-
盲源分离 (blind signal separation, BSS) 是信号处理技术中新发展起来的方法。与传统的信号处理技术相比,具有很多优良的特点。它仅利用所观测到的数据,用统计的方法对信号进行分离。由于对观测信号不需要获得先验知识,所以被广泛用于定位跟踪、多输入多输出、数字水印等领域[1-9]。传统的噪声独立成份分析算法中常用的去除噪声算法主要有:偏差去除技术、极大似然估计、最大后验估计和稀疏码收缩等方法。
文献[5-6]提出了一种基于偏差消除方法用于消除观测数据中的高斯噪声。极大似然估计主要用于对混合矩阵的估计[7],然而该方法随着信号维数的增加,其计算量会迅速增长,极大地降低了算法的效率。极大后验估计和稀疏码收缩法[8-11]除了计算量的问题外还对数据的模型做了精确的假设,因而上述方法难以满足多类型噪声的环境。本文将传统的噪声独立成分分离方法推广到多类型噪声环境,利用该方法在不增加计算量的基础上可以将混有多种噪声的独立源信号分离出来。
HTML
-
无噪声独立成分混合模型是基于信号源之间相互独立且为非高斯的假设,估计信号与源信号的关系可以表示为:
式中,${\boldsymbol{s}} = {[{s_1},{s_2}, \cdots ,{s_n}]^{\rm{T}}}$是$ n$维相互独立的源信号;$x = {[{x_1},{x_2}, \cdots ,{x_m}]^{\rm{T}}}$是$ m$维观测信号;${\boldsymbol{A}}$为$m \times n$混合矩阵。为简单起见,通常假定信号源的维数和观测信号的维数相等,即$m = n$,混合问题的实质相当于线性变换,于是问题的解就变成了对矩阵${\boldsymbol{A}}$的估计。利用经典独立成分分析方法,信号源可以表示为:
式中,$W$是$n \times n$估计矩阵;$y$是$n$维相互独立的估计信号。如果预先对观测信号进行白化处理,那么估计出的信号也是白化的且均值为0。为便于分析,可以先对估计矩阵作正交化处理,即:
-
当噪声混入源信号后,相应的观测信号可以表示为:
或
如果独立的噪声成分分别加载到各自的信号源之上,即:${s'_i} = {s_i} + {n_i}$,那么所观测的噪声独立成分可以表示为:$\boldsymbol{x}'{\boldsymbol{ = }}\boldsymbol{As}'$,在这种情况下,混合矩阵的估计仍然可以通过传统的ICA分离算法得到。如果噪声协方差具有如下关系:
利用简单的数学关系可以得到此时被估计噪声的另一种表示形式:$\boldsymbol{n}' = {\boldsymbol{A}^{ - 1}}\boldsymbol{n}$。因而式 (5) 可以重写为:$\boldsymbol{x} = \boldsymbol{A}(\boldsymbol{s} + \boldsymbol{n}')$[5-6]。一般地,如果噪声成分分别加载到源信号之上,又或者噪声成分的协方差具有特定的形式,那么混合信号的估计就可以用经典的ICA分离算法得到。
然而,当噪声的类型为多种,特别是在源信号中混有冲击噪声和高斯噪声时,那么式 (4) 和式 (5) 可表示为:
和
在这种情况下,脉冲噪声会对经典的ICA分离算法有显著的影响,使得估计的分离矩阵精度难以保证,甚至失去原有的分离性能,因而对混合噪声中的脉冲成分分析是必要的。
1.1. 独立成分的混合
1.2. 噪声混合模型
-
由于对观测数据进行白化处理会使得ICA问题变得简单,因此可以对噪声成分进行白化投影处理。
设$\boldsymbol{E} = ({e_1},{e_2}, \cdots ,{e_n})$是协方差矩阵${\boldsymbol{C}_x}{\boldsymbol{ = }}\boldsymbol{x}{\boldsymbol{x}^{\rm{T}}}$对应的特征向量,且$\boldsymbol{D} = {\rm{diag}}({d_1},{d_2}, \cdots ,{d_n})$是由矩阵${\boldsymbol{C}_x}$的特征值组成的角对称矩阵,那么白化矩阵可以表示为:
因而,对观测到的噪声成分,白化处理可以表示为:
为了分析观测数据中的脉冲成分,本文提出利用基于S估计原理,构造合适的非多项式函数对观测数据进行投影处理,定义为:
式中,$\boldsymbol{B}$是一个与白化向量$\boldsymbol{z}$无关的可逆矩阵;$\boldsymbol{w}$和$\lambda $是常数;$w$为随机型单位向量。由式 (11) 可以得到非多项式函数的另一种表示形式为:
式中,${K_0},{K_1}$是常数。从式 (12) 可以看出,利用非多项式函数对观测数据进行投影,其实质是分析${\left\| {F(z,\boldsymbol{w})} \right\|^2}$。为了减少脉冲噪声对投影结果的影响,非多项式函数应该有界或者随着$\left| \boldsymbol{z} \right|$的增长其对应值不应增长过快[12-13]。如果选择合适的基于S估计的非多项式函数,根据稳健估计特性,那么脉冲噪声可从观测数据中分辨出来。一个合适的非多项式函数应该具有如下特点:
1) 非多项式函数$ g$连续并且在统计上不应该有困难。2) $ g$函数必须抓住噪声数据分布中在计算投影时的数据部分。
根据S估计的理论基础,并结合仿真试验,本文给出了两个用于数据投影的非多项式函数:
式中,$\xi = {\boldsymbol{w}^{\rm{T}}}z$;$a,{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} b$是常数,选取为$1 \le a \le 4$,$1 \le b \le 2$;$ c$是一个与投影数据有关的阈值,其值为:
式中,$ l$为观测数据的样本长度。当投影数据满足:
此时观测数据中的成分${x_{ik}}(i = 1,2, \cdots ,l)$被估计为脉冲噪声。
-
由于阈值是随观测数据而变化,实验表明观测数据中如果脉冲噪声不太严重,又或者脉冲噪声为稀疏型分布的情况下,式 (16) 具有良好的检验性能。由式 (16) 的结果仅能判断数据脉冲噪声的存在性,为了消除脉冲噪声对分离性能的影响,本文给出了去除脉冲噪声并重构数据的方法为:
实验表明,式 (17) 对于平稳型数据具有良好的处理效果,而式 (18) 处理超高斯型数据中的脉冲噪声问题时效果显著。式 (17) 和式 (18) 是基于观测数据含有脉冲噪声而提出的,当数据中没有脉冲噪声时,上述处理方法仍然有效。由于进行了平均运算,其作用机理相当于滤波,因此不会对源数据有实质的影响。
-
通过上述分析,可以得到关于多类型噪声环境中的独立成分分析的分离算法:
1) 对观测的噪声数据中心化处理使其均值为0;
2) 利用式 (10) 对数据进行白化处理;
3) 选择初始化任意单位向量$\boldsymbol{w}$;
4) 利用合适的非多项式函数,如式 (13)、式 (14) 对观测数据进行投影,并计算阈值$ c$;
5) 当${\left\| {F({z_k},\boldsymbol{w})} \right\|^2} \ge c$,则${x_{ik}}(i = 1,2, \cdots ,l)$被判断为脉冲噪声;
6) 利用式 (17) 或式 (18) 去除脉冲噪声并重构数据;
7) 利用噪声ICA分离算法迭代:
其中,$f(u) = \tanh (u)$,或$f(u) = u\exp \left( { - \frac{{{u^2}}}{2}} \right)$;
$\tilde \sum = {(\boldsymbol{C} - \sum )^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}\sum {(\boldsymbol{C} - \sum )^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}$,$\boldsymbol{C} = \boldsymbol{x}{\boldsymbol{x}^{\rm{T}}}$,$\sum $为高斯噪声的方差。
8) 单位化迭代结果$\boldsymbol{w} \leftarrow \frac{\boldsymbol{w}}{{\left\| \boldsymbol{w} \right\|}}$;
9) 如果仍未收敛,则返回步骤7)。
2.1. 非多项式函数
2.2. 脉冲噪声的消除
2.3. 多类型噪声中的分离算法
-
为了分析算法的有效性,本文利用混有高斯白噪声和脉冲噪声的超高斯和次高斯信号进行仿真分析。观测信号由式 (7) 或者式 (8) 给出。为了便于比较,所有的实验中高斯噪声协方差矩阵设定为${\rm{1}}{\rm{.113 3 }}\boldsymbol{I}$,混合的脉冲噪声为:
所有的实验中混合矩阵$\boldsymbol{A}$随机产生,观测信号的白化处理由式 (10) 给出,用于分析混合噪声中的脉冲成分,非多项式函数可以选取式 (13) 或式 (14),而阈值的计算则由式 (15) 得到。
此外,为公平起见,用于实验的源信号、参数设置一致。为了评价算法的分离性能,本文引入了Amari指数[14]进行分析,其计算可以表示为:
式中,${p_{ij}}$为矩阵$\boldsymbol{P}{\boldsymbol{ = }}\boldsymbol{WA}$的$ i$行,$ j$列元素;$\boldsymbol{W}$是经过分离算法给出的分离矩阵;$\boldsymbol{A}$是随机产生的混合矩阵。根据文献[14]的结论,指数${I_A}$的值越低,分离的效果越好,当$10\log {I_A} < - 10$,表明对源信号成功分离。为了保证分离效果的真实性,所有仿真结果均进行100次蒙特卡洛试验。
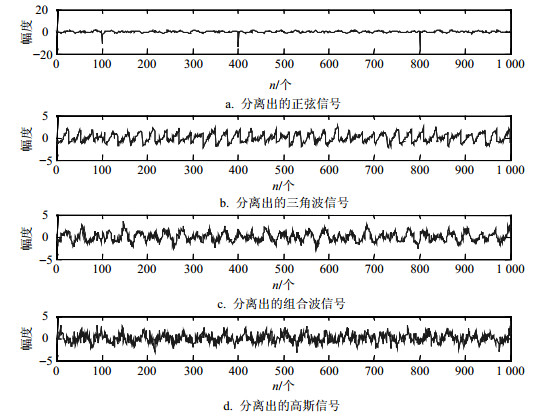
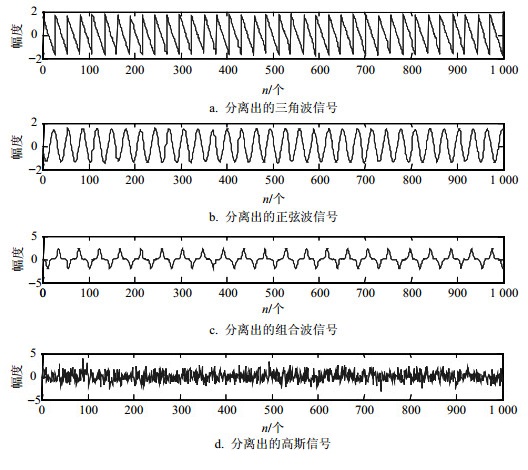
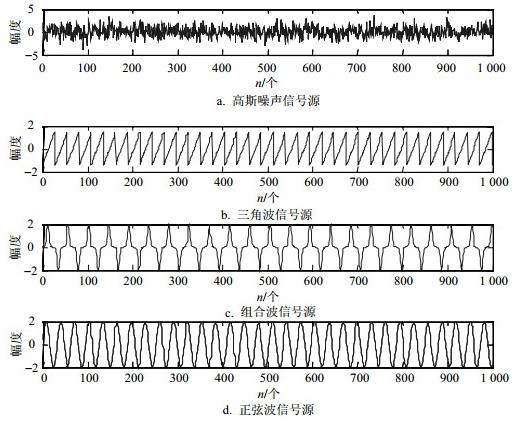
首先,本文对传统的噪声ICA算法和本文提出的多类型噪声ICA算法在源信号混有高斯白噪声和脉冲噪声的情况下进行比较。3种用于仿真的源信号为三角波信号、由多种不同频率正弦波叠加的信号、正弦信号,其幅值分别为1.8、2、2,图 2和图 3分别给出了分离信号的结果。
从分离结果可以看出,当混入脉冲噪声成分时,传统的噪声ICA算法失去了应有的性能,此时虽然算法整体上仍然具有收敛性,然而其分离出的信号已经失去意义。相比之下,由图 3可以看出,本文提出的算法能够成功分离出相应的源信号。
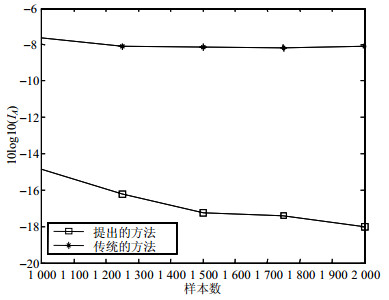
图 4显示了两种算法在多类型噪声的环境中随信号样本数量增长的分离性能结果。
仿真结果显示,本文提出的算法随着样本数量增加,分离性能提高;然而,由于未考虑到脉冲噪声的影响,即使增加信号样本数量,传统的噪声ICA算法仍然无法成功分离源信号。
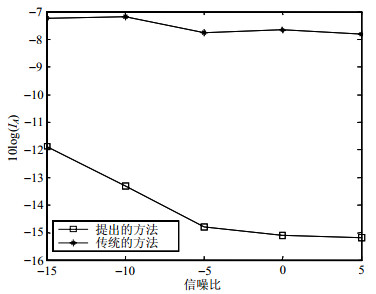
图 5给出了两种算法在不同信噪比下的分离性能。
可以看出,本文的算法性能随信噪比的增加而改善。虽然传统的噪声ICA算法的性能随信噪比的增加而局部改善,然而由于脉冲噪声影响,使得估计矩阵的精度大幅度降低,甚至导致算法无法收敛,即使收敛,分离的结果仍不能满足分离信号的要求。
-
本文提出了一种用于在多类型噪声环境中的独立成分分离算法。利用S估计原理给出了用于分析脉冲噪声的非多项式函数,并提出了脉冲噪声的阈值估计及脉冲噪声的去处和重构信号的方法。仿真结果表明,本文提出的算法能够在多类型噪声中实现对独立成分的分离,并显示出良好的性能。

 ISSN
ISSN 










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: