intercellular communication among immune cells. Hence, in this study, we collected 11 single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data of CD45+ cells, and deciphered the intercellular communication network among different immune cells in TIME. The results demonstrated that there were significantly more intercellular communications in tumor samples, and 12 differential intercellular communications were detected between tumor and normal samples, including some chemokine -chemokine receptor signaling, interleukin-interleukin-receptor signaling and notch signaling. Most of these signaling and downstream transcription factors (TFs) have been implicated in tumor progression. Survival analysis of some TFs based on the cancer genome altas (TCGA) pan-cancer data indicated that these identified TFs were significantly associated with the overall survival in patients with different cancers. In summary, this study provides a comprehensive view of the intercellular communication landscape among immune cells in TIME, and identifies some specific intercellular communications involved in tumor immunity. We believe that our study provides valuable clues for understanding the mechanisms of tumor progression in TIME and provides possible diagnostic strategies for the tumor diagnosis and treatment.
The intercellular communication in tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) provides an important niche for tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Most of single cell level studies focus on the crosstalk between tumor cells and immune cells, lacking of research on the intercellular communication among immune cells. Hence, in this study, we collected 11 single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data of CD45+ cells, and deciphered the intercellular communication network among different immune cells in TIME. The results demonstrated that there were significantly more intercellular communications in tumor samples, and 12 differential intercellular communications were detected between tumor and normal samples, including some chemokine -chemokine receptor signaling, interleukin-interleukin-receptor signaling and notch signaling. Most of these signaling and downstream transcription factors (TFs) have been implicated in tumor progression. Survival analysis of some TFs based on the cancer genome altas (TCGA) pan-cancer data indicated that these identified TFs were significantly associated with the overall survival in patients with different cancers. In summary, this study provides a comprehensive view of the intercellular communication landscape among immune cells in TIME, and identifies some specific intercellular communications involved in tumor immunity. We believe that our study provides valuable clues for understanding the mechanisms of tumor progression in TIME and provides possible diagnostic strategies for the tumor diagnosis and treatment.
2022, 51(2): 184-193.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021301
Abstract:
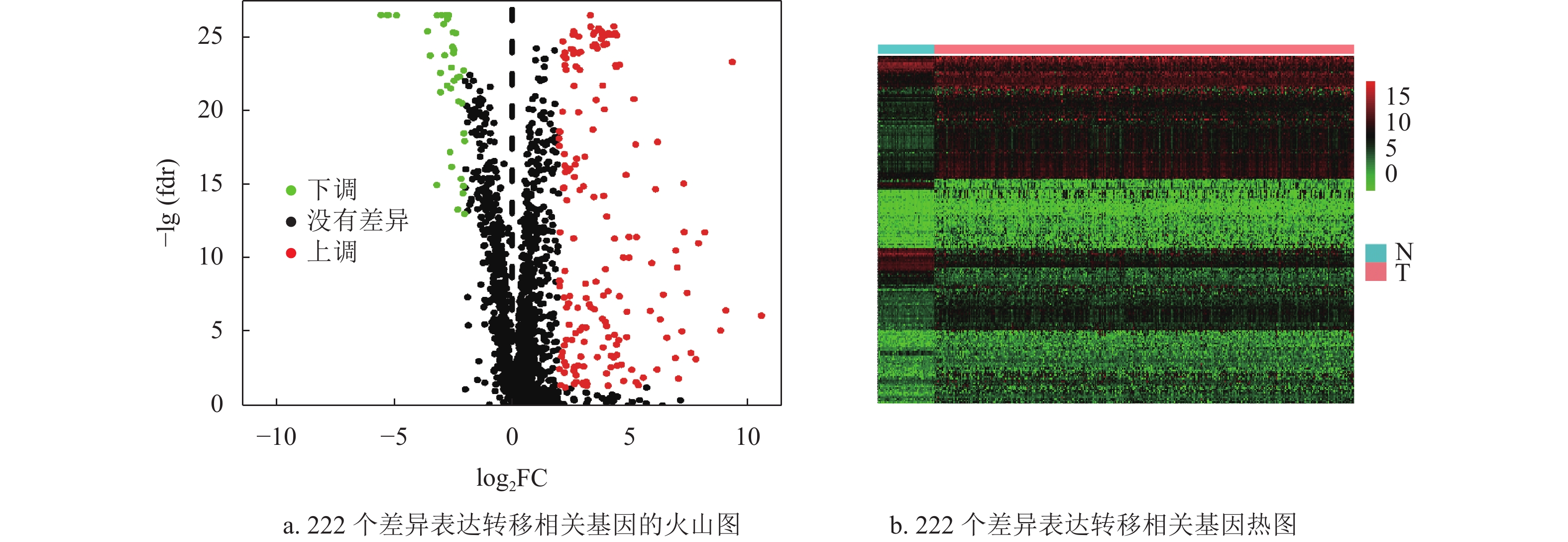
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor with high aggressiveness and metastasis. This study aims to construct a predictive model based on metastasis-related genes (MTGs). Cox analysis and Lasso regression analysis were used to build the prognostic model, and the relationship between the risk score of this model and the survival and clinical characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients was analyzed. The results of the study constructed a prognostic model containing four MTGs. In the the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) training set, HCC patients in the low-risk group had lower risk scores, fewer deaths and higher 5-year survival (P < 0.01), Cox analysis showed that the model could predict survival of HCC patients independently of other clinical characteristics (P < 0.01), and the AUC values of 1-, 2- and 3-years were all greater than 0.74 in the time-dependent ROC curve prediction analysis. Meanwhile, the validation set also confirmed the above results. Taken together, we constructed a MTGs prognostic model and it was expected to be an independent prognostic factor for prognostic prediction judgment of HCC patients.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor with high aggressiveness and metastasis. This study aims to construct a predictive model based on metastasis-related genes (MTGs). Cox analysis and Lasso regression analysis were used to build the prognostic model, and the relationship between the risk score of this model and the survival and clinical characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients was analyzed. The results of the study constructed a prognostic model containing four MTGs. In the the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) training set, HCC patients in the low-risk group had lower risk scores, fewer deaths and higher 5-year survival (P < 0.01), Cox analysis showed that the model could predict survival of HCC patients independently of other clinical characteristics (P < 0.01), and the AUC values of 1-, 2- and 3-years were all greater than 0.74 in the time-dependent ROC curve prediction analysis. Meanwhile, the validation set also confirmed the above results. Taken together, we constructed a MTGs prognostic model and it was expected to be an independent prognostic factor for prognostic prediction judgment of HCC patients.
2022, 51(2): 194-199.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021109
Abstract:
BATS codes combining fountain codes and network coding are a new class of erasure codes which effectively guarantee the reliable transmission of packets in multi-hop network. However, conventional BATS codes do not make use of the feedback information. For improving the decoding performance of BATS codes, we design an improved BATS codes encoding and decoding algorithm based on the important information. And the important information is selected by the source node combined with the destination node for the next coding process. Furthermore, the coded packets from the important information are recoded at the intermediate nodes for the reliable recovery of the important information at the destination node. Simulation results show that the proposed improved scheme achieves better decoding performance compared with the conventional BATS code and the traditional limited feedback used in fountain code.
BATS codes combining fountain codes and network coding are a new class of erasure codes which effectively guarantee the reliable transmission of packets in multi-hop network. However, conventional BATS codes do not make use of the feedback information. For improving the decoding performance of BATS codes, we design an improved BATS codes encoding and decoding algorithm based on the important information. And the important information is selected by the source node combined with the destination node for the next coding process. Furthermore, the coded packets from the important information are recoded at the intermediate nodes for the reliable recovery of the important information at the destination node. Simulation results show that the proposed improved scheme achieves better decoding performance compared with the conventional BATS code and the traditional limited feedback used in fountain code.
2022, 51(2): 200-206.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021260
Abstract:
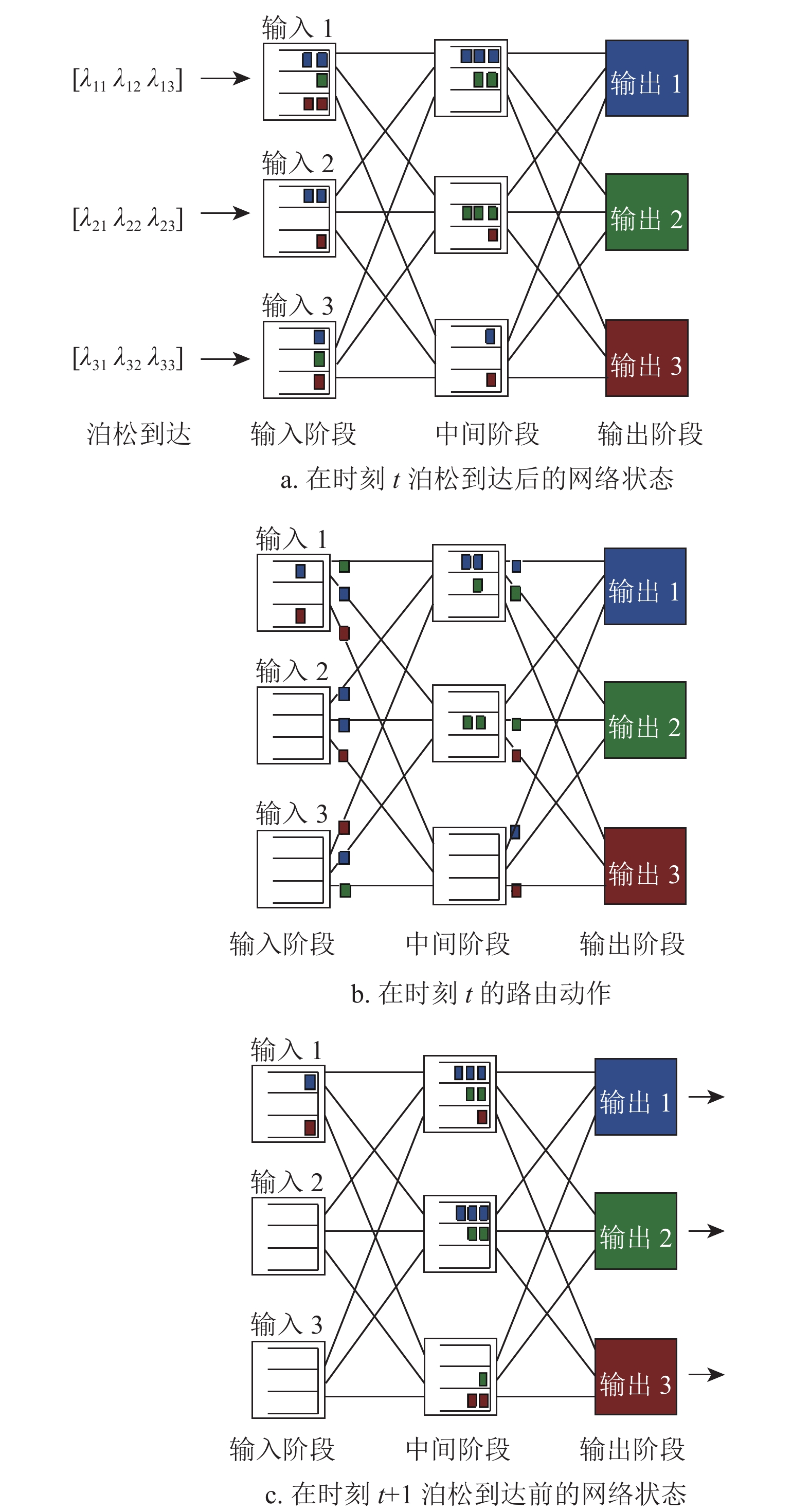
Multi-stage networks are widely used in machine learning clusters. Due to the large number of available paths in a multi-stage network, packet routing is a combinatorial optimization problem. Existing routing algorithms based on heuristics lack performance guarantee, which seriously affects the packet transmission delay. This paper proposes a packet routing method based on reinforcement learning for multi-stage networks, using a novel policy iteration algorithm to compute an optimal routing policy by learning. In the policy evaluation step, this algorithm uses the maximum likelihood estimator of the value function, which overcomes the low sample efficiency problem of Monte Carlo (MC) or Temporal-Difference (TD) value function estimators in reinforcement learning. To deal with the high computational complexity of the combinatorial optimization problem in the policy improvement step, this algorithm decomposes the optimization over a combinatorial action space into a sequential optimization of each action. Experiments based on NS-3 network simulator show that the routing policy learnt by the algorithm reduces 13.9% of the average packet transmission delay compared to existing best routing heuristics.
Multi-stage networks are widely used in machine learning clusters. Due to the large number of available paths in a multi-stage network, packet routing is a combinatorial optimization problem. Existing routing algorithms based on heuristics lack performance guarantee, which seriously affects the packet transmission delay. This paper proposes a packet routing method based on reinforcement learning for multi-stage networks, using a novel policy iteration algorithm to compute an optimal routing policy by learning. In the policy evaluation step, this algorithm uses the maximum likelihood estimator of the value function, which overcomes the low sample efficiency problem of Monte Carlo (MC) or Temporal-Difference (TD) value function estimators in reinforcement learning. To deal with the high computational complexity of the combinatorial optimization problem in the policy improvement step, this algorithm decomposes the optimization over a combinatorial action space into a sequential optimization of each action. Experiments based on NS-3 network simulator show that the routing policy learnt by the algorithm reduces 13.9% of the average packet transmission delay compared to existing best routing heuristics.
2022, 51(2): 207-212.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021266
Abstract:
To meet the requirements of wireless system on high selectivity and miniaturization, a filter topology based on hybrid-electromagnetic cross-coupling is proposed in this paper. Differing from the traditional third-order filter which can only produce one transmission zero through using cross-coupling, the proposed hybrid-electromagnetic cross-coupled topology can introduce two transmission zeros on both sides of the passband, then greatly improves the selectivity of the low-order filter. Thus, a design scheme for miniaturized high selectivity filter can be achieved. Based on this topology, a third-order filter based on microstrip quarter-wavelength resonators is designed to verify the principle of transmission zeros generated by this topology. Then, in order to obtain wider bandwidth, a hybrid microstrip/slot-line resonator filter is designed. This structure can achieve larger coupling coefficient and larger bandwidth with a miniaturized size.
To meet the requirements of wireless system on high selectivity and miniaturization, a filter topology based on hybrid-electromagnetic cross-coupling is proposed in this paper. Differing from the traditional third-order filter which can only produce one transmission zero through using cross-coupling, the proposed hybrid-electromagnetic cross-coupled topology can introduce two transmission zeros on both sides of the passband, then greatly improves the selectivity of the low-order filter. Thus, a design scheme for miniaturized high selectivity filter can be achieved. Based on this topology, a third-order filter based on microstrip quarter-wavelength resonators is designed to verify the principle of transmission zeros generated by this topology. Then, in order to obtain wider bandwidth, a hybrid microstrip/slot-line resonator filter is designed. This structure can achieve larger coupling coefficient and larger bandwidth with a miniaturized size.
2022, 51(2): 213-218.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021128
Abstract:
Aiming at solving the characterization and optimization of information freshness in the sixth generation (6G) communication system, we firstly model information freshness based on the age of information (AoI) in the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication system and formulate an AoI minimization problem subjected to the energy consumption. However, the nonconvex problem is difficult to solve due to discreteness of AoI optimization and the complicated energy consumption expression. A reinforcement learning-based scheme is proposed to design the UAV’s trajectory, in which the reward function related to AoI is constructed to realize a fast and intelligent UAV trajectory decision, thus reducing the AoI of UAV communication system. The simulation results show that, compared with the benchmark schemes, the proposed trajectory design scheme can improve the information freshness by 8.51%~21.82%. In addition, the proposed scheme has a superior convergence.
Aiming at solving the characterization and optimization of information freshness in the sixth generation (6G) communication system, we firstly model information freshness based on the age of information (AoI) in the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) communication system and formulate an AoI minimization problem subjected to the energy consumption. However, the nonconvex problem is difficult to solve due to discreteness of AoI optimization and the complicated energy consumption expression. A reinforcement learning-based scheme is proposed to design the UAV’s trajectory, in which the reward function related to AoI is constructed to realize a fast and intelligent UAV trajectory decision, thus reducing the AoI of UAV communication system. The simulation results show that, compared with the benchmark schemes, the proposed trajectory design scheme can improve the information freshness by 8.51%~21.82%. In addition, the proposed scheme has a superior convergence.
2022, 51(2): 219-226.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021204
Abstract:
Radio frequency (RF) stealth and radar stealth are two approaches to decrease threatened area and probability RF stealth and radar stealth are two approaches to decrease threatened area and probability of intercept, which are the key factors of stealthy penetration combat. It is essential to efficiently and objectively evaluate performances of the RF stealth and radar stealth efficiency of RF system of aircraft for special combat missions. In this article, the research progress of parameter characterization and evaluation methods for stealth capabilities are introduced and reviewed, and the technical features and drawbacks of these methods are also summarized. Several advices of stealth characterization for RF systems are proposed, which may be beneficial to evaluate stealthy performances of aircraft in actual combat environment.
Radio frequency (RF) stealth and radar stealth are two approaches to decrease threatened area and probability RF stealth and radar stealth are two approaches to decrease threatened area and probability of intercept, which are the key factors of stealthy penetration combat. It is essential to efficiently and objectively evaluate performances of the RF stealth and radar stealth efficiency of RF system of aircraft for special combat missions. In this article, the research progress of parameter characterization and evaluation methods for stealth capabilities are introduced and reviewed, and the technical features and drawbacks of these methods are also summarized. Several advices of stealth characterization for RF systems are proposed, which may be beneficial to evaluate stealthy performances of aircraft in actual combat environment.
2022, 51(2): 227-233.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021227
Abstract:
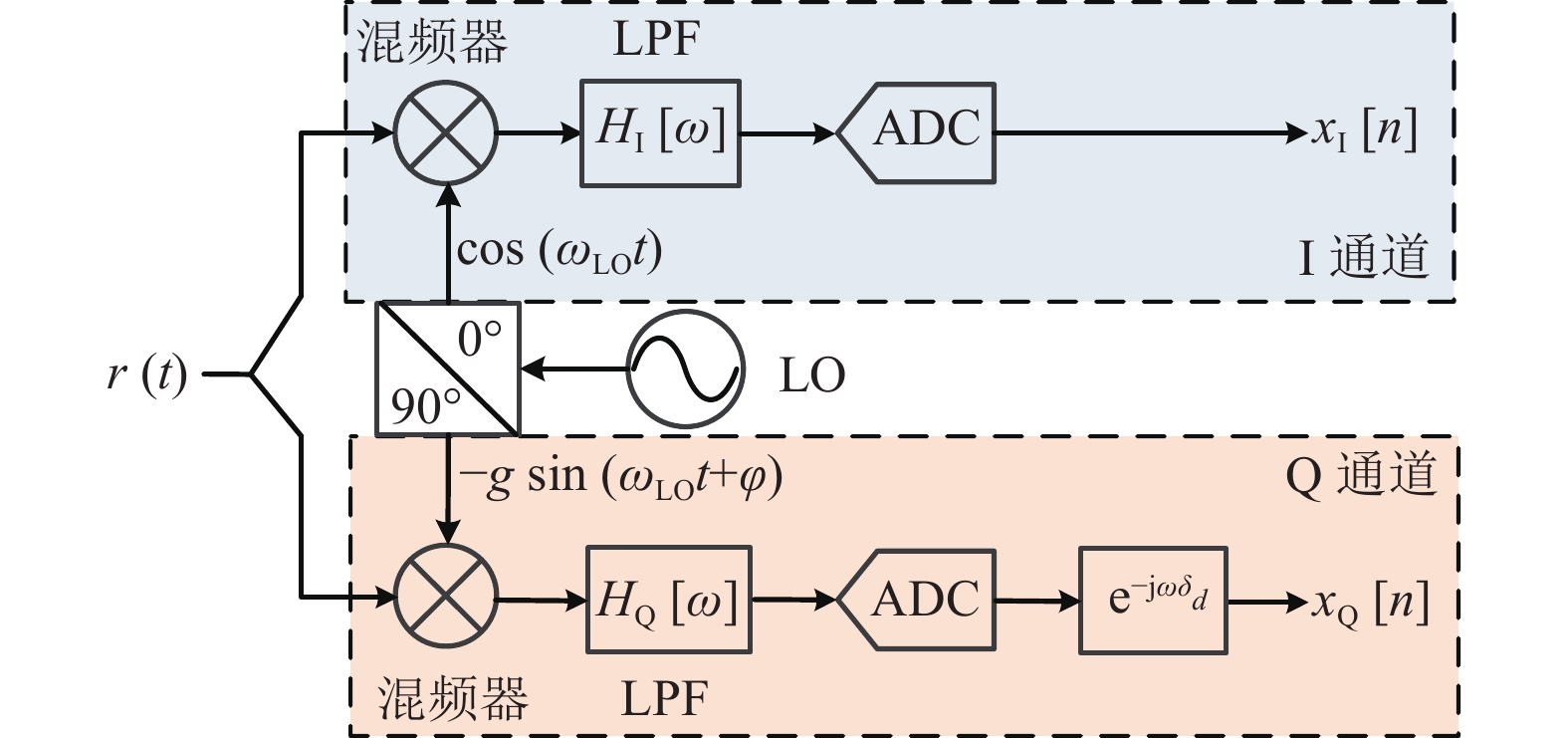
The zero-IF architecture has been widely used in recent years, but inphase/quadrature (I/Q) imbalance deteriorates the quality of received signals seriously. Eliminating I/Q imbalance through back-end compensation algorithms is one of the most efficient methods, but the existing literature does not comprehensively study the time mismatch (TM) error in broadband I/Q imbalance. An augmented error model of wideband I/Q imbalance including TM errors is established in this paper. The data-aided method is used to estimate the imbalance value in this paper, and then the polynomial fitting is applied to decompose the phase mismatch. Based on the decomposed error, a corresponding compensation structure based on a real-valued finite impulse response (FIR) filter with nonlinear phase is proposed to eliminate the separated imbalance errors. The design of the compensation filter firstly selects the optimal delay value according to the theory of least square (LS) to ensure the causality, and then utilizes the conjugate gradient square (CGS) algorithm based on the Krylov subspace, incorporating the design idea of increasing the transition band frequency interval to design the compensation filter. The experimental results show that the designed compensation filter improves the compensation accuracy of the imbalance error under the premise of ensuring the attenuation characteristics of the transition band, and the system with I/Q augmented imbalance can obtain a nearly 77 dB relative image ratio (RIR) improvement after introducing the compensation structure designed in this paper.
The zero-IF architecture has been widely used in recent years, but inphase/quadrature (I/Q) imbalance deteriorates the quality of received signals seriously. Eliminating I/Q imbalance through back-end compensation algorithms is one of the most efficient methods, but the existing literature does not comprehensively study the time mismatch (TM) error in broadband I/Q imbalance. An augmented error model of wideband I/Q imbalance including TM errors is established in this paper. The data-aided method is used to estimate the imbalance value in this paper, and then the polynomial fitting is applied to decompose the phase mismatch. Based on the decomposed error, a corresponding compensation structure based on a real-valued finite impulse response (FIR) filter with nonlinear phase is proposed to eliminate the separated imbalance errors. The design of the compensation filter firstly selects the optimal delay value according to the theory of least square (LS) to ensure the causality, and then utilizes the conjugate gradient square (CGS) algorithm based on the Krylov subspace, incorporating the design idea of increasing the transition band frequency interval to design the compensation filter. The experimental results show that the designed compensation filter improves the compensation accuracy of the imbalance error under the premise of ensuring the attenuation characteristics of the transition band, and the system with I/Q augmented imbalance can obtain a nearly 77 dB relative image ratio (RIR) improvement after introducing the compensation structure designed in this paper.
2022, 51(2): 234-241.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021305
Abstract:
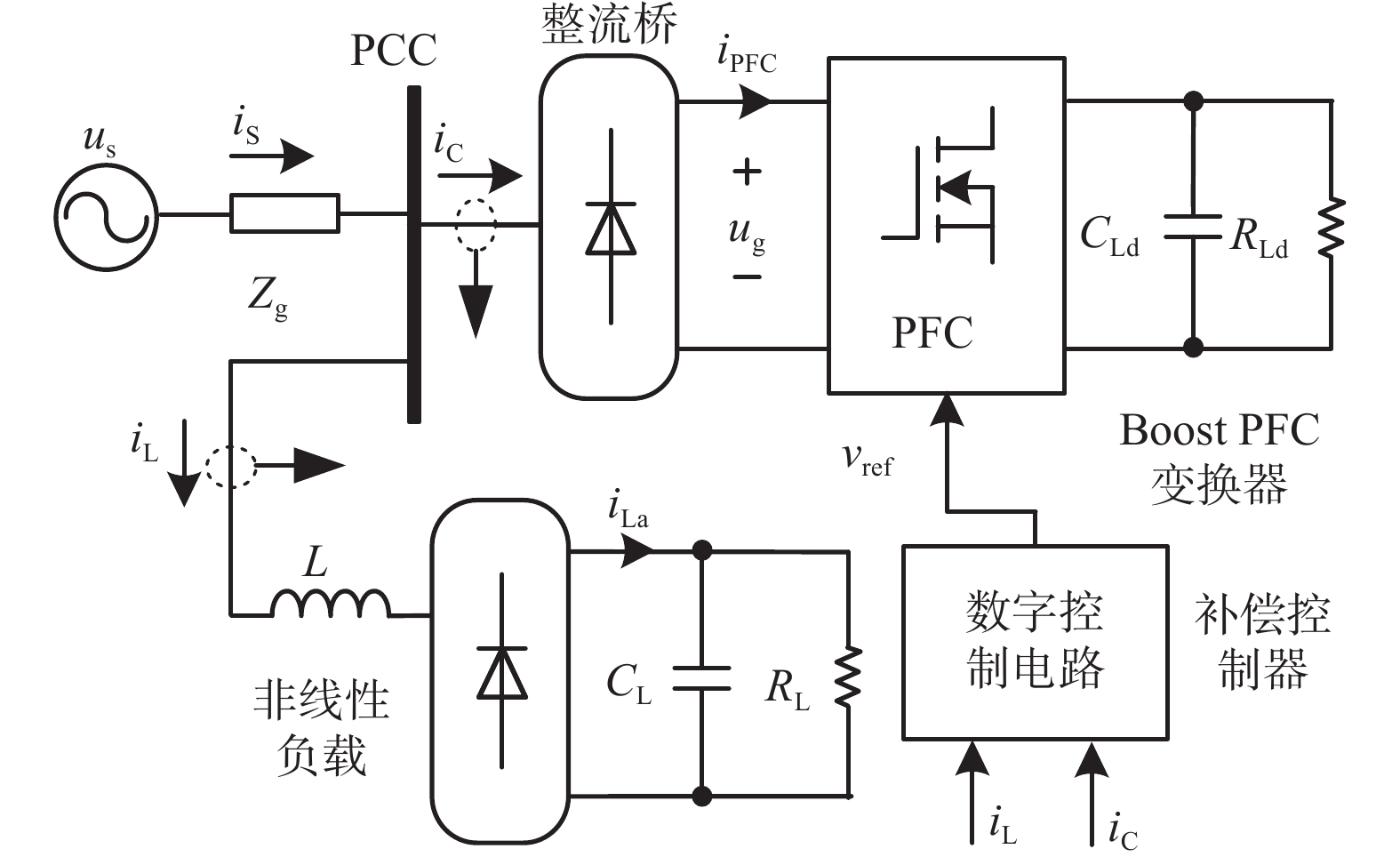
Aiming at the problem of harmonic and reactive power compensation in low-voltage distribution networks, a power factor correction (PFC) single-phase converter connected in distribution networks is studied, and an average current mode harmonic compensation control strategy is proposed. The principle and capability of compensation are analyzed and the inner current loop compensator is designed according to its compensation characteristics. Without changing the structure of the distribution network, the control strategy only needs to change part of the control circuit of the PFC converter to realize the unified control with the distribution network harmonic and reactive power compensation. Secondly, the discrete difference method is used to replace the traditional virtual two-phase static coordinate system to reduce the computation cost. The research results show that the harmonic and fundamental reactive components of nonlinear load current and the power of boost PFC converter affect the compensation ability of the converter, and the compensation effect is the best when nonlinear load harmonic and reactive power are compensated simultaneously. Finally, the simulation and experiment verify the feasibility of the control strategy and the accuracy of the theoretical analysis.
Aiming at the problem of harmonic and reactive power compensation in low-voltage distribution networks, a power factor correction (PFC) single-phase converter connected in distribution networks is studied, and an average current mode harmonic compensation control strategy is proposed. The principle and capability of compensation are analyzed and the inner current loop compensator is designed according to its compensation characteristics. Without changing the structure of the distribution network, the control strategy only needs to change part of the control circuit of the PFC converter to realize the unified control with the distribution network harmonic and reactive power compensation. Secondly, the discrete difference method is used to replace the traditional virtual two-phase static coordinate system to reduce the computation cost. The research results show that the harmonic and fundamental reactive components of nonlinear load current and the power of boost PFC converter affect the compensation ability of the converter, and the compensation effect is the best when nonlinear load harmonic and reactive power are compensated simultaneously. Finally, the simulation and experiment verify the feasibility of the control strategy and the accuracy of the theoretical analysis.
2022, 51(2): 242-250.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021304
Abstract:
Event detection (ED) is a fundamental task of event extraction, which aims to detect triggers in text and determine their event types. Most existing methods regard event detection as a sentence-level classification problem, ignoring the correlations between events in different sentences. A novel event detection framework, named document embedding networks combined with semantic space (DENSS), is proposed in this paper. The document-level information is utilized to alleviate semantic ambiguity and enhance contextual understanding. Specifically, the representations of event types and triggers are obtained through an off-the-shelf pre-trained model and a designed multi-level attention mechanism. Then the feature vectors of event types and triggers are mapped into a shared semantic space, where the distance represents the correlation of different events. The experimental results on the benchmark dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms most existing methods, and justify the effectiveness of document-level information with shared semantic space.
Event detection (ED) is a fundamental task of event extraction, which aims to detect triggers in text and determine their event types. Most existing methods regard event detection as a sentence-level classification problem, ignoring the correlations between events in different sentences. A novel event detection framework, named document embedding networks combined with semantic space (DENSS), is proposed in this paper. The document-level information is utilized to alleviate semantic ambiguity and enhance contextual understanding. Specifically, the representations of event types and triggers are obtained through an off-the-shelf pre-trained model and a designed multi-level attention mechanism. Then the feature vectors of event types and triggers are mapped into a shared semantic space, where the distance represents the correlation of different events. The experimental results on the benchmark dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms most existing methods, and justify the effectiveness of document-level information with shared semantic space.
2022, 51(2): 251-258.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021235
Abstract:
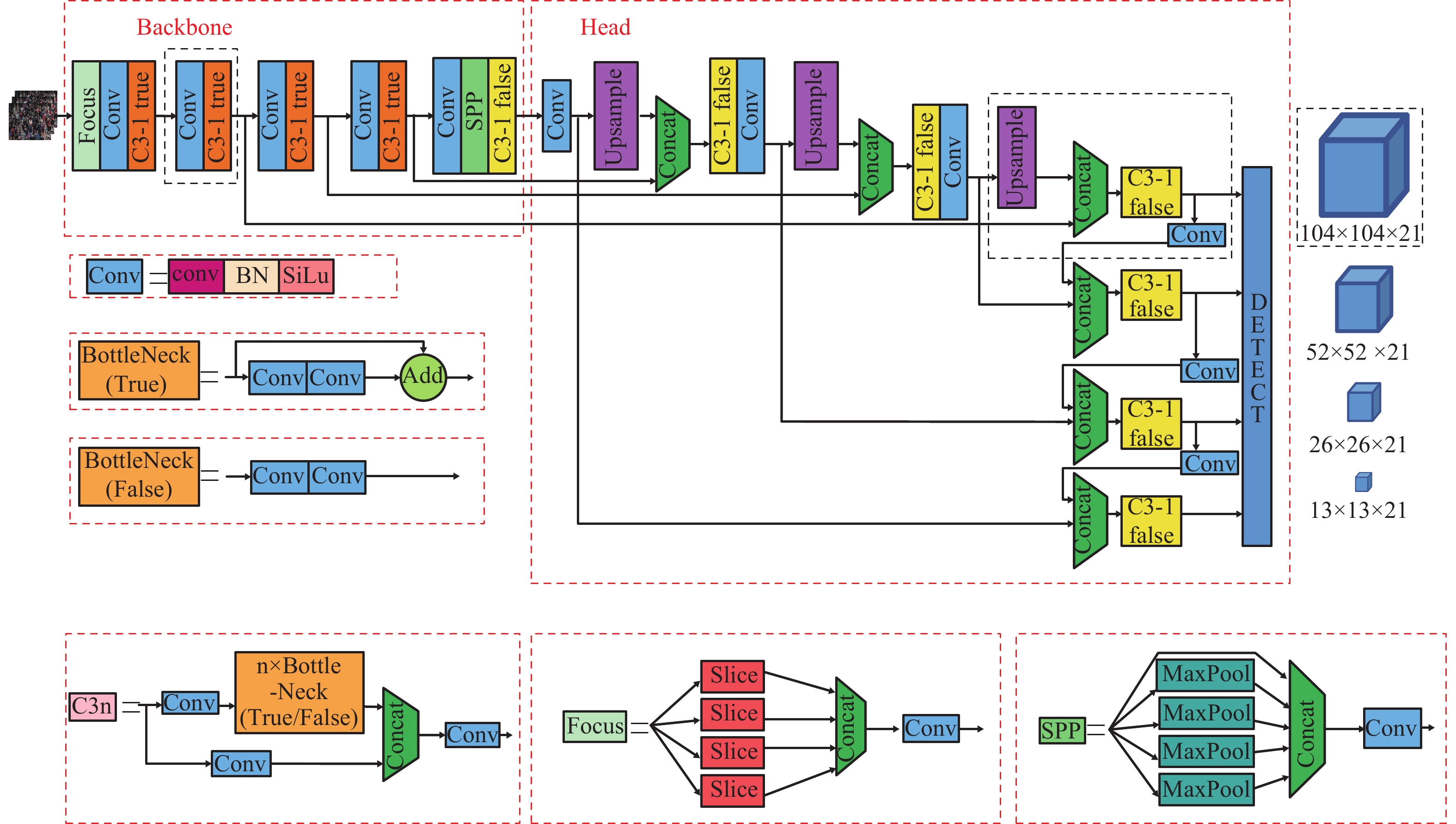
For object detection, one immediate problem is the insufficiency of feature extraction on small objects, which is easy to make false detection and miss the inspection on small targets. To solve the problem of small object detection, an improved detection algorithm based on YOLOv5 was proposed. The algorithm uses the method of Mosaic-8 on data augmentation. A shallow feature map is added to the YOLOv5 network and loss function is adjusted to improve the sensibility of network on small targets. The target box regression formula is modified to solve the problem of gradient disappearance in training process, which realized accurate precision on small targets. The improved algorithm is applied to mask wearing detection under crowed environment. Experimental results show that the proposal algorithm has stronger feature extraction ability and higher detection accuracy on small object detection compared to the original YOLOv5 algorithm.
For object detection, one immediate problem is the insufficiency of feature extraction on small objects, which is easy to make false detection and miss the inspection on small targets. To solve the problem of small object detection, an improved detection algorithm based on YOLOv5 was proposed. The algorithm uses the method of Mosaic-8 on data augmentation. A shallow feature map is added to the YOLOv5 network and loss function is adjusted to improve the sensibility of network on small targets. The target box regression formula is modified to solve the problem of gradient disappearance in training process, which realized accurate precision on small targets. The improved algorithm is applied to mask wearing detection under crowed environment. Experimental results show that the proposal algorithm has stronger feature extraction ability and higher detection accuracy on small object detection compared to the original YOLOv5 algorithm.
2022, 51(2): 259-263.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021335
Abstract:
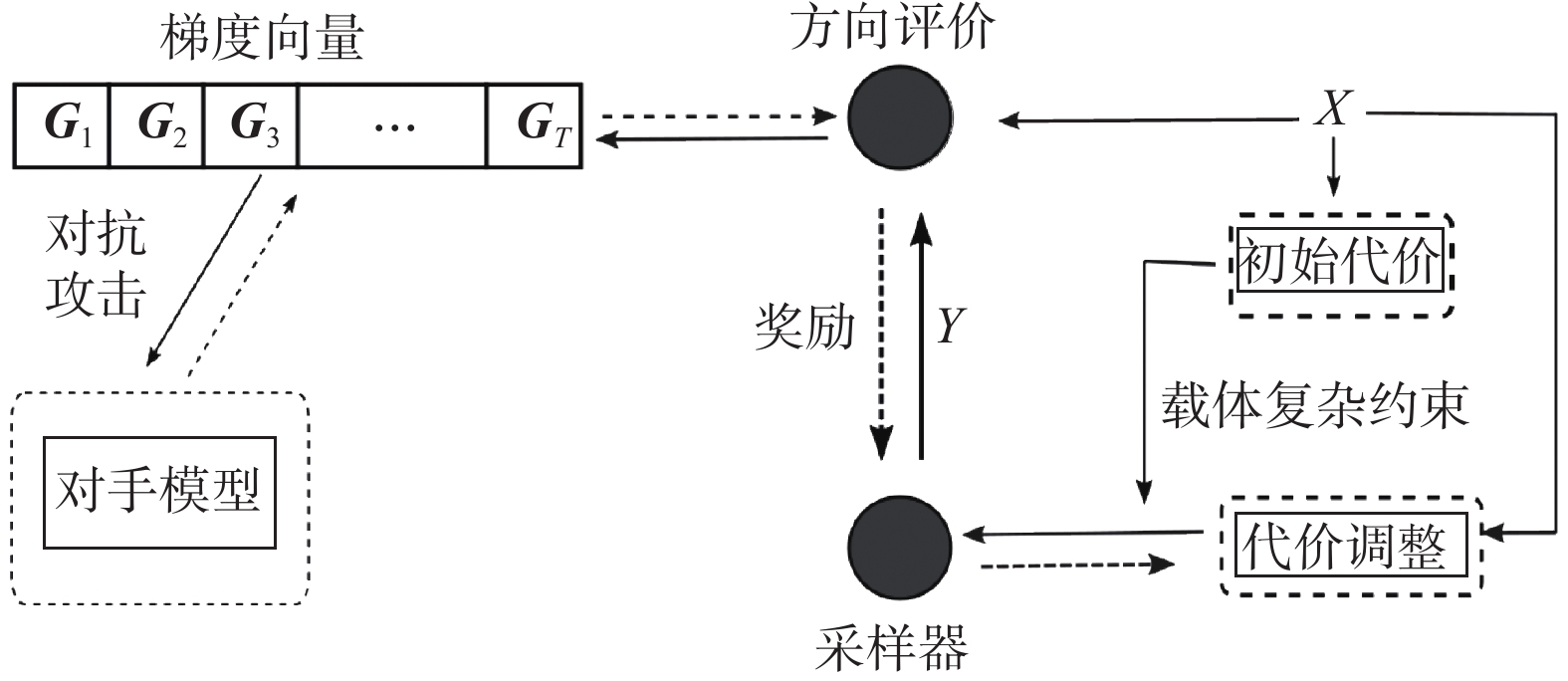
Steganography is to conceal the presence of secret communication. Traditional steganographic schemes rely on complex artificial rules that are difficult to construct. Steganalysers based on the rich models and deep learning achieve state-of-the-art performance. The security performance of existing steganographic methods is being challenged. In this paper, a search method based on image steganography model against attack is proposed to find a suitable steganography policy. The steganographic model constructs the parametric policy. The adversary model distinguishes the distribution of stego from cover to find the potential hiding artefacts. To obtain the corresponding evaluations, the adversarial attack is performed on adversary model. The security game between steganographic part and adversary is established via corresponding information, thus finding the target steganographic policy. The steganographic model and adversary model are implemented as deep neural networks. On the data set Bossbase, the payload is 0.2 and 0.4 bpp, the steganalysers are SRM and maxSRMd2. Four configurations with three steganographic schemes are compared. The experimental results show that the scheme proposed in this paper can obtain effective policy for image steganography, and the security performance is competitive compared with these schemes.
Steganography is to conceal the presence of secret communication. Traditional steganographic schemes rely on complex artificial rules that are difficult to construct. Steganalysers based on the rich models and deep learning achieve state-of-the-art performance. The security performance of existing steganographic methods is being challenged. In this paper, a search method based on image steganography model against attack is proposed to find a suitable steganography policy. The steganographic model constructs the parametric policy. The adversary model distinguishes the distribution of stego from cover to find the potential hiding artefacts. To obtain the corresponding evaluations, the adversarial attack is performed on adversary model. The security game between steganographic part and adversary is established via corresponding information, thus finding the target steganographic policy. The steganographic model and adversary model are implemented as deep neural networks. On the data set Bossbase, the payload is 0.2 and 0.4 bpp, the steganalysers are SRM and maxSRMd2. Four configurations with three steganographic schemes are compared. The experimental results show that the scheme proposed in this paper can obtain effective policy for image steganography, and the security performance is competitive compared with these schemes.
2022, 51(2): 264-273.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021165
Abstract:
In order to improve the clarity of fused images, a multi-modal medical image fusion algorithm based on guided filter and adaptive sparse representation is proposed. Specifically, this algorithm adopts Gaussian filter to decompose the input images into detail layers and base layers. Subsequently, the weight maps of base layers are obtained based on saliency characteristics and guided filters, which are further utilized to fuse the base layers in combination with the weighted average rule; at the same time, the detail layers are fused through an adaptive sparse representation algorithm. Finally, the fused layers are directly added into the base layers to obtain the fused image. This algorithm is compared with other six classical algorithms on quality evaluation and visual analysis. In addition, the time complexity of the algorithm is also compared with that of two sparse representation-based algorithms. The results show that this algorithm outperforms other algorithms in the preservation of texture and edge information. Meanwhile, its time complexity is significantly better than that of sparse representation-based algorithms.
In order to improve the clarity of fused images, a multi-modal medical image fusion algorithm based on guided filter and adaptive sparse representation is proposed. Specifically, this algorithm adopts Gaussian filter to decompose the input images into detail layers and base layers. Subsequently, the weight maps of base layers are obtained based on saliency characteristics and guided filters, which are further utilized to fuse the base layers in combination with the weighted average rule; at the same time, the detail layers are fused through an adaptive sparse representation algorithm. Finally, the fused layers are directly added into the base layers to obtain the fused image. This algorithm is compared with other six classical algorithms on quality evaluation and visual analysis. In addition, the time complexity of the algorithm is also compared with that of two sparse representation-based algorithms. The results show that this algorithm outperforms other algorithms in the preservation of texture and edge information. Meanwhile, its time complexity is significantly better than that of sparse representation-based algorithms.
2022, 51(2): 274-281.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021181
Abstract:
Most of the existing link prediction methods are aimed at homogenous networks without considering that the real networks are heterogeneous networks with different node or edge properties. This kind of methods cannot make full use of the topological structure information of different types of nodes or edges. Under this circumstance, this paper proposes a link prediction method based on heterogeneous phantom features, which divides users in the network by gender differences as node types, and constructs heterogeneous phantom features distinguishing node types for link prediction in heterogeneous networks. On this basis, a link prediction algorithm that combines the characteristics of the homogeneous phantom and the heterogeneous phantom is proposed. Compared with the performance of the existing prediction method on the real data set, the AUC value is increased by 17.0%~23.1%, and the precision value is increased by 7.6%~20.1%. This method can be used in online social networks to explore the role and influence of user gender differences on interpersonal communication, and then to analyze the evolutionary dynamics of heterogeneous networks.
Most of the existing link prediction methods are aimed at homogenous networks without considering that the real networks are heterogeneous networks with different node or edge properties. This kind of methods cannot make full use of the topological structure information of different types of nodes or edges. Under this circumstance, this paper proposes a link prediction method based on heterogeneous phantom features, which divides users in the network by gender differences as node types, and constructs heterogeneous phantom features distinguishing node types for link prediction in heterogeneous networks. On this basis, a link prediction algorithm that combines the characteristics of the homogeneous phantom and the heterogeneous phantom is proposed. Compared with the performance of the existing prediction method on the real data set, the AUC value is increased by 17.0%~23.1%, and the precision value is increased by 7.6%~20.1%. This method can be used in online social networks to explore the role and influence of user gender differences on interpersonal communication, and then to analyze the evolutionary dynamics of heterogeneous networks.
2022, 51(2): 282-289.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021196
Abstract:
The existing studies show that the network structure can be enhanced by constructing subgraph network based on subgraph interaction relationship, but the complexity of such algorithms is high. In view of this, this paper weights the original network based on the topological attributes of different order subgraph networks, obtains the first-order and second-order weighted networks, and intuitively reflects the interaction relationships of subgraphs in the form of weights. At the same time, the weights of the two weighted networks can be calculated directly through the topology of the original network, which avoids the construction process of subgraph network and greatly reduces the complexity of the algorithm. Finally, the key nodes identification task is taken as the research object to illustrate the performance of the two weighted networks in the application of structure mining. In this paper, two new centrality indices are defined based on weighted networks, which are compared with seven classical centrality indices in eight real networks. The experimental results show that the centrality indices based on weighted network has better performance.
The existing studies show that the network structure can be enhanced by constructing subgraph network based on subgraph interaction relationship, but the complexity of such algorithms is high. In view of this, this paper weights the original network based on the topological attributes of different order subgraph networks, obtains the first-order and second-order weighted networks, and intuitively reflects the interaction relationships of subgraphs in the form of weights. At the same time, the weights of the two weighted networks can be calculated directly through the topology of the original network, which avoids the construction process of subgraph network and greatly reduces the complexity of the algorithm. Finally, the key nodes identification task is taken as the research object to illustrate the performance of the two weighted networks in the application of structure mining. In this paper, two new centrality indices are defined based on weighted networks, which are compared with seven classical centrality indices in eight real networks. The experimental results show that the centrality indices based on weighted network has better performance.
2022, 51(2): 290-294.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021298
Abstract:
A color fundus image enhancement algorithm is proposed, which it is considering the matching of hue preserving, brightness enhancement and detail enhancement to deal with the problems of poor contrast, low brightness, and color distortion after other image enhancement methods. Firstly, the fundus image in RGB space is converted to HSV space for adaptive power-law transformation based on brightness to solve the problem of brightness balance of fundus image. Secondly, the limited contrast adaptive histogram equalization method is used in Lab color space to improve the detail information of fundus image. Finally, experiments are carried out on Diaretdb0 fundus image database and compared with other enhancement algorithms. The experimental results show that this method has better visual effect than other image enhancement algorithms, improves low contrast and the color distortion of color fundus images. The underwater color image quality evaluation was increased by 37.6%, average gradient was increased by 54.23%, visual parameter measurement index was increased by 7%. It provides a new pre-processing method for the recognition, segmentation and classification of fundus images.
A color fundus image enhancement algorithm is proposed, which it is considering the matching of hue preserving, brightness enhancement and detail enhancement to deal with the problems of poor contrast, low brightness, and color distortion after other image enhancement methods. Firstly, the fundus image in RGB space is converted to HSV space for adaptive power-law transformation based on brightness to solve the problem of brightness balance of fundus image. Secondly, the limited contrast adaptive histogram equalization method is used in Lab color space to improve the detail information of fundus image. Finally, experiments are carried out on Diaretdb0 fundus image database and compared with other enhancement algorithms. The experimental results show that this method has better visual effect than other image enhancement algorithms, improves low contrast and the color distortion of color fundus images. The underwater color image quality evaluation was increased by 37.6%, average gradient was increased by 54.23%, visual parameter measurement index was increased by 7%. It provides a new pre-processing method for the recognition, segmentation and classification of fundus images.
