2022 Vol. 51, No. 4
2022, 51(4): 481-481.
Abstract:
2022, 51(4): 482-487.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022068
Abstract:
In this paper, we use Bayesian decision to distinguish signal state from decoy state in one decoy-state quantum key distribution. The analysis results show that we can still only get the conclusion that the signal state and decoy state have the same\begin{document}$ i $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
In this paper, we use Bayesian decision to distinguish signal state from decoy state in one decoy-state quantum key distribution. The analysis results show that we can still only get the conclusion that the signal state and decoy state have the same
2022, 51(4): 488-492.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022008
Abstract:
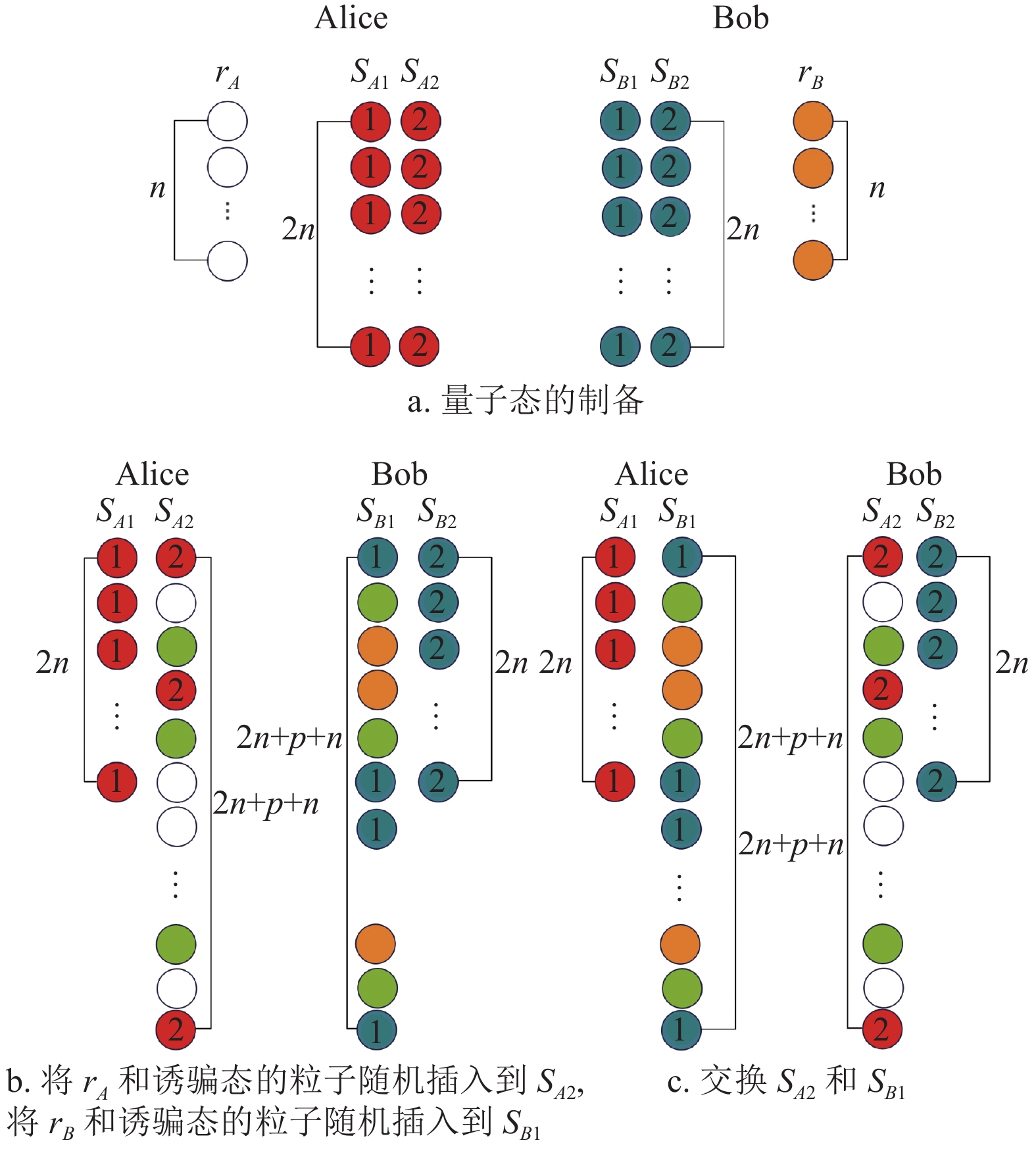
In order to solve the problem of complicated steps and large communication volume caused by the participation of trusted or semi-trusted third parties in the existing mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocols, a new two-party quantum key agreement protocol is proposed based on Bell states and their entangled exchange properties. The key agreement protocol can realize identity mutual authentication and fair key agreement between participants without the participation of trusted or semi-trusted third parties, thus reducing the communication complexity of the protocol. The security analysis shows that its identity authentication process can resist impersonation attack, and its key agreement process can resist external attacks and participant attacks. In addition, compared with the existing mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocols, the quantum bit efficiency of the protocol is also higher, and its quantum state preparation and measurement are easier to achieve with existing technologies.
In order to solve the problem of complicated steps and large communication volume caused by the participation of trusted or semi-trusted third parties in the existing mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocols, a new two-party quantum key agreement protocol is proposed based on Bell states and their entangled exchange properties. The key agreement protocol can realize identity mutual authentication and fair key agreement between participants without the participation of trusted or semi-trusted third parties, thus reducing the communication complexity of the protocol. The security analysis shows that its identity authentication process can resist impersonation attack, and its key agreement process can resist external attacks and participant attacks. In addition, compared with the existing mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocols, the quantum bit efficiency of the protocol is also higher, and its quantum state preparation and measurement are easier to achieve with existing technologies.
2022, 51(4): 493-493.
Abstract:
2022, 51(4): 494-499.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021391
Abstract:
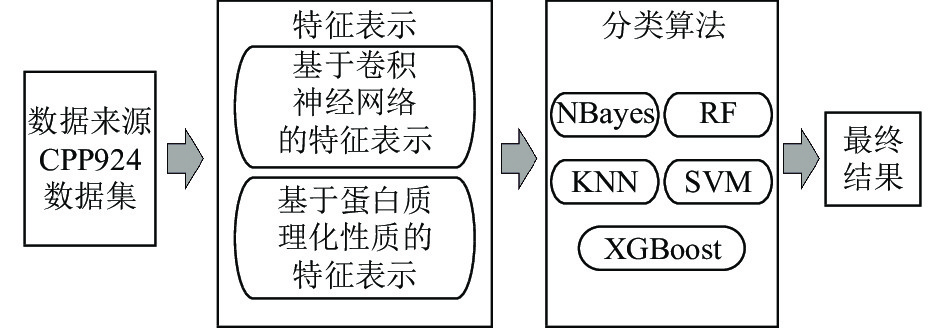
Cell-penetrating peptides(CPPs) are a special class of peptides with unique medical value. Therefore, it’s important to efficiently identify CPPs by computational methods. The current mainstream method is to use different feature extraction algorithms to extract sequence features and then use machine learning classifier for classification. This paper proposed a novel classification method: ConvCPP, which uses an improved convolution neural network to extract protein sequence features. The improvements include adding an attention layer before the convolution layer and optimizing the pooling layer. Ablation experiments were designed to verify the effectiveness of the improvement. After that, a variety of other feature extraction algorithms based on protein sequence features are combined, and two feature selection algorithms are tested, and finally the optimal vector representation is obtained. Then, according to the vector, the protein sequences are classified and recognized with a variety of machine learning classifiers. On the benchmark data set, the proposed method shows better prediction performance than the state-of-the-art CPPs predictors.
Cell-penetrating peptides(CPPs) are a special class of peptides with unique medical value. Therefore, it’s important to efficiently identify CPPs by computational methods. The current mainstream method is to use different feature extraction algorithms to extract sequence features and then use machine learning classifier for classification. This paper proposed a novel classification method: ConvCPP, which uses an improved convolution neural network to extract protein sequence features. The improvements include adding an attention layer before the convolution layer and optimizing the pooling layer. Ablation experiments were designed to verify the effectiveness of the improvement. After that, a variety of other feature extraction algorithms based on protein sequence features are combined, and two feature selection algorithms are tested, and finally the optimal vector representation is obtained. Then, according to the vector, the protein sequences are classified and recognized with a variety of machine learning classifiers. On the benchmark data set, the proposed method shows better prediction performance than the state-of-the-art CPPs predictors.
2022, 51(4): 500-505.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022004
Abstract:
The analysis and prediction of influencing factors of length of stay in intensive care unit (ICU) of cardiac surgery patients is conducive to the early intervention and cost control of inpatients, and is of great significance to the treatment and nursing of cardiac surgery patients. This paper uses the intensive care database medical information mart for intensive care IV (MIMIC-IV) as the experimental data set, 7567 patients were included. 41 important predictors were selected from 126 influencing factors by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso). This paper constructs a prediction model of length of stay in cardiac surgery intensive care unit based on gradient enhanced decision tree (GBDT) algorithm. The experimental results show that under the condition of training all predictors, the average accuracy of GBDT model is 0.688 higher than that of traditional logistic regression algorithm, which is 0.603. The GBDT algorithm with the selected important predictors has the same effect on the final average accuracy as that with all factors, which shows that this method can optimize data collection, accurately predict length of stay in ICU, and provide algorithm support for clinical decision support system.
The analysis and prediction of influencing factors of length of stay in intensive care unit (ICU) of cardiac surgery patients is conducive to the early intervention and cost control of inpatients, and is of great significance to the treatment and nursing of cardiac surgery patients. This paper uses the intensive care database medical information mart for intensive care IV (MIMIC-IV) as the experimental data set, 7567 patients were included. 41 important predictors were selected from 126 influencing factors by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso). This paper constructs a prediction model of length of stay in cardiac surgery intensive care unit based on gradient enhanced decision tree (GBDT) algorithm. The experimental results show that under the condition of training all predictors, the average accuracy of GBDT model is 0.688 higher than that of traditional logistic regression algorithm, which is 0.603. The GBDT algorithm with the selected important predictors has the same effect on the final average accuracy as that with all factors, which shows that this method can optimize data collection, accurately predict length of stay in ICU, and provide algorithm support for clinical decision support system.
2022, 51(4): 506-513.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021325
Abstract:
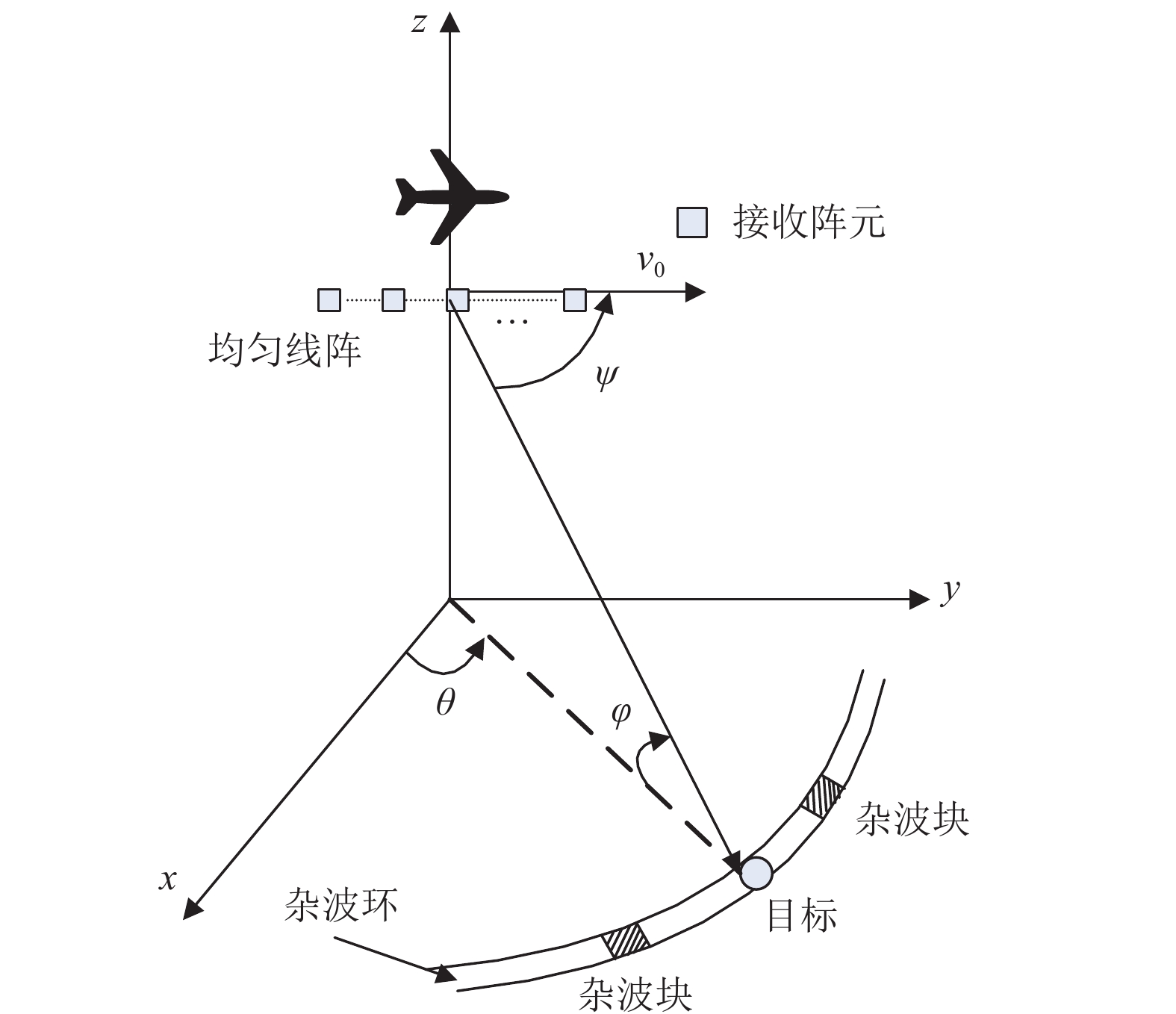
In the airborne radar signal processing, the strong ground clutter is a major problem affecting the signal detection performance. The space-time adaptive processing (STAP) is an effective technique to suppress the clutter. In practical processing, because of the non-stationarity of the clutter, the STAP usually faces the problem of a small number of available valid samples. In order to solve this problem, an angle-Doppler channel selection method based on sparse recovery is proposed. We utilize a small number of samples to estimate the full-dimensional clutter covariance matrix (CCM) via the sparse recovery method and evaluate the importance of each channel with the estimated full-dimensional CCM. Then we select the appropriate channels to construct the reduced-dimensional clutter covariance matrix for the STAP processing. The proposed algorithm can solve the problem of few samples with good performance of the reduced-dimension STAP (RD-STAP). The numerical simulation verifies that the algorithm is effective and better than several typical STAP algorithms. The relationship between output performance and the number of channels under different sample numbers is also discussed.
In the airborne radar signal processing, the strong ground clutter is a major problem affecting the signal detection performance. The space-time adaptive processing (STAP) is an effective technique to suppress the clutter. In practical processing, because of the non-stationarity of the clutter, the STAP usually faces the problem of a small number of available valid samples. In order to solve this problem, an angle-Doppler channel selection method based on sparse recovery is proposed. We utilize a small number of samples to estimate the full-dimensional clutter covariance matrix (CCM) via the sparse recovery method and evaluate the importance of each channel with the estimated full-dimensional CCM. Then we select the appropriate channels to construct the reduced-dimensional clutter covariance matrix for the STAP processing. The proposed algorithm can solve the problem of few samples with good performance of the reduced-dimension STAP (RD-STAP). The numerical simulation verifies that the algorithm is effective and better than several typical STAP algorithms. The relationship between output performance and the number of channels under different sample numbers is also discussed.
2022, 51(4): 514-521.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021313
Abstract:
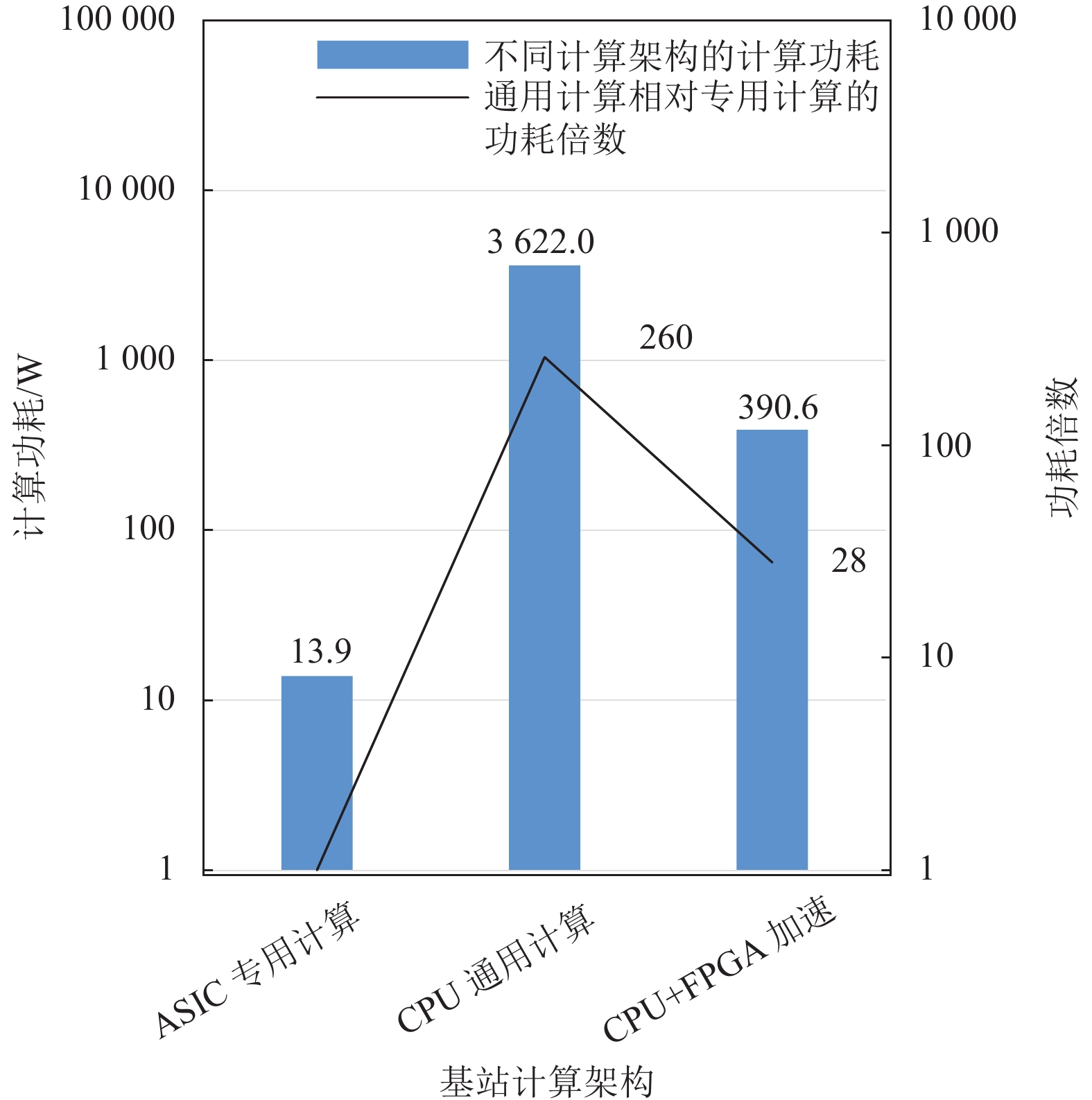
Massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is a key enabling technology for future 5G-Advanced/5G mobile networks to effectively increase spectrum utilization by using large-scale antennas. It is expected that with the evolution to 6G massive MIMO will support more antennas and more complex algorithms, and thus baseband energy efficiency (EE) will be one of the crucial challenges to improve network energy efficiency. In such a system, base station (BS) computing architectures consist of dedicated (ASIC) and general-purpose (CPU) computing architectures. It is very difficult to choose the optimal computing architecture due to the lack of quantitative modeling of the computational requirements and EE of the baseband. Hence, it is necessary to study the power consumption model of different computing architectures related to combined logic units and processing cycles. Based on the proposed power consumption model, the closed forms of EE equations are derived with unit floating point operations per-second per-Watt. Numerical results show that the current EE of dedicated computing is 30 times and 200 times higher than that of the general-purpose computing (with hardware acceleration) and CPU general-purpose computing architecture respectively.
Massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is a key enabling technology for future 5G-Advanced/5G mobile networks to effectively increase spectrum utilization by using large-scale antennas. It is expected that with the evolution to 6G massive MIMO will support more antennas and more complex algorithms, and thus baseband energy efficiency (EE) will be one of the crucial challenges to improve network energy efficiency. In such a system, base station (BS) computing architectures consist of dedicated (ASIC) and general-purpose (CPU) computing architectures. It is very difficult to choose the optimal computing architecture due to the lack of quantitative modeling of the computational requirements and EE of the baseband. Hence, it is necessary to study the power consumption model of different computing architectures related to combined logic units and processing cycles. Based on the proposed power consumption model, the closed forms of EE equations are derived with unit floating point operations per-second per-Watt. Numerical results show that the current EE of dedicated computing is 30 times and 200 times higher than that of the general-purpose computing (with hardware acceleration) and CPU general-purpose computing architecture respectively.
2022, 51(4): 522-528, 534.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022006
Abstract:
The deployment of low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellites is an important supplement to the existing satellite navigation systems and also an effective approach to navigation augmentation. The design of LEO satellite constellation is studied in this paper, in order to optimize its performance in regional navigation augmentation. Different from the near-circular-orbit-based scheme adopted by most LEO constellations for global navigation augmentation, an elliptical-orbit-based constellation scheme is employed in our design. Owing to the slow-motion speed, the large coverage area, and the long residence time of satellites in the apogee of elliptical orbit, the elliptical-orbit-based scheme is specifically suitable for regional navigation augmentation. In addition, under the framework of Flower constellation, the orbit parameter of each satellite is optimized to ensure that the trajectory of its sub-satellite point repeatedly passes through the center of the region, thus extending the zenith crossing time of the satellite. By the aforementioned constellation design, the key navigation performance metrics, such as zenith crossing time, coverage multiplicity, and geometric dilution of precision, are effectively improved. In the simulations with BeiDou-3 system (BDS-3) being the navigation system to be augmented, it is validated that with the same number of LEO satellites, the proposed design achieves better navigation augmentation performance.
The deployment of low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellites is an important supplement to the existing satellite navigation systems and also an effective approach to navigation augmentation. The design of LEO satellite constellation is studied in this paper, in order to optimize its performance in regional navigation augmentation. Different from the near-circular-orbit-based scheme adopted by most LEO constellations for global navigation augmentation, an elliptical-orbit-based constellation scheme is employed in our design. Owing to the slow-motion speed, the large coverage area, and the long residence time of satellites in the apogee of elliptical orbit, the elliptical-orbit-based scheme is specifically suitable for regional navigation augmentation. In addition, under the framework of Flower constellation, the orbit parameter of each satellite is optimized to ensure that the trajectory of its sub-satellite point repeatedly passes through the center of the region, thus extending the zenith crossing time of the satellite. By the aforementioned constellation design, the key navigation performance metrics, such as zenith crossing time, coverage multiplicity, and geometric dilution of precision, are effectively improved. In the simulations with BeiDou-3 system (BDS-3) being the navigation system to be augmented, it is validated that with the same number of LEO satellites, the proposed design achieves better navigation augmentation performance.
2022, 51(4): 529-534.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022050
Abstract:
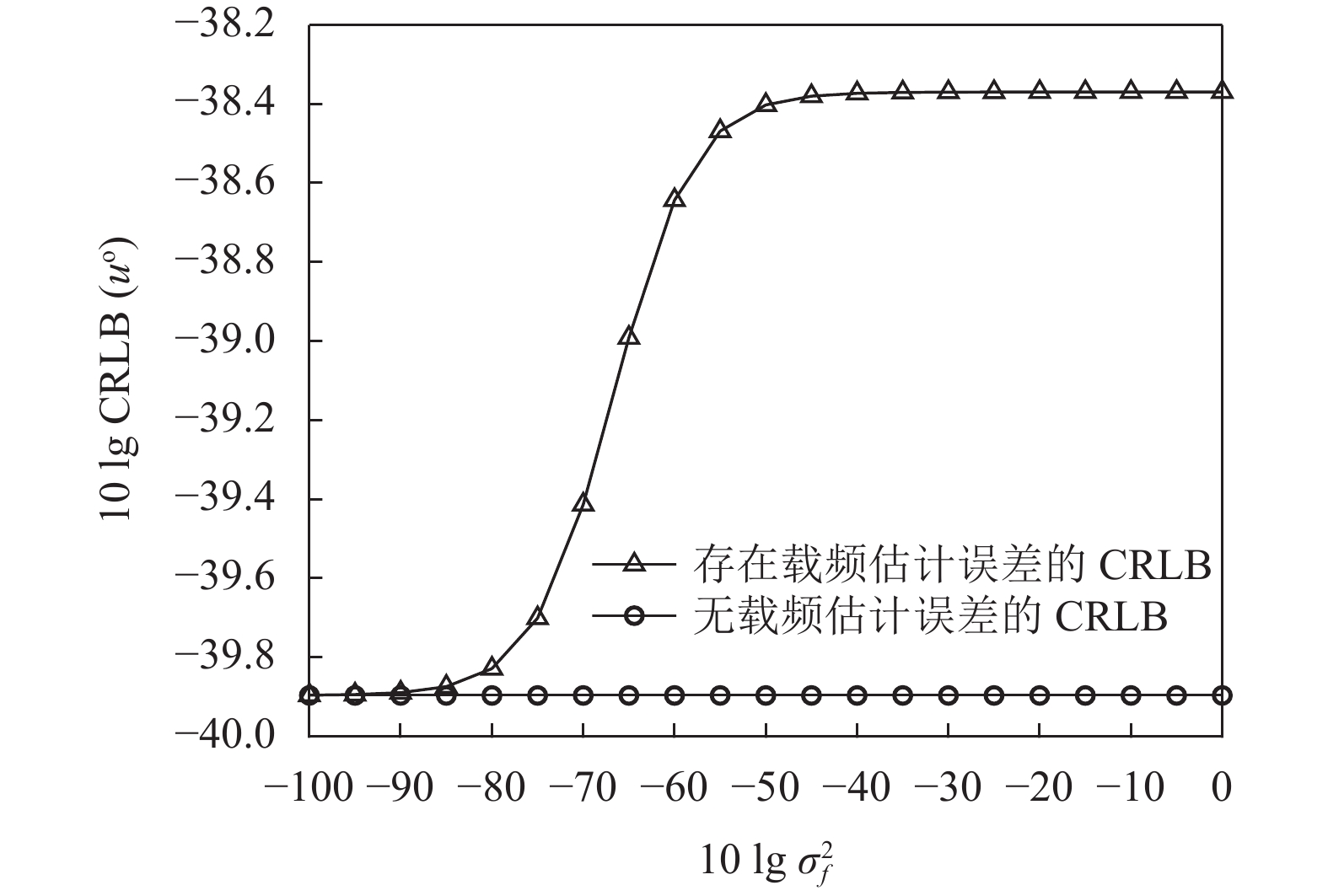
In the non-cooperative scenario where the carrier frequency is not known exactly, the source localization using Doppler frequency shift is investigated. By taking the erroneous carrier frequency into account, a source localization algorithm is proposed based on Doppler frequency shift. The Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) with erroneous carrier frequency is derived firstly, and then the proposed source localization algorithm is compared with the one ignoring erroneous carrier frequency. By simulations, it is found that although the CRLB with erroneous carrier frequency is 1.5 dB worse than the one without erroneous carrier frequency, the performance of the source localization algorithm ignoring erroneous carrier frequency deteriorates sharply. When the source localization algorithm ignoring erroneous carrier frequency starts to deviate from the CRLB, the proposed source localization algorithm can still reach the CRLB. It is not until the noise increases by nearly 40 dB that the proposed source localization algorithm begins to deviate from the CRLB. This proves that the proposed source localization algorithm is more robust and accuracy.
In the non-cooperative scenario where the carrier frequency is not known exactly, the source localization using Doppler frequency shift is investigated. By taking the erroneous carrier frequency into account, a source localization algorithm is proposed based on Doppler frequency shift. The Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) with erroneous carrier frequency is derived firstly, and then the proposed source localization algorithm is compared with the one ignoring erroneous carrier frequency. By simulations, it is found that although the CRLB with erroneous carrier frequency is 1.5 dB worse than the one without erroneous carrier frequency, the performance of the source localization algorithm ignoring erroneous carrier frequency deteriorates sharply. When the source localization algorithm ignoring erroneous carrier frequency starts to deviate from the CRLB, the proposed source localization algorithm can still reach the CRLB. It is not until the noise increases by nearly 40 dB that the proposed source localization algorithm begins to deviate from the CRLB. This proves that the proposed source localization algorithm is more robust and accuracy.
2022, 51(4): 535-541, 564.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022052
Abstract:
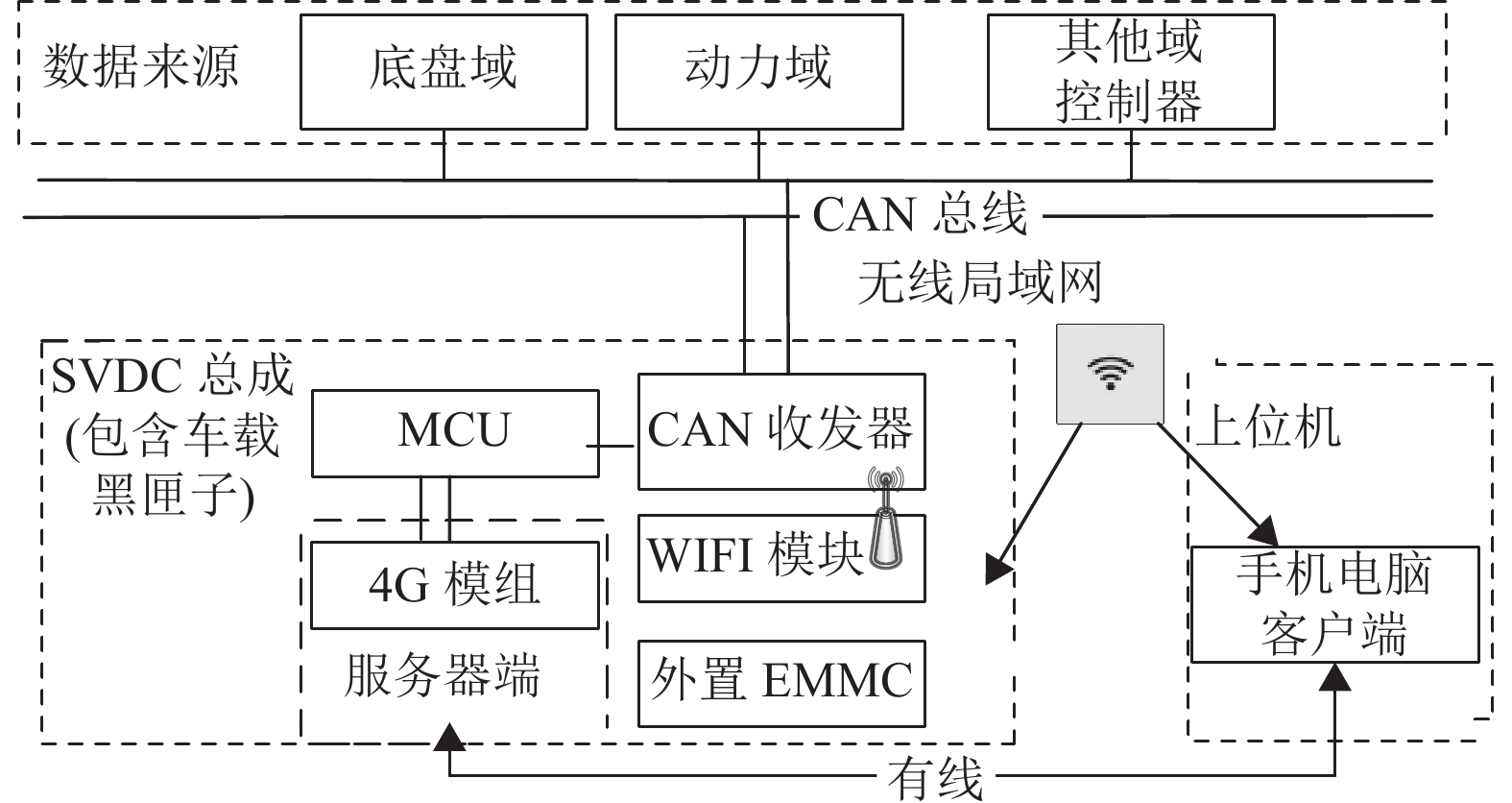
In view of the multi-task information characteristics of the intelligent vehicle domain controller, a data export system for multi-task network communication is proposed. The system decomposes the absolute path required by task management into sub directory fields with low coupling, extends the function of single-file breakpoint resuming to multi-task scenarios to improve the efficiency of data transmission. Next, according to the storage characteristics of driving data, a variable-step data extraction method is proposed, and the time stamp information is used to realize the rapid retrieval and positioning of effective data. The experimental results show that the method achieves efficient data transmission and accurate extraction, which proves the effectiveness of the method.
In view of the multi-task information characteristics of the intelligent vehicle domain controller, a data export system for multi-task network communication is proposed. The system decomposes the absolute path required by task management into sub directory fields with low coupling, extends the function of single-file breakpoint resuming to multi-task scenarios to improve the efficiency of data transmission. Next, according to the storage characteristics of driving data, a variable-step data extraction method is proposed, and the time stamp information is used to realize the rapid retrieval and positioning of effective data. The experimental results show that the method achieves efficient data transmission and accurate extraction, which proves the effectiveness of the method.
2022, 51(4): 542-549.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021402
Abstract:
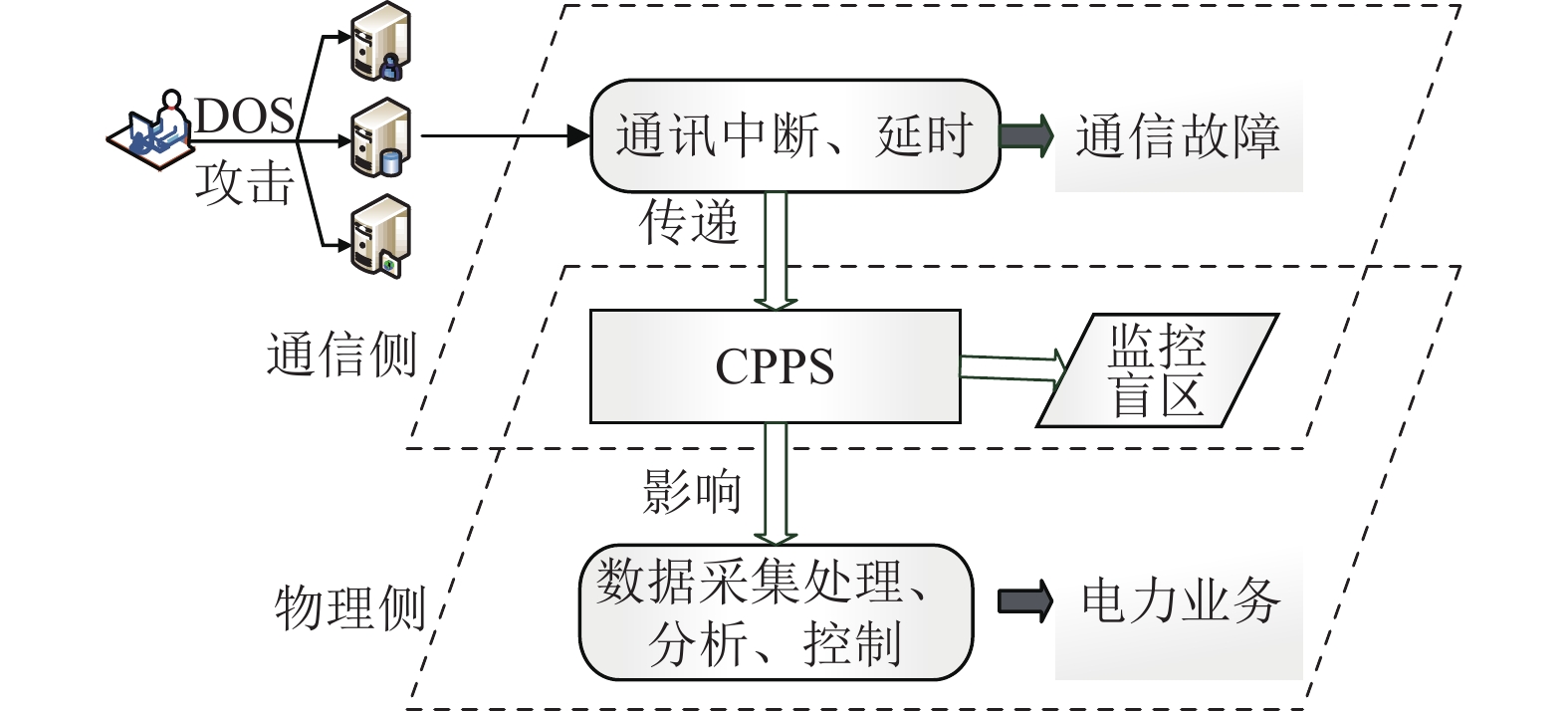
The network attacks against the power system of hostile countries can cause great damage with less attack resources. From the perspective of attackers, this paper proposes a network attack strategy for weak state of power system. Firstly, tthe correlation matrix based on the grid topology data is established, and the load shedding caused by the attack under different information acquisition amounts is calculated through the linear programming model. Then an automatic attack strategy is proposed to maximize the attack effect. The effectiveness of the proposed strategy is verified by simulation analysis in different scenarios.
The network attacks against the power system of hostile countries can cause great damage with less attack resources. From the perspective of attackers, this paper proposes a network attack strategy for weak state of power system. Firstly, tthe correlation matrix based on the grid topology data is established, and the load shedding caused by the attack under different information acquisition amounts is calculated through the linear programming model. Then an automatic attack strategy is proposed to maximize the attack effect. The effectiveness of the proposed strategy is verified by simulation analysis in different scenarios.
2022, 51(4): 550-557.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021347
Abstract:
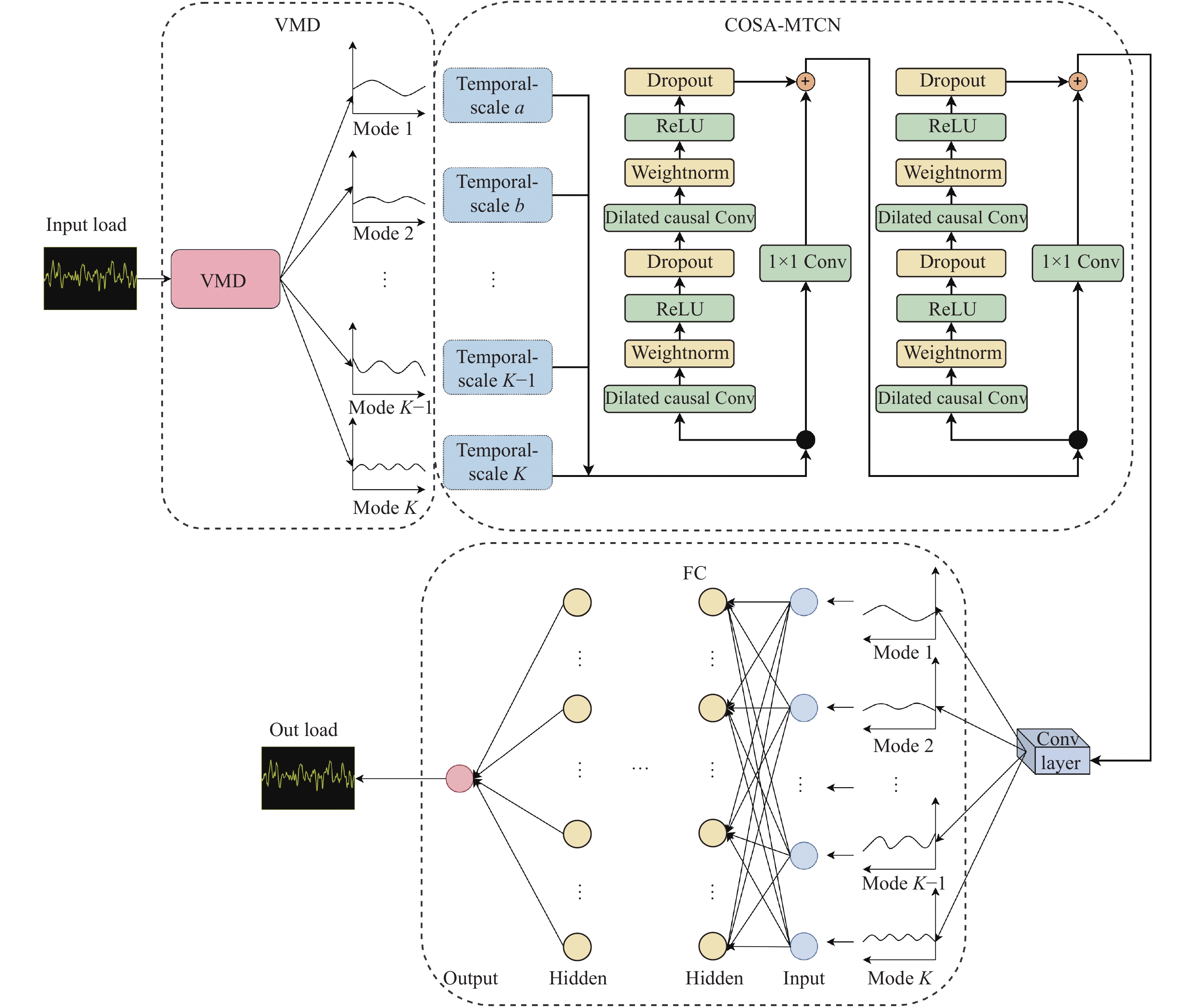
Accurate power load forecasting plays an important role in ensuring the stable operation of the power system. In view of the low precision of traditional short-term power load forecasting methods, the sub-sequence fusion problem is not considered after modal decomposition, this paper proposes a multi-scale short-term power load forecasting based on variational mode decomposition (VMD) and temporal convolutional network (TCN) methods. First, VMD is used to decompose the power load data into several sub-components to solve the problems of non-linearity and randomness in the power load data, then TCN is applied to train several components with different time scales, finally a fully connected network is used to analyze each component. Time-scale decomposition signals are fused to realize short-term power load forecasting and improve forecasting accuracy. The experimental results show that the root mean square error (RMSE) is reduced by 40% and the curve fitting is improved by 1.1% compared with the traditional prediction method of VMD and improved long-short-term memory network.
Accurate power load forecasting plays an important role in ensuring the stable operation of the power system. In view of the low precision of traditional short-term power load forecasting methods, the sub-sequence fusion problem is not considered after modal decomposition, this paper proposes a multi-scale short-term power load forecasting based on variational mode decomposition (VMD) and temporal convolutional network (TCN) methods. First, VMD is used to decompose the power load data into several sub-components to solve the problems of non-linearity and randomness in the power load data, then TCN is applied to train several components with different time scales, finally a fully connected network is used to analyze each component. Time-scale decomposition signals are fused to realize short-term power load forecasting and improve forecasting accuracy. The experimental results show that the root mean square error (RMSE) is reduced by 40% and the curve fitting is improved by 1.1% compared with the traditional prediction method of VMD and improved long-short-term memory network.
2022, 51(4): 558-564.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022061
Abstract:
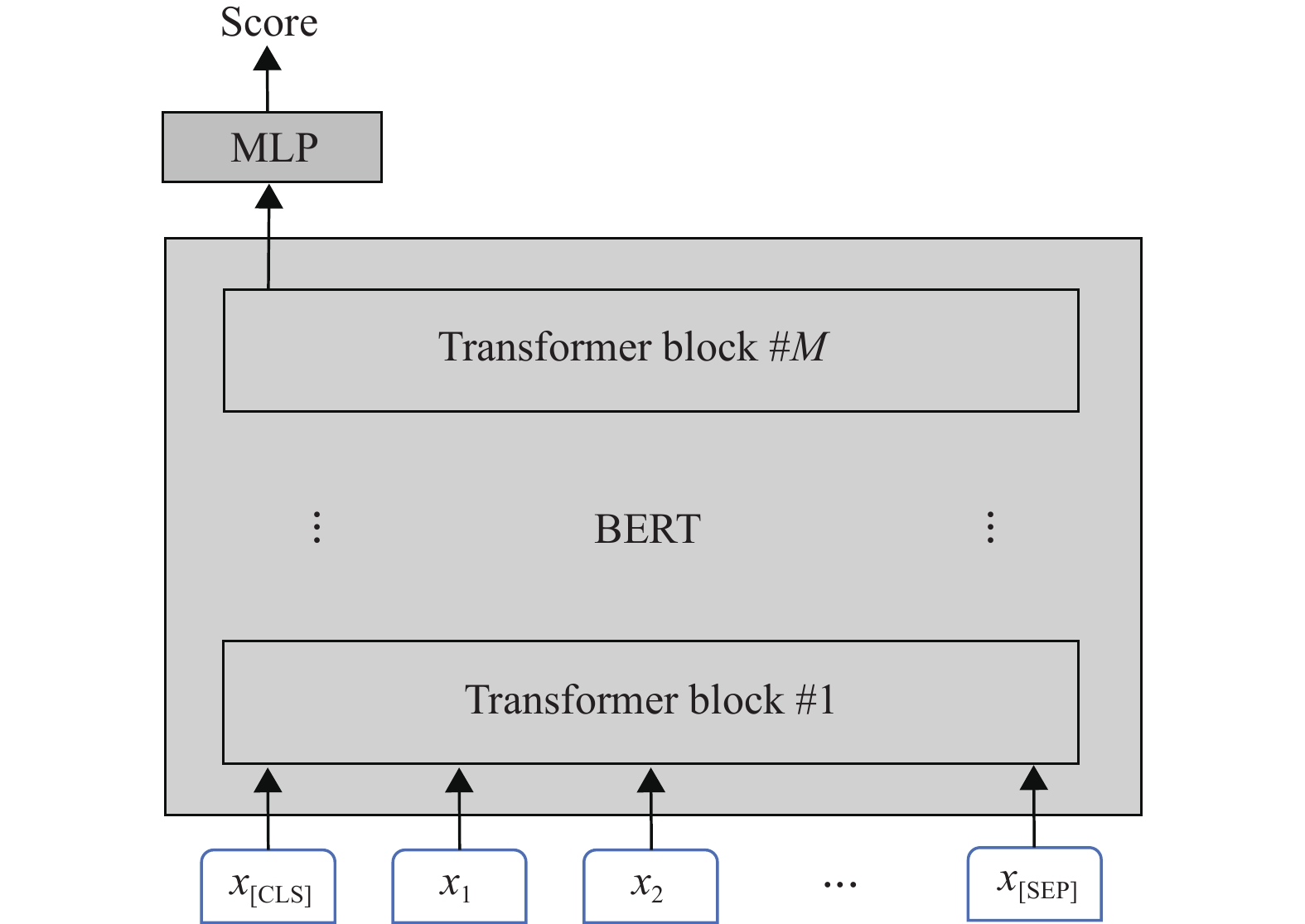
This paper proposes a gradient-similarity based multi-topic jointly pre-training method for automated essay scoring (AES). Specifically, in the pre-training stage, the training data of multiple topics are used at the same time, and the similarity between the gradient vector of a sample from other topics and the gradient vector of target topic is calculated as the loss weight for this sample. Besides, this paper also designs three types of handcrafted features, combining deep learning with feature engineering. Comparative experiments are conducted on publicly available datasets, and the results show that compared with the existing baselines, both proposed multi-topic jointly pre-training method and handcrafted features can effectively improve the scoring accuracy of the AES model.
This paper proposes a gradient-similarity based multi-topic jointly pre-training method for automated essay scoring (AES). Specifically, in the pre-training stage, the training data of multiple topics are used at the same time, and the similarity between the gradient vector of a sample from other topics and the gradient vector of target topic is calculated as the loss weight for this sample. Besides, this paper also designs three types of handcrafted features, combining deep learning with feature engineering. Comparative experiments are conducted on publicly available datasets, and the results show that compared with the existing baselines, both proposed multi-topic jointly pre-training method and handcrafted features can effectively improve the scoring accuracy of the AES model.
2022, 51(4): 565-571.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021350
Abstract:
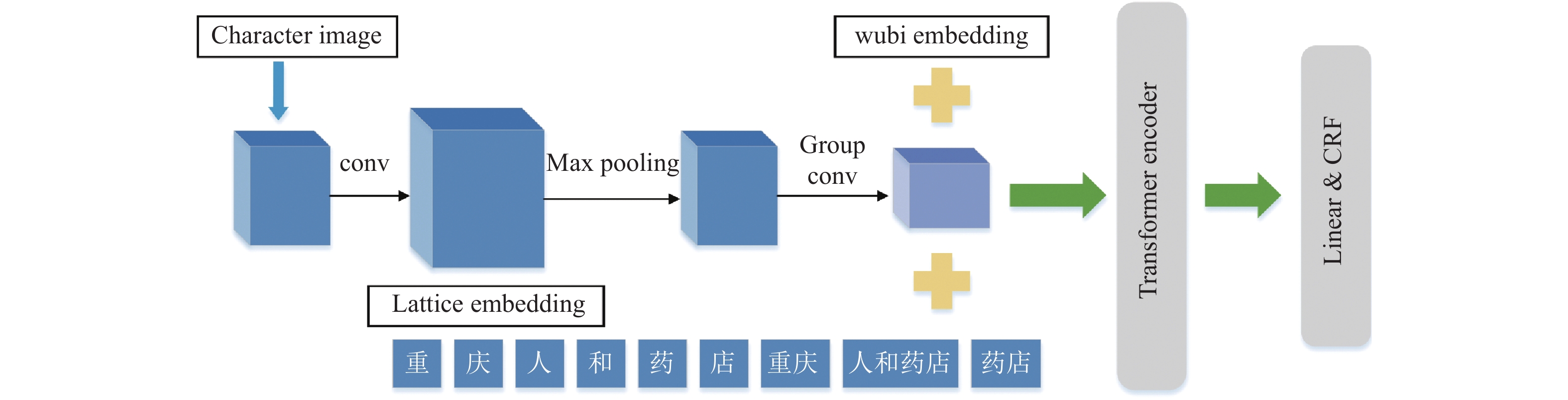
Chinese electronic medical record texts are highly professional, with complex grammar,it is difficult to use named entity recognition (NER) for natural language processing (NLP). In order to accurately identify medical entities from electronic medical record data, a named entity recognition algorithm combining semantic and boundary information is proposed. In this algorithm, the graphic information of Chinese characters is extracted by using the convolutional neural network (CNN) structure and the semantic information of the Chinese characters is enriched with Wubi features. And then the text information is matched with medical dictionary as a potential phrase of characters by using the Lattice in the FLAT model. Finally, the Lattice model incorporating semantic information is used for named entity recognition in Chinese electronic medical records. The experimental results show that this method has better recognition performance than other existing methods on the Yidu-S4K data set, and the F1 value on the Resume dataset is 96.06%.
Chinese electronic medical record texts are highly professional, with complex grammar,it is difficult to use named entity recognition (NER) for natural language processing (NLP). In order to accurately identify medical entities from electronic medical record data, a named entity recognition algorithm combining semantic and boundary information is proposed. In this algorithm, the graphic information of Chinese characters is extracted by using the convolutional neural network (CNN) structure and the semantic information of the Chinese characters is enriched with Wubi features. And then the text information is matched with medical dictionary as a potential phrase of characters by using the Lattice in the FLAT model. Finally, the Lattice model incorporating semantic information is used for named entity recognition in Chinese electronic medical records. The experimental results show that this method has better recognition performance than other existing methods on the Yidu-S4K data set, and the F1 value on the Resume dataset is 96.06%.
2022, 51(4): 572-579.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022001
Abstract:
A node scheduling algorithm based on enhanced version of coral reef optimization algorithm (shortly for ECRO) is proposed to solve the life maximization problem of heterogeneous directional sensor networks for connectivity and differentiated target coverage requirements. Based on cover sets theory, ECRO is utilized to get the cover sets, which can cover all the targets and satisfy their connectivity and coverage quality requirements. The improvement of coral reef optimization (shortly for CRO) lies in the three aspects. Firstly, the population is initialized by the SOBOL sequence and an opposition learning strategy. Secondly the operator of harmony search algorithm, immigration in biogeography-based optimization and a self-adaptive mutation strategy in differential evolution algorithm are introduced into the brooding procedure of the coral larvae formation to conserve the excellent solutions of the population and enhance the diversity of the descent and the ability of optimization for coral reef. Moreover, an opposition learning strategy and differential strategy with the optimal individual are utilized to improve the performance of the worst individual of the population. Extensive simulation experiments both in numerical benchmark functions and node scheduling are conducted to validate the proposed ECRO. The results show that the proposed ECRO outperforms the compared algorithms, which demonstrate the superiority of the proposed algorithm ECRO.
A node scheduling algorithm based on enhanced version of coral reef optimization algorithm (shortly for ECRO) is proposed to solve the life maximization problem of heterogeneous directional sensor networks for connectivity and differentiated target coverage requirements. Based on cover sets theory, ECRO is utilized to get the cover sets, which can cover all the targets and satisfy their connectivity and coverage quality requirements. The improvement of coral reef optimization (shortly for CRO) lies in the three aspects. Firstly, the population is initialized by the SOBOL sequence and an opposition learning strategy. Secondly the operator of harmony search algorithm, immigration in biogeography-based optimization and a self-adaptive mutation strategy in differential evolution algorithm are introduced into the brooding procedure of the coral larvae formation to conserve the excellent solutions of the population and enhance the diversity of the descent and the ability of optimization for coral reef. Moreover, an opposition learning strategy and differential strategy with the optimal individual are utilized to improve the performance of the worst individual of the population. Extensive simulation experiments both in numerical benchmark functions and node scheduling are conducted to validate the proposed ECRO. The results show that the proposed ECRO outperforms the compared algorithms, which demonstrate the superiority of the proposed algorithm ECRO.
2022, 51(4): 580-585, 607.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021314
Abstract:
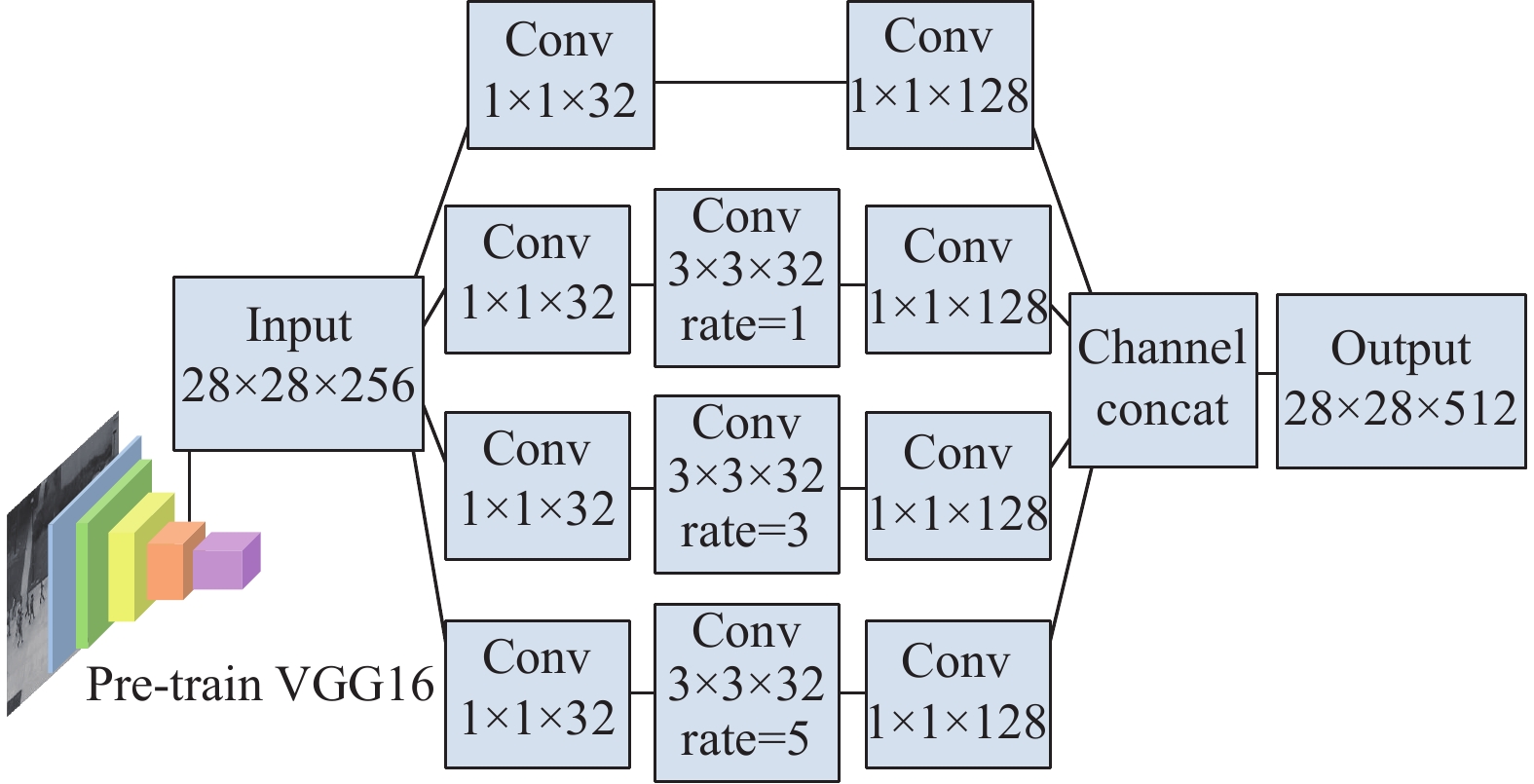
For the classification problem of unlabeled high-dimensional images, the commonly used deep neutral networks have difficulty in producing good classification results in the unlabeled datasets. This paper proposes an unsupervised feature-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks (Feature-GAN), which learns the feature level transformation from one domain to another in unsupervised manner. It maps the source domain image features to the target domain image features and keeps the label information, and these generated labeled features can be used to train a classifier adapted to the target domain features. This model avoids the generation process of the image itself in the complex image domain adaptation problem and focuses on feature generation. The model is easy to train and has high stability. Experiments show that the proposed method can be widely applied to complex image classification scenarios, and it outperforms traditional sample generation-based unsupervised domain adaptation algorithms in terms of accuracy, convergence speed, and stability.
For the classification problem of unlabeled high-dimensional images, the commonly used deep neutral networks have difficulty in producing good classification results in the unlabeled datasets. This paper proposes an unsupervised feature-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks (Feature-GAN), which learns the feature level transformation from one domain to another in unsupervised manner. It maps the source domain image features to the target domain image features and keeps the label information, and these generated labeled features can be used to train a classifier adapted to the target domain features. This model avoids the generation process of the image itself in the complex image domain adaptation problem and focuses on feature generation. The model is easy to train and has high stability. Experiments show that the proposed method can be widely applied to complex image classification scenarios, and it outperforms traditional sample generation-based unsupervised domain adaptation algorithms in terms of accuracy, convergence speed, and stability.
2022, 51(4): 586-591.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021333
Abstract:
A novel method for abnormal event detection is proposed based on multi-scale feature prediction. Firstly, dilated convolution network is used to extract the features of different size receptive fields and fuse them so that address the objects of different scale in video frame. Secondly, a lightweight channel-wise attention module is applied to reduce the impact of background information. Finally, in order to make full use of the context information between video frames, a deep feature prediction module is applied to predict the features of the current moment based on the features of the historical moment, and the prediction error is used for abnormality judgment. Experiments were performed on the two benchmark data sets of USCD Ped2 and UMN to test and evaluate the proposed method. The experiments results show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods.
A novel method for abnormal event detection is proposed based on multi-scale feature prediction. Firstly, dilated convolution network is used to extract the features of different size receptive fields and fuse them so that address the objects of different scale in video frame. Secondly, a lightweight channel-wise attention module is applied to reduce the impact of background information. Finally, in order to make full use of the context information between video frames, a deep feature prediction module is applied to predict the features of the current moment based on the features of the historical moment, and the prediction error is used for abnormality judgment. Experiments were performed on the two benchmark data sets of USCD Ped2 and UMN to test and evaluate the proposed method. The experiments results show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods.
2022, 51(4): 592-599.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021377
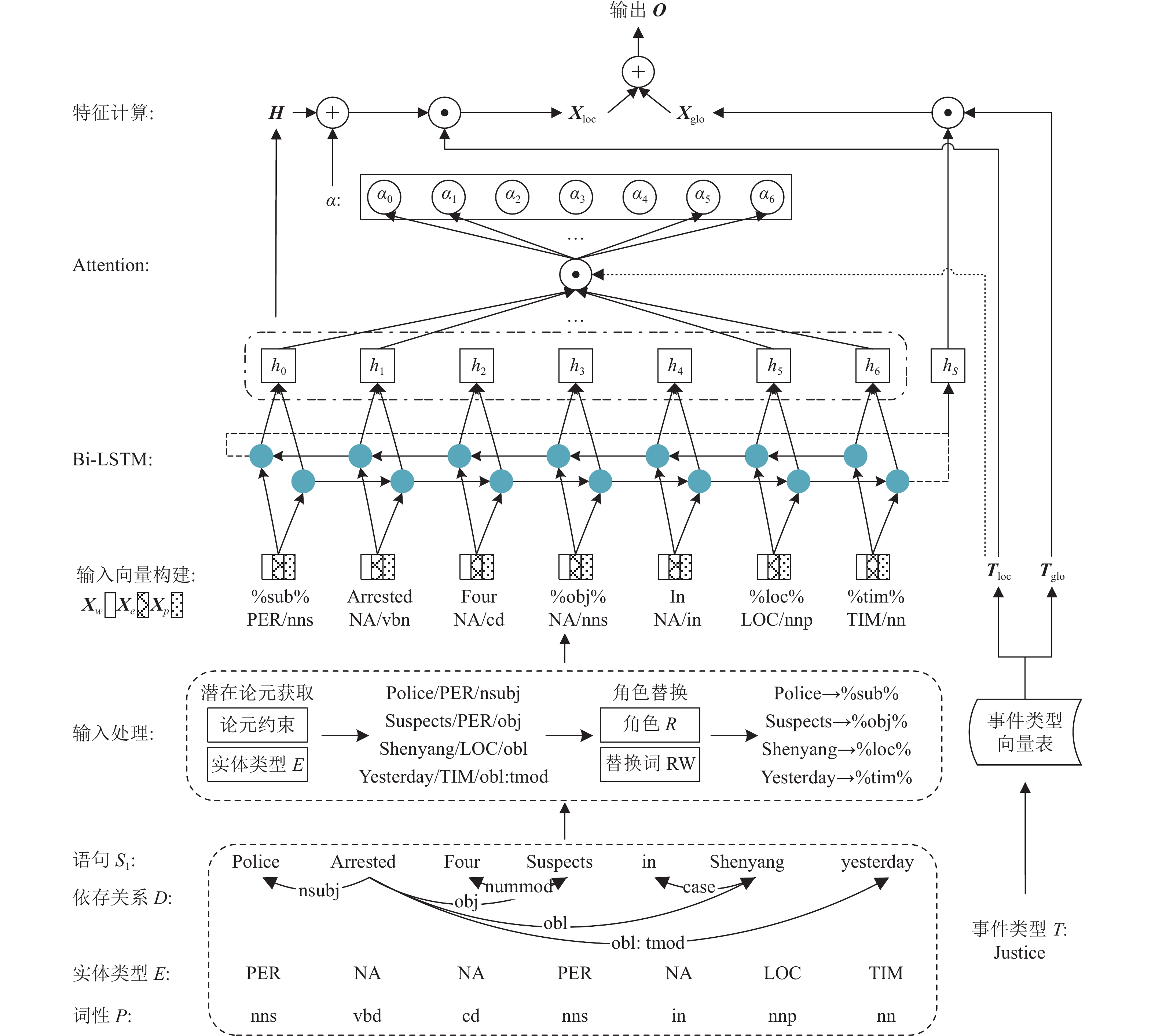
Abstract:
To address the problems of vague criteria for trigger word definition and the high cost of corpus annotation, a deep learning model for event detection called pattern and type based neural network (PTNN) is proposed. First, potential theorems are obtained based on entities' syntactic and semantic features. Then, the potential theorems are abstracted as roles. The embedding representation of PTNN is constructed by combining syntactic, semantic, and role features to enhance the representation of event patterns. Last, event detection and type determination are accomplished by using Bi-LSTM (bidirectional long short-term memory) with an event type-based attention mechanism. The model achieves event detection by enhancing event pattern features instead of identifying trigger words, thus avoiding the challenging problem of trigger word annotation. Such an approach demonstrates the positive effect of event patterns for event detection on neural networks. Experiments demonstrate that it improves the state-of-the-art of event detection by 3%.
To address the problems of vague criteria for trigger word definition and the high cost of corpus annotation, a deep learning model for event detection called pattern and type based neural network (PTNN) is proposed. First, potential theorems are obtained based on entities' syntactic and semantic features. Then, the potential theorems are abstracted as roles. The embedding representation of PTNN is constructed by combining syntactic, semantic, and role features to enhance the representation of event patterns. Last, event detection and type determination are accomplished by using Bi-LSTM (bidirectional long short-term memory) with an event type-based attention mechanism. The model achieves event detection by enhancing event pattern features instead of identifying trigger words, thus avoiding the challenging problem of trigger word annotation. Such an approach demonstrates the positive effect of event patterns for event detection on neural networks. Experiments demonstrate that it improves the state-of-the-art of event detection by 3%.
2022, 51(4): 600-607.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2020383
Abstract:
In the field of indirect contrast enhancement, an S-type function based on the contrast sensitivity of human visual system is proposed, in order to overcome the limitations of traditional transformation functions under low illumination. This method models the contrast sensitivity of the human retina as an exponential function of logarithmic intensity, since there are different retinal response values for different stimulus intensities. This method uses the sensitivity model as the exponent of Steven's power law to derive a transfer function for perceived brightness. At the same time, a parameter optimization method is proposed, which maintains the average brightness of the input image, and stretches the image histogram while ensuring minimal information loss. Experimental results show that this method has less information loss and better computational complexity performance while maintaining the average brightness of the input image. It has certain advantages in existing methods in terms of contrast enhancement performance, average brightness and preservation of details.
In the field of indirect contrast enhancement, an S-type function based on the contrast sensitivity of human visual system is proposed, in order to overcome the limitations of traditional transformation functions under low illumination. This method models the contrast sensitivity of the human retina as an exponential function of logarithmic intensity, since there are different retinal response values for different stimulus intensities. This method uses the sensitivity model as the exponent of Steven's power law to derive a transfer function for perceived brightness. At the same time, a parameter optimization method is proposed, which maintains the average brightness of the input image, and stretches the image histogram while ensuring minimal information loss. Experimental results show that this method has less information loss and better computational complexity performance while maintaining the average brightness of the input image. It has certain advantages in existing methods in terms of contrast enhancement performance, average brightness and preservation of details.
2022, 51(4): 608-614.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021219
Abstract:
Aiming at taking the source Twitter texts as the research object, this paper deeply explores semantic information of Twitter body content and emphasizes structural features of heterogeneous rumor spreading social networks, so as to improve rumor detection effect. This paper combines one-hot encoding word embedding method and multi-head attention mechanism to extract primary semantic feature of source Twitter text content. Furthermore, the content-capsule module is constructed based on CapsNet to extract the deeper semantic features of text content, and the structure features of rumor propagation in social networks are extracted by combining with GCN-capsule module. In order to further enrich the input, two kinds of capsule vectors are fused with a dynamic routing mechanism. And then the classification results of source tweets are output,and source tweets rumors detection is finished. Experimental results show that the accuracy of the model proposed in this paper reaches 93.6%.
Aiming at taking the source Twitter texts as the research object, this paper deeply explores semantic information of Twitter body content and emphasizes structural features of heterogeneous rumor spreading social networks, so as to improve rumor detection effect. This paper combines one-hot encoding word embedding method and multi-head attention mechanism to extract primary semantic feature of source Twitter text content. Furthermore, the content-capsule module is constructed based on CapsNet to extract the deeper semantic features of text content, and the structure features of rumor propagation in social networks are extracted by combining with GCN-capsule module. In order to further enrich the input, two kinds of capsule vectors are fused with a dynamic routing mechanism. And then the classification results of source tweets are output,and source tweets rumors detection is finished. Experimental results show that the accuracy of the model proposed in this paper reaches 93.6%.
2022, 51(4): 615-622, 629.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021280
Abstract:
This paper presents a method of social robot recognition. This method extracts the characteristics of account sentiment diversity and uses the RoBERTa (robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach) model to classify the sentiment of blog posts. At the same time, the single-pass method is used to cluster blog posts and construct blog similarity graph. On this basis, attention-GCNII (A-GCNII) model, which adds Attention mechanism on the basis of graph convolutional network via initial residual and identity mapping (GCNII) model, is proposed to identify social robots by capturing user metadata features and user relationship structure features under the same topic in social networks. The results of comparative experiments on real Sina Weibo datasets show that our proposed method performs well in recognition accuracy and recognition effect.
This paper presents a method of social robot recognition. This method extracts the characteristics of account sentiment diversity and uses the RoBERTa (robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach) model to classify the sentiment of blog posts. At the same time, the single-pass method is used to cluster blog posts and construct blog similarity graph. On this basis, attention-GCNII (A-GCNII) model, which adds Attention mechanism on the basis of graph convolutional network via initial residual and identity mapping (GCNII) model, is proposed to identify social robots by capturing user metadata features and user relationship structure features under the same topic in social networks. The results of comparative experiments on real Sina Weibo datasets show that our proposed method performs well in recognition accuracy and recognition effect.
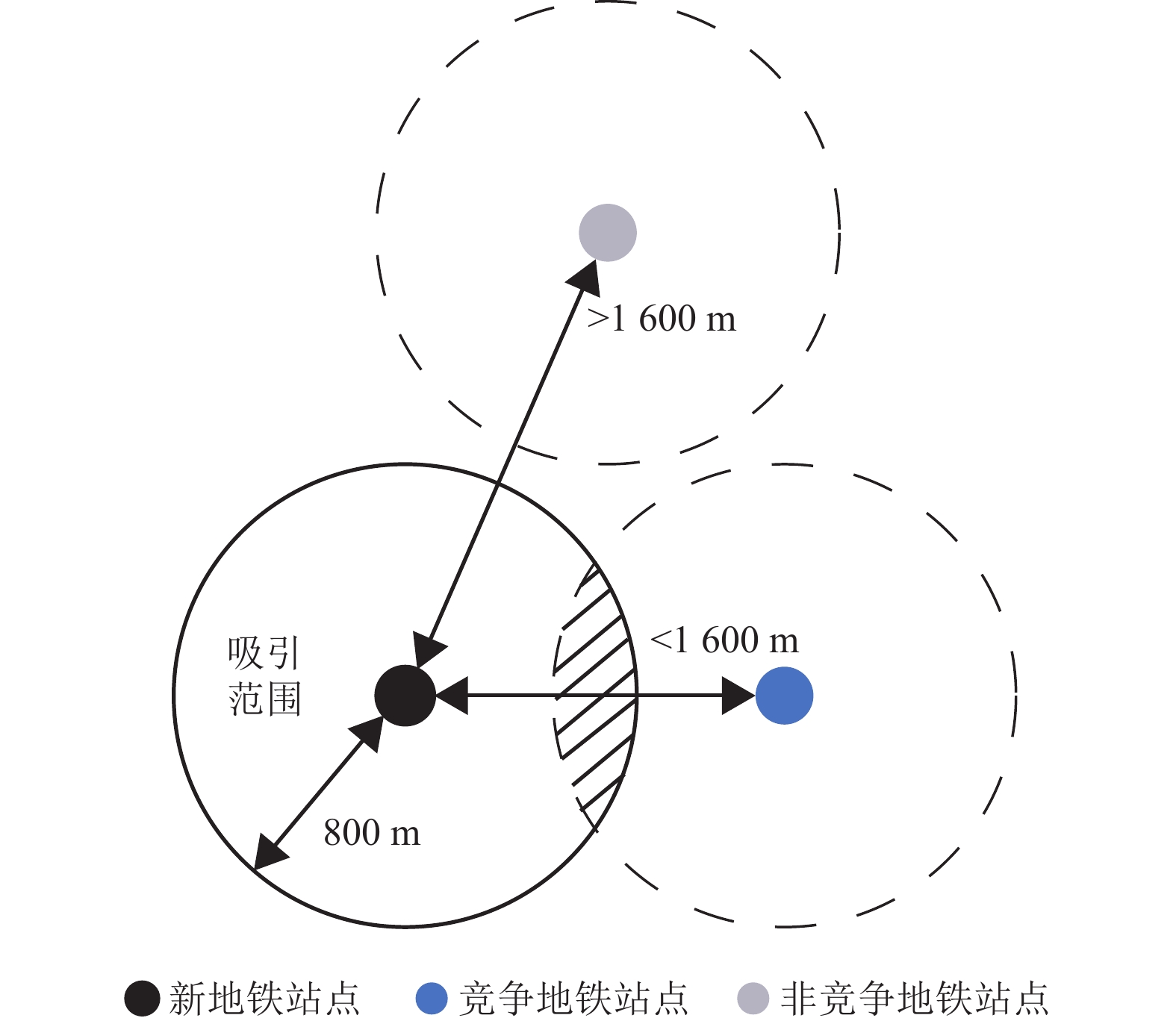
2022, 51(4): 623-629.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022031
Abstract:
Data fusion method is used to obtain the individual travel information of bus and subway passengers before and after the opening of the new subway line. The important human mobility index, center of mass, is used to locate the center of mass of passengers’ bus boarding locations, and the impact of the distance between a subway station and the center of mass on passengers’ choice of subway stations is analyzed. Results show that 86.15% of the passengers choose subway stations closer to their center of mass, and the distance is a key factor affecting passengers’ station choice behavior. Based on the findings above, we develop a Logit model to predict whether a passenger will choose to use the new subway station. The prediction accuracy, precision, recall and specificity are 83.87%, 84.23%, 83.66% and 84.09%, respectively, indicating that the model performs well. The results of this study can be used to evaluate the impact of planned new subway stations on the adjacent existing subway stations and contribute to the design of subway operation plan.
Data fusion method is used to obtain the individual travel information of bus and subway passengers before and after the opening of the new subway line. The important human mobility index, center of mass, is used to locate the center of mass of passengers’ bus boarding locations, and the impact of the distance between a subway station and the center of mass on passengers’ choice of subway stations is analyzed. Results show that 86.15% of the passengers choose subway stations closer to their center of mass, and the distance is a key factor affecting passengers’ station choice behavior. Based on the findings above, we develop a Logit model to predict whether a passenger will choose to use the new subway station. The prediction accuracy, precision, recall and specificity are 83.87%, 84.23%, 83.66% and 84.09%, respectively, indicating that the model performs well. The results of this study can be used to evaluate the impact of planned new subway stations on the adjacent existing subway stations and contribute to the design of subway operation plan.
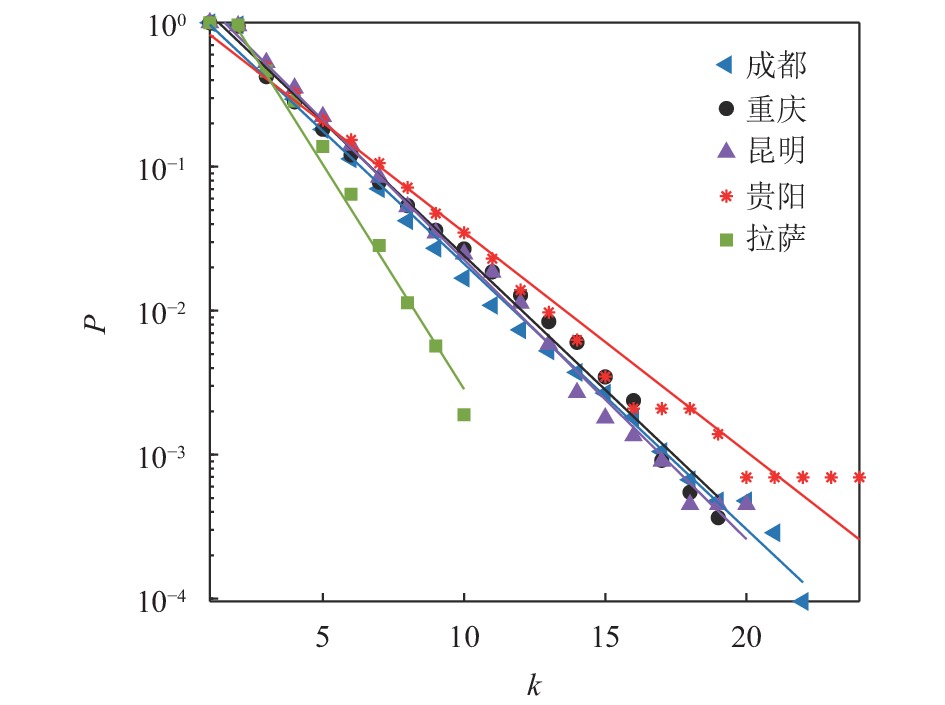
2022, 51(4): 630-640.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021336
Abstract:
Take Chongqing, Chengdu, Kunming, Guiyang and Lhasa for examples, bus stop network robustness is studied when the nodes fail based on the number of lines at a station. The results are compared with the widely studied random failure, degree-based attack and betweenness-based attack. It includes the following three aspects: network topological characteristics analysis, static robustness analysis under different nodes failure modes, and dynamic robustness analysis based on the load-capacity cascading failure model. The results show: 1) the cumulative degree distribution and the cumulative distribution of the number of lines at a station in each city approximately obey the exponential distribution; 2) the static robustness of the bus stop network is closely related to the network topological characteristics, the greater exponent of the cumulative degree distribution, the worse the robustness on the network under degree-based attack; 3) in contrary to results of static robustness, the destructive to the network in dynamic degree-based attack is less than that in static degree-based attack when cascading failure is considered.
Take Chongqing, Chengdu, Kunming, Guiyang and Lhasa for examples, bus stop network robustness is studied when the nodes fail based on the number of lines at a station. The results are compared with the widely studied random failure, degree-based attack and betweenness-based attack. It includes the following three aspects: network topological characteristics analysis, static robustness analysis under different nodes failure modes, and dynamic robustness analysis based on the load-capacity cascading failure model. The results show: 1) the cumulative degree distribution and the cumulative distribution of the number of lines at a station in each city approximately obey the exponential distribution; 2) the static robustness of the bus stop network is closely related to the network topological characteristics, the greater exponent of the cumulative degree distribution, the worse the robustness on the network under degree-based attack; 3) in contrary to results of static robustness, the destructive to the network in dynamic degree-based attack is less than that in static degree-based attack when cascading failure is considered.

 ISSN
ISSN