-
随着计算机技术、通信技术与传感技术之间的深度渗透以及智能终端设备的日益普及,为可穿戴式传感器的研究提供了有力的技术支撑和广阔的市场前景,其应用领域涉及体育[1]、游戏[2]、医疗[3]和科研[4-5]等。具备触觉感知功能的可穿戴电子设备是当今的研究热点之一,触觉作为人体最大的感官系统,在信息交互和传感认知过程中具有重要的作用[6-8]。将触觉传感器集成于可穿戴设备实现对用户生理参数检测并快速、准确地做出健康评估,亦或是智能机器人通过穿戴这类柔性电子仿生皮肤可以更加灵活、全面地完成人机交互[9-10]。
触觉力感知为触觉传感器范畴中最常见的一种,为克服以硅基体或光电式等触觉力传感器存在柔性差、不易穿戴等缺点,填充型高分子柔性导电复合材料,尤其碳系填料,因具备加工性好、工艺简单、电阻率易于调节等优点在柔性电子仿生皮肤研究中得到广泛应用。炭黑具有价格低廉及良好的力学特性,碳纳米管因较大的长径比呈现较低的渗流阈值,被应用于力敏复合材料研究中。为进一步提升力敏传感器的穿戴舒适度和力学特性,本文将形状和尺寸各异的炭黑/碳纳米管两相填料并用填充硅橡胶(CB/CNTs/SR)制备力敏复合材料,提出了一种表面具有微圆顶阵列结构特点的柔性、可穿戴触觉传感器。
HTML
-
通过在导电复合材料表面构造微结构可以提升触觉传感器的力敏特性[11-13],本文基于3D打印技术和硅橡胶流体成型特点制备了微圆顶结构柔性触觉传感器。图 1为微圆顶结构触觉传感器结构及传感机理示意图,图 1a为触觉敏感单元,选用CB/CNTs/SR为力敏复合材料,与叉指型电极接触面留有微圆顶状触头阵列;图 1b为单个微圆顶结构及受力时敏感机理示意图,压阻式触觉力敏感单元的输出电阻由体电阻和接触电阻组成,触觉力作用下,微圆顶阵列结构与电极接触状态由点-面接触转为面-面接触。同时力敏复合材料受力被压缩,隧道效应增强,导电填料间形成导电通路,两者间的协同作用共同构成了触觉感知机理。为进一步研究本文的微圆顶结构柔性触觉传感器在触觉力作用下的应变特点,借助ANSYS有限元仿真软件进行模拟,图 1c和图 1d分别是微圆顶触觉传感器受力时应力和形变结果。
-
力敏复合材料和微圆顶阵列结构触觉传感器制备方式采用溶液共混法,具体制备流程如图 2所示。填料为CB3100型炭黑(瑞士SPC公司,平均粒径约为30 nm,电阻率约为8×10-3Ω·cm)、TNM5型碳纳米管(中国科学院成都有机化学有限公司,平均长度约为20 μm,电阻率约为3~6×10-2Ω·cm),母体选GD401室温硫化硅橡胶(中昊晨光化工研究院有限公司),依次取质量分数3%的炭黑和2%碳纳米管于烧杯中并加入适量分散剂,使用超声波材料分散仪进行超声分散10 min,并利用磁力搅拌机对悬浮液均匀搅拌20 min。加入硅橡胶并均匀搅拌30 min,使得炭黑/碳纳米管均匀分散在母体中,分散剂充分挥发。经抽真空处理除去CB/CNTs/SR溶液因搅拌混入的气泡后,将复合材料注入基于3D打印技术制备具有微圆顶特征的模具,并置于恒温箱中固化成形,脱模后可获得微圆顶触觉传感器。
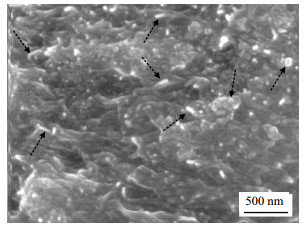
为表征双相填料并用在母体中的分散情况,测试了如图 3所示的炭黑/碳纳米管/硅橡胶复合材料电子扫描显微镜图。在CB/CNTs/SR导电复合材料中,CNTs分布在CB团聚体之间,通过SR分子链将其连接起来,使得CB和CNTs在硅橡胶基体中的分散性得到大幅度的改善。CB和CNTs双相导电填料并用会在导电橡胶体系中产生“协同效应”[14],CB和CNTs形成“葡萄串”结构,CNTs可以看作葡萄串的梗,起到连接、固定分散的CB颗粒的作用。硅橡胶基体的橡胶分子链作为骨架,与CNTs和CB形成的葡萄串结构相互交错,协同补强,将CB颗粒间的点-点接触及CNTs间的线-线接触优化为三维立体状接触网络,有利于力的传递和导电通路的形成。炭黑/碳纳米管并用产生的“协同效应”增强了导电复合材料的力学强度,并易于构成稳定的导电网络。
1.1. 传感器结构设计
1.2. 力敏材料及传感器制备
-
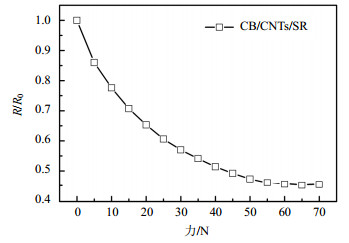
使用LS-WD-100型微机控制电子万能试验机(深圳力森科技有限公司)对本文提出的微圆顶阵列结构柔性触觉传感器在0~70 N范围内进行压力加载实验。图 4为微圆顶触觉传感器力敏特性测试平台,测试过程中,以5 N为步进,记录对应加载力作用下微圆顶阵列结构触觉传感器输出电阻值,其力敏特性测试结果如图 5所示,R为传感器受力作用时输出电阻值,R0为初值电阻值。
-
足部信息尤其足底压力的时空分布,对于鞋类设计与舒适度评估、运动员训练、步态分析以及诸如帕金森症、内外八字、糖尿病足等疾病的诊疗、预判等均具有重要的意义[15-16]。
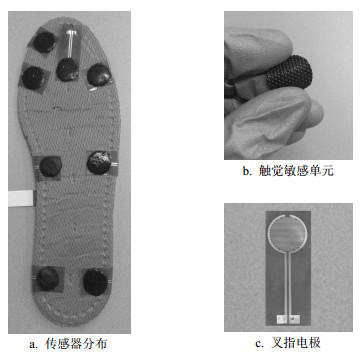
为了拓展本文的微圆顶阵列结构柔性触觉传感器应用范围,将该微圆顶阵列结构的触觉传感器集成于鞋垫进行足底压力分布测试,根据足底受力特点[17],压敏单元在足底分布如图 6a所示;图 6b为本文的微圆顶阵列结构触觉敏感单元实物图,可以看出,该力敏单元具有轻薄、柔软等特点;图 6c为基于柔性印刷电路板技术制备的叉指型电极,将力敏传感单元粘接在其表面制备成柔性压力传感器,力敏传感单元和电极良好的柔软性共同保证了触觉传感器的穿戴舒适性。
为提升足底压力检测系统的便携性,本文基于高性能、低功耗微处理器CC2530和多通道模数转换器LTC2495构建足底压力信息采集系统,其系统工作流程如图 7所示。
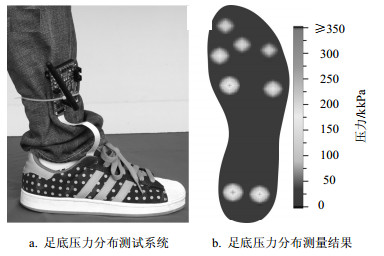
用户通过图 8a所示的穿戴该便携式数据采集系统可实时监测足底压力时空分布特点,并于如图 8b所示的LabVIEW上位机进行图形化显示。
2.1. 传感特性
2.2. 触觉感知实验
-
为提升触觉传感器穿戴舒适度和力敏特性,基于炭黑/碳纳米管/硅橡胶复合材料制备了一种具有微圆顶阵列结构特点的柔性可穿戴触觉传感器。阐述了微圆顶触觉传感器的结构特点、制备流程,并结合ANSYS分析其触觉感知机理。对触觉传感器进行力敏特性表征实验并进行足底压力分布感知应用,可用作穿戴触觉传感器实现柔性触觉感知。

 ISSN
ISSN 














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: