2023 Vol. 52, No. 3
2023, 52(3): 322-330.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023007
Abstract:
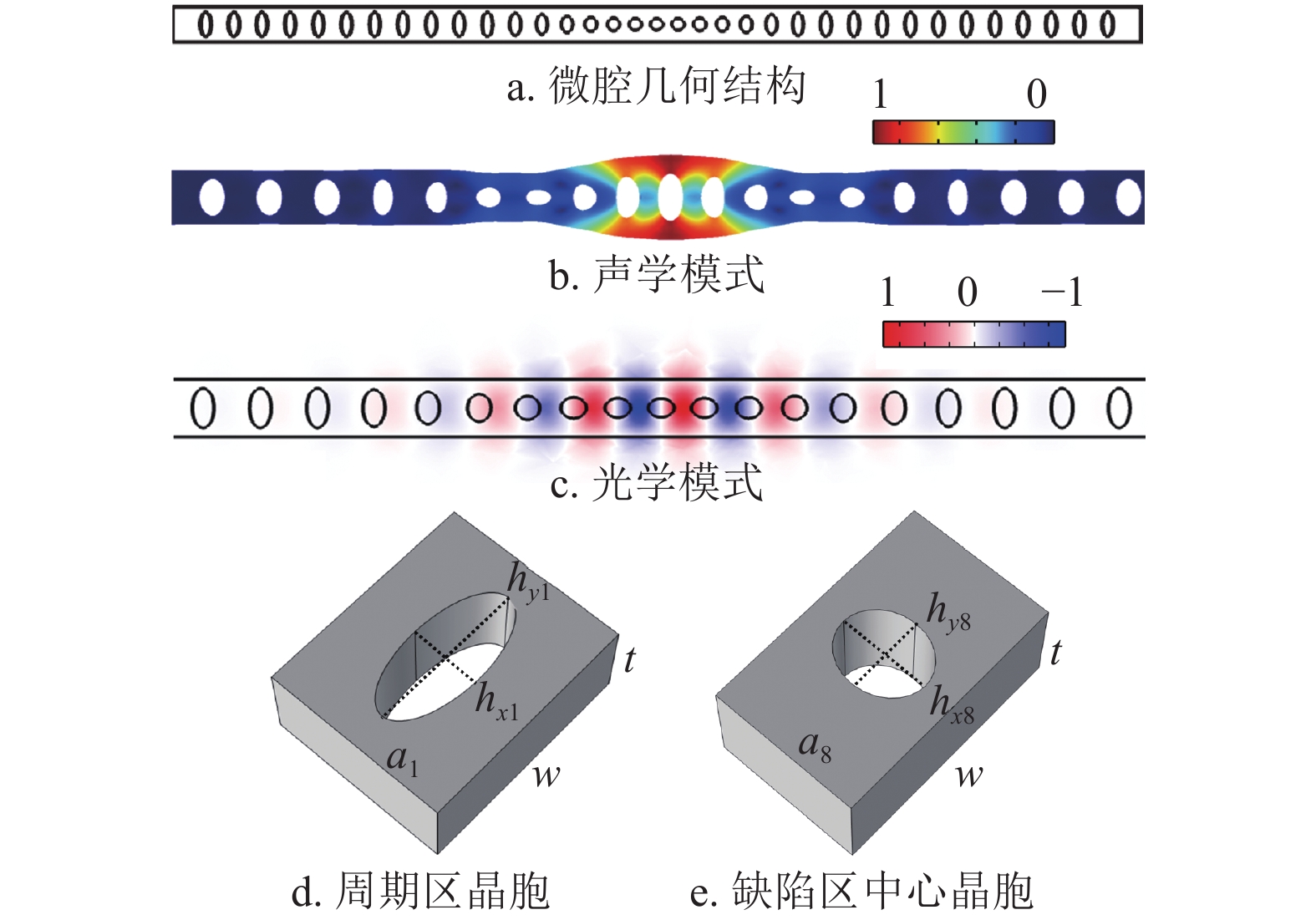
A one-dimensional optomechanical crystal nanobeam was designed and fabricated using typical CMOS process. The optical mode (in the fiber optic communication band) and the acoustic mode (~5.344 GHz) were characterized at very low temperatures (28 mK), and the phonon counting experiment was achieved using pulsed optical pumping and single photon detection methods. This kind of pulsed optical pumping can scatter photons at the cavity frequency and can generate (or reduce) acoustic phonon numbers. This pulsed light pumping method can also reduce the heating effect of light and maintain low phonon occupancy; then the pump photons are selectively filtered by cascading narrow-bandwidth fiber Fabry-Pérot filters, after which the scattered photons are measured to accurately calculate the average phonon occupancy of the mechanical mode. The experimentally obtained average phonon occupancy is\begin{document}$ 0.14 \pm 0.03 $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
A one-dimensional optomechanical crystal nanobeam was designed and fabricated using typical CMOS process. The optical mode (in the fiber optic communication band) and the acoustic mode (~5.344 GHz) were characterized at very low temperatures (28 mK), and the phonon counting experiment was achieved using pulsed optical pumping and single photon detection methods. This kind of pulsed optical pumping can scatter photons at the cavity frequency and can generate (or reduce) acoustic phonon numbers. This pulsed light pumping method can also reduce the heating effect of light and maintain low phonon occupancy; then the pump photons are selectively filtered by cascading narrow-bandwidth fiber Fabry-Pérot filters, after which the scattered photons are measured to accurately calculate the average phonon occupancy of the mechanical mode. The experimentally obtained average phonon occupancy is
2023, 52(3): 331-340.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022101
Abstract:
Pulse coupled neural networks have been proposed for a variety of applications in the field of image processing. Its improved version, the dual channel pulse coupled neural network, also has excellent performance in the field of image fusion. In order to combine the excellent parallel performance of quantum computing with dual channel pulse coupled neural networks and reduce their algorithmic complexity, the dual channel quantum pulse coupled neural network (DQPCNN) is proposed. In this model, quantum logic gates are used to construct quantum modules, such as quantum full adder, quantum multiplier, quantum comparator and a quantum image convolution module for DQPCNN. And these modules are employed to perform the required calculations for DQPCNN. The effectiveness of the DQPCNN is demonstrated by simulation experiments, and the complexity of the DQPCNN is lower than other models.
Pulse coupled neural networks have been proposed for a variety of applications in the field of image processing. Its improved version, the dual channel pulse coupled neural network, also has excellent performance in the field of image fusion. In order to combine the excellent parallel performance of quantum computing with dual channel pulse coupled neural networks and reduce their algorithmic complexity, the dual channel quantum pulse coupled neural network (DQPCNN) is proposed. In this model, quantum logic gates are used to construct quantum modules, such as quantum full adder, quantum multiplier, quantum comparator and a quantum image convolution module for DQPCNN. And these modules are employed to perform the required calculations for DQPCNN. The effectiveness of the DQPCNN is demonstrated by simulation experiments, and the complexity of the DQPCNN is lower than other models.
2023, 52(3): 341-347.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022270
Abstract:
How to subtly embed secret information in carriers (text, image, audio) has been a challenge for researchers. From the perspective of quantum information, a new idea of information hiding is proposed to construct quantum entangled states to realize the hiding and transmission of secret information without destroying the carrier data in this paper. In order to increase the transmission capacity of secret information, the quantum secret information compressed by Schur transform is encoded into the phase of the entangled state for transmission. During the bit transmission, the new protocol can securely and covertly send secret quantum bit information. The receiver can extract the secret information and obtain a lossless quantum image by using the quantum Fourier transform (QFT) and the measurement results of the received quantum state. In addition, a specific method is given to extract the secret quantum state information and then convert the quantum bits to classical bits, which can effectively increase the capacity of secret information transmission. This scheme ensures the security of the secret information transmission without sacrificing the carrier image quality.
How to subtly embed secret information in carriers (text, image, audio) has been a challenge for researchers. From the perspective of quantum information, a new idea of information hiding is proposed to construct quantum entangled states to realize the hiding and transmission of secret information without destroying the carrier data in this paper. In order to increase the transmission capacity of secret information, the quantum secret information compressed by Schur transform is encoded into the phase of the entangled state for transmission. During the bit transmission, the new protocol can securely and covertly send secret quantum bit information. The receiver can extract the secret information and obtain a lossless quantum image by using the quantum Fourier transform (QFT) and the measurement results of the received quantum state. In addition, a specific method is given to extract the secret quantum state information and then convert the quantum bits to classical bits, which can effectively increase the capacity of secret information transmission. This scheme ensures the security of the secret information transmission without sacrificing the carrier image quality.
2023, 52(3): 348-356.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022169
Abstract:
Bit depth enhancement has great application value, such as low-bit image acquisition, high-bit display, and image compression. However, existing bit depth enhancement algorithms either cannot effectively suppress false contours that appear in low-bit images or require high-performance graphical processing units and a vast number of training samples, making them lack practicality. To this end, we propose an adaptive false contour elimination filter-based bit depth enhancement algorithm, named FACE-BDE. FACE-BDE consists of three innovative modules: a false contour elimination filter design module, an adaptive filter size selection module, and a false contour region detection module. Experiments show that our algorithm can preserve real contours and details when eliminating false contours of different sizes, thus achieving 0.28 dB gain on the testsets, and the visibility of false contours is significantly unnoticeable than that of similar algorithms.
Bit depth enhancement has great application value, such as low-bit image acquisition, high-bit display, and image compression. However, existing bit depth enhancement algorithms either cannot effectively suppress false contours that appear in low-bit images or require high-performance graphical processing units and a vast number of training samples, making them lack practicality. To this end, we propose an adaptive false contour elimination filter-based bit depth enhancement algorithm, named FACE-BDE. FACE-BDE consists of three innovative modules: a false contour elimination filter design module, an adaptive filter size selection module, and a false contour region detection module. Experiments show that our algorithm can preserve real contours and details when eliminating false contours of different sizes, thus achieving 0.28 dB gain on the testsets, and the visibility of false contours is significantly unnoticeable than that of similar algorithms.
2023, 52(3): 357-365.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022415
Abstract:
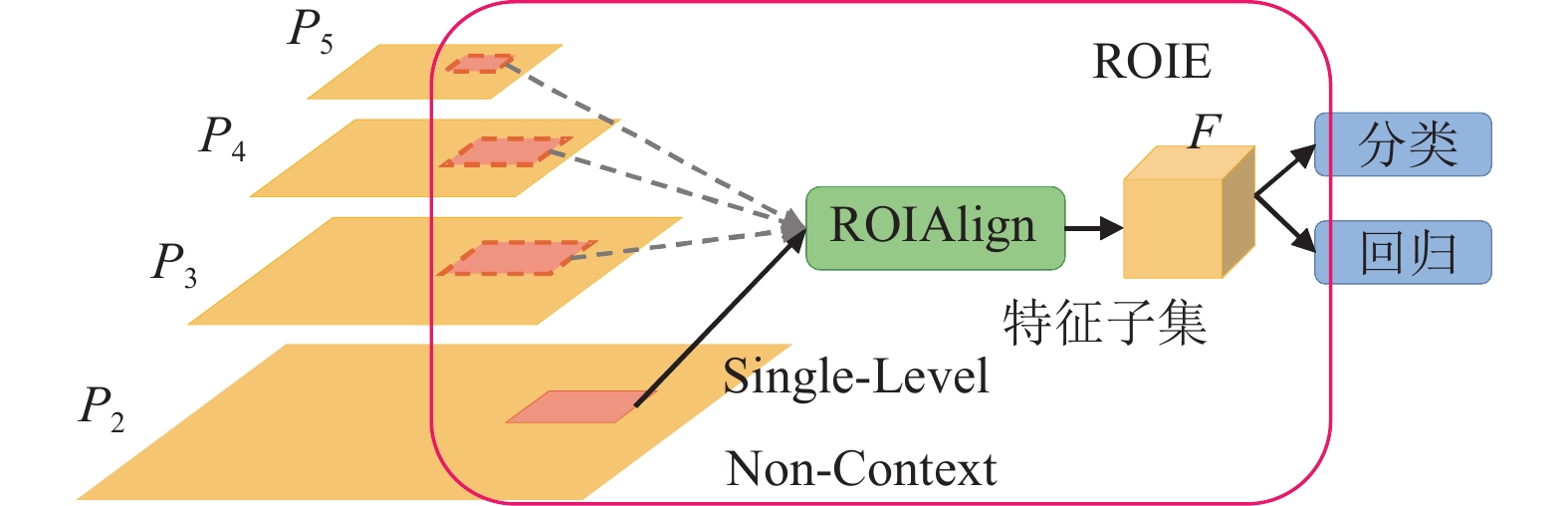
The current deep-learning based SAR ship instance segmentation models fail to consider the full level information of features and the context information of targets, which leads to low instance segmentation accuracy. In order to address this problem, a SAR ship instance segmentation method based on a full-level context information squeeze-and-excitation region of interest (ROI) extractor is proposed. This method proposes a novel ROI extractor(ROIE), called FL-CI-SE-ROIE. First of all, FL-CI-SE-ROIE can extract ROI at all levels, which can retain the full level features of the target, thus enhancing the multi-scale description capability of the network. Then, FL-CI-SE-ROIE expands the ROI context information, which can gain the context information of targets, thus enhancing the background identification capability. Finally, FL-CI-SE-ROIE introduces a squeeze and excitation(SE) module, which can balance ROI context information in different ranges, thus suppressing background interference, and further improving the accuracy of instance segmentation. The experimental results on the public polygon segmentation SAR ship detection dataset (PSeg-SSDD) show that the SAR ship instance segmentation accuracy of the proposed method is higher than that of the current 9 comparison models.
The current deep-learning based SAR ship instance segmentation models fail to consider the full level information of features and the context information of targets, which leads to low instance segmentation accuracy. In order to address this problem, a SAR ship instance segmentation method based on a full-level context information squeeze-and-excitation region of interest (ROI) extractor is proposed. This method proposes a novel ROI extractor(ROIE), called FL-CI-SE-ROIE. First of all, FL-CI-SE-ROIE can extract ROI at all levels, which can retain the full level features of the target, thus enhancing the multi-scale description capability of the network. Then, FL-CI-SE-ROIE expands the ROI context information, which can gain the context information of targets, thus enhancing the background identification capability. Finally, FL-CI-SE-ROIE introduces a squeeze and excitation(SE) module, which can balance ROI context information in different ranges, thus suppressing background interference, and further improving the accuracy of instance segmentation. The experimental results on the public polygon segmentation SAR ship detection dataset (PSeg-SSDD) show that the SAR ship instance segmentation accuracy of the proposed method is higher than that of the current 9 comparison models.
2023, 52(3): 366-371.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022158
Abstract:
With the rapid growth of data, the requirements of the reliability and effectiveness for distributed storage systems are increasing. Locally repairable codes (LRCs) have better locality, which can effectively realize the reliable and efficient storage of massive data in distributed storage system. It has become a research hotspot to construct locally repairable codes with (r, t) locality. Therefore, this paper proposes a construction method of optimal locally repairable codes based on resolvable balanced incomplete block design (RBIBD), which can construct binary optimal single parity LRCs with (r, t) locality of information symbols. The performance analyses show that, the constructed LRCs reach the minimum distance bound, and compared with the LRCs proposed by Xia et al., the LRCs proposed in this paper perform better in code rate. In particular, when the availability t=2, the LRCs is also the code with the optimal code rate.
With the rapid growth of data, the requirements of the reliability and effectiveness for distributed storage systems are increasing. Locally repairable codes (LRCs) have better locality, which can effectively realize the reliable and efficient storage of massive data in distributed storage system. It has become a research hotspot to construct locally repairable codes with (r, t) locality. Therefore, this paper proposes a construction method of optimal locally repairable codes based on resolvable balanced incomplete block design (RBIBD), which can construct binary optimal single parity LRCs with (r, t) locality of information symbols. The performance analyses show that, the constructed LRCs reach the minimum distance bound, and compared with the LRCs proposed by Xia et al., the LRCs proposed in this paper perform better in code rate. In particular, when the availability t=2, the LRCs is also the code with the optimal code rate.
2023, 52(3): 372-378.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022236
Abstract:
Recent years, microsystem has become one of the hot issues in electronic information field. This paper introduces a new three-dimensional integrated radio frequency (RF)-analog-digital microsystem. The architecture, process and verification of the microsystem are described in detail from the aspects of scheme and implementation. The traditional RF frontend is 250 mm × 120 mm size, while the microsystem is only 37 mm × 37 mm size, reducing its area by 95%. Based on the integrated ceramic three-dimensional package architecture, the microsystem integrates a variety of bare chips and passive devices to realize the electrical interconnection of internal signals. A new heat dissipation scheme is adopted to customize and develop a high thermal conductivity composite heat sink cover plate. The thermal conductivity is increased from 15 W/(m·K) to 150 W/(m·K) above. The thermal conductive silica gel is filled between the FC bare chip and the cover plate to form a new heat dissipation route and achieve efficient heat dissipation.
Recent years, microsystem has become one of the hot issues in electronic information field. This paper introduces a new three-dimensional integrated radio frequency (RF)-analog-digital microsystem. The architecture, process and verification of the microsystem are described in detail from the aspects of scheme and implementation. The traditional RF frontend is 250 mm × 120 mm size, while the microsystem is only 37 mm × 37 mm size, reducing its area by 95%. Based on the integrated ceramic three-dimensional package architecture, the microsystem integrates a variety of bare chips and passive devices to realize the electrical interconnection of internal signals. A new heat dissipation scheme is adopted to customize and develop a high thermal conductivity composite heat sink cover plate. The thermal conductivity is increased from 15 W/(m·K) to 150 W/(m·K) above. The thermal conductive silica gel is filled between the FC bare chip and the cover plate to form a new heat dissipation route and achieve efficient heat dissipation.
2023, 52(3): 379-389.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022127
Abstract:
To solve the problem that X-ray with single energy could not simultaneously expose each part of a complex workpiece, a multi-energy digital radiography (DR) fusion network based on detail enhancement, namely dual-encoder nest connection-based fusion network, is proposed. In this network, the inception module is used as the basic convolution layer and a trainable LOG (Laplacian of Gaussian) convolution module is designed in the auxiliary branch of the dual-encoder to extract multi-scale edge features and add them to the main branch to enhance the global features. In the training stage, a local energy consistency loss function based on image block is proposed to reduce the local errors of input and output. In the fusion process, channel and spatial attention mechanisms are used as the fusion strategy to fuse the multi-scale enhanced features extracted from dual-encoder, and the fused multi-scale features are input into the nest connected decoder for reconstruction. Experimental results show that the proposed fusion network has the effect of detail enhancement and can reproduce the internal structure and defects of complex workpiece completely and clearly.
To solve the problem that X-ray with single energy could not simultaneously expose each part of a complex workpiece, a multi-energy digital radiography (DR) fusion network based on detail enhancement, namely dual-encoder nest connection-based fusion network, is proposed. In this network, the inception module is used as the basic convolution layer and a trainable LOG (Laplacian of Gaussian) convolution module is designed in the auxiliary branch of the dual-encoder to extract multi-scale edge features and add them to the main branch to enhance the global features. In the training stage, a local energy consistency loss function based on image block is proposed to reduce the local errors of input and output. In the fusion process, channel and spatial attention mechanisms are used as the fusion strategy to fuse the multi-scale enhanced features extracted from dual-encoder, and the fused multi-scale features are input into the nest connected decoder for reconstruction. Experimental results show that the proposed fusion network has the effect of detail enhancement and can reproduce the internal structure and defects of complex workpiece completely and clearly.
2023, 52(3): 390-397.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021400
Abstract:
Aiming at the problems of low efficiency in the construction of knowledge graph in specific fields, insufficient utilization of existing knowledge graph in the field, and difficulty in extracting domain semantic professional entities from traditional models, a Chinese named entity recognition (NER) model based on Bert (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers) multi knowledge graph fusion and embedding (BERT-FKG) is proposed in this paper. It realizes the attribute sharing among entities through semantic fusion for multiple knowledge graphs and enriches the knowledge of sentence embedding. The proposed model shows better performance in Chinese NER tasks in open domain and medical field. The experimental results show that multiple domain knowledge graphs share the attributes of similar entities by calculating semantic similarity, which can make the model absorb more domain knowledge and improve the accuracy in NER tasks.
Aiming at the problems of low efficiency in the construction of knowledge graph in specific fields, insufficient utilization of existing knowledge graph in the field, and difficulty in extracting domain semantic professional entities from traditional models, a Chinese named entity recognition (NER) model based on Bert (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers) multi knowledge graph fusion and embedding (BERT-FKG) is proposed in this paper. It realizes the attribute sharing among entities through semantic fusion for multiple knowledge graphs and enriches the knowledge of sentence embedding. The proposed model shows better performance in Chinese NER tasks in open domain and medical field. The experimental results show that multiple domain knowledge graphs share the attributes of similar entities by calculating semantic similarity, which can make the model absorb more domain knowledge and improve the accuracy in NER tasks.
2023, 52(3): 398-412.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022106
Abstract:
Network user identity identification (UII) is significant to maintain network security and promotes the construction of network identity management system. UII is not only the fundamental for user network portrait, action prediction, and accurate delivery service, but also the technical pillar for social bot detection, network social governance, and crack down cybercrime. The progress of UII technology and its applications in bot detection, community detection, and user identity linkage across social networks are analyzed. At first, from the definition and development history of UII, the classification of UII methods is introduced. Second, a brief overview of bot detection methods with different characteristics is performed, and their main applicable scenarios are pointed out. Then, social bots related community detection techniques are analyzed. Furthermore, the existing methods for user identity linkage across social network platforms are surveyed and categorized. Finally, we discusses the current challenges of user identity research and its future prospects.
Network user identity identification (UII) is significant to maintain network security and promotes the construction of network identity management system. UII is not only the fundamental for user network portrait, action prediction, and accurate delivery service, but also the technical pillar for social bot detection, network social governance, and crack down cybercrime. The progress of UII technology and its applications in bot detection, community detection, and user identity linkage across social networks are analyzed. At first, from the definition and development history of UII, the classification of UII methods is introduced. Second, a brief overview of bot detection methods with different characteristics is performed, and their main applicable scenarios are pointed out. Then, social bots related community detection techniques are analyzed. Furthermore, the existing methods for user identity linkage across social network platforms are surveyed and categorized. Finally, we discusses the current challenges of user identity research and its future prospects.
2023, 52(3): 413-422.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022082
Abstract:
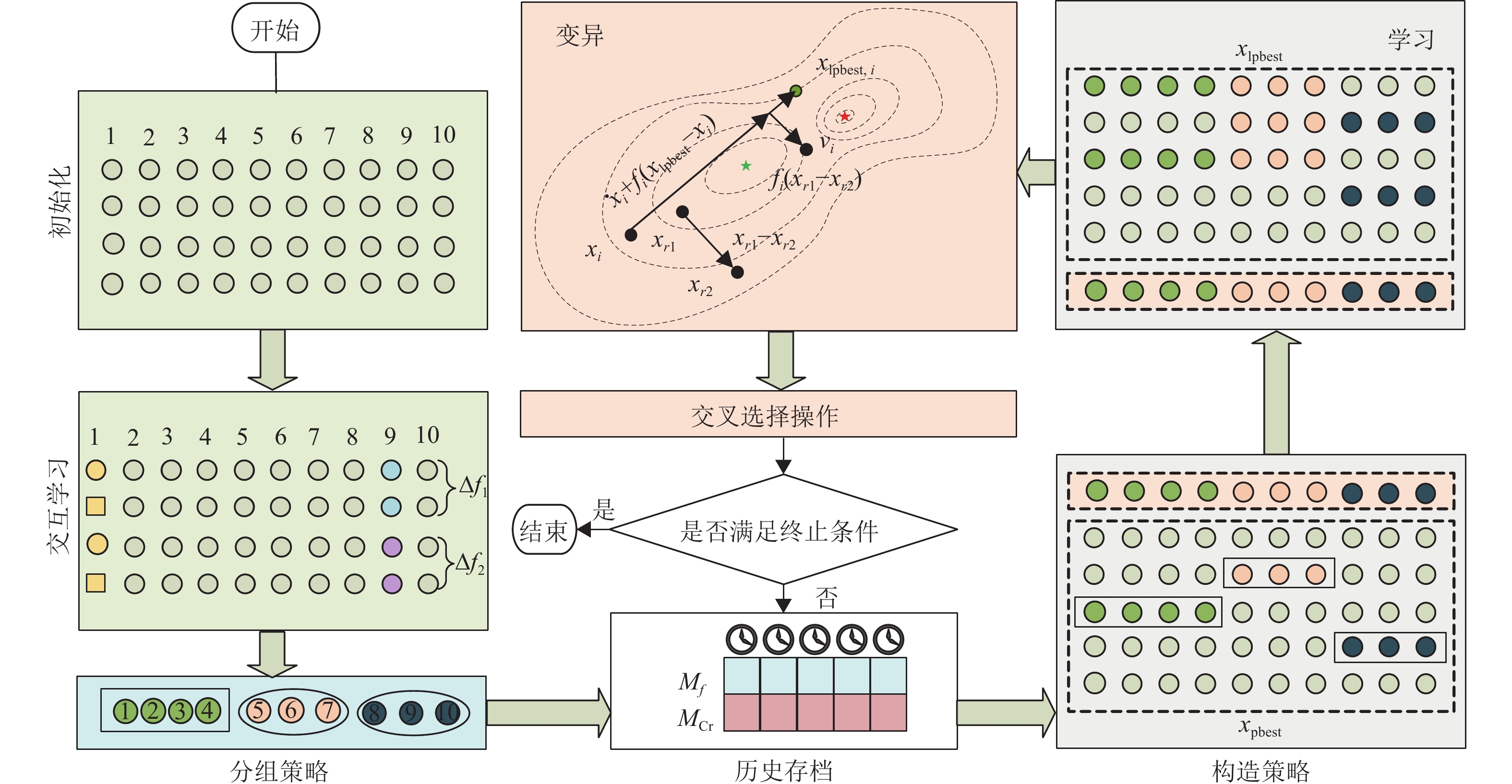
The dependence among decision variables in complex optimization problems leads to the appearance of a large number of local optimal solutions in the fitness landscape of functions, which are difficult to be solved by classical evolutionary algorithms. In this paper, a constructive learning success-history based adaptive differential evolution (CLSHADE) algorithm is proposed to solve partially separable function optimization problems. Firstly, CLSHADE uses the differential grouping technology (DG) to reduce the complexity of a complex problem by dividing it into multiple sub-problems. Then, a constructive learning strategy, based on the grouping structure, is designed. It learns from the constructed optimal solution in a certain probability to guide the search direction and improve the search performance of the CLSHADE. The experimental results on the partially separable function of CEC 2017 demonstrate the effectiveness of the CLSHADE.
The dependence among decision variables in complex optimization problems leads to the appearance of a large number of local optimal solutions in the fitness landscape of functions, which are difficult to be solved by classical evolutionary algorithms. In this paper, a constructive learning success-history based adaptive differential evolution (CLSHADE) algorithm is proposed to solve partially separable function optimization problems. Firstly, CLSHADE uses the differential grouping technology (DG) to reduce the complexity of a complex problem by dividing it into multiple sub-problems. Then, a constructive learning strategy, based on the grouping structure, is designed. It learns from the constructed optimal solution in a certain probability to guide the search direction and improve the search performance of the CLSHADE. The experimental results on the partially separable function of CEC 2017 demonstrate the effectiveness of the CLSHADE.
2023, 52(3): 423-429.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022086
Abstract:
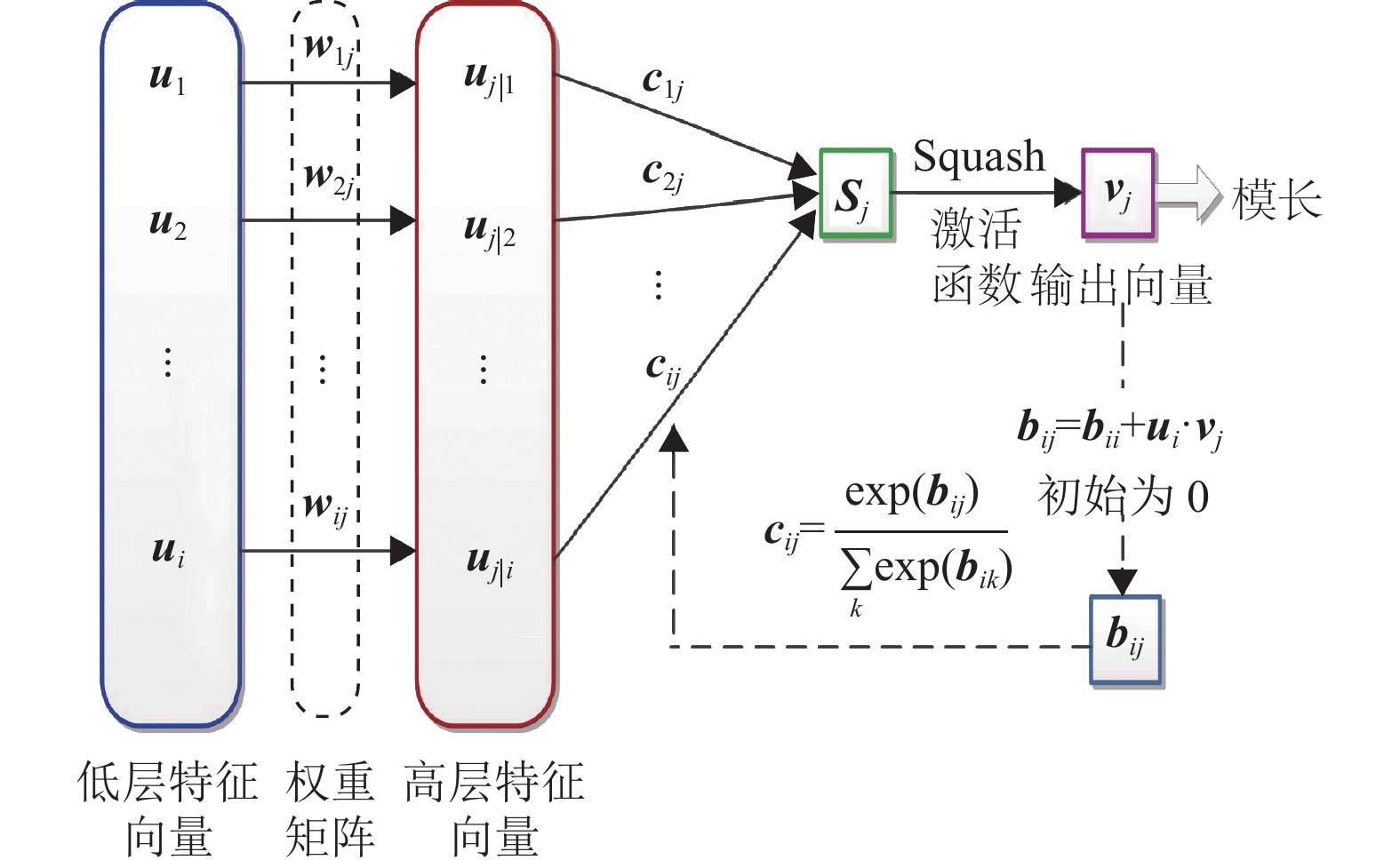
Aiming at the problems of many parameters, large amount of computation and slow training speed of the current speech emotion recognition model, this paper proposes a lightweight network model suitable for small data sets. The model is based on the capsule network, and the deep separable convolution module is introduced to replace the original convolution layer in the capsule network to reduce the amount of calculation. Transfer learning is used to extract the universal underlying image features, and then spectrogram is used to finely tune the over fitting phenomenon of the whole network weakening model on small data sets. The angle cosine is used to calculate the vector similarity in the dynamic routing structure so as to improve the performance of the dynamic routing algorithm. The experimental results show that the recognition rate and operation speed of the lightweight capsule network are better than the seven deep learning network models.
Aiming at the problems of many parameters, large amount of computation and slow training speed of the current speech emotion recognition model, this paper proposes a lightweight network model suitable for small data sets. The model is based on the capsule network, and the deep separable convolution module is introduced to replace the original convolution layer in the capsule network to reduce the amount of calculation. Transfer learning is used to extract the universal underlying image features, and then spectrogram is used to finely tune the over fitting phenomenon of the whole network weakening model on small data sets. The angle cosine is used to calculate the vector similarity in the dynamic routing structure so as to improve the performance of the dynamic routing algorithm. The experimental results show that the recognition rate and operation speed of the lightweight capsule network are better than the seven deep learning network models.
2023, 52(3): 430-437.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022172
Abstract:
By crawling weather data and combining with user load data in Jinhua City, a deep random forest algorithm is introduced to implement short-term user load forecasting. With four evaluation indicators, by comparing the support vector regression algorithm, the K-nearest neighbor algorithm, the Bayesian ridge regression algorithm, the random forest algorithm, and several neural network algorithms, it is found that the deep random forest algorithm has the best performance, and followed by the support vector regression. However, the neural network algorithm performed mediocre on this dataset.
By crawling weather data and combining with user load data in Jinhua City, a deep random forest algorithm is introduced to implement short-term user load forecasting. With four evaluation indicators, by comparing the support vector regression algorithm, the K-nearest neighbor algorithm, the Bayesian ridge regression algorithm, the random forest algorithm, and several neural network algorithms, it is found that the deep random forest algorithm has the best performance, and followed by the support vector regression. However, the neural network algorithm performed mediocre on this dataset.
2023, 52(3): 438-443.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022147
Abstract:
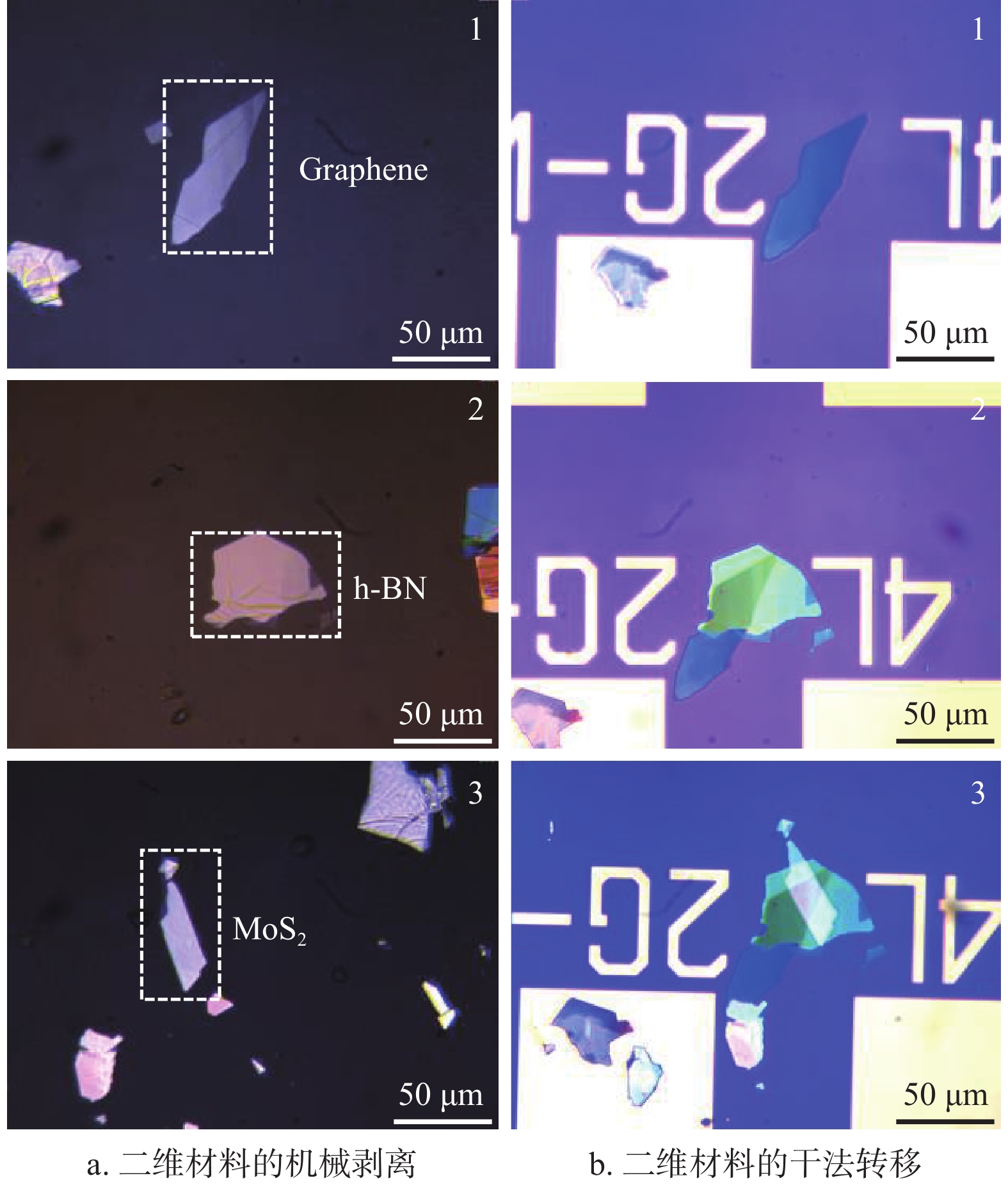
In this work, we report the fabrication and characterization of an MoS2 inverter by a dry transfer method, where the inverter consists of an MoS2 transistor and an MoS2 resistor connected in series with graphene flakes serving as electrodes. To improve the electrical performance of the MoS2 transistor and invertor, we utilize thermal evaporation (Au) through a stencil mask to improve the contact quality between the graphene electrodes and metal electrodes on the substrate. Upon such enhancement, we find that the MoS2 transistor exhibits an ION/IOFF > 105; the MoS2 inverter shows a typical logic-conversion feature with voltage gain > 6. Our work demonstratesthat the dry transfer technique has great potential in the preparation and application of two-dimensional transistors, inverters and logic circuits.
In this work, we report the fabrication and characterization of an MoS2 inverter by a dry transfer method, where the inverter consists of an MoS2 transistor and an MoS2 resistor connected in series with graphene flakes serving as electrodes. To improve the electrical performance of the MoS2 transistor and invertor, we utilize thermal evaporation (Au) through a stencil mask to improve the contact quality between the graphene electrodes and metal electrodes on the substrate. Upon such enhancement, we find that the MoS2 transistor exhibits an ION/IOFF > 105; the MoS2 inverter shows a typical logic-conversion feature with voltage gain > 6. Our work demonstratesthat the dry transfer technique has great potential in the preparation and application of two-dimensional transistors, inverters and logic circuits.
2023, 52(3): 444-450.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022240
Abstract:
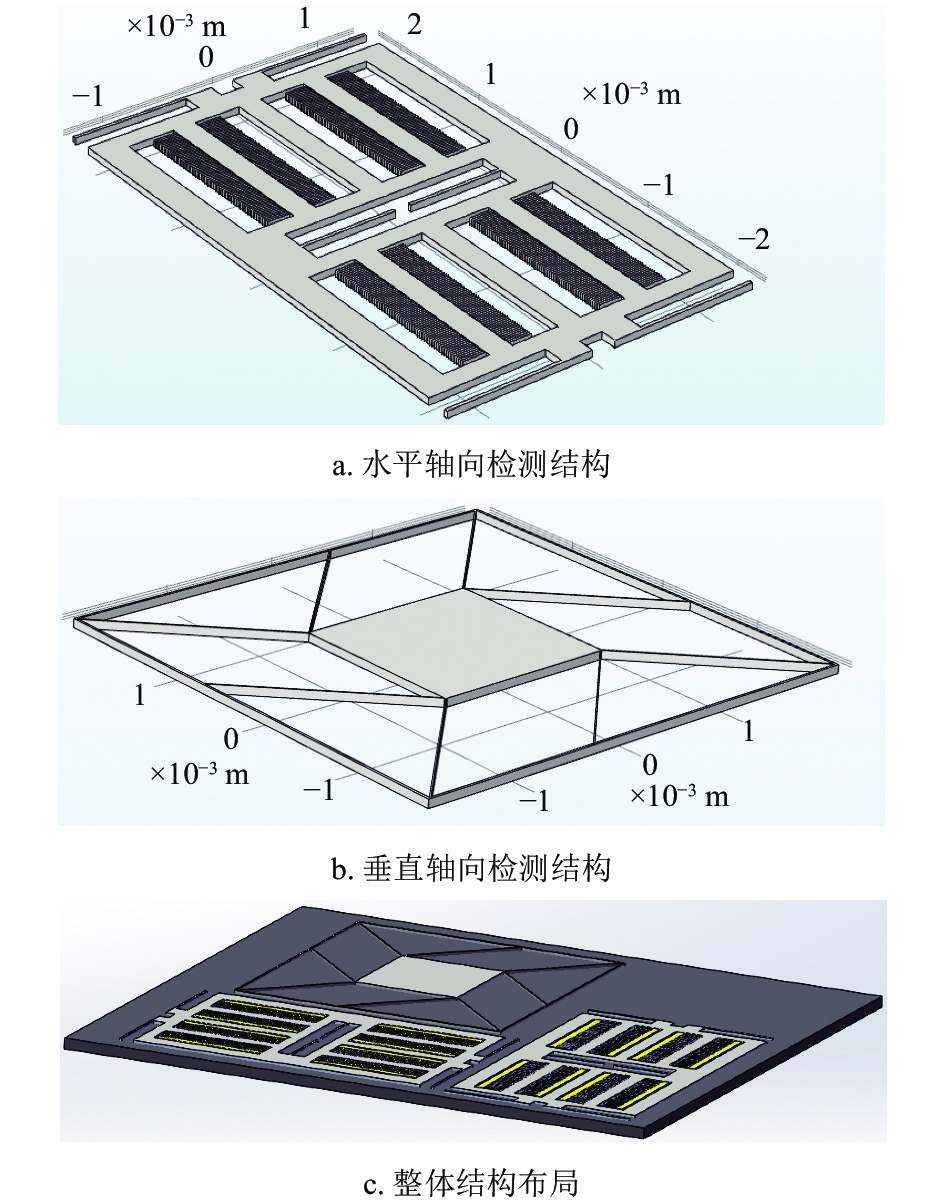
Micro-Electro-Mechanical system (MEMS) inertial sensors (such as accelerometers, gyroscopes) have the characteristics of high performance, low power consumption, low cost, high integration, high reliability, and small size. Cross-talk is a major issue in designing MEMS accelerator, which greatly affects the measurement of acceleration in the sensitive direction. In this paper, we propose a three-mass three-axis MEMS capacitive accelerometer structure with a range of ±16 g for reducing the problem. The static and modal analysis of the structure is made to ensure good anti-overload capability of the accelerometer. The simulation results show that the structure achieves modal separation and avoids modal interference, and the cross-sensitivity is less than 0.3%, which effectively reduces the cross-talk.
Micro-Electro-Mechanical system (MEMS) inertial sensors (such as accelerometers, gyroscopes) have the characteristics of high performance, low power consumption, low cost, high integration, high reliability, and small size. Cross-talk is a major issue in designing MEMS accelerator, which greatly affects the measurement of acceleration in the sensitive direction. In this paper, we propose a three-mass three-axis MEMS capacitive accelerometer structure with a range of ±16 g for reducing the problem. The static and modal analysis of the structure is made to ensure good anti-overload capability of the accelerometer. The simulation results show that the structure achieves modal separation and avoids modal interference, and the cross-sensitivity is less than 0.3%, which effectively reduces the cross-talk.
2023, 52(3): 451-457.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022078
Abstract:
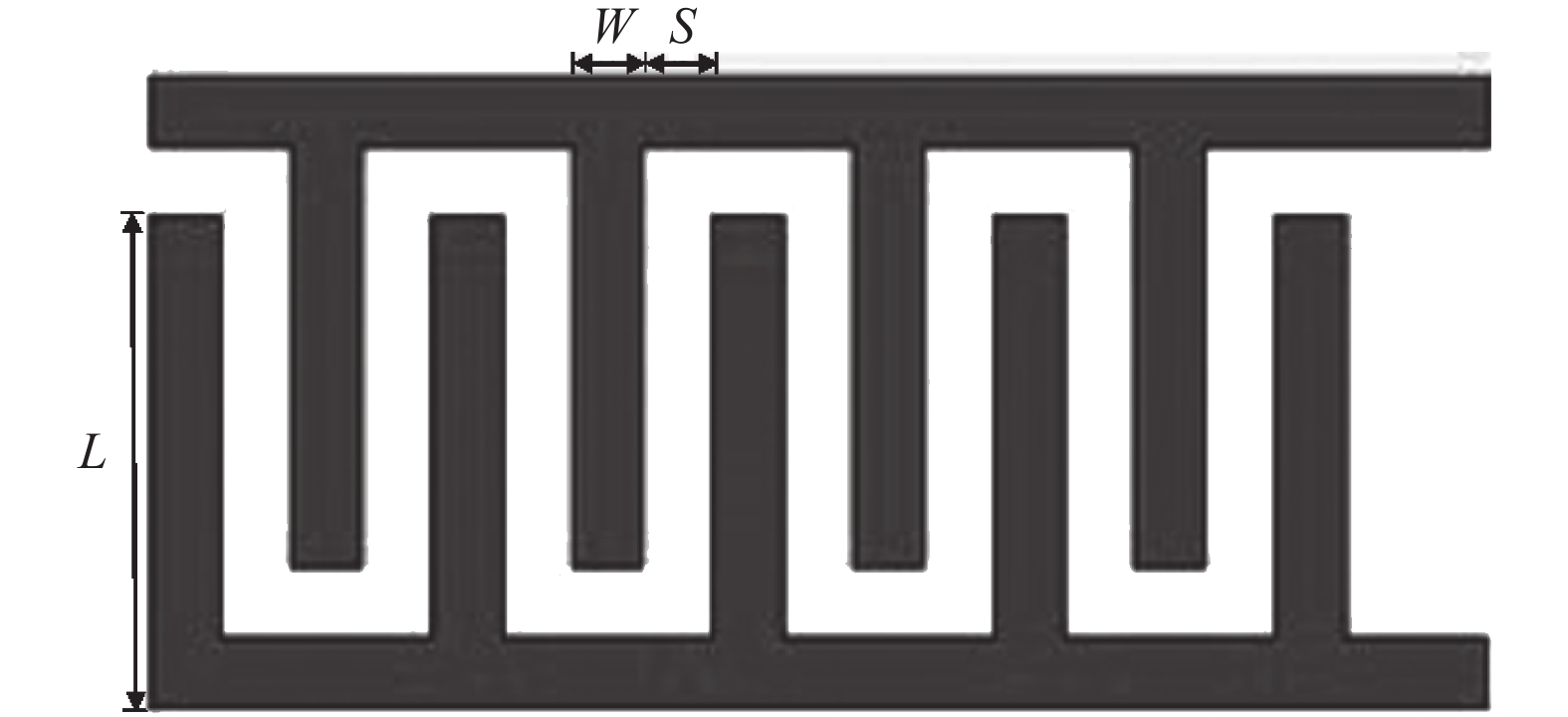
In this paper, the COMSOL Multiphysics simulation software is used to establish a three-dimensional model of a UV sensor patch with an interdigital electrode structure, and its electrical characteristics are studied. In order to reduce the initial resistance of the sensor and facilitate the measurement of the back-end circuit, a number of different simulation models are set up based on the structural parameters such as the width, spacing, and thickness of the interdigitated fingers by using the control variable method. Under the current physics interface in the AC/DC module, a steady state study is selected, and the results show that different structural parameters will have an impact on the electric field distribution and initial resistance of the electrodes and sensors. Through observation and analysis, it is found that the finger width of the interdigital electrode is 0.6 mm, the spacing is 0.4 mm, and the initial resistance is the smallest when the thickness is 5 μm. In addition, a new annular interdigitated electrode structure was designed, and its related electrical properties were initially explored. It is found that its initial resistance value is in the same order of magnitude as the optimized rectangular interdigital electrode, which has a good guiding significance for relevant practical experiments.
In this paper, the COMSOL Multiphysics simulation software is used to establish a three-dimensional model of a UV sensor patch with an interdigital electrode structure, and its electrical characteristics are studied. In order to reduce the initial resistance of the sensor and facilitate the measurement of the back-end circuit, a number of different simulation models are set up based on the structural parameters such as the width, spacing, and thickness of the interdigitated fingers by using the control variable method. Under the current physics interface in the AC/DC module, a steady state study is selected, and the results show that different structural parameters will have an impact on the electric field distribution and initial resistance of the electrodes and sensors. Through observation and analysis, it is found that the finger width of the interdigital electrode is 0.6 mm, the spacing is 0.4 mm, and the initial resistance is the smallest when the thickness is 5 μm. In addition, a new annular interdigitated electrode structure was designed, and its related electrical properties were initially explored. It is found that its initial resistance value is in the same order of magnitude as the optimized rectangular interdigital electrode, which has a good guiding significance for relevant practical experiments.
2023, 52(3): 458-474.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022216
Abstract:
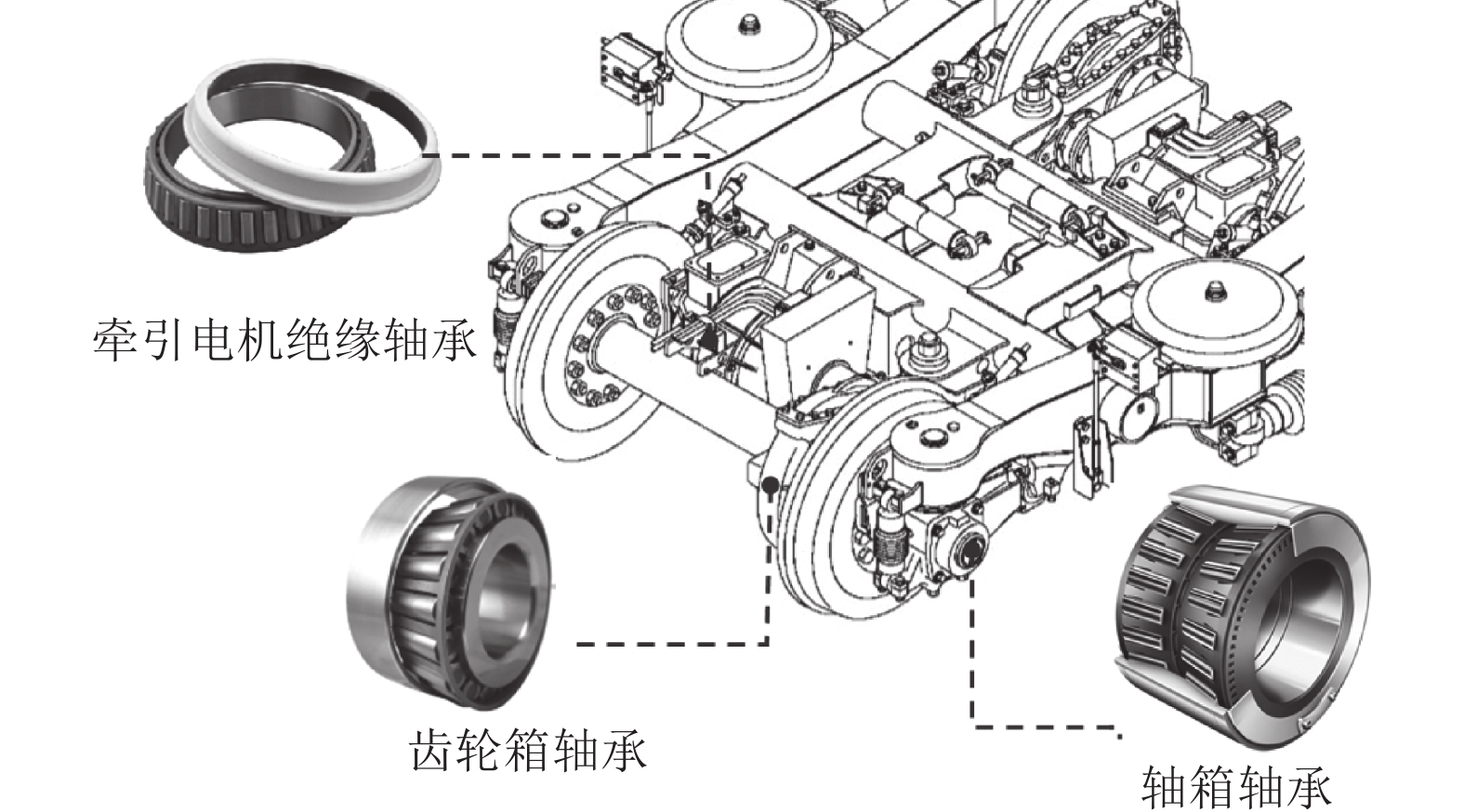
Rolling bearing is regarded as the key component of high-speed trains. The characteristics of high-speed, long-term and continuous operation of China’s Electric Multiple Units (EMUs), as well as the variable operating environment, make the working environment and internal stress state of EMUs’ bearing more complex than those of general bearing, which puts forward higher requirements for the design, manufacture and reliability of bearing. To realize the localization of China's high-speed railway core technology, a number of researches were carried out on the EMUs’ bearing in recent years. This paper firstly introduces the design and manufacturing technology of the EMUs’ bearing, and discusses the typical in-service failure modes of the EMUs’ bearing, as well as the failure mechanisms and effects. Consequently, the fault diagnosis methods of the EMUs’ bearing are classified and summarized, and the reliability modeling and life evaluation methods of the EMUs’ bearing are reviewed. Finally, the reliability test of the EMUs’ bearing is briefly described. This paper summarizes the research of bearing and its reliability for EMU trains, which can provide a reference for the design and manufacturing technology of the bearing of China’s high-speed EMUs.
Rolling bearing is regarded as the key component of high-speed trains. The characteristics of high-speed, long-term and continuous operation of China’s Electric Multiple Units (EMUs), as well as the variable operating environment, make the working environment and internal stress state of EMUs’ bearing more complex than those of general bearing, which puts forward higher requirements for the design, manufacture and reliability of bearing. To realize the localization of China's high-speed railway core technology, a number of researches were carried out on the EMUs’ bearing in recent years. This paper firstly introduces the design and manufacturing technology of the EMUs’ bearing, and discusses the typical in-service failure modes of the EMUs’ bearing, as well as the failure mechanisms and effects. Consequently, the fault diagnosis methods of the EMUs’ bearing are classified and summarized, and the reliability modeling and life evaluation methods of the EMUs’ bearing are reviewed. Finally, the reliability test of the EMUs’ bearing is briefly described. This paper summarizes the research of bearing and its reliability for EMU trains, which can provide a reference for the design and manufacturing technology of the bearing of China’s high-speed EMUs.
2023, 52(3): 475-480.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022371
Abstract:
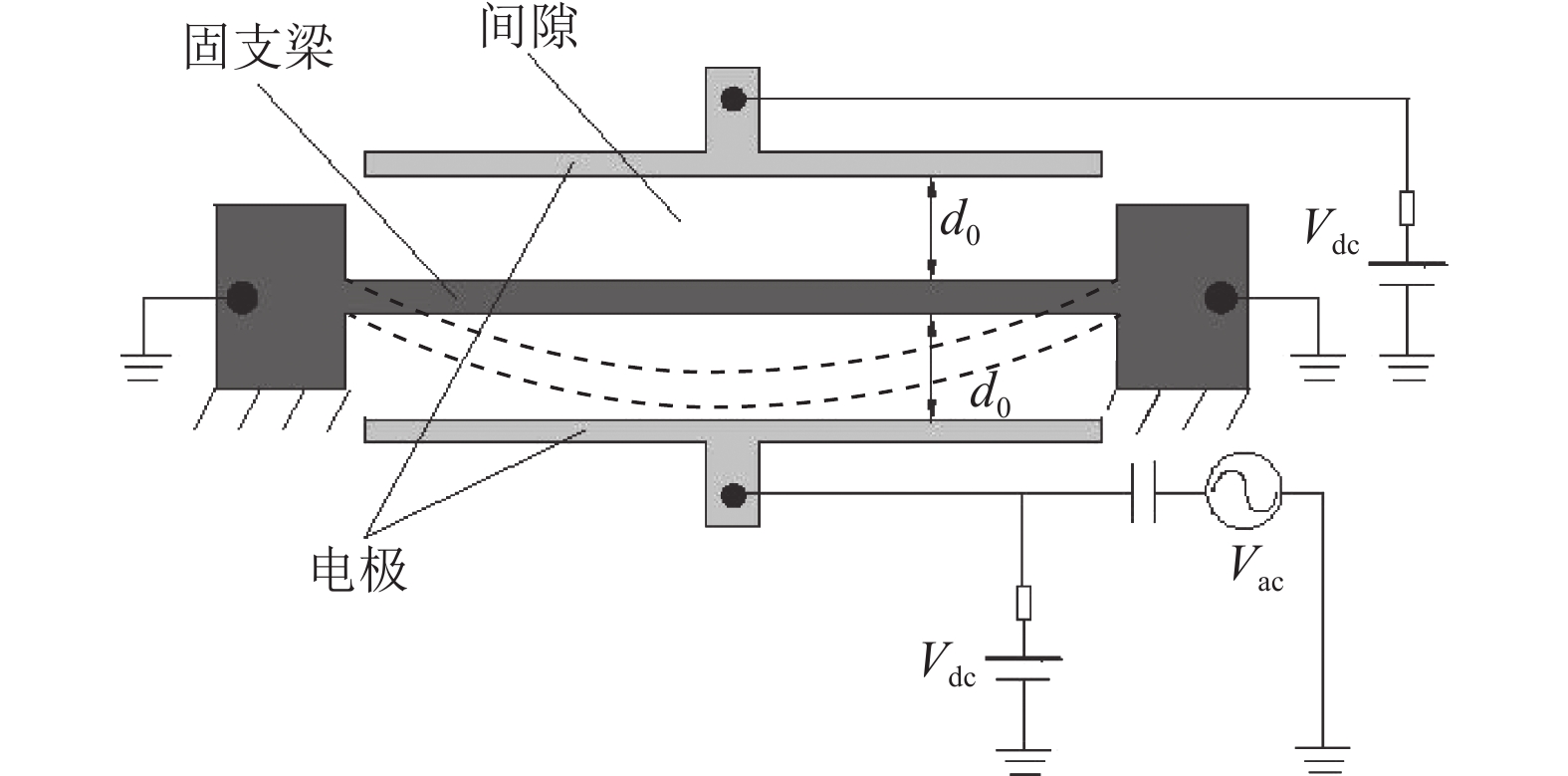
Non-linear factors such as periodic oscillation, bifurcation and chaos under the high-energy output of micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) silicon resonators will limit the accuracy of oscillation frequency control. This paper proposes an output feedback synchronous control method for clamped-clamped beam micro-electro-mechanical silicon resonators and improves its oscillation frequency control performance through oscillator synchronization. First, the system structure and nonlinear characteristics of the MEM silicon resonator with clamped-clamped beam MEM silicon resonators are analyzed and a dynamic model that fully considers the nonlinear characteristics of the system is established. On this basis, an output feedback synchronization controller based on synchronization error is designed, it can realize the synchronous control of multi-MEM silicon resonators and make the corresponding synchronous error asymptotically converge to zero. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is proved by simulation experiments.
Non-linear factors such as periodic oscillation, bifurcation and chaos under the high-energy output of micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) silicon resonators will limit the accuracy of oscillation frequency control. This paper proposes an output feedback synchronous control method for clamped-clamped beam micro-electro-mechanical silicon resonators and improves its oscillation frequency control performance through oscillator synchronization. First, the system structure and nonlinear characteristics of the MEM silicon resonator with clamped-clamped beam MEM silicon resonators are analyzed and a dynamic model that fully considers the nonlinear characteristics of the system is established. On this basis, an output feedback synchronization controller based on synchronization error is designed, it can realize the synchronous control of multi-MEM silicon resonators and make the corresponding synchronous error asymptotically converge to zero. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is proved by simulation experiments.

 ISSN
ISSN