-
HVDC输电线路区内外故障快速识别是实现故障保护的前提,以电压变化率du/dt为核心判据的直流线路行波保护受过渡电阻影响较大,往往不能有效判别区内高阻接地故障与区外故障[1-2]。文献[3]提出采用理论计算电压和实测电压的相关性来区分输电线路区内外故障,该方法可以实现输电线路区内外故障的快速诊断,但所需时间相对较长。由于区内外故障空间位置不同,因此信号传至保护安装处所经历的元件不同。在平波电抗器、直流滤波器等元件的作用下,直流电流信号中不同的频率成份的衰减程度差别较大。文献[4-5]对直流电流的暂态特性进行了研究,分别提出了多分辨奇异谱熵和支持向量机以及多重分形谱方法来判别区内外故障。上述方法可以准确实现区内外故障的判别,但相对复杂。本文在上述研究的基础上,采用频带能量比法实现区内外故障的快速判别。该方法采用总体经验模态分解法(EEMD)对HVDC系统故障时的直流电流信号进行分解,将信号分解为几个固有模态分量(IMF)之和,计算各模态能量,通过对比分析,找出特征区别,考虑一定的裕度,定义能量比判据指标,实现区内外故障快速识别。该方法仅需要直流电流信号,计算方法简单,能够满足选择性和快速性等要求。通过在PSCAD平台下对大量的故障进行模拟仿真,验证了该方法的可行性和鲁棒性。
HTML
-
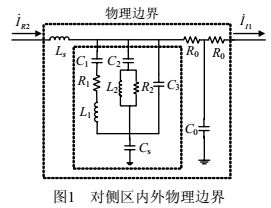
由于直流输电线路区内外故障在平波电抗器、直流滤波器的两侧,在其作用下,直流电流所含有的频率成份差别较大[5]。由直流滤波器和平波电抗器构成了直流输电线路区内外的物理边界[6]。若以直流输电系统逆变侧保护安装处的直流电流信号为分析对象,则对侧区外出现故障时,暂态电流传变至逆变侧保护安装处所经历的路径中有平波电抗器、直流滤波器以及整条直流输电线路的分布电感和电容。因此,对侧区内外物理边界如图 1所示。
当本侧区外出现故障时,故障处的暂态电流传至逆变侧保护安装处所经历的路径中仅有直流滤波器和平波电抗器。因此,本侧区内外物理边界如图 2所示。
由于整流侧与逆变侧平波电抗器、直流滤波器结构和参数大致一样,因此,对侧区外和本侧区外物理边界差别主要在于直流线路参数。由于线路有分布电容和电感,一定程度上对直流电流信号有滤波作用,必将导致两者传至保护安装处的频率成份具有差别。
为了得到本侧和对侧区内外物理边界的幅频响应,本文采用TLS-ESPRIT辨识方法[7]得到本侧和对侧物理边界的传递函数,进而求取幅频特性。具体操作是,断开两侧电源,在图 1和图 2组成的元件一端施加激励电源,另一端接地。测量得到输入的电压和输出的电压信号,采用辨识方法,最终得到本侧和对侧的传递函数分别为:
根据本侧和对侧传递函数,分别得到幅频特性曲线如图 3、图 4所示。
由图 3、图 4可以看出,无论是本侧还是对侧区外,平波电抗器和直流滤波器对高频信号都具有较大的衰减作用。对比图 3和图 4得出,由于对侧区外故障,直流电流所经历的物理边界除了本侧的直流滤波器和平波电抗器外,还包含了整条输电线路,由于直流线路分布电感、电容的存在,导致对侧区外高频信号衰减情况明显高于本侧区外。对侧区外幅频特性曲线基本上呈线性衰减,本侧区外时,在100 rad/s之前几乎无衰减,之后呈迅速衰减趋势。基于此差别,采用频谱分析的方法,可以实现本侧区外、对侧区外以及区内故障的判别。
-
经验模态分解(EMD)[8]的基本原理是将任何时间序列信号视为由一些互不相干、简单非正弦的信号分量组合而成。具体算法步骤如下:
1) 寻找信号x(t)的所有极值点,形成上下包络线xh(t)和xL(t),计算平均值m(t)为:
2) 设变量h(t)为:
若h(t)满足IMF的标准,则其视为第一个IMF,记为c1(t),否则将其视为原信号,重复步骤1)和步骤2)k次直到满足要求为止,最后得:
筛选IMF的终止准则表述为:
当SD位于0.2~0.3之间时,则终止筛选。
3) 得到信号的第一个IMF分量${c_1}(t) = {h_{1k}}(t)$及剩余信号${r_1}(t) = x(t) - {c_1}(t)$。
4) 将r1(t)其视为原始新信号,重复步骤1)~步骤3),得出所有的IMF分量。则原始信号可表示为:
由于EMD分解算法本身的问题,在对一般正常的信号处理是有效的,而对异常信号计算出的IMF分量就会出现模态混叠现象,从而使分解出来的IMF分量失去物理意义。文献[9]在EMD算法基础上进行改进,提出在待分析的原始信号上加入白噪声,实现信号光滑性。由于白噪声是0均值的,因此通过多次加入白噪声,然后再对其EMD分解,最后对IMF分量求平均即可消除这种添加的0均值白噪声的影响,进而形成EEMD算法[9]。
-
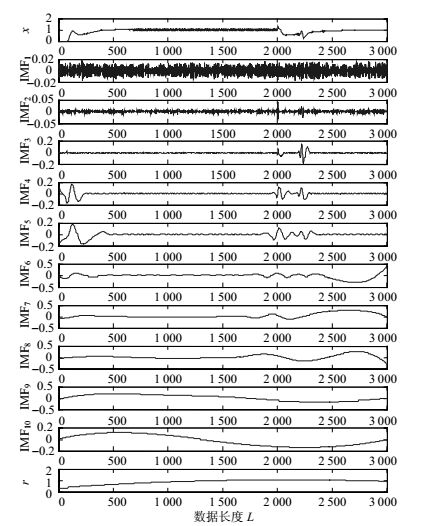
对HVDC系统进行故障仿真,故障发生时刻设置为1 s,持续0.05 s后故障切除,分别测得HVDC系统直流线路对侧区外、本侧区外以及区内故障时的逆变侧直流电流信号。采用EEMD方法对其进行分解,得到10个IMF分量。以直流线路对侧区外故障时的直流电流信号为例,分解结果如图 5所示。
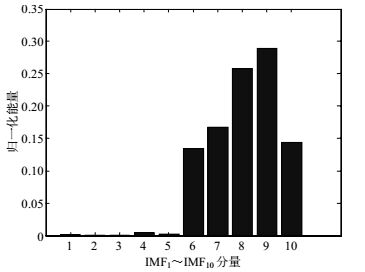
计算归一化的各频带能量,得到能量分布如图 6所示。为了与本侧区外、区内以及系统正常运行情况进行对比,本文采用同样方法,得到本侧区外以及系统正常运行情况下的直流电流能量分布图,如图 7~图 9所示。
对图 6~图 9进行全面的分析与对比,可以得到如下特征区别:
1) 正常运行时,电流成份比较单一,主要集中在IMF1~IMF4分量,IMF6~IMF10分量几乎为0。故障时,IMF6~IMF10相对较大,而IMF1和IMF2分量几乎为0,这是正常与故障的最大区别。
2) 区内故障时,频带中主要含有IMF8分量,其能量值占总体的一半左右。
3) 对侧区外故障,主要成份为IMF6~IMF10分量,并且相对比较均匀。本侧区外故障时,频带中主要成份为IMF9分量,其他分量很小。
由上述特征区别,结合定量分析,确定正常、区内外故障的判据。正常运行时,IMF1是其频带能量中最大值,并且占其总值的1/2以上,而故障时,IMF1很小,尤其是区外故障时,几乎为0。另外,为了避免单一分量受外界因素的影响,降低指标的鲁棒性,在考虑一定的裕度下,增加了IMF2分量。最终,定义k0指标来区别正常与故障:
当满足指标k0时,则可判定系统处于正常运行状态。
区内故障时,频带中主要含有IMF8分量,其他分量很小,IMF8分量占总体的一半左右。而区外故障时,IMF8分量占总体的比值相对较小。由于区内故障时,故障位置不一样,其物理边界虽然不含有直流滤波器和平波电抗器,但是由于直流输电线路的作用,其频带分布会有微小的差别,尤其对侧区内和本侧区内相比,其物理边界多了整个直流输电线路的作用。因此,本文在选指标的时候,分别得到对侧区内故障的频带分布和本侧区内故障的频带分布,求取平均值,并考虑一定的裕度,得到区内外故障判别指标k1为:
当满足指标k1时,则可判定区内故障,否则为区外故障。本侧区外故障时,频带能量主要集中在IMF9分量,其占总体比值的一半以上,考虑一定的裕度,定义k2指标来实现对侧区外和本侧区外故障的判别:
当满足指标k2时,可判定为本侧区外故障,否则为对侧区外故障。由此得出,区内外故障的逻辑判断流程如图 10所示。
-
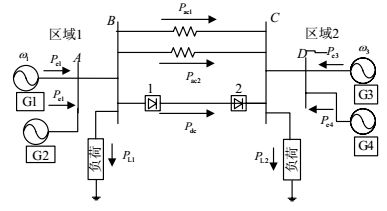
以四机两区域交直流并联系统为仿真算例,系统结构如图 11所示。
区域1和区域2各有两个等值电势源,稳态运行时,交流线路单回传输功率${P_{{\rm{ac}}1}} = {P_{{\rm{ac}}2}} = 103\;{\rm{MW}}$,直流传输有功功率为 ${P_{{\rm{dcref}}}} = 198\;{\rm{MW}}$ ,负荷 ${P_{{\rm{L}}1}} = 302\;{\rm{MW}}$ ,负荷 ${P_{{\rm{L}}2}} = 556\;{\rm{MW}}$ 。控制方式为整流侧定电流控制,逆变侧定电压控制。
为验证本文方法的有效性,分别对系统正常运行和多种故障类型情况进行仿真分析。正常运行情况下,分别对系统结构、电源数量对结果的影响进行仿真分析。故障情况下,分别对故障位置、故障过渡电阻和量测噪声对结果的影响进行仿真分析。
仿真分析1,正常运行情况仿真,仿真结果如表 1所示。
电网结构 系统容量 k0 Ns1 Nv1 0.80 Nv2 0.70 Ns2 Nv1 0.83 Nv2 0.54 1) 系统结构描述,图 11所示电网结构(Ns1),切除一条交流输电线路(Ns1);
2) 电源数量,4个电势源运行(Nv1),两个电势源运行(Nv2)。
仿真分析2,过渡电阻对算法的影响仿真,仿真结果如表 2所示。
故障位置 过渡电阻 k0 k1 k2 Dp1 r1 0.002 2 0.257 4 0.288 6 r2 0.001 5 0.158 5 0.331 0 Dp2 r1 0.005 4 0.604 0 r2 0.001 6 0.654 8 Dp3 r1 0.002 9 0.521 8 r2 0.000 3 0.525 7 Dp4 r1 0.001 7 0.701 5 r2 0.004 0 0.382 2 Dp5 r1 0.000 9 0.070 4 0.826 9 r2 0.001 6 0.230 5 0.479 5 1) 故障位置位于对侧区外(Dp1),对侧区内(Dp2),中间位置(Dp3),本侧区内(Dp4),本侧区外(Dp5);
2) 故障过渡电阻设定为两种类型,金属性接地故障,电阻0.005 Ω(r1),高阻接地故障,过渡电阻50 Ω(r2)。
仿真分析3,量测噪声对算法的影响仿真。
为进一步验证算法的鲁棒性,本文在理想测量信号基础上分别叠加信噪比30 dB(SNR1)和60 dB(SNR2)的随机噪声,形成含量测噪声的电气量信号。根据上述算法,得到仿真结果如表 3所示。
故障位置 信噪比 k0 k1 k2 Dp1 SNR1 0.004 7 0.269 0 0.298 3 SNR2 0.005 9 0.178 8 0.320 8 Dp2 SNR1 0.002 4 0.672 1 SNR2 0.002 1 0.603 9 Dp3 SNR1 0.007 4 0.547 6 SNR2 0.001 5 0.507 5 Dp4 SNR1 0.003 6 0.681 2 SNR2 0.004 0 0.393 1 Dp5 SNR1 0.004 2 0.069 5 0.762 3 SNR2 0.003 0 0.263 5 0.576 1 由表 1~表 3的仿真结果得出,本文算法受过渡电阻和量测噪声的影响较小,从而证明该算法能够满足选择性的要求,且鲁棒性较好。
-
采用频谱特性分析方法对HVDC区内外故障判别进行了研究,由于故障位置不同,其形成的物理边界存在区别,直流电流信号经EEMD分解后各IMF分量具有明显的特征区别,通过对能量分布图的详细比较,选取了3个能量指标,通过这3个指标可以判别正常运行、直流线路区内、对侧区外以及本侧区外故障。通过在四机两区域模型下不同工况多种故障类型进行仿真分析,结果验证了该方法的可行性。通过研究得到较为有意义的结论如下:
1) 正常运行时,电流成份比较单一,主要集中在IMF1~IMF4分量,其他分量几乎为0;
2) 故障时电流成份主要集中在IMF6~IMF10分量,其他成份几乎为0;
3) 系统容量、电网结构、过渡电阻以及量测噪声对该方法影响较小,因此具有较强的鲁棒性;
本文方法仅需要单侧电气量信息,简单易实现,且鲁棒性较好,能够满足选择性和速动性的要求。因此,该研究结果对直流线路故障保护具有一定的参考价值。

 ISSN
ISSN 
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: