Latest Articles
Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes/issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023124
Abstract:
Semantic segmentation is currently one of the basic technologies in the field of scene understanding. Existing semantic segmentation networks usually result in complex structures, a large number of parameters, excessive loss of image feature information, and low computational efficiency. To address these problems, this work proposes a lightweight semantic segmentation network named MLWP-Net (Multi-Link Wavelet-Pooled Network) which combines features with multiple connections and wavelet pooling based on the encoder-decoder framework and discrete wavelet transform (DWT). In the encoding phase, a lightweight feature extraction bottleneck was designed by combining with the depthwise separable convolution, dilated convolution, and channel compression, using a multi-link strategy to fuse multi-level features; besides, a low-frequency-mixed wavelet pooling operation was employed to replace the traditional downsampling operation for effectively reducing the information loss during the encoding process. In the decoding stage, a multi-branch parallel dilated convolutional decoder is designed to fuse multiple features linked to the different layers in the encoder to recover the image resolution in parallel. The experimental results show that our MLWP-Net achieves 74.1% and 68.2% mIoU segmentation accuracy on the datasets of Cityscapes and Camvid with only 0.74M parameters, which demonstrates its effectiveness for semantic segmentation.
Semantic segmentation is currently one of the basic technologies in the field of scene understanding. Existing semantic segmentation networks usually result in complex structures, a large number of parameters, excessive loss of image feature information, and low computational efficiency. To address these problems, this work proposes a lightweight semantic segmentation network named MLWP-Net (Multi-Link Wavelet-Pooled Network) which combines features with multiple connections and wavelet pooling based on the encoder-decoder framework and discrete wavelet transform (DWT). In the encoding phase, a lightweight feature extraction bottleneck was designed by combining with the depthwise separable convolution, dilated convolution, and channel compression, using a multi-link strategy to fuse multi-level features; besides, a low-frequency-mixed wavelet pooling operation was employed to replace the traditional downsampling operation for effectively reducing the information loss during the encoding process. In the decoding stage, a multi-branch parallel dilated convolutional decoder is designed to fuse multiple features linked to the different layers in the encoder to recover the image resolution in parallel. The experimental results show that our MLWP-Net achieves 74.1% and 68.2% mIoU segmentation accuracy on the datasets of Cityscapes and Camvid with only 0.74M parameters, which demonstrates its effectiveness for semantic segmentation.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022358
Abstract:
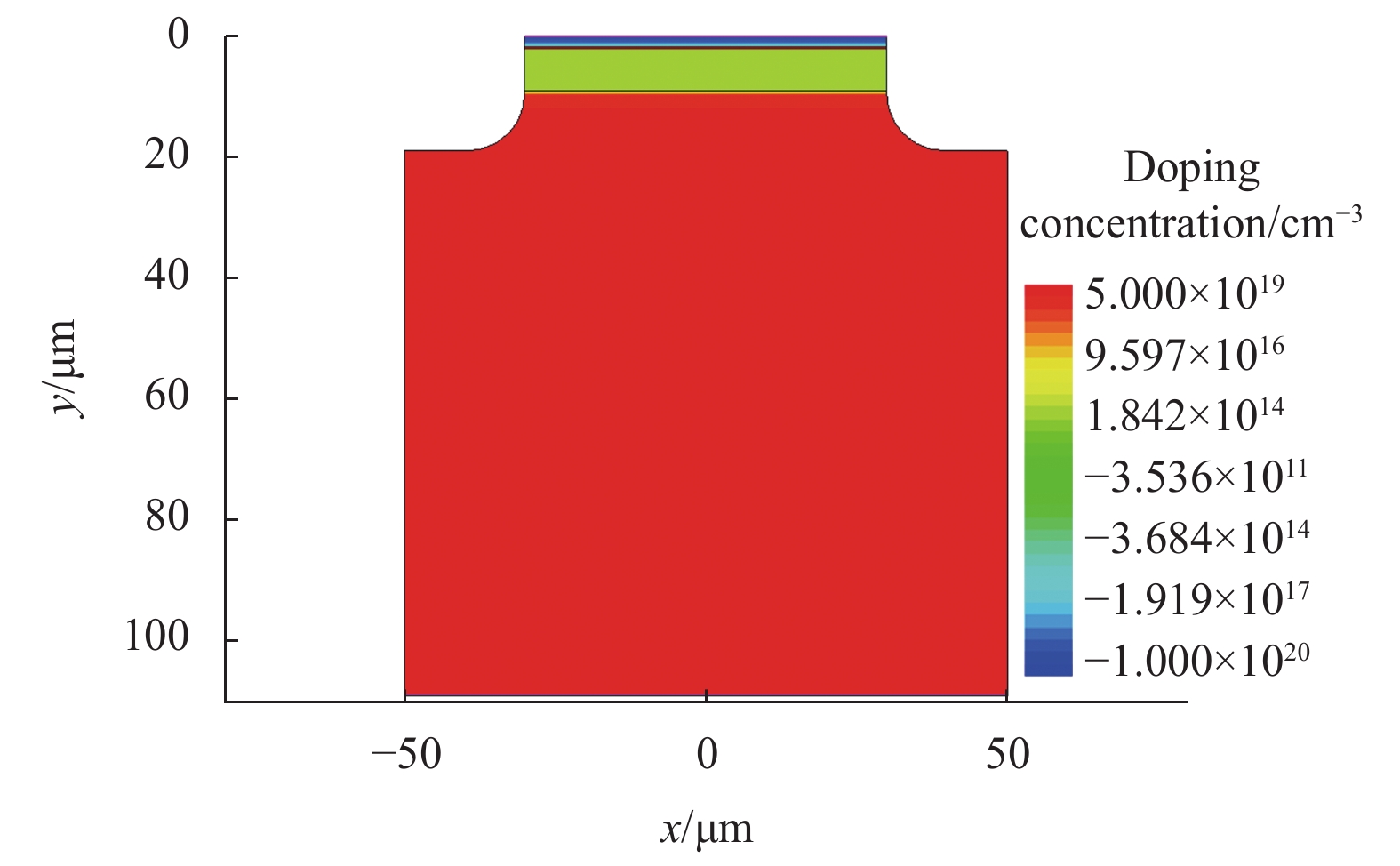
In this paper, a PIN diode model is established through TCAD device modeling, and a High-Power Microwave (HPM) coupling simulation circuit is built on a PIN limiter to simulate effects of HPM. The transient voltage response of the PIN limiter under different HPM frequencies are obtained by simulation, as well as the internal electric field, carrier and junction temperature distribution of the PIN diode. The simulation results show that the flat-top leakage negative voltage of PIN limiter decreases with the increase of HPM frequency, and the flat-top leakage forward voltage of PIN limiter decreases with the increase of HPM frequency. The limiting capability of the PIN limiter inside the PIN diode first increases and then decreases with the increase of the microwave frequency. When the HPM frequency is low, the internal lattice temperature accumulation of the PIN diode is concentrated at the interface of the I layer. Therefore, the HPM damage sensitive position of the PIN limiter varies with frequency.
In this paper, a PIN diode model is established through TCAD device modeling, and a High-Power Microwave (HPM) coupling simulation circuit is built on a PIN limiter to simulate effects of HPM. The transient voltage response of the PIN limiter under different HPM frequencies are obtained by simulation, as well as the internal electric field, carrier and junction temperature distribution of the PIN diode. The simulation results show that the flat-top leakage negative voltage of PIN limiter decreases with the increase of HPM frequency, and the flat-top leakage forward voltage of PIN limiter decreases with the increase of HPM frequency. The limiting capability of the PIN limiter inside the PIN diode first increases and then decreases with the increase of the microwave frequency. When the HPM frequency is low, the internal lattice temperature accumulation of the PIN diode is concentrated at the interface of the I layer. Therefore, the HPM damage sensitive position of the PIN limiter varies with frequency.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023064
Abstract:
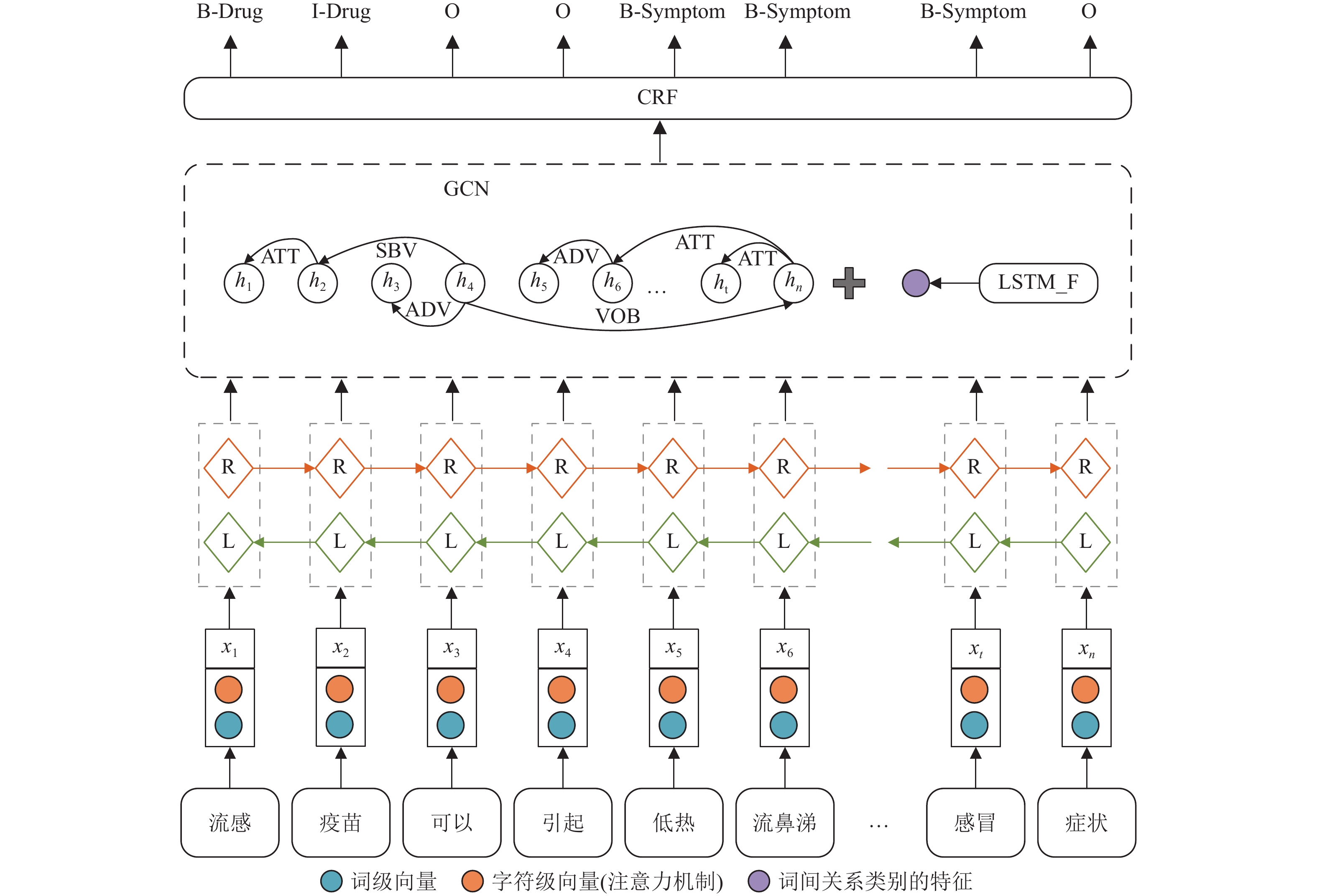
Entities such as drug names are difficult to identify accurately in Chinese medical questioning texts due to the frequent occurrence of colloquial irregular expressions and jargon. To make full use of the important role of inter-word relations in Chinese sentences, a medical named entity recognition model for enhancing global information is proposed. The model enhances the word embedding representation using an attention mechanism and enriches the global information representation of sentences in two ways simultaneously, based on the use of the sequence processing capability of bidirectional long and short-term memory networks to obtain contextual information. Firstly, a graphical convolutional network layer was constructed to enrich inter-word dependencies based on syntactic relationships to obtain additional dependencies between words; secondly, an auxiliary task was constructed to predict the class of syntactic dependencies between words. Experimental results on the Chinese medical consultation dataset show that the model is very competitive, with an F1 value of 94.54%. Significant improvements were achieved in the recognition of entity classes such as drugs and symptoms compared to other models. Experiments on the Weibo public dataset also show that the model has general-domain applications.
Entities such as drug names are difficult to identify accurately in Chinese medical questioning texts due to the frequent occurrence of colloquial irregular expressions and jargon. To make full use of the important role of inter-word relations in Chinese sentences, a medical named entity recognition model for enhancing global information is proposed. The model enhances the word embedding representation using an attention mechanism and enriches the global information representation of sentences in two ways simultaneously, based on the use of the sequence processing capability of bidirectional long and short-term memory networks to obtain contextual information. Firstly, a graphical convolutional network layer was constructed to enrich inter-word dependencies based on syntactic relationships to obtain additional dependencies between words; secondly, an auxiliary task was constructed to predict the class of syntactic dependencies between words. Experimental results on the Chinese medical consultation dataset show that the model is very competitive, with an F1 value of 94.54%. Significant improvements were achieved in the recognition of entity classes such as drugs and symptoms compared to other models. Experiments on the Weibo public dataset also show that the model has general-domain applications.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022309
Abstract:
The modernization of social governance requires a complex system approach to manage the social issues. This article made a brief introduction on the fundamentals of complex systems at the beginning, and then focused on their applications in typical scenarios of social governance including epidemic prevention and control, rumor control, intelligent transportation and smart fire safety, finally the current challenges as well as the future perspectives on the emerging governance techniques were summarized.
The modernization of social governance requires a complex system approach to manage the social issues. This article made a brief introduction on the fundamentals of complex systems at the beginning, and then focused on their applications in typical scenarios of social governance including epidemic prevention and control, rumor control, intelligent transportation and smart fire safety, finally the current challenges as well as the future perspectives on the emerging governance techniques were summarized.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022070
Abstract:
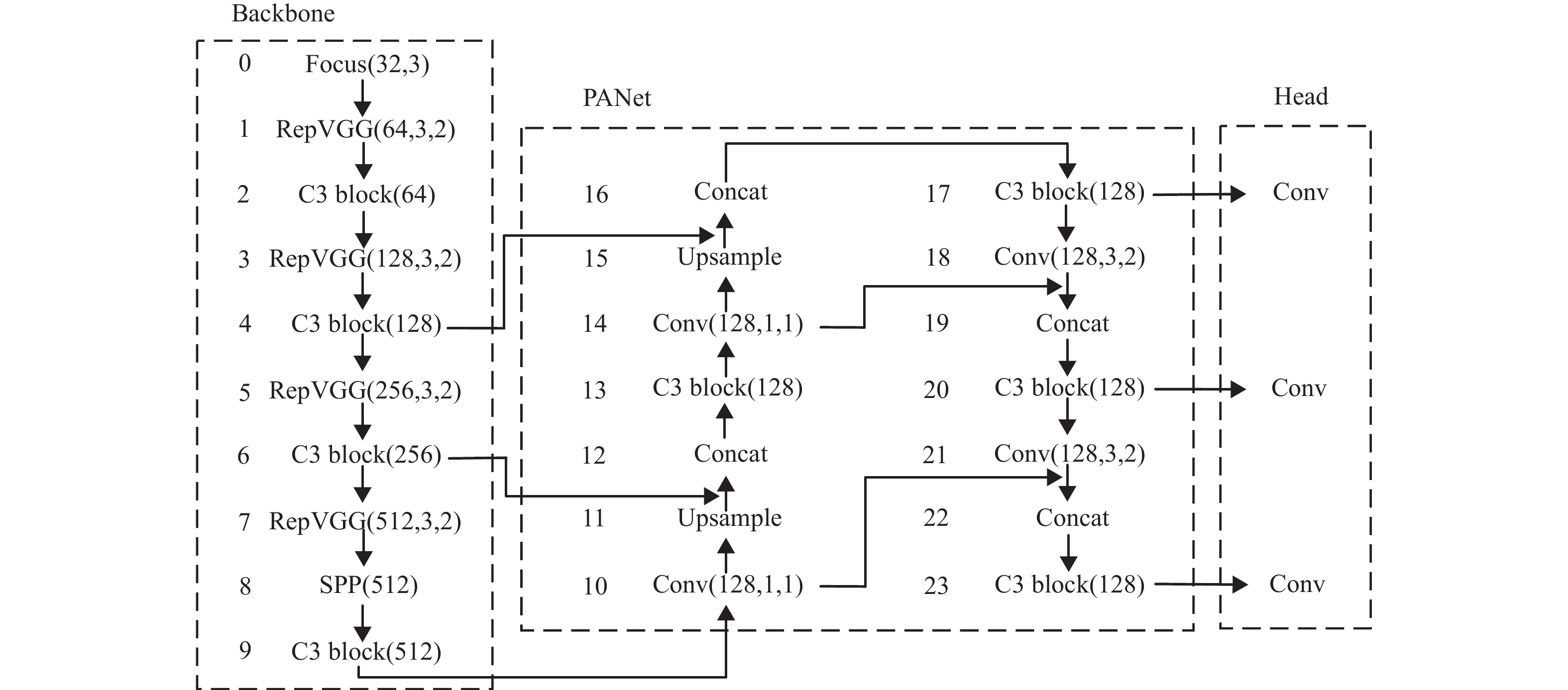
Infrared aerial object detection has been widely used in transportation, agriculture, military security, and other areas. The main challenges are small objects, mutual occlusion, little texture information, weak edge features, and large deformation of non-rigid bodies. To address these problems, based on YOLOv5 and structural re-parameterization (Rep), an improved object detection network Rep-YOLO is proposed for infrared aerial object detection. Firstly, the RepVGG module is introduced in the backbone network to improve the model feature extraction capability. During the model inference, the branches of the RepVGG module are structurally re-parameterized to reduce the branch and the complexity of the network structure. Secondly, the path aggregation network (PANet) in the neck of the detection network is improved by combining the priori feature, to increase the accuracy and speed balance capability. Finally, experiments are conducted on two publicly available infrared datasets, showing that the algorithm can effectively detect aerial infrared objects. Compared with the baseline (YOLOv5s), the statistical results on ComNet dataset show the mean average precision (mAP) is increased by 5.9%, while the parameters and model size are reduced by about 29.7% and 23.2%, respectively. In addition, the model deployment verification of our Rep-YOLO is carried out on the airborne platform Jetson Nano. It provides reliable technical support for the improvement of the detection algorithm and its practical application with UAV platforms.
Infrared aerial object detection has been widely used in transportation, agriculture, military security, and other areas. The main challenges are small objects, mutual occlusion, little texture information, weak edge features, and large deformation of non-rigid bodies. To address these problems, based on YOLOv5 and structural re-parameterization (Rep), an improved object detection network Rep-YOLO is proposed for infrared aerial object detection. Firstly, the RepVGG module is introduced in the backbone network to improve the model feature extraction capability. During the model inference, the branches of the RepVGG module are structurally re-parameterized to reduce the branch and the complexity of the network structure. Secondly, the path aggregation network (PANet) in the neck of the detection network is improved by combining the priori feature, to increase the accuracy and speed balance capability. Finally, experiments are conducted on two publicly available infrared datasets, showing that the algorithm can effectively detect aerial infrared objects. Compared with the baseline (YOLOv5s), the statistical results on ComNet dataset show the mean average precision (mAP) is increased by 5.9%, while the parameters and model size are reduced by about 29.7% and 23.2%, respectively. In addition, the model deployment verification of our Rep-YOLO is carried out on the airborne platform Jetson Nano. It provides reliable technical support for the improvement of the detection algorithm and its practical application with UAV platforms.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023257
Abstract:
Spanning across disciplines with research interests in fundamental matter, life forms, and societal dynamics, the study of complex systems plays a pivotal role in deciphering and forecasting natural and social phenomena, thereby confronting intricate problems of human concern. The wealth of diverse real-world complex system data accumulated through early research has paved the way for a novel paradigm in complexity science research, which is intensively data-driven and steered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) methodologies. This innovative approach provides fresh insights into the characterization, forecasting, and knowledge extraction of complex systems. This article offers a visionary review of AI-driven studies in complex systems, highlighting the pioneering developments spearheaded by AI. It further scrutinizes exemplary works in the domain that leverage AI methodologies and concludes by contemplating the prospective evolution of AI theory and techniques under the lens of complex systems.
Spanning across disciplines with research interests in fundamental matter, life forms, and societal dynamics, the study of complex systems plays a pivotal role in deciphering and forecasting natural and social phenomena, thereby confronting intricate problems of human concern. The wealth of diverse real-world complex system data accumulated through early research has paved the way for a novel paradigm in complexity science research, which is intensively data-driven and steered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) methodologies. This innovative approach provides fresh insights into the characterization, forecasting, and knowledge extraction of complex systems. This article offers a visionary review of AI-driven studies in complex systems, highlighting the pioneering developments spearheaded by AI. It further scrutinizes exemplary works in the domain that leverage AI methodologies and concludes by contemplating the prospective evolution of AI theory and techniques under the lens of complex systems.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023131
Abstract:
Fundus retinal vessels segmentation can assist doctors in the diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, due to the complex topological structure of blood vessels and unclear boundaries, it greatly increases the difficulty of segmentation. A graph convolutional feature fusion network is proposed based on the U-shaped structure to address these issues. This network uses a graph convolution module to model the global contextual information between pixels in encoder features, making up for the lack of global modeling ability in ordinary convolutions; Then, a multi-scale feature fusion module is used to fuse the encoder features and decoder features to reduce the impact of noise information in the feature layer on the segmentation results; Finally, a multi-level feature fusion module is used to fuse and output the features of each layer of the decoder, reducing the loss of spatial information and the reuse of deep features during the downsampling process. Verified on the public datasets DRIVE, CHASEDB1, and START, the F1 values were 82.90%, 83.79%, and 80.63%, respectively, and the AUC values were 98.13%, 98.78%, and 98.36%, respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to recent retinal segmentation algorithms.
Fundus retinal vessels segmentation can assist doctors in the diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, due to the complex topological structure of blood vessels and unclear boundaries, it greatly increases the difficulty of segmentation. A graph convolutional feature fusion network is proposed based on the U-shaped structure to address these issues. This network uses a graph convolution module to model the global contextual information between pixels in encoder features, making up for the lack of global modeling ability in ordinary convolutions; Then, a multi-scale feature fusion module is used to fuse the encoder features and decoder features to reduce the impact of noise information in the feature layer on the segmentation results; Finally, a multi-level feature fusion module is used to fuse and output the features of each layer of the decoder, reducing the loss of spatial information and the reuse of deep features during the downsampling process. Verified on the public datasets DRIVE, CHASEDB1, and START, the F1 values were 82.90%, 83.79%, and 80.63%, respectively, and the AUC values were 98.13%, 98.78%, and 98.36%, respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to recent retinal segmentation algorithms.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023111
Abstract:
The loss of metallic area (LMA) directly affects the bearing strength and other characteristics of the steel wire rope, therefore its detection and quantitative analysis are of great significance for the safe and reliable operation of the equipment. Aiming at the problems of difficult coil winding and fuzzy parameter determination in the current main magnetic flux detection, a split coil structure based on printed circuit boards (PCB) is proposed based on the simulation model. The number of coils turns, coil layers, and other parameters in the design process are analyzed for their effect on the detection signal. Meanwhile, the main magnetic flux detection model is established to explore the influence of the defect width on the inductive voltage signal, and a compensation method is proposed for the signal loss caused by the reduction of the damage width. Finally, the steel wire bundle is used as an example to verify the quantitative detection of LMA. Experiment results show that the quantitative error of the proposed method is within 1%, and it can effectively detect the LMA of steel wire rope.
The loss of metallic area (LMA) directly affects the bearing strength and other characteristics of the steel wire rope, therefore its detection and quantitative analysis are of great significance for the safe and reliable operation of the equipment. Aiming at the problems of difficult coil winding and fuzzy parameter determination in the current main magnetic flux detection, a split coil structure based on printed circuit boards (PCB) is proposed based on the simulation model. The number of coils turns, coil layers, and other parameters in the design process are analyzed for their effect on the detection signal. Meanwhile, the main magnetic flux detection model is established to explore the influence of the defect width on the inductive voltage signal, and a compensation method is proposed for the signal loss caused by the reduction of the damage width. Finally, the steel wire bundle is used as an example to verify the quantitative detection of LMA. Experiment results show that the quantitative error of the proposed method is within 1%, and it can effectively detect the LMA of steel wire rope.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022252
Abstract:
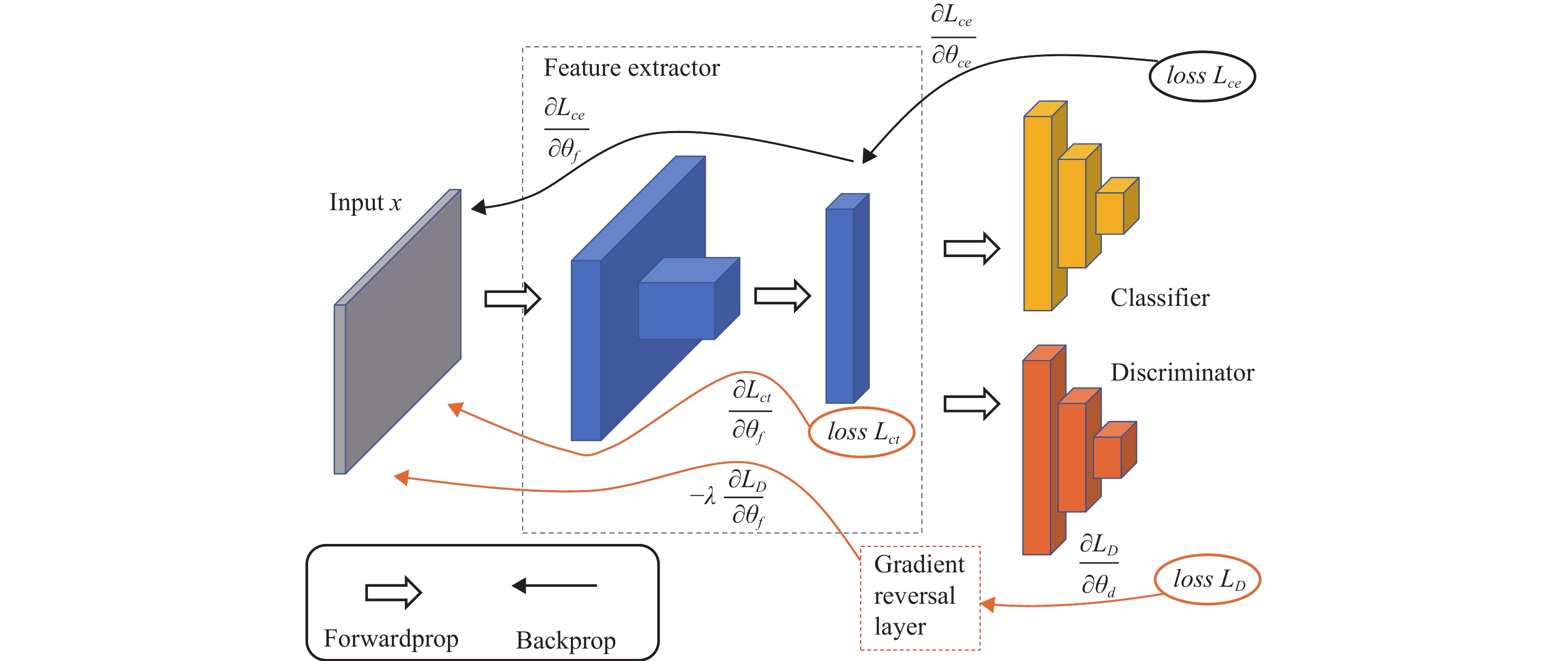
Benefiting from the development of deep learning, the neural networks improve signal recognition performance has achieved great progress. However, most of the existing deep learning-based signal recognition methods are supervised, which requires a large amount of well-labeled data for training, but the cost of signal labeling is quite expensive. This encourages the semi-supervised methods to make full use of unlabeled data to assist the training of deep models, but existing semi-supervised signal recognition methods do not consider noise influence. Therefore, a semi-supervised signal recognition method is proposed based on deep residual network (Resnet) by using gradient reversal layers to improve noise effect on performance. Experimental results on open source datasets RML2016.10A, RML2016.10B and RML2016.10C show that the proposed semi-supervised method effectively extracts discriminative features from unlabeled data by using a small amount of labeled data information, which alleviates noise influence.
Benefiting from the development of deep learning, the neural networks improve signal recognition performance has achieved great progress. However, most of the existing deep learning-based signal recognition methods are supervised, which requires a large amount of well-labeled data for training, but the cost of signal labeling is quite expensive. This encourages the semi-supervised methods to make full use of unlabeled data to assist the training of deep models, but existing semi-supervised signal recognition methods do not consider noise influence. Therefore, a semi-supervised signal recognition method is proposed based on deep residual network (Resnet) by using gradient reversal layers to improve noise effect on performance. Experimental results on open source datasets RML2016.10A, RML2016.10B and RML2016.10C show that the proposed semi-supervised method effectively extracts discriminative features from unlabeled data by using a small amount of labeled data information, which alleviates noise influence.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023080
Abstract:
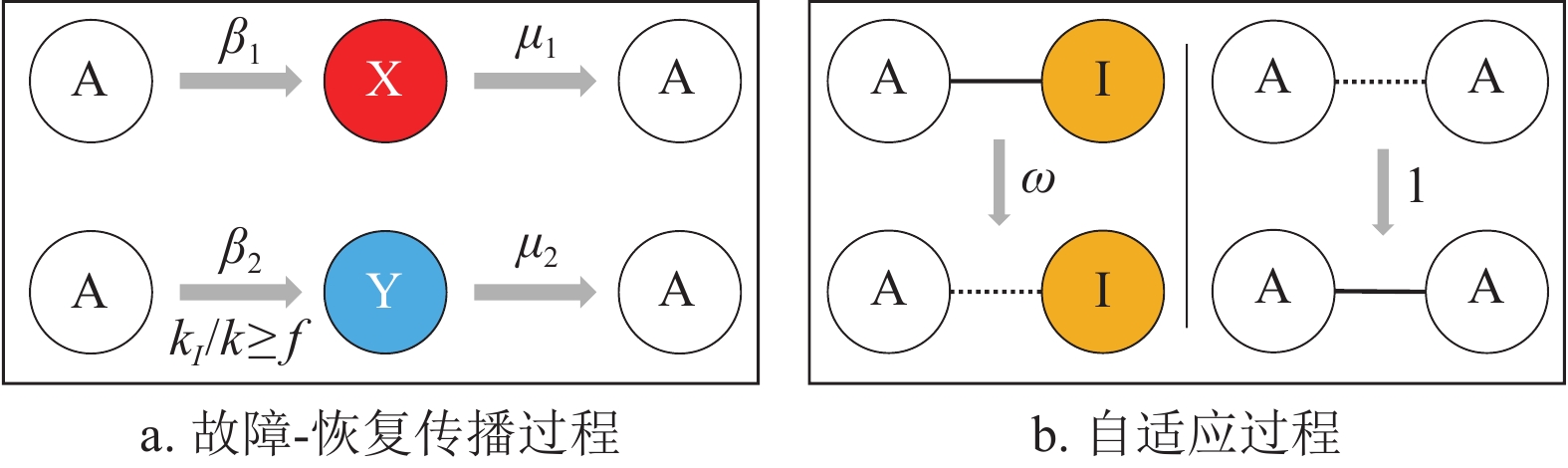
In the failure-recovery dynamics, nodes can recover spontaneously with probability after failure due to internal or external factors. Considering the ability of individual components to actively change their connectivity, we establish a failure-recovery propagation model on adaptive networks. In this model, active nodes disconnect from their failed neighbors to improve the local environment and thus reduce the probability of external failure. A theoretical framework based on pairwise approximation is established to predict the time evolution of the failure rate and the final failure size of the system. Numerous computer simulations validate the accuracy of the theoretical predictions and reveal the system’s rich phase transitions and hysteresis phenomena. Adaptive behavior can cause the hysteresis region of the system to appear or disappear under different adaptive edge-cutting rates and external failure rates, and the system exhibits a bistable region that is influenced by the initial failure size.
In the failure-recovery dynamics, nodes can recover spontaneously with probability after failure due to internal or external factors. Considering the ability of individual components to actively change their connectivity, we establish a failure-recovery propagation model on adaptive networks. In this model, active nodes disconnect from their failed neighbors to improve the local environment and thus reduce the probability of external failure. A theoretical framework based on pairwise approximation is established to predict the time evolution of the failure rate and the final failure size of the system. Numerous computer simulations validate the accuracy of the theoretical predictions and reveal the system’s rich phase transitions and hysteresis phenomena. Adaptive behavior can cause the hysteresis region of the system to appear or disappear under different adaptive edge-cutting rates and external failure rates, and the system exhibits a bistable region that is influenced by the initial failure size.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023211
Abstract:
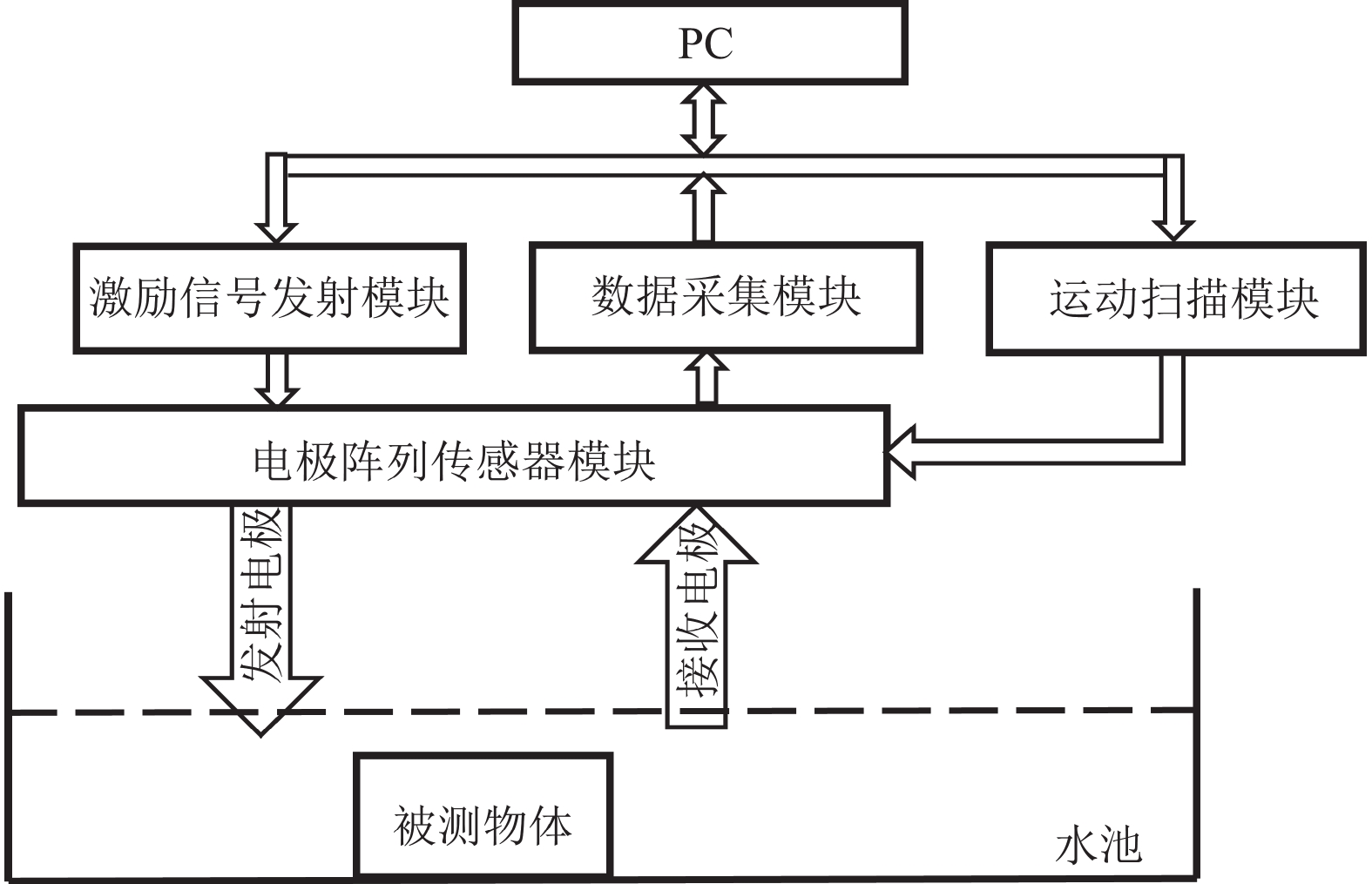
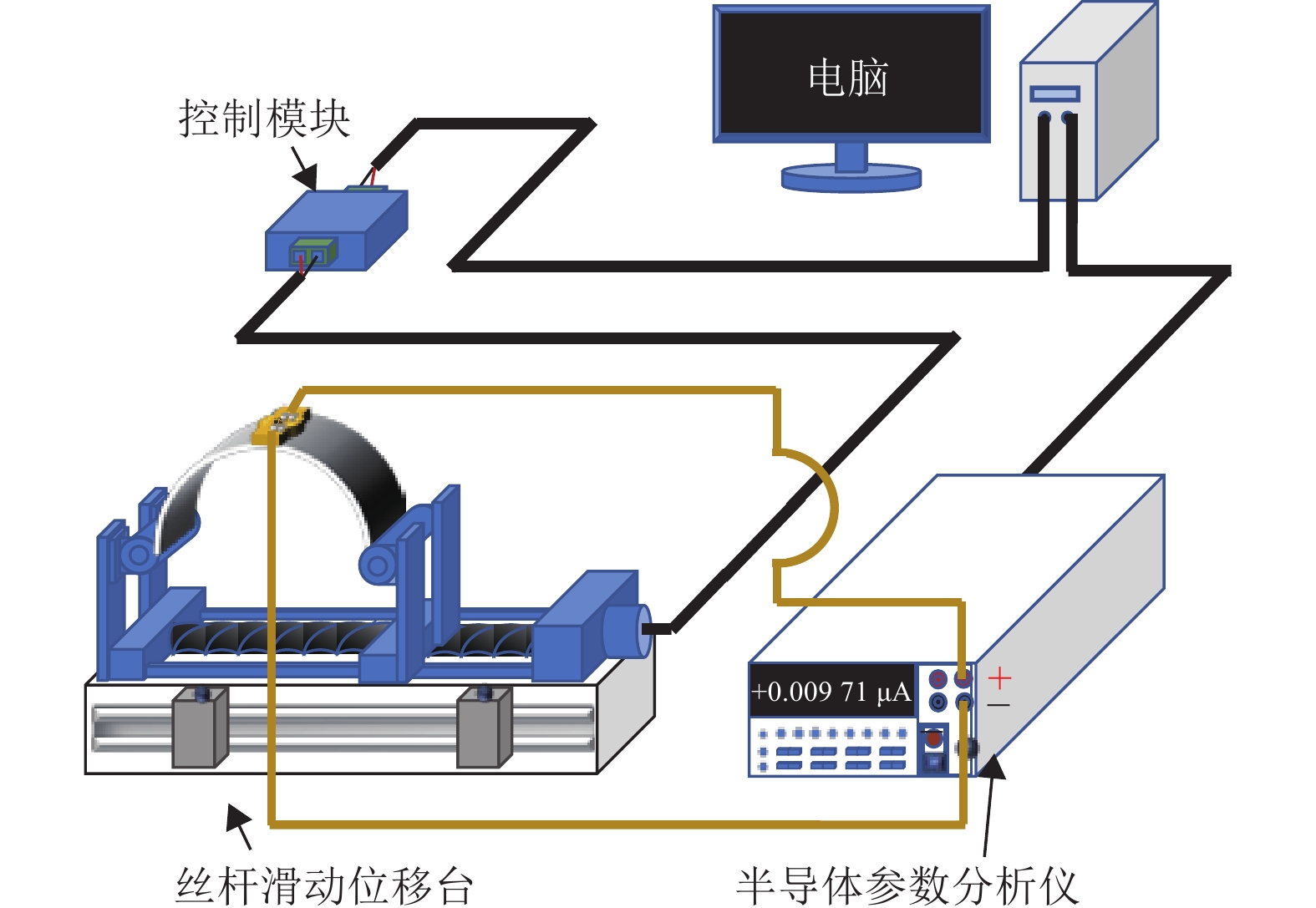
Underwater active electric field amplitude imaging is inspired by the biological mechanism that weakly electric fish actively emit electric signals to identify their surroundings. The current active underwater imaging technology still has some shortcomings in the complex and dark underwater environment, so a new solution has been proposed, which is to utilize the underwater active electric field principle recognition to complete the imaging of complex shapes of short-range target objects. Aiming at the previous problems of limited coverage of electrode arrays, small imaging resolution, high cost caused by the large number of electrodes when imaging larger objects, and the lack of examples of imaging complex geometric features of objects, we designed a magnitude imaging platform with continuous motion scanning of linear electrode arrays and data acquisition to image experimental objects of different volume sizes, different materials and complex shapes, and compared the results, and finally investigated Finally, we investigate how to extract the object position and area information in the imaging pictures based on the maximum point of the transverse and longitudinal amplitude integral slope curves. The experiments show the effectiveness of motion scanning amplitude imaging of linear electrode array based on the active electric field principle, and the motion scanning compensation method effectively solves the drawbacks of limited receiving electrodes and acquisition channels and the time cost of manual fixed-point acquistion, and improves the efficiency and resolution of its imaging of objects in water, which provides a practical method for the further engineering application of this technology and the related characterization research.
Underwater active electric field amplitude imaging is inspired by the biological mechanism that weakly electric fish actively emit electric signals to identify their surroundings. The current active underwater imaging technology still has some shortcomings in the complex and dark underwater environment, so a new solution has been proposed, which is to utilize the underwater active electric field principle recognition to complete the imaging of complex shapes of short-range target objects. Aiming at the previous problems of limited coverage of electrode arrays, small imaging resolution, high cost caused by the large number of electrodes when imaging larger objects, and the lack of examples of imaging complex geometric features of objects, we designed a magnitude imaging platform with continuous motion scanning of linear electrode arrays and data acquisition to image experimental objects of different volume sizes, different materials and complex shapes, and compared the results, and finally investigated Finally, we investigate how to extract the object position and area information in the imaging pictures based on the maximum point of the transverse and longitudinal amplitude integral slope curves. The experiments show the effectiveness of motion scanning amplitude imaging of linear electrode array based on the active electric field principle, and the motion scanning compensation method effectively solves the drawbacks of limited receiving electrodes and acquisition channels and the time cost of manual fixed-point acquistion, and improves the efficiency and resolution of its imaging of objects in water, which provides a practical method for the further engineering application of this technology and the related characterization research.
Power cable partial discharge pattern recognition based on topological data analysis for time series
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022398
Abstract:
In partial discharge pattern recognition of power cables, phase resolved partial discharge (PRPD) spectrum as well as statistical features often affect the recognition accuracy due to insufficient discrimination. A novel partial discharge feature extraction and identification method based on time series topology data analysis (TDA) is proposed in this paper. First, a reconstruction parameter selection method combining symbolic entropy and particle swarm optimization (PSO) is proposed, which reconstructs the preprocessed PD time domain signal in phase space and generates a 3D PD data point cloud; secondly, Based on the TDA method, Persistent Homology features are extracted, and persistence diagram and persistence barcodes are generated accordingly, calculated and visually expressed as a Betty curve. Finally, the Betty curves are input into the 1D-CNN model. Identify patterns and conduct comparative experiments. The approach using TDA for feature extraction and pattern recognition has shown excellent discrimination capabilities, improving overall recognition accuracy by up to 15.34% (98.55% accuracy achieved), compared to models using PRPD and statistical features. This demonstrates the effectiveness of TDA in accurately selecting parameters for phase space reconstruction.
In partial discharge pattern recognition of power cables, phase resolved partial discharge (PRPD) spectrum as well as statistical features often affect the recognition accuracy due to insufficient discrimination. A novel partial discharge feature extraction and identification method based on time series topology data analysis (TDA) is proposed in this paper. First, a reconstruction parameter selection method combining symbolic entropy and particle swarm optimization (PSO) is proposed, which reconstructs the preprocessed PD time domain signal in phase space and generates a 3D PD data point cloud; secondly, Based on the TDA method, Persistent Homology features are extracted, and persistence diagram and persistence barcodes are generated accordingly, calculated and visually expressed as a Betty curve. Finally, the Betty curves are input into the 1D-CNN model. Identify patterns and conduct comparative experiments. The approach using TDA for feature extraction and pattern recognition has shown excellent discrimination capabilities, improving overall recognition accuracy by up to 15.34% (98.55% accuracy achieved), compared to models using PRPD and statistical features. This demonstrates the effectiveness of TDA in accurately selecting parameters for phase space reconstruction.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023001
Abstract:
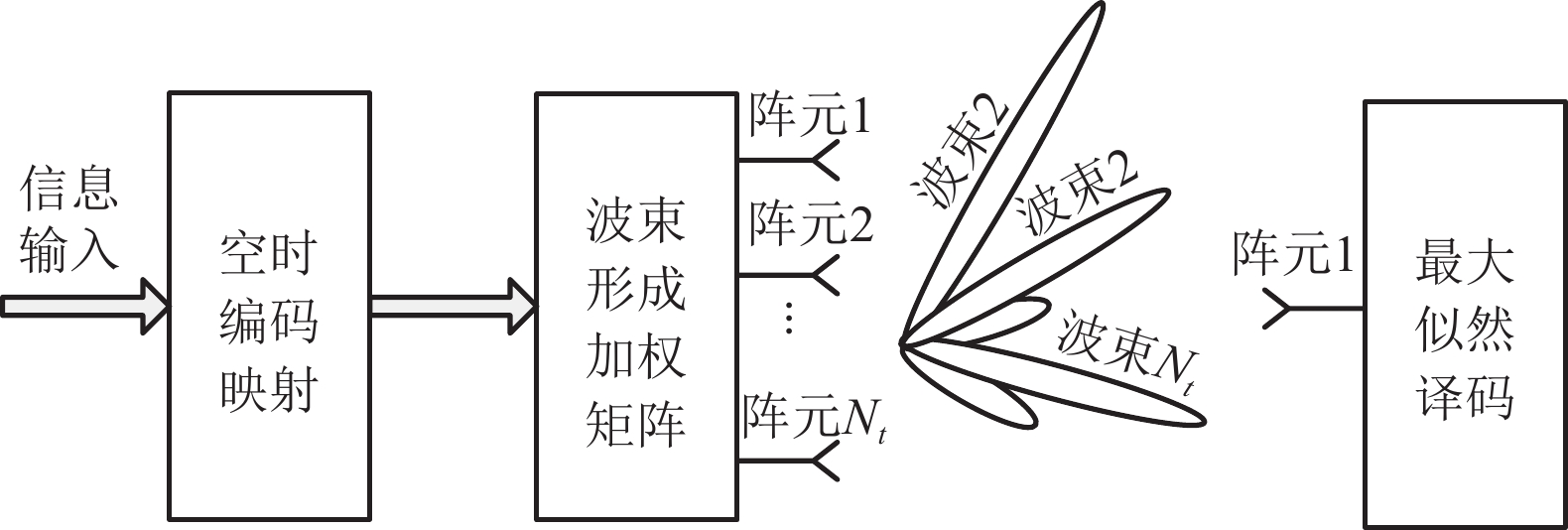
Based on beamforming beam switching spatial modulation algorithm, not only can it improve spectrum efficiency, but it can also use antenna array gain to enhance energy efficiency. In this paper, the statistical average covariance matrix is constructed using channel response, and orthogonal feature vectors are constructed as weighted vectors for the array. This forms multiple independent equivalent transmission channels, utilizing beamforming gain and diversity gain to improve the transmission reliability and capacity of wireless communication. Furthermore, an antenna subarray grouping method is employed to overcome the adverse effects of channel correlation. Both performance analysis and simulation results indicate that the feature beam angle spatial modulation scheme can obtain more beam combinations, significantly improving decoding performance and spectrum efficiency.
Based on beamforming beam switching spatial modulation algorithm, not only can it improve spectrum efficiency, but it can also use antenna array gain to enhance energy efficiency. In this paper, the statistical average covariance matrix is constructed using channel response, and orthogonal feature vectors are constructed as weighted vectors for the array. This forms multiple independent equivalent transmission channels, utilizing beamforming gain and diversity gain to improve the transmission reliability and capacity of wireless communication. Furthermore, an antenna subarray grouping method is employed to overcome the adverse effects of channel correlation. Both performance analysis and simulation results indicate that the feature beam angle spatial modulation scheme can obtain more beam combinations, significantly improving decoding performance and spectrum efficiency.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022333
Abstract:
With the rapid increase of vehicles, the road network has become increasingly congested. It is of great significance to study the maximization of road network traffic efficiency, personal traffic time and path optimization. The existing methods periodically monitor congestion and replan paths. The previous path obtained by this kind of algorithm often leads to the detour of the next replanning, which is not conducive to the global optimization. This paper proposes a path planning algorithm based on congestion prediction. By analyzing the temporal and spatial correlation in a large number of historical traffic flow data, the traffic flow parameters at the future time are predicted, and then the congestion state classification is obtained through entropy weight method and fuzzy comprehensive judgment. Then a more reasonable path is planned by comprehensively considering the current and future congestion conditions. The simulation results show that compared with the dynamic path planning algorithm, this algorithm reduces the travel time by 5.35% and the travel distance by 11.72%.
With the rapid increase of vehicles, the road network has become increasingly congested. It is of great significance to study the maximization of road network traffic efficiency, personal traffic time and path optimization. The existing methods periodically monitor congestion and replan paths. The previous path obtained by this kind of algorithm often leads to the detour of the next replanning, which is not conducive to the global optimization. This paper proposes a path planning algorithm based on congestion prediction. By analyzing the temporal and spatial correlation in a large number of historical traffic flow data, the traffic flow parameters at the future time are predicted, and then the congestion state classification is obtained through entropy weight method and fuzzy comprehensive judgment. Then a more reasonable path is planned by comprehensively considering the current and future congestion conditions. The simulation results show that compared with the dynamic path planning algorithm, this algorithm reduces the travel time by 5.35% and the travel distance by 11.72%.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022332
Abstract:
In order to solve the influence of the fence effect on the frequency estimation accuracy and improve the frequency estimation accuracy and anti-noise performance, a high-precision frequency estimation algorithm based on Chrip-Z transformation(CZT) is proposed. The process of frequency estimation is divided into two processes: coarse estimation and fine estimation. The FFT algorithm is used to analyze the signal in the frequency domain to obtain a rough estimation value of the signal frequency. Based on the rough estimation value of the signal frequency, the frequency refinement interval is determined. The frequency spectrum in this interval is refined, and the frequency estimation value is corrected by using the amplitude of the maximum spectral line of the refined spectrum and its left and right spectral lines to obtain an accurate frequency estimation value. Simulations show that the proposed algorithm can obtain high-precision method frequency estimates with a lower refinement multiple, and has better anti-noise performance. The range measurement experiment using FMCW radar verifies that the practical application effect of the proposed algorithm is better than the existing algorithm.
In order to solve the influence of the fence effect on the frequency estimation accuracy and improve the frequency estimation accuracy and anti-noise performance, a high-precision frequency estimation algorithm based on Chrip-Z transformation(CZT) is proposed. The process of frequency estimation is divided into two processes: coarse estimation and fine estimation. The FFT algorithm is used to analyze the signal in the frequency domain to obtain a rough estimation value of the signal frequency. Based on the rough estimation value of the signal frequency, the frequency refinement interval is determined. The frequency spectrum in this interval is refined, and the frequency estimation value is corrected by using the amplitude of the maximum spectral line of the refined spectrum and its left and right spectral lines to obtain an accurate frequency estimation value. Simulations show that the proposed algorithm can obtain high-precision method frequency estimates with a lower refinement multiple, and has better anti-noise performance. The range measurement experiment using FMCW radar verifies that the practical application effect of the proposed algorithm is better than the existing algorithm.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2024032
Abstract:
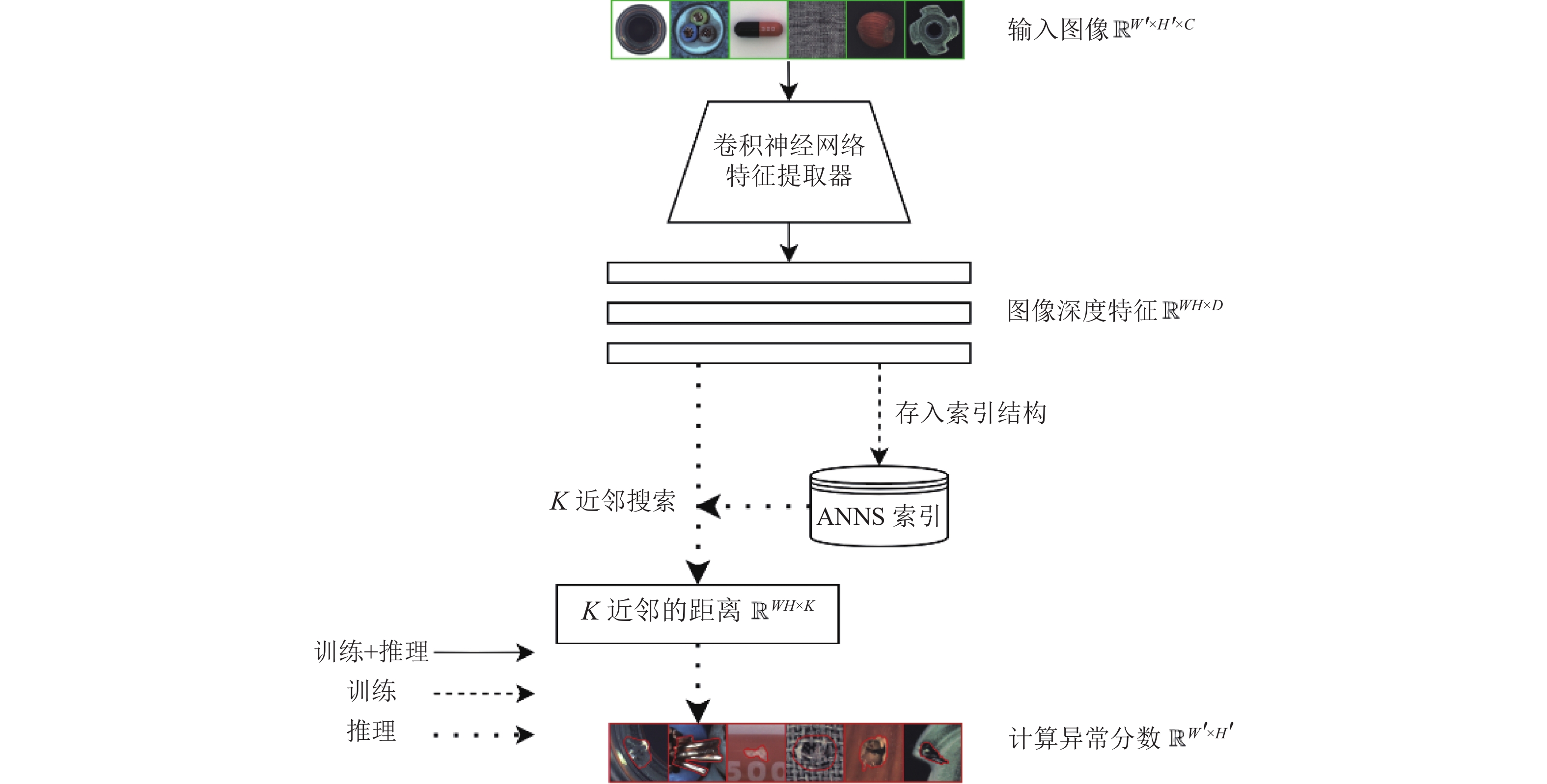
An accurate and stable approach to image anomaly detection is to query the K-nearest neighbours of the image features from normal examples and estimate the anomaly score, relying on approximate nearest neighbour search (ANNS) indices. ANNS query operation has high computational cost on large datasets, unpractical for low-latency and high-throughput scenarios. Based on locality sensitive hashing and Bloom filters, an approximated membership query (AMQ) based approach is proposed to predict anomalies by approximate membership of features. AMQ can address the performance bottleneck of search-based methods, given its lower complexity and better compatibility with single-instruction multiple-data parallelism than ANNS. Experimental results on MVTec-AD show that the accuracy of AMQ-based method is just decreased about 1% in comparison with ANNS-based methods, while the inference latency, the throughput and the memory footprint are significantly improved, close to the efficiency of end-to-end deep learning anomaly detection models.