Expression and Clinical Significance of INHBA in Colorectal Cancer Based on Bioinformatics Databases
2022, 51(2): 295-304.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021348
Abstract:
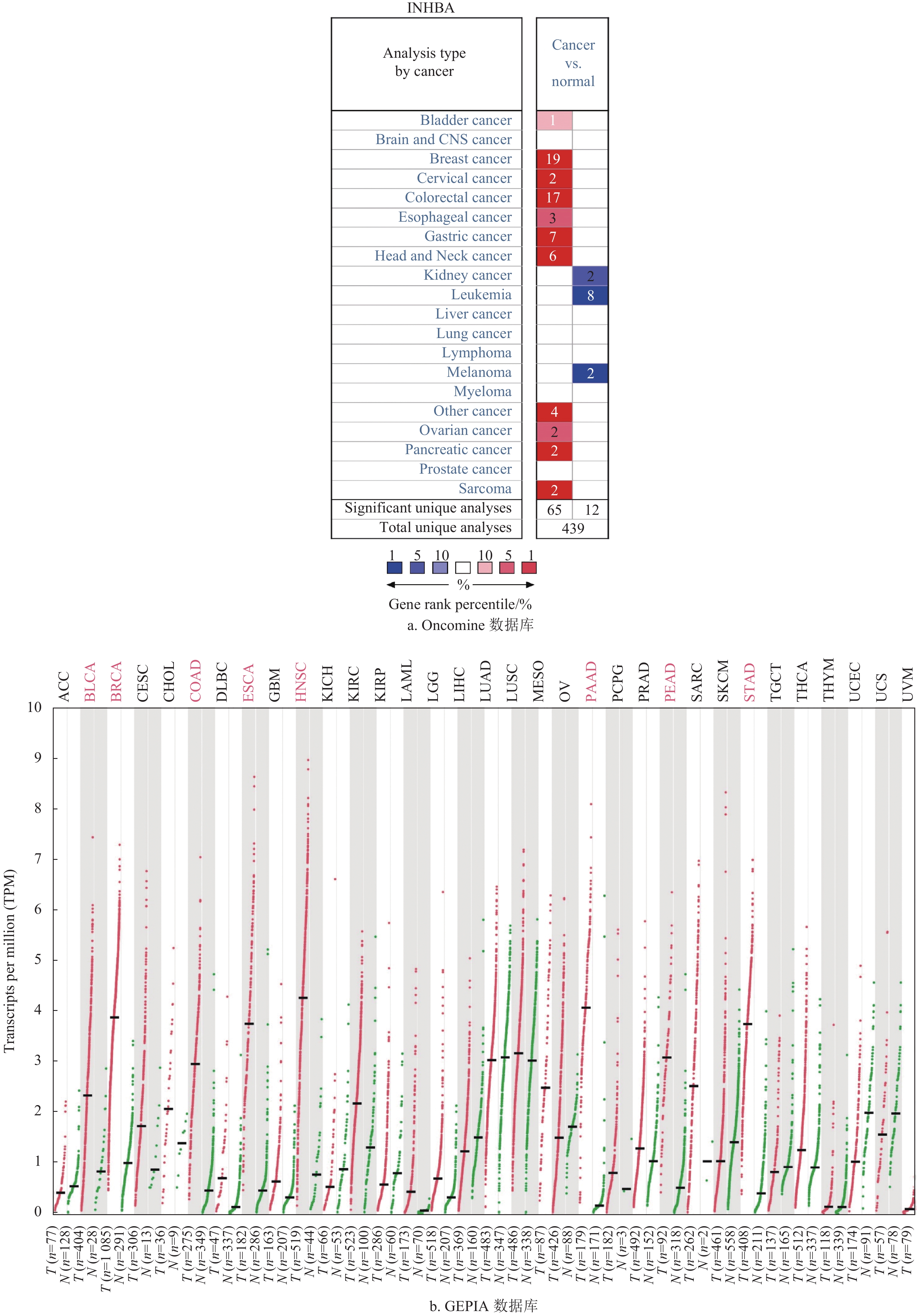
Inhibitors beta A (INHBA), as a member of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily, have pro-cancer or anti-cancer effects in different tumors. This study aims to investigate the expression and clinical significance of INHBA in colorectal cancer through bioinformatics databases. The results showed that INHBA expression was significantly upregulated in colorectal cancer, and its high expression was positively correlated with clinical stages, T stages and N stages of colorectal cancer. The methylation level of INHBA promoter was significantly reduced in both colon and rectal cancer. Survival analysis showed that colorectal cancer patients with high INHBA expression had poor prognosis. Moreover, INHBA expression was positively correlated with the infiltration levels of most immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, especially macrophages. INHBA high expression was also closely related to the high infiltration levels of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and vascular endothelial cells (VECs). Taken together, INHBA is highly expressed in colorectal cancer tissues and involved in the development of colorectal cancer, which is expected to be a potential marker for prognosis and treatment.
Inhibitors beta A (INHBA), as a member of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily, have pro-cancer or anti-cancer effects in different tumors. This study aims to investigate the expression and clinical significance of INHBA in colorectal cancer through bioinformatics databases. The results showed that INHBA expression was significantly upregulated in colorectal cancer, and its high expression was positively correlated with clinical stages, T stages and N stages of colorectal cancer. The methylation level of INHBA promoter was significantly reduced in both colon and rectal cancer. Survival analysis showed that colorectal cancer patients with high INHBA expression had poor prognosis. Moreover, INHBA expression was positively correlated with the infiltration levels of most immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, especially macrophages. INHBA high expression was also closely related to the high infiltration levels of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and vascular endothelial cells (VECs). Taken together, INHBA is highly expressed in colorectal cancer tissues and involved in the development of colorectal cancer, which is expected to be a potential marker for prognosis and treatment.
2022, 51(2): 305-313.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021238
Abstract:
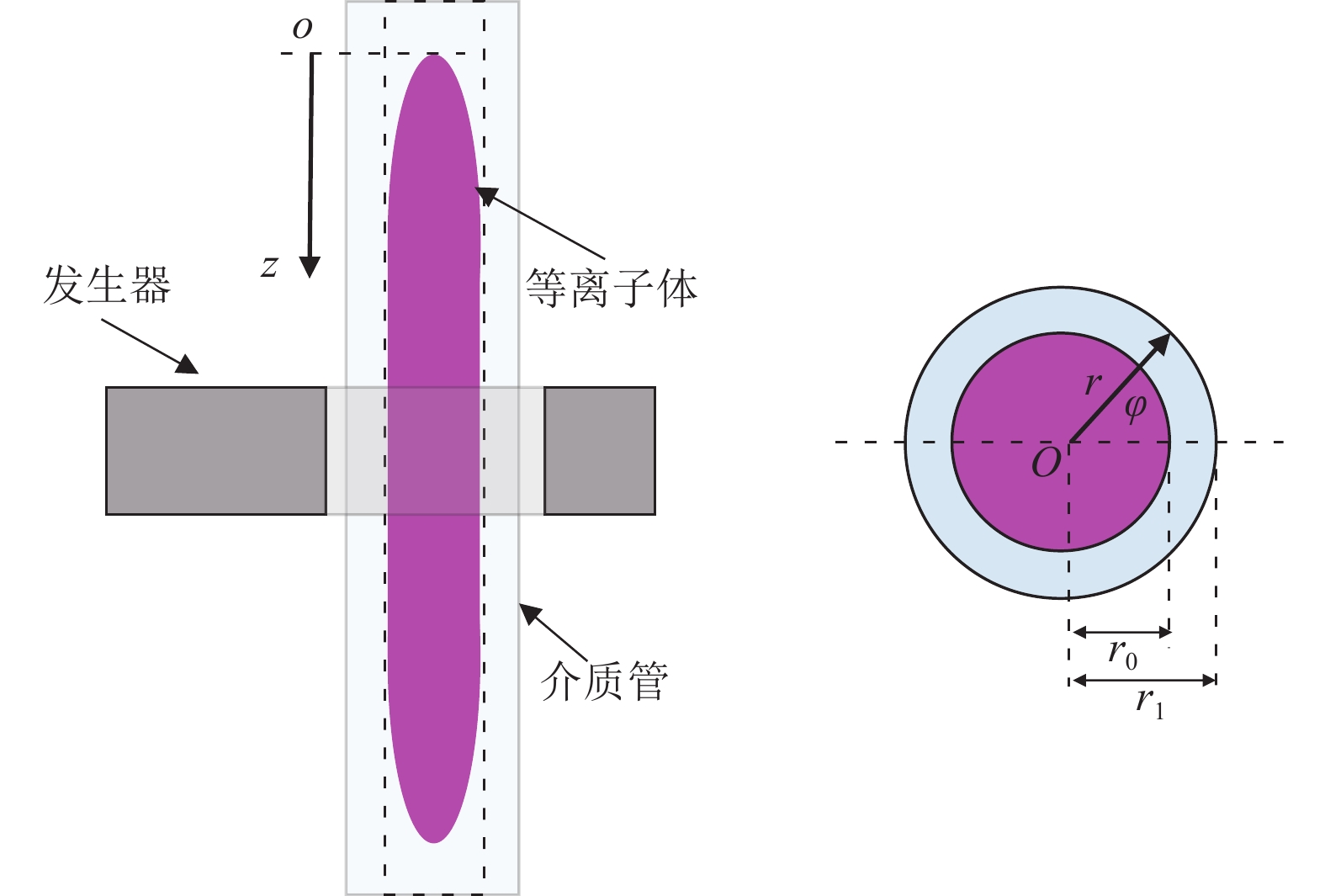
In this work, we proposed the electromagnetic model to solve the numerical modelling of the surface wave plasma discharges at atmospheric pressure due to the complexity and vast computing of the common models. According to the discharge characteristics of atmospheric pressure surface-wave plasma, the electromagnetic model was established and simplified reasonably. The results obtained by experimental diagnosis and numerical calculation were compared to verify the reliability of the model and the applicable range of parameters. The effective electron collision frequency obtained by fitting to the experimental data is (1.5±0.25)×1011 s−1, which matches the measured values reported by others. On this foundation, we put emphasis on the influences of plasma density and electromagnetic parameters (electric field distribution and propagation constant) on the external controlling parameters, such as dielectric constant, excitation frequency of 2.45 GHz and 915 MHz, and geometry size of discharge tube (tube thickness and inner radius). The results showed that the electron density and its axial gradient increase with the increasing of the dielectric constant, excitation frequency and tube thickness, but decrease with the tube inner diameter. With regard to the distribution of electric field, the maintenance of plasma is due to the axial component of electric field. As the increase of excitation frequency, the skin depth of surface wave in the media of plasma increases and the radial profile of Ez becomes more uniform. The attenuation and phase constants increase slightly with the dielectric constant and tube thickness, but decrease with the excitation frequency and inner diameter. Simulation results could be used to analyze qualitatively the correlation of the plasma parameters and external controlling parameters.
