2023 Vol. 52, No. 5
2023, 52(5): 642-648.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022019
Abstract:
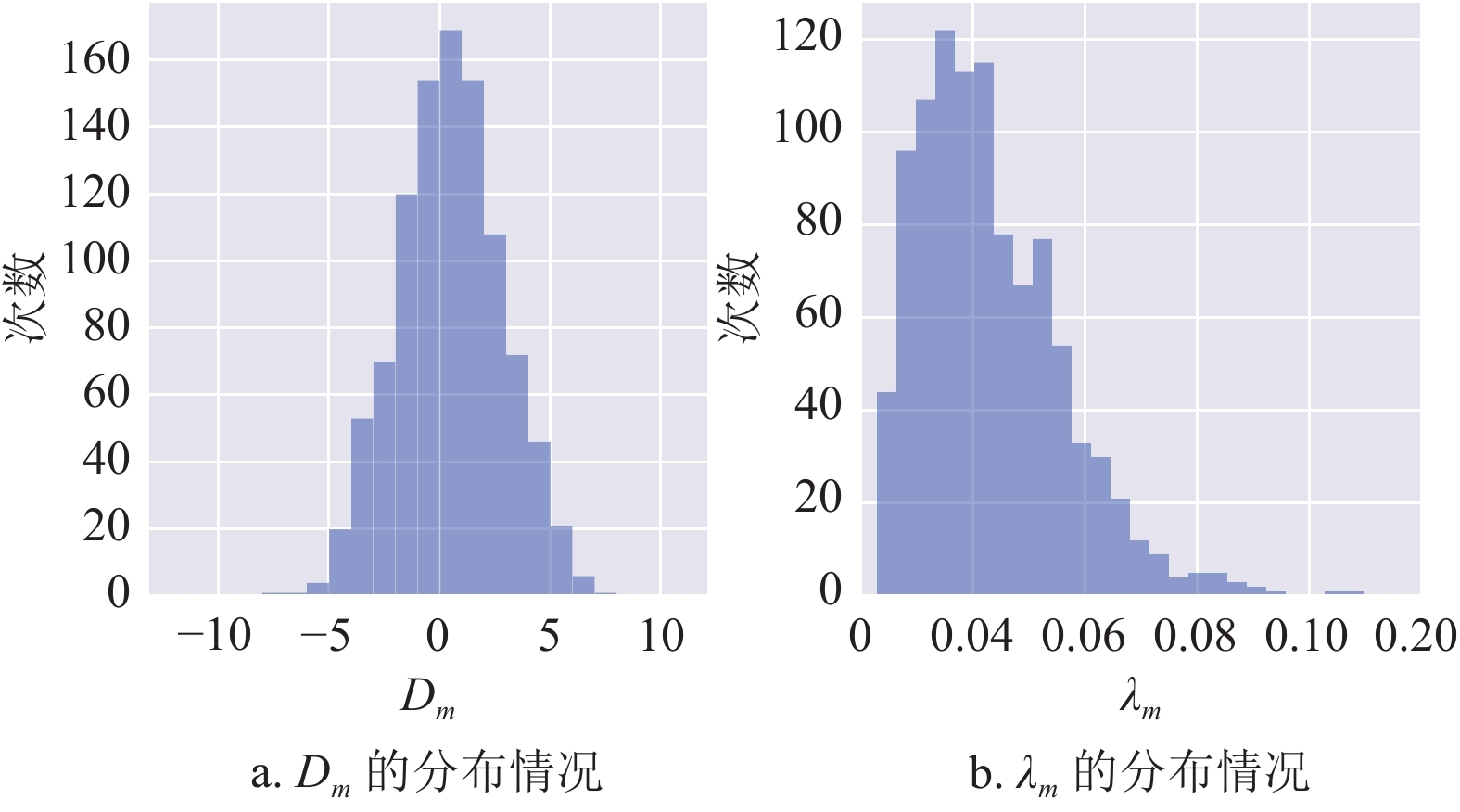
In this paper, we discuss the application of Quantum Approximation Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) in portfolio optimization problems, which, under discrete constraints, is proved to be NP-hard. We introduce the fundamental framework of QAOA and the corresponding modeling of portfolio optimization problems. We illustrate several variants of QAOA applicable to portfolio optimization problems. Next, we examine their performances and the performance of the classical method with numerical simulation and hypothesis testing. The average approximation ratio of each quantum algorithm is at least 7% higher than that of the classical algorithm.
In this paper, we discuss the application of Quantum Approximation Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) in portfolio optimization problems, which, under discrete constraints, is proved to be NP-hard. We introduce the fundamental framework of QAOA and the corresponding modeling of portfolio optimization problems. We illustrate several variants of QAOA applicable to portfolio optimization problems. Next, we examine their performances and the performance of the classical method with numerical simulation and hypothesis testing. The average approximation ratio of each quantum algorithm is at least 7% higher than that of the classical algorithm.
2023, 52(5): 649-658.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022076
Abstract:
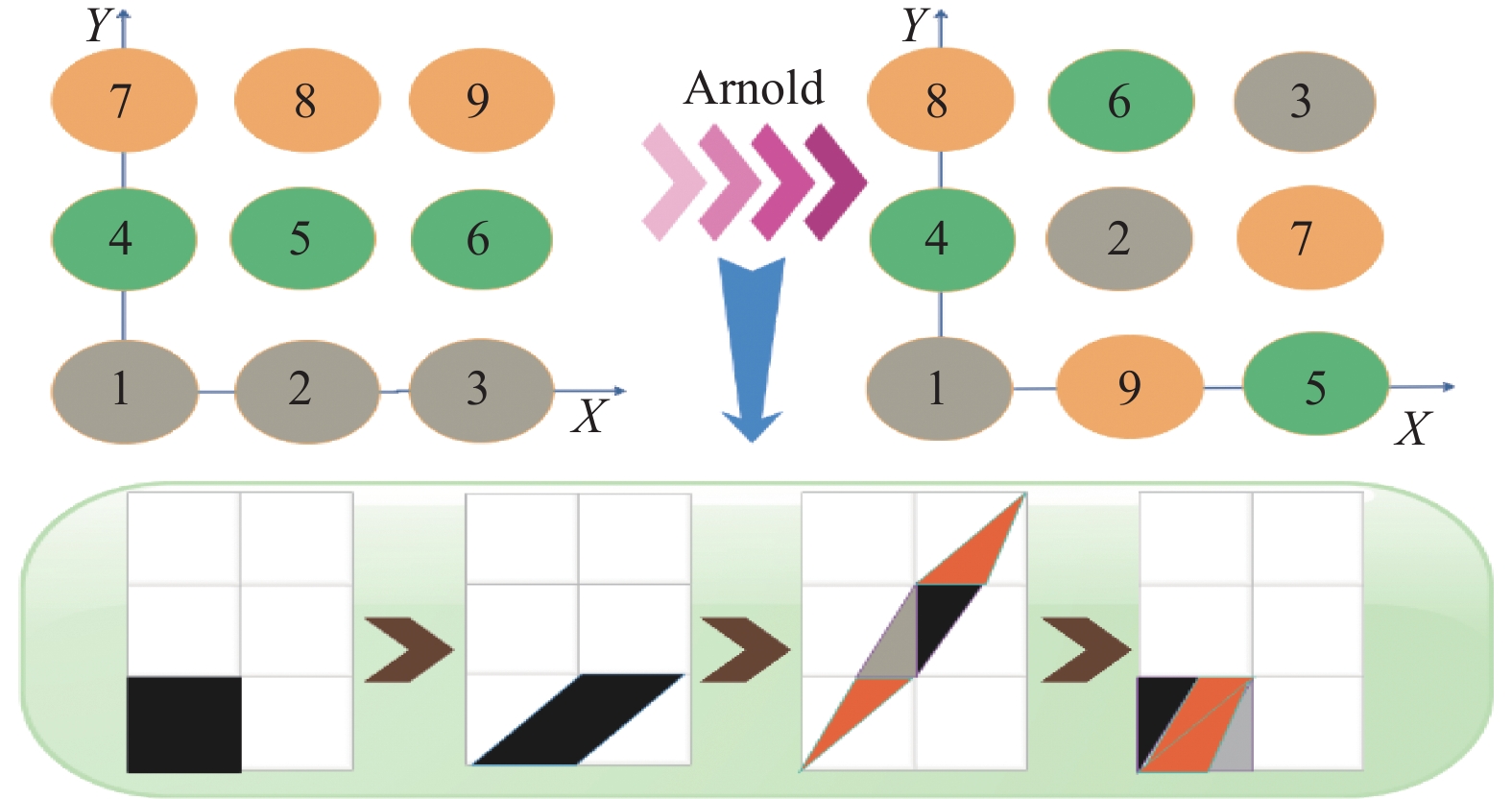
Aiming at the problem that digital images are vulnerable to attacks during network transmission and cause information leakage. This paper introduces quantum walk and Latin square matrix on the basis of Arnold scrambling, and designs a new type of color image encryption scheme. In the new scheme, the three channels of the color image are separated at first and the Arnold transform is used to scramble the pixel points of the image. Then quantum walk and Latin square matrix are used to process the pixel values of the scrambled image, the modulus diffusion algorithm is used on the processed image to further change the pixel value of the image. Finally, the color encrypted image is obtained by merging the three-channels encrypted images. Quantum walk, as an excellent random sequence generation tool, provides random sequences for algorithms. We conducted experimental simulations on the encryption algorithm, and analyzed the experimental results in the histogram, correlation, information entropy, noise attack, cropping attack and other aspects. The results show that the histogram of the encrypted image is distributed evenly, the correlation between pixels is close to 0, and the information entropy is 7.9993, close to 8, indicating that the algorithm has a relatively good ability to resist statistical analysis. After decrypting the encrypted image after noise attack and cropping attack, the original image information can still be seen, indicating that the robustness of the algorithm is good. The key space of the encryption algorithm is large enough and the key sensitivity is good. The NPCR(normalized pixel contrast ratio) value is close to 99.61%, and the UACI(unified average changing intensity) value is 33.45%. It has the ability to resist differential attacks.
Aiming at the problem that digital images are vulnerable to attacks during network transmission and cause information leakage. This paper introduces quantum walk and Latin square matrix on the basis of Arnold scrambling, and designs a new type of color image encryption scheme. In the new scheme, the three channels of the color image are separated at first and the Arnold transform is used to scramble the pixel points of the image. Then quantum walk and Latin square matrix are used to process the pixel values of the scrambled image, the modulus diffusion algorithm is used on the processed image to further change the pixel value of the image. Finally, the color encrypted image is obtained by merging the three-channels encrypted images. Quantum walk, as an excellent random sequence generation tool, provides random sequences for algorithms. We conducted experimental simulations on the encryption algorithm, and analyzed the experimental results in the histogram, correlation, information entropy, noise attack, cropping attack and other aspects. The results show that the histogram of the encrypted image is distributed evenly, the correlation between pixels is close to 0, and the information entropy is 7.9993, close to 8, indicating that the algorithm has a relatively good ability to resist statistical analysis. After decrypting the encrypted image after noise attack and cropping attack, the original image information can still be seen, indicating that the robustness of the algorithm is good. The key space of the encryption algorithm is large enough and the key sensitivity is good. The NPCR(normalized pixel contrast ratio) value is close to 99.61%, and the UACI(unified average changing intensity) value is 33.45%. It has the ability to resist differential attacks.
2023, 52(5): 659-666.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023086
Abstract:
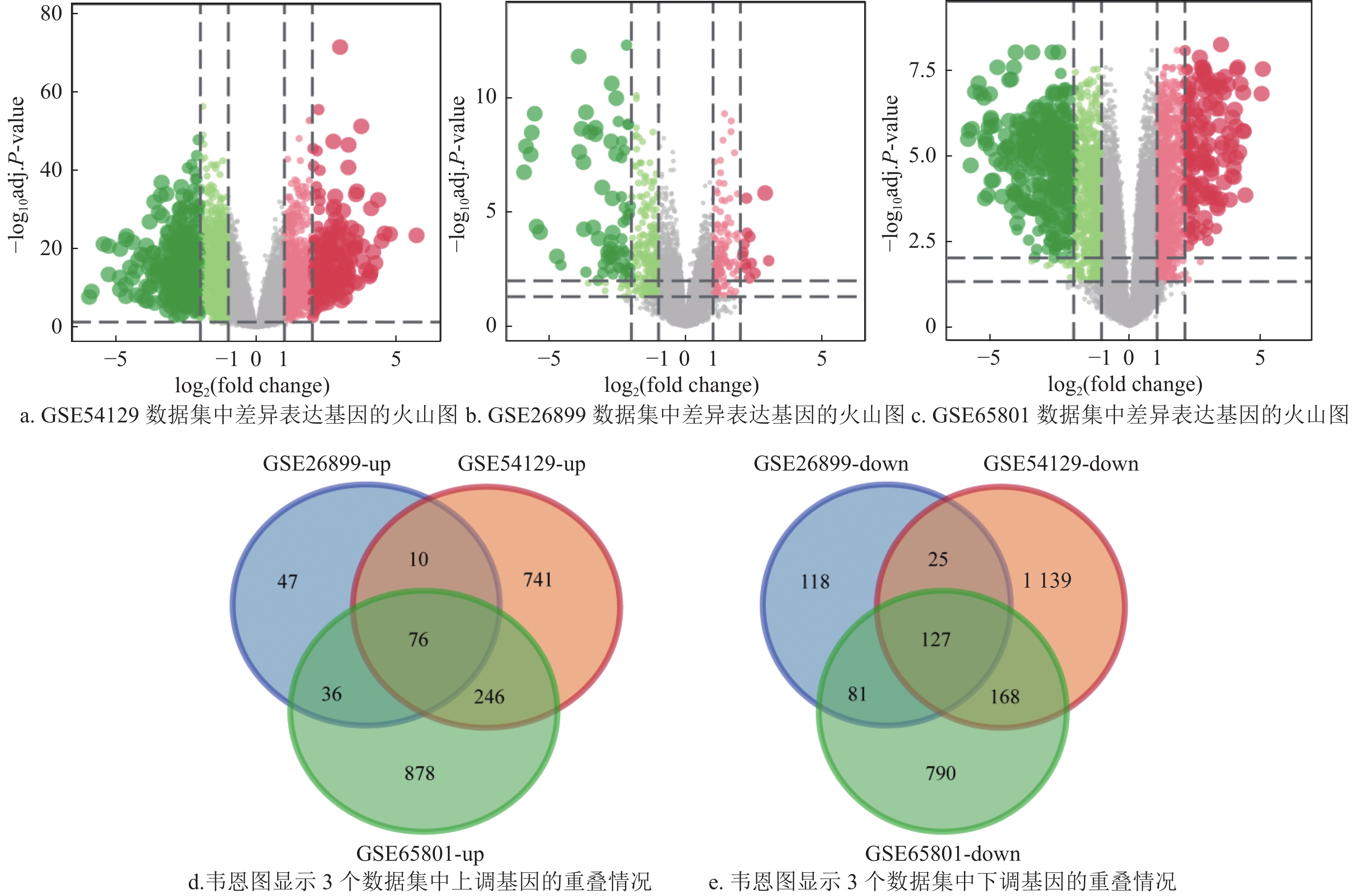
This study aims to predict candidate small-molecule drugs for the treatment of Gastric Cancer (GC) and identify their potential targets by using drug repositioning and bioinformatics methods, providing new ideas for GC therapy. In this study, 203 differentially expressed genes were first identified in GC datasets GSE54129, GSE26899 and GSE65801, and 10 candidate small-molecule compounds were screened by the Connectivity Map (CMap) analysis. Then, the topological properties of the protein-protein interaction network composed of differentially expressed genes were analyzed, and TIMP1, PDGFRB, COL1A1, etc. were identified as hub genes. Furthermore, molecular docking results showed that the newly identified small-molecule drug levonorgestrel had strong binding ability with TIMP1, and its binding energy was −9.24 kcal/mol; the binding energy of the reported GC drug Cediranib to the target PDGFRB was −6.28 kcal/mol. In addition, the expression patterns, diagnostic value and prognostic value of the potential target genes TIMP1 and PDGFRB were validated in the GC datasets.
This study aims to predict candidate small-molecule drugs for the treatment of Gastric Cancer (GC) and identify their potential targets by using drug repositioning and bioinformatics methods, providing new ideas for GC therapy. In this study, 203 differentially expressed genes were first identified in GC datasets GSE54129, GSE26899 and GSE65801, and 10 candidate small-molecule compounds were screened by the Connectivity Map (CMap) analysis. Then, the topological properties of the protein-protein interaction network composed of differentially expressed genes were analyzed, and TIMP1, PDGFRB, COL1A1, etc. were identified as hub genes. Furthermore, molecular docking results showed that the newly identified small-molecule drug levonorgestrel had strong binding ability with TIMP1, and its binding energy was −9.24 kcal/mol; the binding energy of the reported GC drug Cediranib to the target PDGFRB was −6.28 kcal/mol. In addition, the expression patterns, diagnostic value and prognostic value of the potential target genes TIMP1 and PDGFRB were validated in the GC datasets.
2023, 52(5): 667-674.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023035
Abstract:
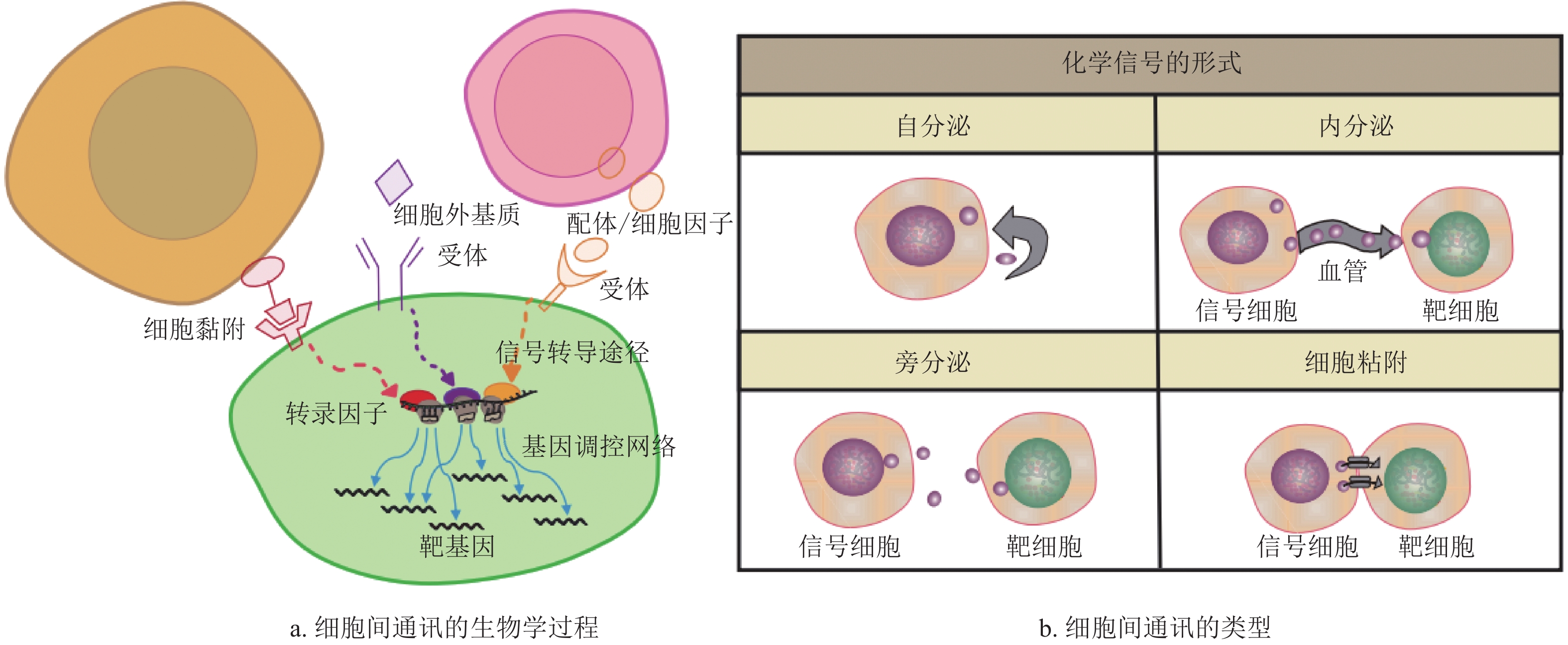
Ligand-Receptor (L-R) interactions that mediate cell communication are essential for both physiological and pathological signaling. With the rapid development of single-cell sequencing technologies, decoding the intercellular communication network and biological function has become a focus of research. To date, many intercellular communication prediction methods and databases have been developed and provided key technical supports for researches on cell-cell communication. This study first explains the basic biological process of intercellular communication, then systematically compares representative databases, algorithms, and benchmark studies for predicting intercellular communication. Finally, this study outlines future challenges and outstanding questions in the field.
Ligand-Receptor (L-R) interactions that mediate cell communication are essential for both physiological and pathological signaling. With the rapid development of single-cell sequencing technologies, decoding the intercellular communication network and biological function has become a focus of research. To date, many intercellular communication prediction methods and databases have been developed and provided key technical supports for researches on cell-cell communication. This study first explains the basic biological process of intercellular communication, then systematically compares representative databases, algorithms, and benchmark studies for predicting intercellular communication. Finally, this study outlines future challenges and outstanding questions in the field.
2023, 52(5): 675-680.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022404
Abstract:
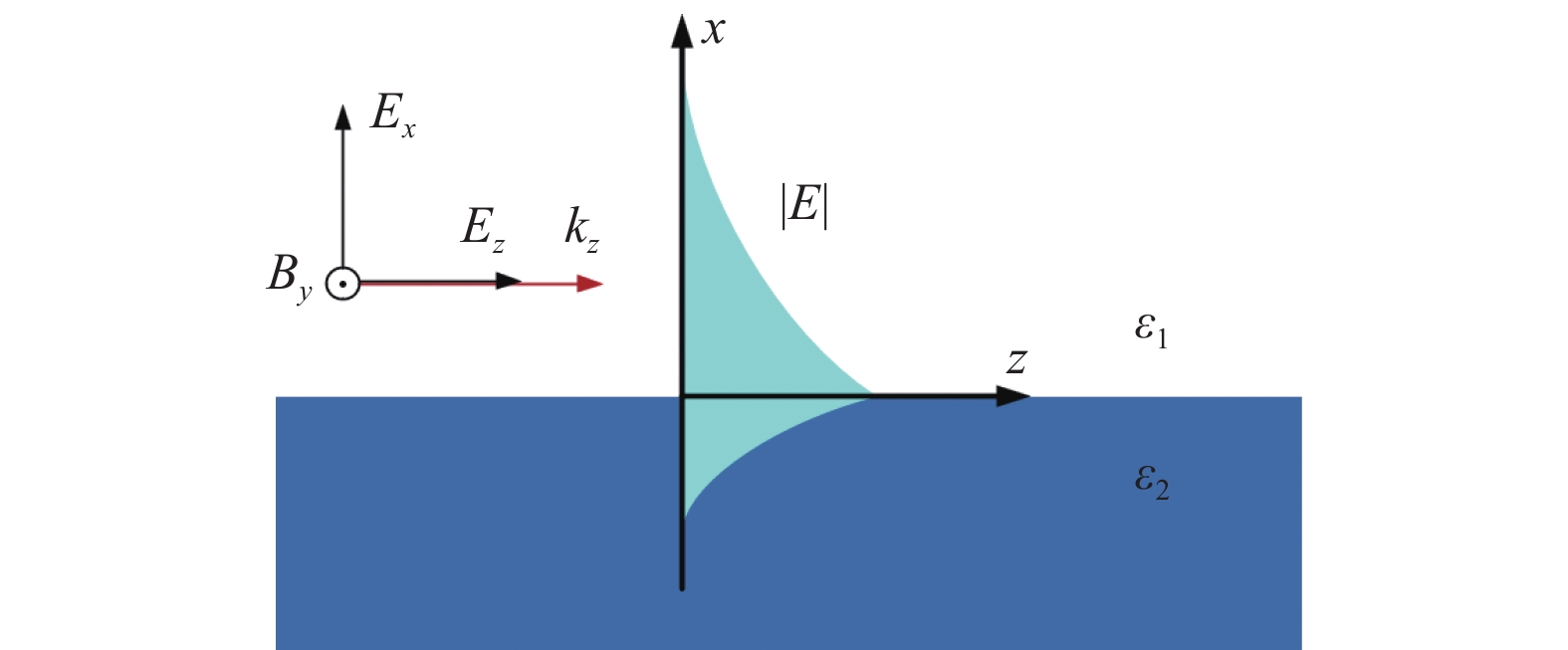
In this paper we present some new investigations on the transverse spin of evanescent waves and obtain the following results: 1) the quantization form of the transverse spin is revealed; 2) from a unified point of view, the transverse spin can be attributed to the presence of an effective rest mass of evanescent waves; 3) the transverse spin can also be described by the spin matrix of the photon field; 4) unlike a free optical field in vacuum whose spin projection on the propagation direction is the only observable, owing to the effective rest mass, the spin projection of evanescent waves on other directions is also an observable, such that one can develop an optical analogy of spintronics, i.e., spinoptics.
In this paper we present some new investigations on the transverse spin of evanescent waves and obtain the following results: 1) the quantization form of the transverse spin is revealed; 2) from a unified point of view, the transverse spin can be attributed to the presence of an effective rest mass of evanescent waves; 3) the transverse spin can also be described by the spin matrix of the photon field; 4) unlike a free optical field in vacuum whose spin projection on the propagation direction is the only observable, owing to the effective rest mass, the spin projection of evanescent waves on other directions is also an observable, such that one can develop an optical analogy of spintronics, i.e., spinoptics.
2023, 52(5): 681-688.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022325
Abstract:
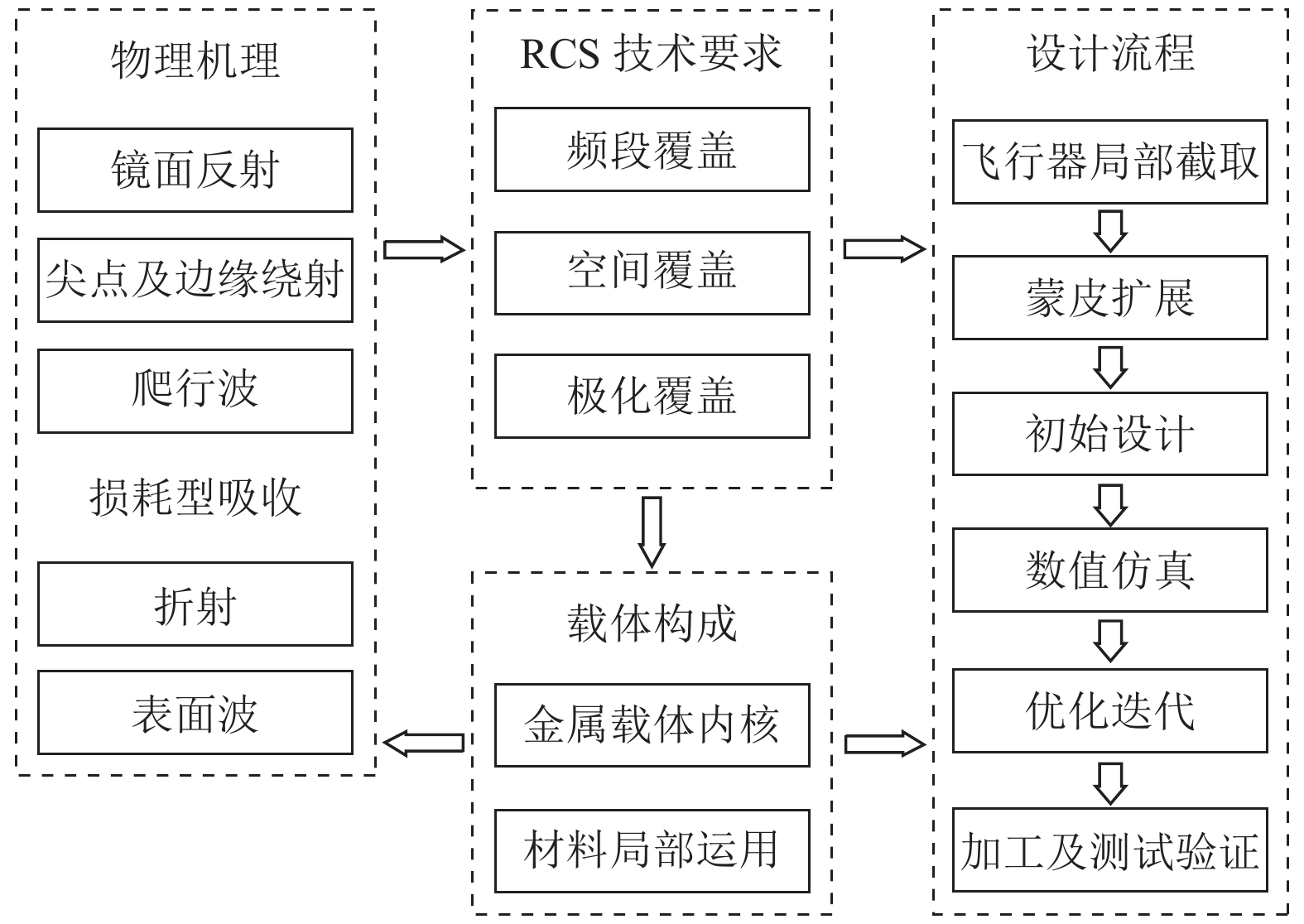
The realization of radar stealth for all kinds of electric apertures and the corresponding designs of low scattering carrier are very concerned in the current engineering field. However, there has been a lack of systematic and universal method. This paper summarizes the background and development trend of related work, and then analyzes the basic electromagnetic scattering mechanisms and high-precision and high-efficiency simulation methods used in the design of low scattering carriers. Facing the general technical requirements, the overall design logic and detailed partition design process are deeply studied, and the specific operation steps based on specific software are also given out. Through example design and result analysis, the scientificity and effectiveness of the design method are demonstrated, and the future research space is also discussed.
The realization of radar stealth for all kinds of electric apertures and the corresponding designs of low scattering carrier are very concerned in the current engineering field. However, there has been a lack of systematic and universal method. This paper summarizes the background and development trend of related work, and then analyzes the basic electromagnetic scattering mechanisms and high-precision and high-efficiency simulation methods used in the design of low scattering carriers. Facing the general technical requirements, the overall design logic and detailed partition design process are deeply studied, and the specific operation steps based on specific software are also given out. Through example design and result analysis, the scientificity and effectiveness of the design method are demonstrated, and the future research space is also discussed.
2023, 52(5): 689-698.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022214
Abstract:
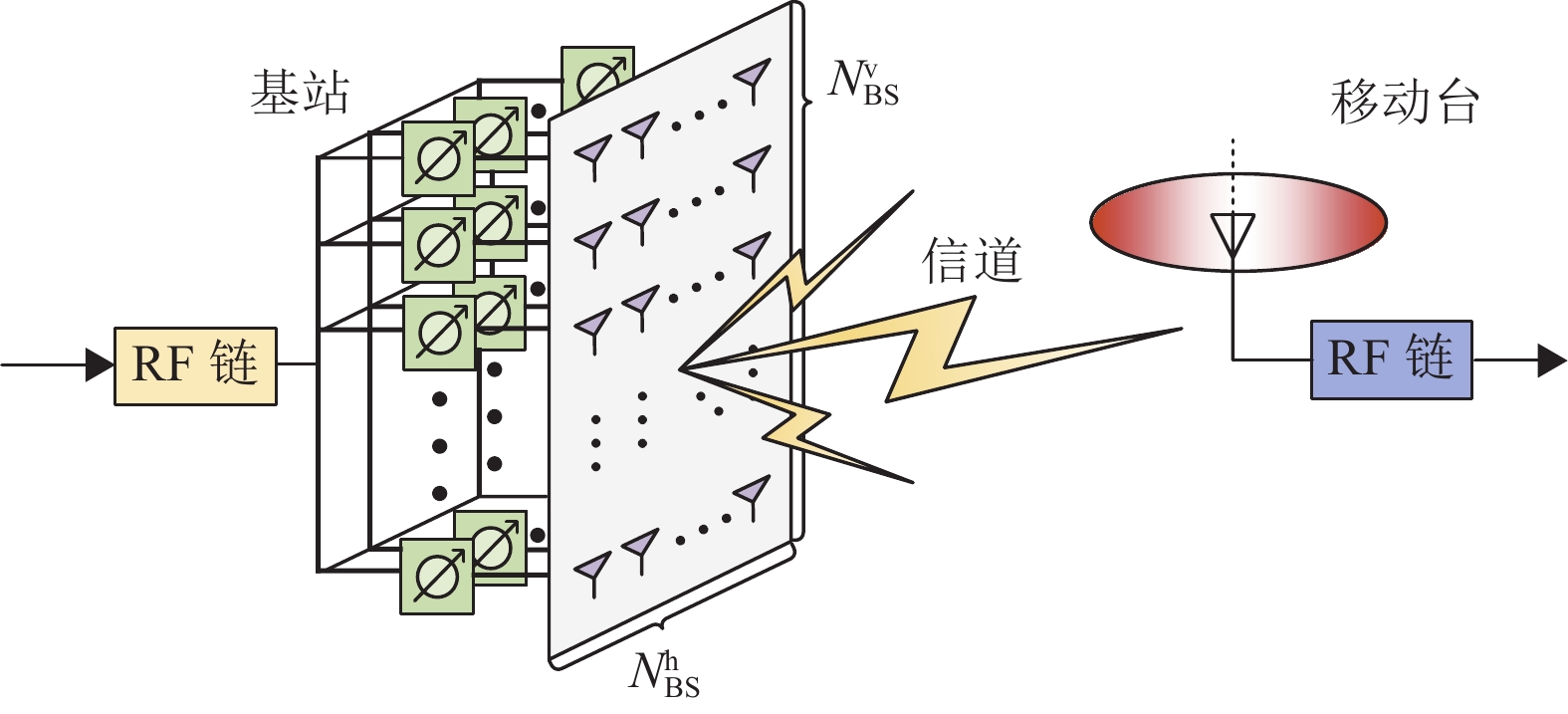
To reduce the time and power overhead of millimeter wave (mmWave) beam training, a beam feature selection and prediction algorithm based on communication scenarios is proposed. First, the optimal feature-beam is selected according to the power loss probability minimization criterion, and a feature-beam set (a subset of beam indices) is generated using the optimal beam probability. Second, to obtain the optimal beam probability for communication scenarios, the local learning based clustering algorithm with feature selection (LLC-fs) is adopted. Finally, since there is an implicit and nonlinear mapping relationship between the scene-based feature-beam set and the optimal beam, the DNN model is used to approximate the mapping, and the offline training model is used to realize the prediction from the feature-beam set to the optimal beam. The simulation results show that the optimal mmWave beam can be predicted online by using the offline-trained scene-based DNN model. The prediction performance can approach the exhaustive beam search algorithm and effectively reduce the overhead of beam search.
To reduce the time and power overhead of millimeter wave (mmWave) beam training, a beam feature selection and prediction algorithm based on communication scenarios is proposed. First, the optimal feature-beam is selected according to the power loss probability minimization criterion, and a feature-beam set (a subset of beam indices) is generated using the optimal beam probability. Second, to obtain the optimal beam probability for communication scenarios, the local learning based clustering algorithm with feature selection (LLC-fs) is adopted. Finally, since there is an implicit and nonlinear mapping relationship between the scene-based feature-beam set and the optimal beam, the DNN model is used to approximate the mapping, and the offline training model is used to realize the prediction from the feature-beam set to the optimal beam. The simulation results show that the optimal mmWave beam can be predicted online by using the offline-trained scene-based DNN model. The prediction performance can approach the exhaustive beam search algorithm and effectively reduce the overhead of beam search.
2023, 52(5): 699-708.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022238
Abstract:
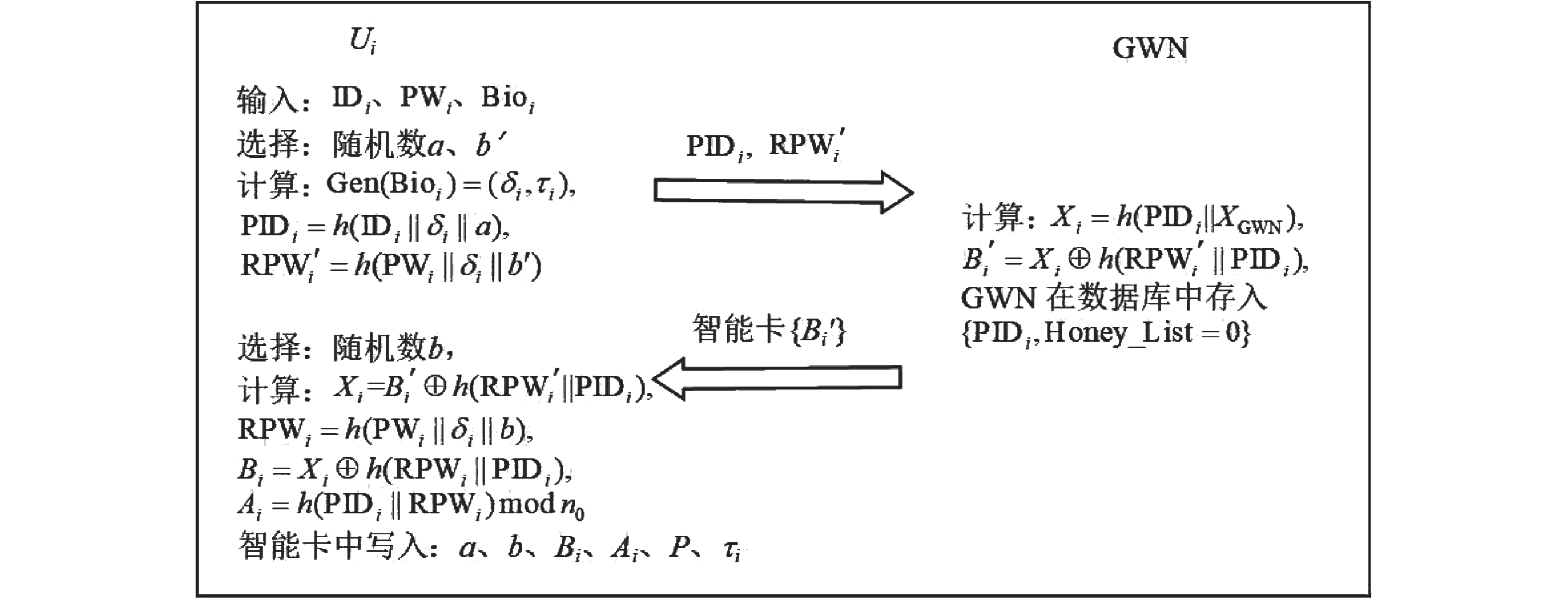
To solve security defects generally lain in many existing protocols, such as offline dictionary attack, lack of anonymity and no forward security, based on the latest security model, this paper adds KSSTI attack and registered legitimate user attack into the security model evaluation standard to form an enhanced security model. Based on this enhanced security model, a multi-factor security enhanced authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks is proposed, which realizes the secure session key negotiation among users and sensor nodes through the gateway. The results of BAN logic and heuristic analysis show that the protocol realizes two-way authentication and meets the important security attributes of anonymity, forward security, resistance to internal attacks, resistance to KSSTI attacks and so on. Compared with the existing protocols, this protocol has higher security level and moderate amount of computation and communication. It is suitable for the application scenarios with high security level requirements and limited computing resources of sensor nodes.
To solve security defects generally lain in many existing protocols, such as offline dictionary attack, lack of anonymity and no forward security, based on the latest security model, this paper adds KSSTI attack and registered legitimate user attack into the security model evaluation standard to form an enhanced security model. Based on this enhanced security model, a multi-factor security enhanced authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks is proposed, which realizes the secure session key negotiation among users and sensor nodes through the gateway. The results of BAN logic and heuristic analysis show that the protocol realizes two-way authentication and meets the important security attributes of anonymity, forward security, resistance to internal attacks, resistance to KSSTI attacks and so on. Compared with the existing protocols, this protocol has higher security level and moderate amount of computation and communication. It is suitable for the application scenarios with high security level requirements and limited computing resources of sensor nodes.
2023, 52(5): 709-717.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022282
Abstract:
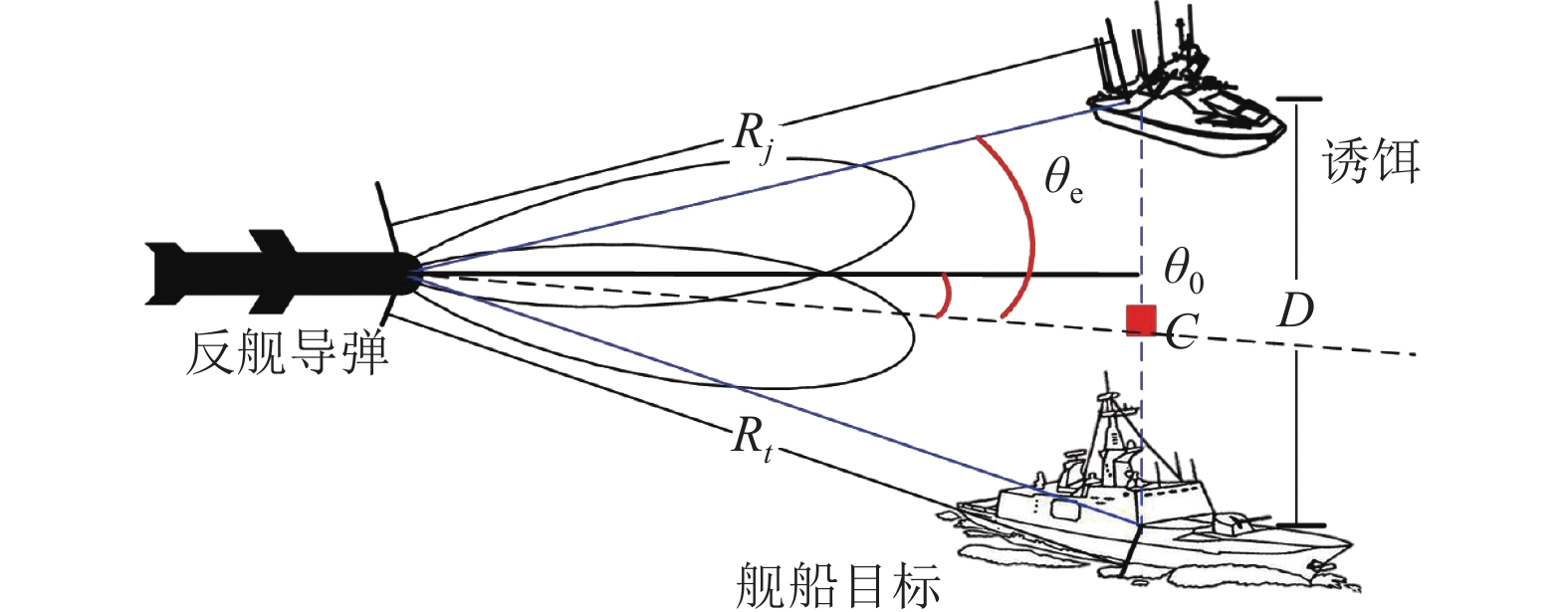
For dynamic analysis of outboard active decoy jamming on the terminal radar guidance, the angular deviation under active decoy jamming is derived based on the measuring principle of monopulse radar, and the jamming difference between sum-difference method of amplitude and the phase method is compared. Combined with the signal and the macro situation, the calculation methods of the critical jamming distance of missile and the critical lateral distance of decoy to achieve effective jamming are analyzed and proposed as the quantitative basis of decoy jamming strategy. By developing a simulation platform to simulate the dynamic process of active decoy jamming, the applicability of the theoretical analysis are verified. The results show that the requirement for the active decoy to achieve effective jamming during the terminal process of anti-ship missiles is that the decoy deployment distance should be greater than the critical lateral distance, and maneuvering decoy can improve the robustness of non-cooperative jamming.
For dynamic analysis of outboard active decoy jamming on the terminal radar guidance, the angular deviation under active decoy jamming is derived based on the measuring principle of monopulse radar, and the jamming difference between sum-difference method of amplitude and the phase method is compared. Combined with the signal and the macro situation, the calculation methods of the critical jamming distance of missile and the critical lateral distance of decoy to achieve effective jamming are analyzed and proposed as the quantitative basis of decoy jamming strategy. By developing a simulation platform to simulate the dynamic process of active decoy jamming, the applicability of the theoretical analysis are verified. The results show that the requirement for the active decoy to achieve effective jamming during the terminal process of anti-ship missiles is that the decoy deployment distance should be greater than the critical lateral distance, and maneuvering decoy can improve the robustness of non-cooperative jamming.
2023, 52(5): 718-727.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022223
Abstract:
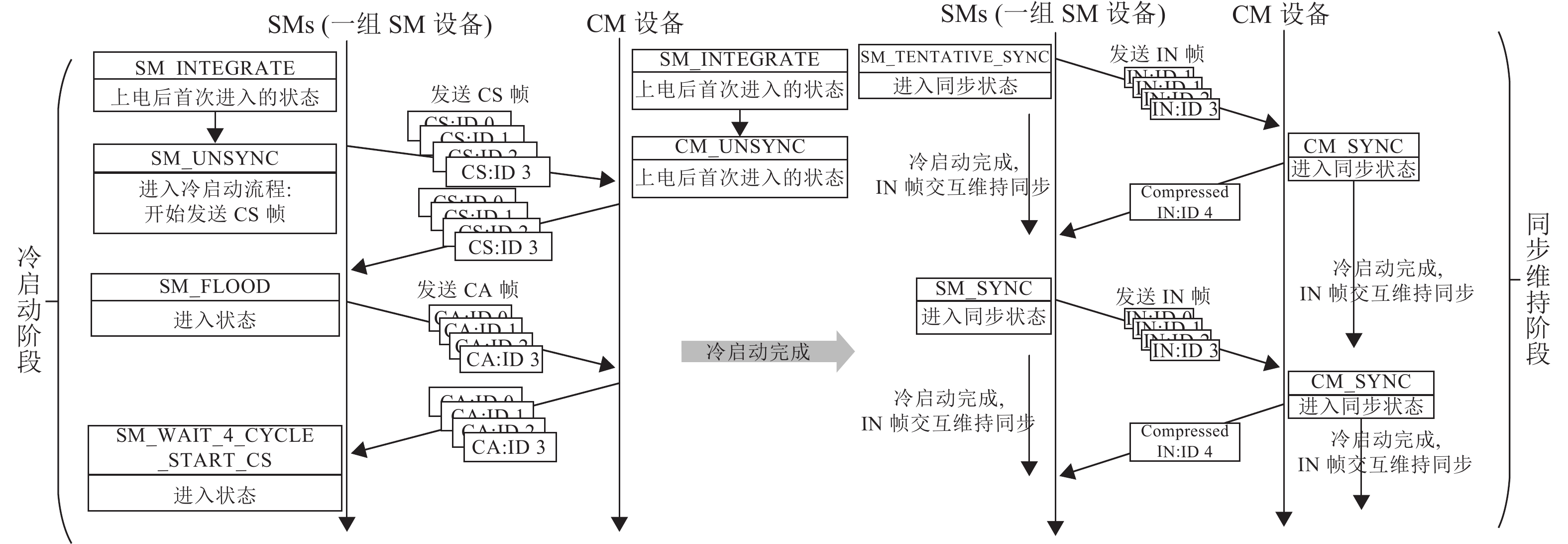
Deterministic network technology like Time-triggered Ethernet (TTE) and Time-sensitive Networking (TSN) is gradually applied to mission critical systems such as avionics, industrial automation and vehicle mounted systems. Time synchronization technology is the essential precondition for these networks’ proper functioning. Nevertheless, there is no analytical model nor comparative analysis for the reliability of time synchronization services in different protocols. Aiming at this problem, we analyze the time synchronization process of the two protocols of above-mentioned networks, and extract the factors that lead to the failure. Then, we propose a theoretical evaluation model of the failure probability for these two protocols. On this basis, the failure scenario and failure probability are compared and analyzed. Finally, we use OPNET simulator to verify the consistency with the theoretical analysis. The time synchronization failure probability evaluation model proposed in this paper can provide reference for relevant personnel.
Deterministic network technology like Time-triggered Ethernet (TTE) and Time-sensitive Networking (TSN) is gradually applied to mission critical systems such as avionics, industrial automation and vehicle mounted systems. Time synchronization technology is the essential precondition for these networks’ proper functioning. Nevertheless, there is no analytical model nor comparative analysis for the reliability of time synchronization services in different protocols. Aiming at this problem, we analyze the time synchronization process of the two protocols of above-mentioned networks, and extract the factors that lead to the failure. Then, we propose a theoretical evaluation model of the failure probability for these two protocols. On this basis, the failure scenario and failure probability are compared and analyzed. Finally, we use OPNET simulator to verify the consistency with the theoretical analysis. The time synchronization failure probability evaluation model proposed in this paper can provide reference for relevant personnel.
2023, 52(5): 728-738.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022217
Abstract:
To solve the problem of low recognition accuracy due to high noise and insufficient feature information of digital instrument images, this paper proposes an image recognition method of high noise digital instrument based on convolution recursive neural network combining projection threshold segmentation and number sequence correction. Firstly, the projection threshold segmentation binarization algorithm is proposed to preprocess the image. The vertical projection method is used to divide the image into different regions, and the binarization threshold is set adaptively according to the noise intensity of different regions to binarization the image and reduce the noise. Secondly, according to the changing characteristics of the number rules between images, the number sequence correction algorithm is used to transform a single number recognition into a number sequence recognition, and the recognition result is obtained by comparing the recognition probability of different number sequences, so as to solve the problem of low recognition accuracy caused by insufficient feature information of a single image. The experimental results show that, compared with the convolutional recursive neural network model, the accuracy of the high-noise digital instrument recognition model proposed in this paper is improved on the high-noise data set by about 61.95%, reaching 93.58%.
To solve the problem of low recognition accuracy due to high noise and insufficient feature information of digital instrument images, this paper proposes an image recognition method of high noise digital instrument based on convolution recursive neural network combining projection threshold segmentation and number sequence correction. Firstly, the projection threshold segmentation binarization algorithm is proposed to preprocess the image. The vertical projection method is used to divide the image into different regions, and the binarization threshold is set adaptively according to the noise intensity of different regions to binarization the image and reduce the noise. Secondly, according to the changing characteristics of the number rules between images, the number sequence correction algorithm is used to transform a single number recognition into a number sequence recognition, and the recognition result is obtained by comparing the recognition probability of different number sequences, so as to solve the problem of low recognition accuracy caused by insufficient feature information of a single image. The experimental results show that, compared with the convolutional recursive neural network model, the accuracy of the high-noise digital instrument recognition model proposed in this paper is improved on the high-noise data set by about 61.95%, reaching 93.58%.
2023, 52(5): 739-746.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022261
Abstract:
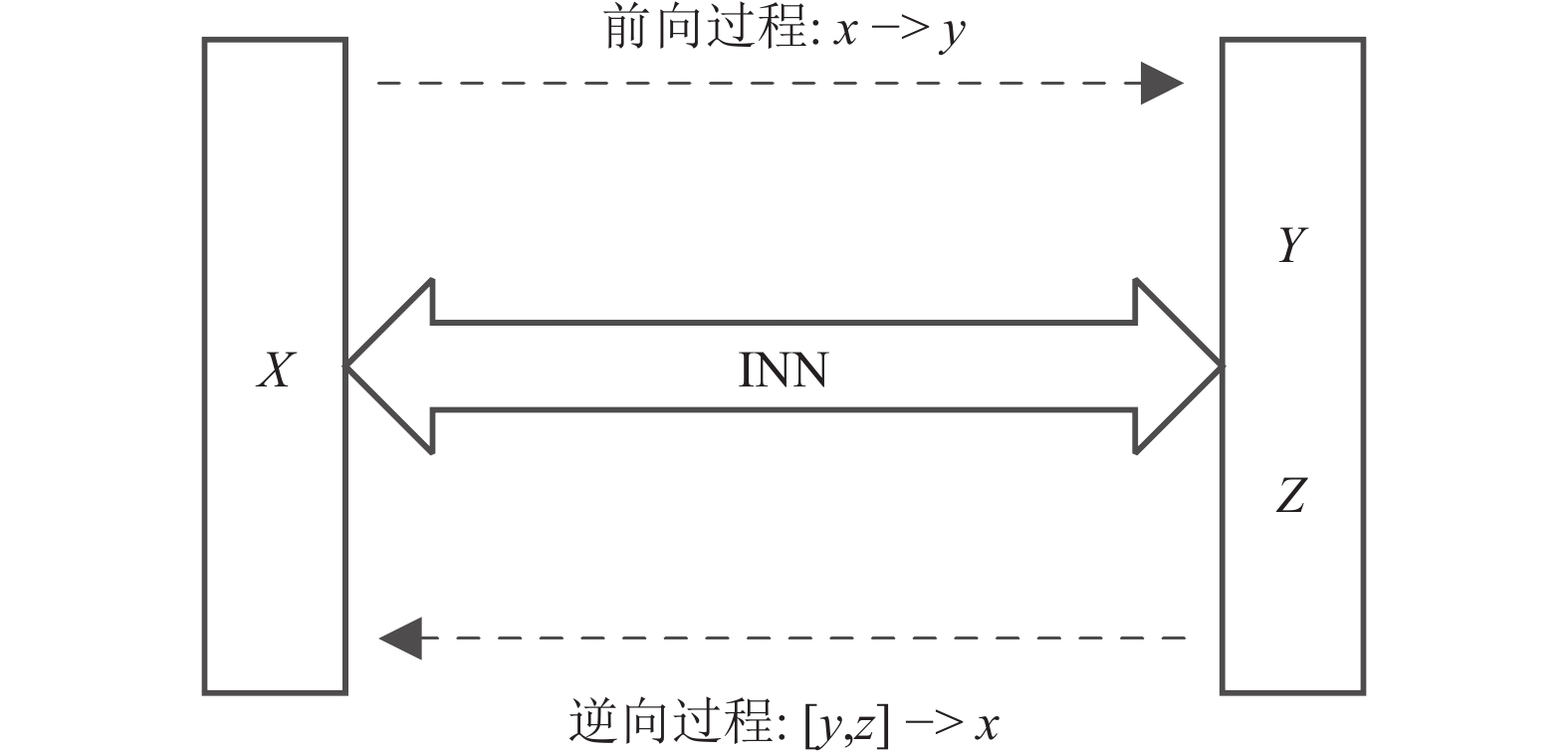
The latent variable of Invertible Rescaling Network (IRN) uses Gaussian distribution to embed the high-frequency information of the image. Because of the independence and randomness of this approach, the high-frequency information of the image cannot be fully preserved, and the embedding effect is general, which affects the performance of the reconstruction. In order to improve the ability of embedding high frequency information and further reduce the complexity of the model, this paper proposes an improved algorithm based on IRN. Firstly, the dense connection structure and channel attention mechanism are adopted to obtain sufficient feature information and reduce the number of parameters in the feature extraction module. Secondly, the latent variable of the network is designed by high frequency sub-band interpolation in wavelet domain to improve the embedding ability of high frequency information. The results show that compared with IRN, the average Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structure Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) of the proposed algorithm are improved by 0.380 dB and 0.014 on the four benchmark test sets Set5, Set14, BSD100 and Urban100, the algorithm parameters in this paper are reduced by about 1.64×106 M, the FLOPs are reduced by about 0.43×109 G, and the running time is reduced by 3 ms. It verifies that the reconstruction performance of the proposed algorithm is excellent and the model complexity is low, which has practical value.
The latent variable of Invertible Rescaling Network (IRN) uses Gaussian distribution to embed the high-frequency information of the image. Because of the independence and randomness of this approach, the high-frequency information of the image cannot be fully preserved, and the embedding effect is general, which affects the performance of the reconstruction. In order to improve the ability of embedding high frequency information and further reduce the complexity of the model, this paper proposes an improved algorithm based on IRN. Firstly, the dense connection structure and channel attention mechanism are adopted to obtain sufficient feature information and reduce the number of parameters in the feature extraction module. Secondly, the latent variable of the network is designed by high frequency sub-band interpolation in wavelet domain to improve the embedding ability of high frequency information. The results show that compared with IRN, the average Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structure Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) of the proposed algorithm are improved by 0.380 dB and 0.014 on the four benchmark test sets Set5, Set14, BSD100 and Urban100, the algorithm parameters in this paper are reduced by about 1.64×106 M, the FLOPs are reduced by about 0.43×109 G, and the running time is reduced by 3 ms. It verifies that the reconstruction performance of the proposed algorithm is excellent and the model complexity is low, which has practical value.
2023, 52(5): 747-755.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022182
Abstract:
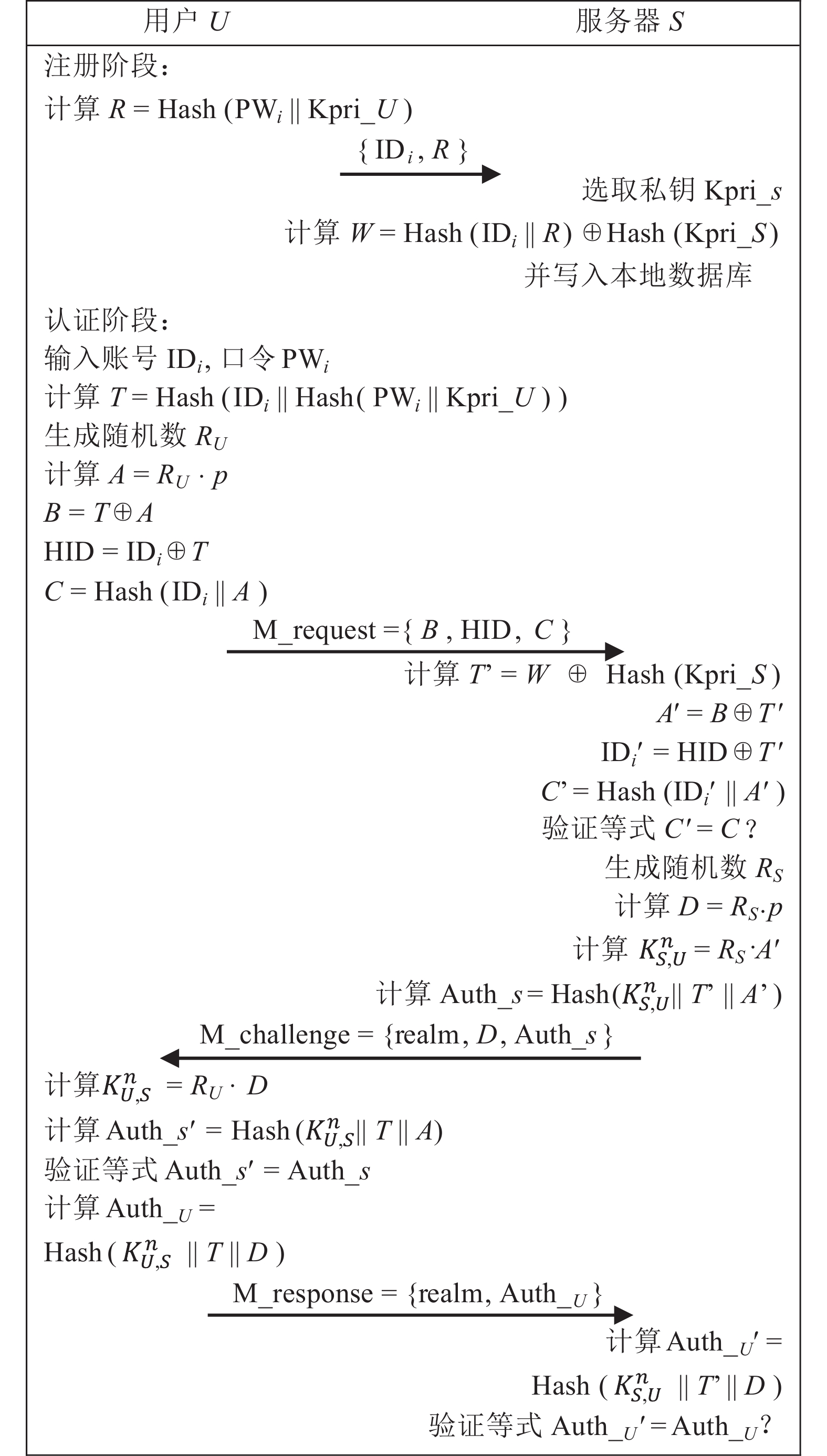
In order to provide user anonymity in SIP (session initialization protocol) authentication protocol and improve the security performance of the protocol, a new anonymous SIP authentication protocol is proposed by combining challenge/response mechanism, elliptic curve cryptography and password authentication. The protocol only uses few point multiplication operations of elliptic curve cryptography, which not only ensures the security of authentication, but also effectively reduces the overall amount of computation. The protocol introduces high-entropy random number in the authentication process. The authentication parties use three handshakes of challenge/response mechanism to realize two-way authentication, and generate the key required for subsequent sessions at the same time. Through the BAN (Burrows, Abadi and Needham) logic analysis of the protocol and the informal analysis aim at many known attacks, it is proved that the protocol has high security performance. Compared with the efficiency of related protocols, the protocol authentication process requires less computation.
In order to provide user anonymity in SIP (session initialization protocol) authentication protocol and improve the security performance of the protocol, a new anonymous SIP authentication protocol is proposed by combining challenge/response mechanism, elliptic curve cryptography and password authentication. The protocol only uses few point multiplication operations of elliptic curve cryptography, which not only ensures the security of authentication, but also effectively reduces the overall amount of computation. The protocol introduces high-entropy random number in the authentication process. The authentication parties use three handshakes of challenge/response mechanism to realize two-way authentication, and generate the key required for subsequent sessions at the same time. Through the BAN (Burrows, Abadi and Needham) logic analysis of the protocol and the informal analysis aim at many known attacks, it is proved that the protocol has high security performance. Compared with the efficiency of related protocols, the protocol authentication process requires less computation.
2023, 52(5): 756-764.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022144
Abstract:
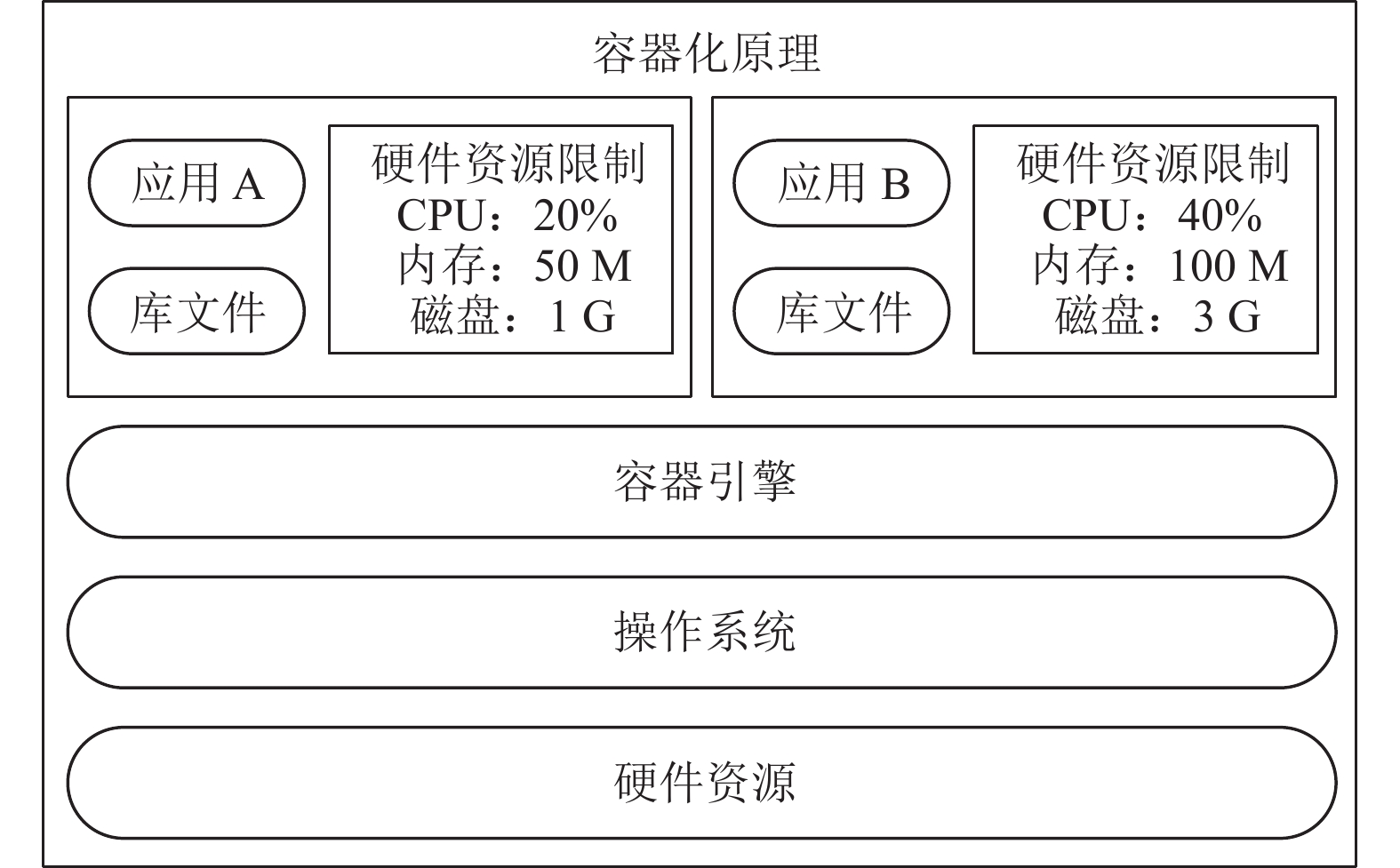
With the development of power grid construction and the continuous growth of the scale of distribution station buildings and equipment, in order to support the development of power grid business applications, more challenges have been put forward to the practicality of edge Internet of things (IOT) agents, and the conventional containerization technology route has appeared a certain bottleneck. Through the introduction and selection of containerization technology, this paper puts forward the lightweight design idea based on the conventional containerization architecture of Kubernetes. The research results of this paper greatly reduce the occupation and consumption of hardware resources by the edge IOT agent device, and realize cloud edge end business collaboration, data collaboration and intelligent collaboration. At the same time, the planning and design of business application app and AI visual learning model algorithm library are carried out on the edge side, which better meets the support of distribution network operation inspection business.
With the development of power grid construction and the continuous growth of the scale of distribution station buildings and equipment, in order to support the development of power grid business applications, more challenges have been put forward to the practicality of edge Internet of things (IOT) agents, and the conventional containerization technology route has appeared a certain bottleneck. Through the introduction and selection of containerization technology, this paper puts forward the lightweight design idea based on the conventional containerization architecture of Kubernetes. The research results of this paper greatly reduce the occupation and consumption of hardware resources by the edge IOT agent device, and realize cloud edge end business collaboration, data collaboration and intelligent collaboration. At the same time, the planning and design of business application app and AI visual learning model algorithm library are carried out on the edge side, which better meets the support of distribution network operation inspection business.
2023, 52(5): 765-772.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022199
Abstract:
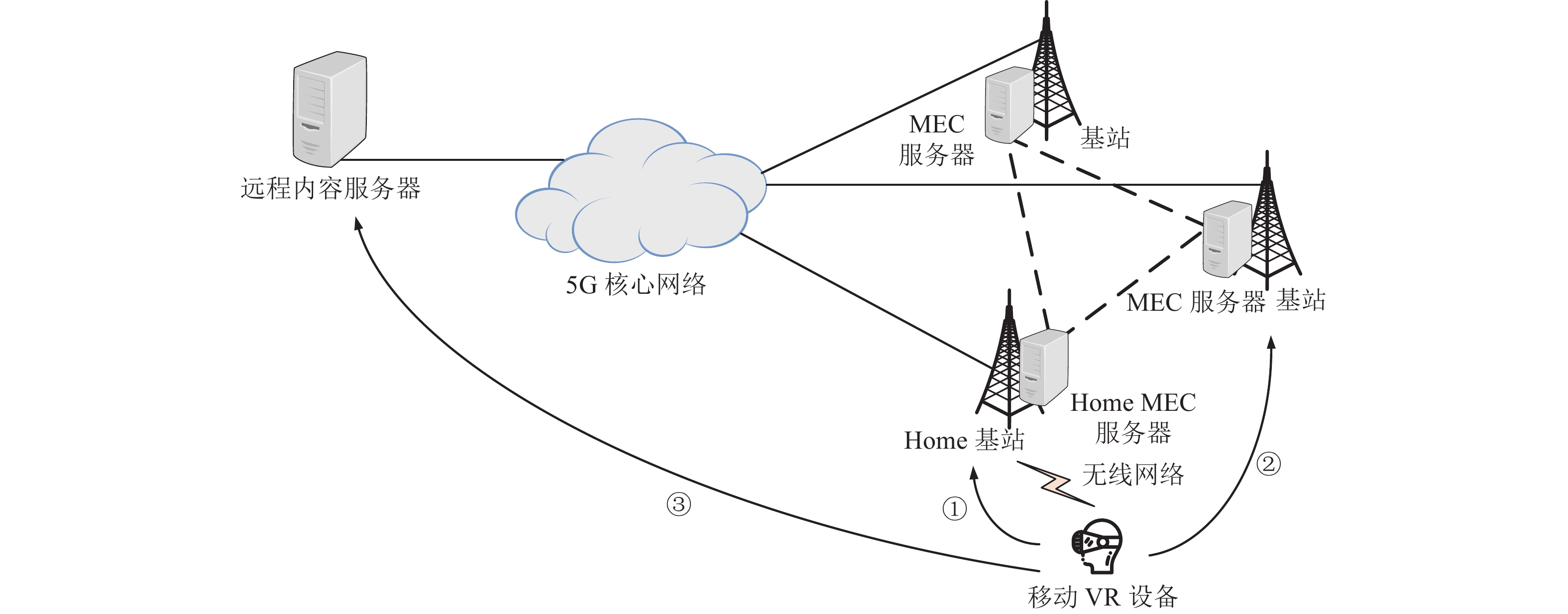
In this paper, a network architecture based on multi-MEC (mobile edge computing) cooperative caching and streaming is proposed to address the problem that the delivery latency of mobile virtual reality (VR) video is too high under traditional delivery architecture. First of all, considering that the mobile VR video needs computing processing when watching and the mobile VR device may not always have the corresponding processing capacity, the MEC in the transmission architecture undertakes the needed computing task. Then, a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) cache model with the optimization goal of minimizing the average delivery latency is established, and the optimal cache placement for mobile VR videos is obtained through the commercial solver Gurobi. Finally, numerical simulation experiments show that the proposed caching and streaming strategy can effectively reduce the average delivery latency of mobile VR videos when compared with existing caching algorithms.
In this paper, a network architecture based on multi-MEC (mobile edge computing) cooperative caching and streaming is proposed to address the problem that the delivery latency of mobile virtual reality (VR) video is too high under traditional delivery architecture. First of all, considering that the mobile VR video needs computing processing when watching and the mobile VR device may not always have the corresponding processing capacity, the MEC in the transmission architecture undertakes the needed computing task. Then, a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) cache model with the optimization goal of minimizing the average delivery latency is established, and the optimal cache placement for mobile VR videos is obtained through the commercial solver Gurobi. Finally, numerical simulation experiments show that the proposed caching and streaming strategy can effectively reduce the average delivery latency of mobile VR videos when compared with existing caching algorithms.
2023, 52(5): 773-779.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022156
Abstract:
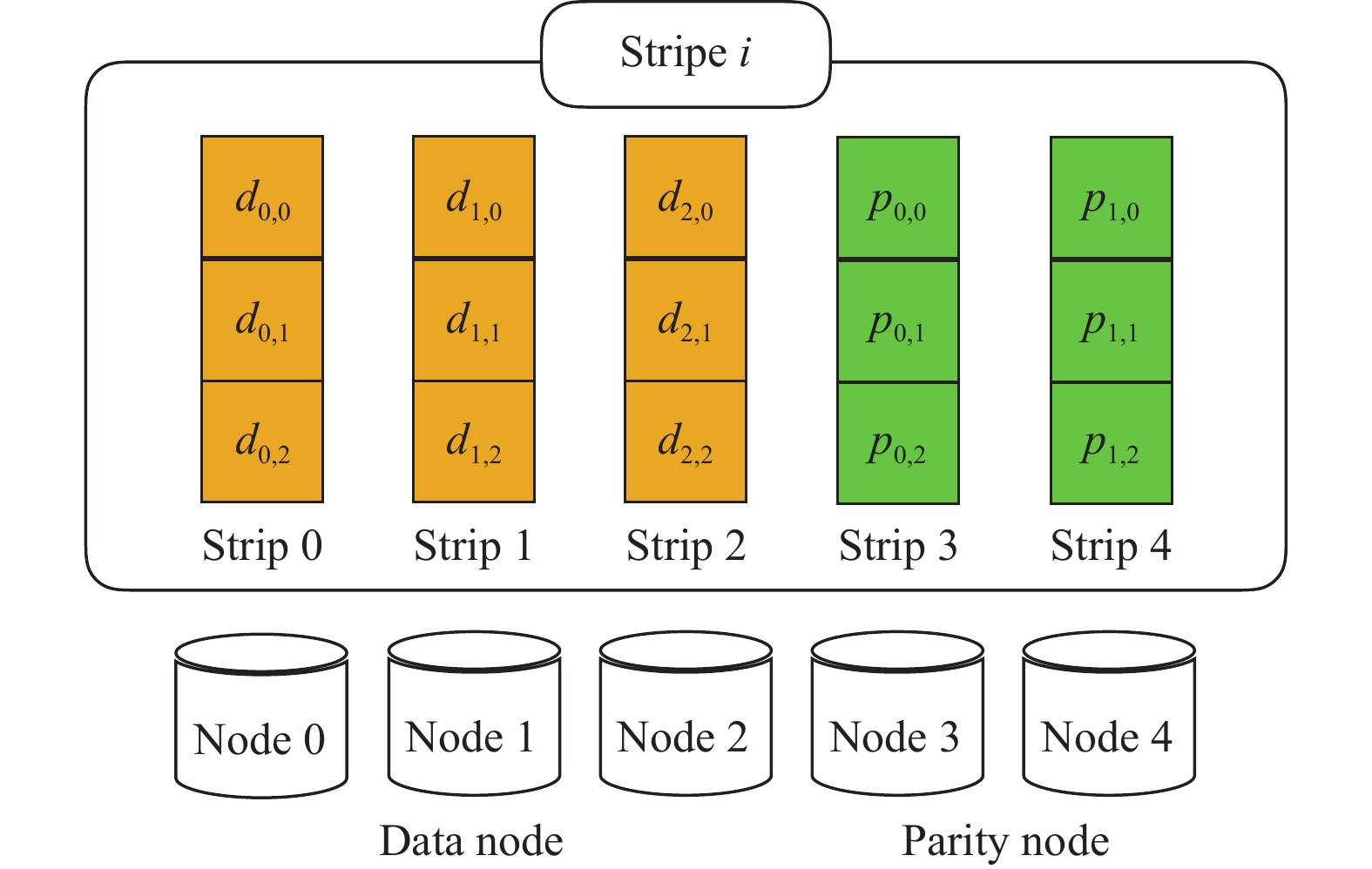
In an erasure-coded cloud storage system, the performance of data updates is often limited by network overhead. To end this, based on Cross-Rack-Aware Update (CAU) data update scheme, we propose an XOR based Tape ARchive Cross-Rack-Aware Updates (TAR-CAU) data update scheme. TAR-CAU is designed in terms of the two design primitives: 1) as the updates are small, we can pack several data blocks of data update into one block to reduce the number of network round trips, and accelerate the data transmission; 2) XOR-based data update scheme is used to accelerate data encoding and decoding. The simulation experiments and local cluster experiments show that, when the data updates are small, TAR-CAU can increase the data update throughput by at least 44% compared with the CAU.
In an erasure-coded cloud storage system, the performance of data updates is often limited by network overhead. To end this, based on Cross-Rack-Aware Update (CAU) data update scheme, we propose an XOR based Tape ARchive Cross-Rack-Aware Updates (TAR-CAU) data update scheme. TAR-CAU is designed in terms of the two design primitives: 1) as the updates are small, we can pack several data blocks of data update into one block to reduce the number of network round trips, and accelerate the data transmission; 2) XOR-based data update scheme is used to accelerate data encoding and decoding. The simulation experiments and local cluster experiments show that, when the data updates are small, TAR-CAU can increase the data update throughput by at least 44% compared with the CAU.
2023, 52(5): 780-788.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022168
Abstract:
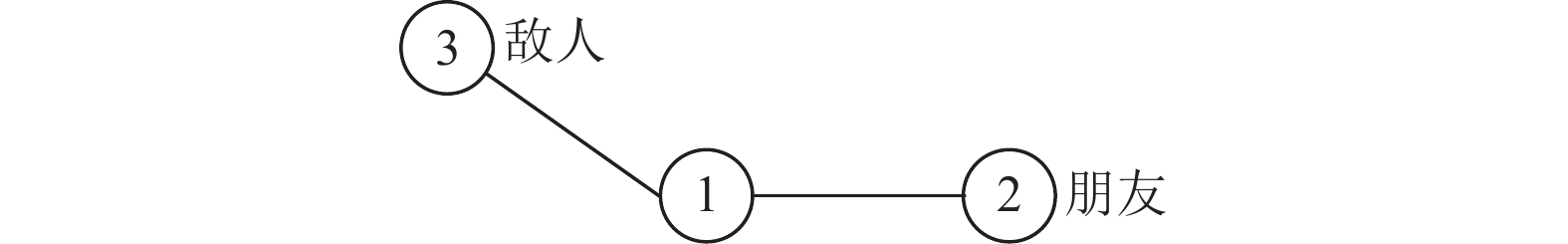
In this paper, a symbolic network representation learning framework signed network representation learning algorithm based on structural balance theory and high-order mutual information (SNSH) is proposed. By reversing the positive and negative relationships in symbolic networks to generate negative graphs, the hidden high-order mutual information in symbolic networks is mined. This method aims to simulate the local implicit features of symbolic networks through the strengthened social balance theory, and obtain a more comprehensive node embedding that conforms to the characteristics of symbolic networks through the high-order mutual information among the local embedding of nodes, the global structure of the network and the characteristic attributes of nodes.
In this paper, a symbolic network representation learning framework signed network representation learning algorithm based on structural balance theory and high-order mutual information (SNSH) is proposed. By reversing the positive and negative relationships in symbolic networks to generate negative graphs, the hidden high-order mutual information in symbolic networks is mined. This method aims to simulate the local implicit features of symbolic networks through the strengthened social balance theory, and obtain a more comprehensive node embedding that conforms to the characteristics of symbolic networks through the high-order mutual information among the local embedding of nodes, the global structure of the network and the characteristic attributes of nodes.
2023, 52(5): 789-799.
doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022157
Abstract:
Compared with the university evaluation rankings issued by professional organizations, the ranking of colleges and universities in the mind of the public often has a more direct impact on college enrollment, scientific research, and social collaboration. In this paper, adopting the questionnaire survey method, we take college students as the representative social group to dig out the difference between the public evaluation ranking of universities and the actual ranking of universities, analyze the correlation between this difference and the economic and demographic indicators of the city where an university is located. And then, we reconstruct the public evaluation ranking of universities and analyze the correlation between the rank change and the economic and demographic indicators of cities to quantitatively measure the influence of city indicators on the public evaluation rankings of universities. We find that the public evaluation ranking of universities which are located in the city with high urbanization level and developed tertiary industry usually are higher than their actual rankings, which shows the remarkable influence of regional economy and city population on the public evaluation of universities.
Compared with the university evaluation rankings issued by professional organizations, the ranking of colleges and universities in the mind of the public often has a more direct impact on college enrollment, scientific research, and social collaboration. In this paper, adopting the questionnaire survey method, we take college students as the representative social group to dig out the difference between the public evaluation ranking of universities and the actual ranking of universities, analyze the correlation between this difference and the economic and demographic indicators of the city where an university is located. And then, we reconstruct the public evaluation ranking of universities and analyze the correlation between the rank change and the economic and demographic indicators of cities to quantitatively measure the influence of city indicators on the public evaluation rankings of universities. We find that the public evaluation ranking of universities which are located in the city with high urbanization level and developed tertiary industry usually are higher than their actual rankings, which shows the remarkable influence of regional economy and city population on the public evaluation of universities.

 ISSN
ISSN