In this work, we proposed the electromagnetic model to solve the numerical modelling of the surface wave plasma discharges at atmospheric pressure due to the complexity and vast computing of the common models. According to the discharge characteristics of atmospheric pressure surface-wave plasma, the electromagnetic model was established and simplified reasonably. The results obtained by experimental diagnosis and numerical calculation were compared to verify the reliability of the model and the applicable range of parameters. The effective electron collision frequency obtained by fitting to the experimental data is (1.5±0.25)×1011 s−1, which matches the measured values reported by others. On this foundation, we put emphasis on the influences of plasma density and electromagnetic parameters (electric field distribution and propagation constant) on the external controlling parameters, such as dielectric constant, excitation frequency of 2.45 GHz and 915 MHz, and geometry size of discharge tube (tube thickness and inner radius). The results showed that the electron density and its axial gradient increase with the increasing of the dielectric constant, excitation frequency and tube thickness, but decrease with the tube inner diameter. With regard to the distribution of electric field, the maintenance of plasma is due to the axial component of electric field. As the increase of excitation frequency, the skin depth of surface wave in the media of plasma increases and the radial profile of Ez becomes more uniform. The attenuation and phase constants increase slightly with the dielectric constant and tube thickness, but decrease with the excitation frequency and inner diameter. Simulation results could be used to analyze qualitatively the correlation of the plasma parameters and external controlling parameters.
2022, 51(2): 314-320.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021088
Abstract:
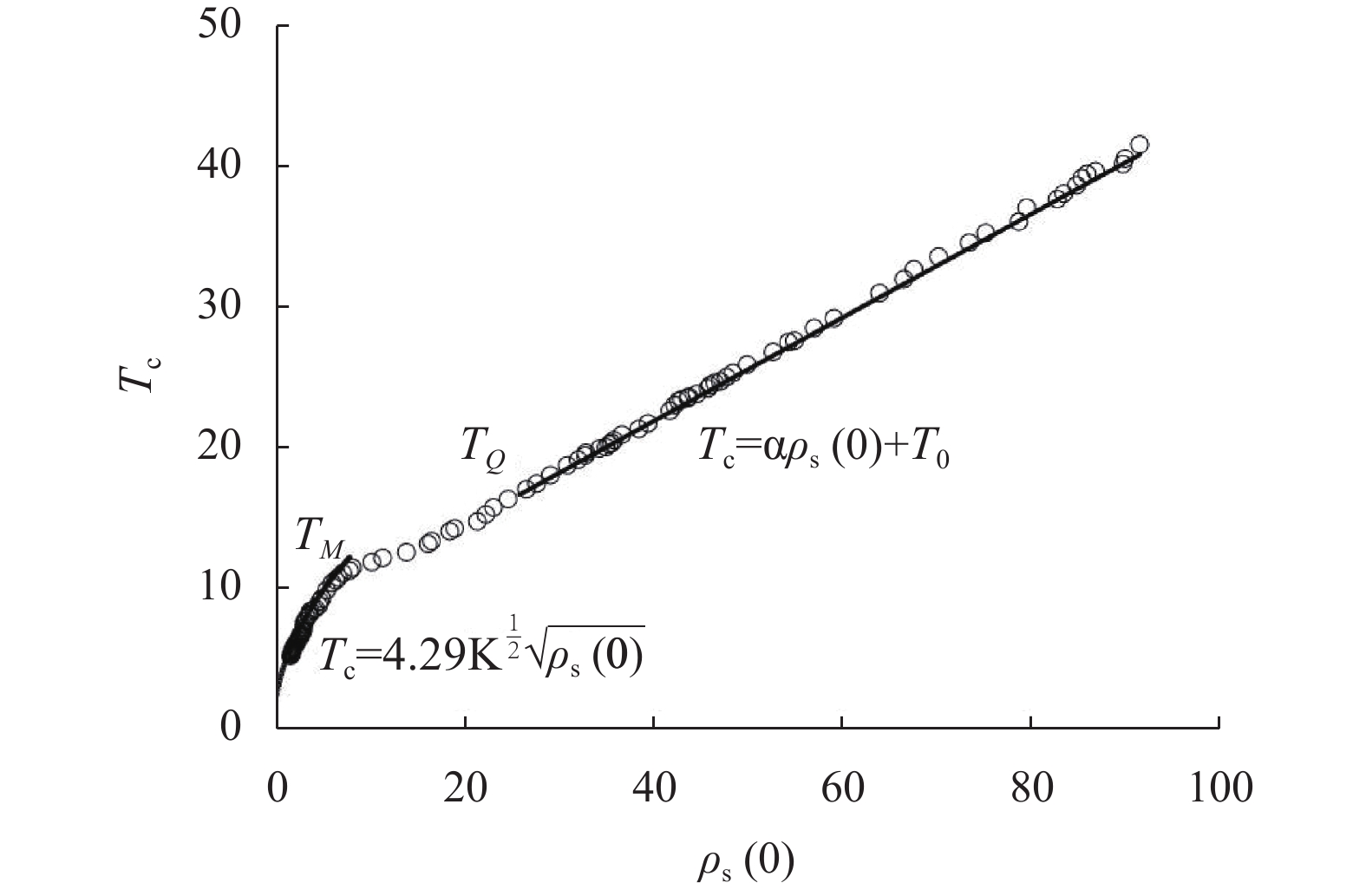
By introducing the imaginary time, we show that Gor’kov’s Ginzburg–Landau equation at zero temperature can be extended to an exact relativistic form. Based on this equation, we propose a quantum field theory with the imaginary time, which is intended to describe the quantum critical phenomena in the zero-temperature overdoped cuprate. By using such a quantum field theory, we show that the anomalous two-class scaling between the transition temperature\begin{document}$ {T_c} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$\;{\rho _s}\left( 0 \right)$\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}${\rm{L}}{{\rm{a}}_{2 - x}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{r}}_x}{\rm{Cu}}{{\rm{O}}_4}$\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ {T_c} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ \xi \left( 0 \right) $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ {T_c} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}${T_{Q}}$\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ {T_c} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ \xi(0) $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ \xi \left( 0 \right) \propto T_c^{ - 1.34} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}${T_{M}}$\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ \xi \left( 0 \right) \propto T_c^{ - 1} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
By introducing the imaginary time, we show that Gor’kov’s Ginzburg–Landau equation at zero temperature can be extended to an exact relativistic form. Based on this equation, we propose a quantum field theory with the imaginary time, which is intended to describe the quantum critical phenomena in the zero-temperature overdoped cuprate. By using such a quantum field theory, we show that the anomalous two-class scaling between the transition temperature

 ISSN
ISSN