An accurate and stable approach to image anomaly detection is to query the K-nearest neighbours of the image features from normal examples and estimate the anomaly score, relying on approximate nearest neighbour search (ANNS) indices. ANNS query operation has high computational cost on large datasets, unpractical for low-latency and high-throughput scenarios. Based on locality sensitive hashing and Bloom filters, an approximated membership query (AMQ) based approach is proposed to predict anomalies by approximate membership of features. AMQ can address the performance bottleneck of search-based methods, given its lower complexity and better compatibility with single-instruction multiple-data parallelism than ANNS. Experimental results on MVTec-AD show that the accuracy of AMQ-based method is just decreased about 1% in comparison with ANNS-based methods, while the inference latency, the throughput and the memory footprint are significantly improved, close to the efficiency of end-to-end deep learning anomaly detection models.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023163
Abstract:
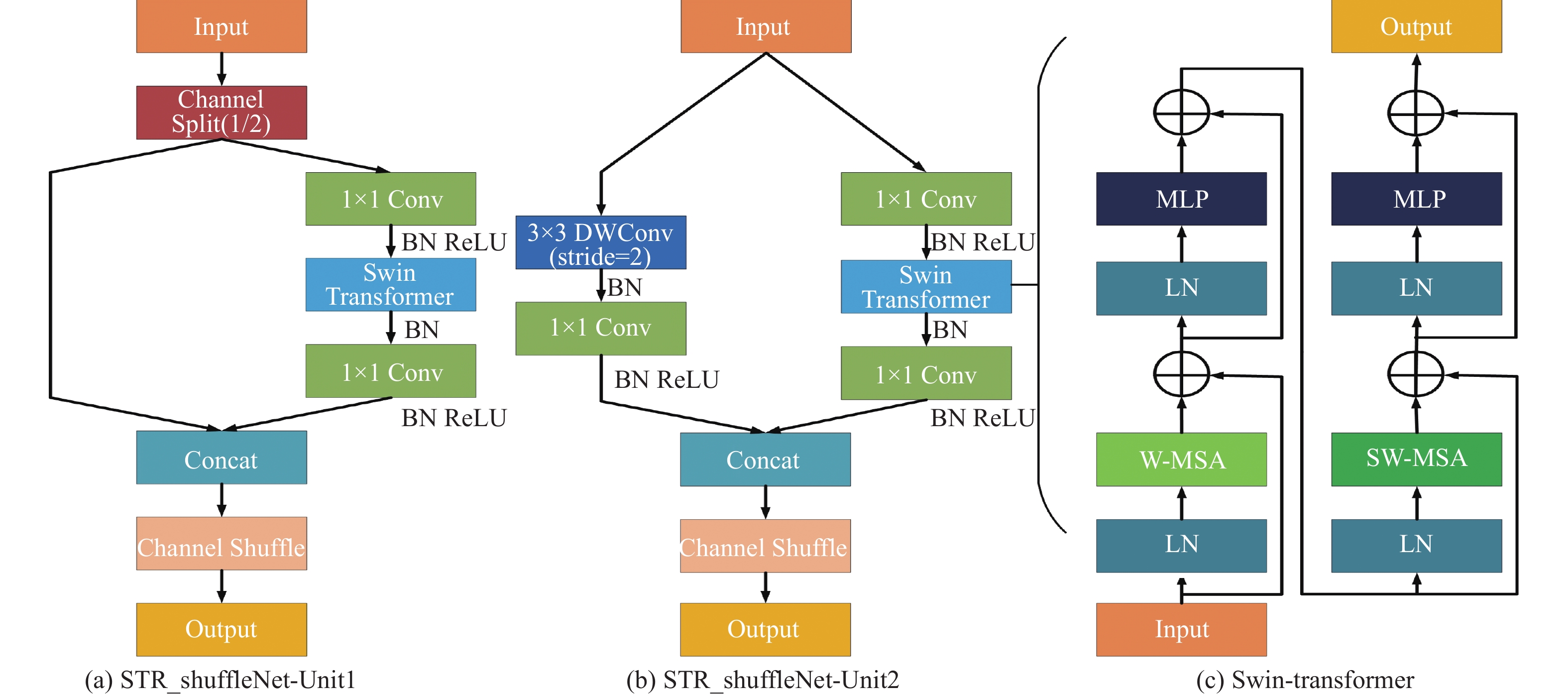
Real-time detection of mine personnel is an essential part of the construction of intelligent mine. It is of great significance to realize early warning and linkage control of dangerous areas by monitoring underground personnel through video, which is of great significance for mine safety production. At present, the visible light image recognition technology needs to be improved for the identification of personnel in the dim environment of underground coal mine. Aiming at the problems of more noise and image blur in the monitoring video caused by uneven illumination and serious coal dust interference in the underground, this paper proposes an improved YOLOv7 mine personnel detection algorithm. Firstly, aiming at the problem of channel isolation caused by direct splicing of ELAN modules, a complex scene detection method based on channel reorganization and feature attention is proposed. The ShuffleNetV2 is used as the backbone network to reduce the number of parameters, improve the reasoning speed of the algorithm, and promote the information flow between channels. At the same time, the Swin Transformer attention mechanism is introduced into shuffle_block to improve the attention of people in the image and suppress the interference of complex environment on personnel detection. At the same time, the excellent global receptive field of Transformer is conducive to the detection of occlusion targets. Secondly, in view of the fact that the feature fusion results did not focus on the expected target and the model lacked targeted strategies to improve the detection performance of small targets, the ACmix module was added to the neck multi-scale fusion network to take into account both global features and local features, which improved the detection ability of the algorithm for small targets. Finally, Efficient IOU Loss is introduced to improve the convergence speed of the algorithm and reduce the difference between the height and width of the target frame and the prior frame to achieve more accurate positioning. Through the verification of public pedestrian data sets and self-built mine personnel detection data sets, it is shown that the detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 3.1% higher than that of the YOLOv7 model, reaching 89.4%. The recall rate increased by 3.8% to 86.4%. A 15.8% speedup of 68.8FPS Meet the mine personnel real-time detection work requirements.
Real-time detection of mine personnel is an essential part of the construction of intelligent mine. It is of great significance to realize early warning and linkage control of dangerous areas by monitoring underground personnel through video, which is of great significance for mine safety production. At present, the visible light image recognition technology needs to be improved for the identification of personnel in the dim environment of underground coal mine. Aiming at the problems of more noise and image blur in the monitoring video caused by uneven illumination and serious coal dust interference in the underground, this paper proposes an improved YOLOv7 mine personnel detection algorithm. Firstly, aiming at the problem of channel isolation caused by direct splicing of ELAN modules, a complex scene detection method based on channel reorganization and feature attention is proposed. The ShuffleNetV2 is used as the backbone network to reduce the number of parameters, improve the reasoning speed of the algorithm, and promote the information flow between channels. At the same time, the Swin Transformer attention mechanism is introduced into shuffle_block to improve the attention of people in the image and suppress the interference of complex environment on personnel detection. At the same time, the excellent global receptive field of Transformer is conducive to the detection of occlusion targets. Secondly, in view of the fact that the feature fusion results did not focus on the expected target and the model lacked targeted strategies to improve the detection performance of small targets, the ACmix module was added to the neck multi-scale fusion network to take into account both global features and local features, which improved the detection ability of the algorithm for small targets. Finally, Efficient IOU Loss is introduced to improve the convergence speed of the algorithm and reduce the difference between the height and width of the target frame and the prior frame to achieve more accurate positioning. Through the verification of public pedestrian data sets and self-built mine personnel detection data sets, it is shown that the detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 3.1% higher than that of the YOLOv7 model, reaching 89.4%. The recall rate increased by 3.8% to 86.4%. A 15.8% speedup of 68.8FPS Meet the mine personnel real-time detection work requirements.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023047
Abstract:
Aiming at the problems of time-consuming pre-training and poor diagnostic accuracy in the process of unsupervised training of traditional DBN, In this paper, an Improved Multi-Objective Dragonfly Optimization Adaptive Deep Belief Network (IMODA-ADBN) is proposed. IMODA-ADBN for analog circuit fault diagnosis. Firstly, an adaptive learning rate is proposed according to the similarities and differences of parameter update directions to improve the convergence speed of the network. Secondly, traditional DBN uses BP algorithm in the supervised tuning process. However, BP algorithm has the problem that it is easy to fall into local optimum. In order to improve the problem, IMODA algorithm is used to replace BP algorithm to improve the accuracy of network classification. In the improved MODA algorithm, Logistic chaotic imprinting and oppositional jumping are added to obtain the Pareto optimal solution, which increases the diversity of the algorithm and improves its performance of the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is tested on eight multi-objective mathematical benchmark problems and compared with three well-known meta-heuristic optimization algorithms (MODA, MOPSO, and NSGA-II), and the stability of IMODA-ADBN network model is proved. Finally, IMODA-ADBN is applied to the diagnosis experiment of a two-stage four-op-amplifier double-second-order low-pass filter. The experimental results show that the proposed IMODA-ADBN can ensure classification accuracy on the basis of fast convergence, and IMODA-ADBN has higher diagnosis rate than other methods mentioned in this paper, which can realize the classification and location of high-difficulty faults.
Aiming at the problems of time-consuming pre-training and poor diagnostic accuracy in the process of unsupervised training of traditional DBN, In this paper, an Improved Multi-Objective Dragonfly Optimization Adaptive Deep Belief Network (IMODA-ADBN) is proposed. IMODA-ADBN for analog circuit fault diagnosis. Firstly, an adaptive learning rate is proposed according to the similarities and differences of parameter update directions to improve the convergence speed of the network. Secondly, traditional DBN uses BP algorithm in the supervised tuning process. However, BP algorithm has the problem that it is easy to fall into local optimum. In order to improve the problem, IMODA algorithm is used to replace BP algorithm to improve the accuracy of network classification. In the improved MODA algorithm, Logistic chaotic imprinting and oppositional jumping are added to obtain the Pareto optimal solution, which increases the diversity of the algorithm and improves its performance of the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is tested on eight multi-objective mathematical benchmark problems and compared with three well-known meta-heuristic optimization algorithms (MODA, MOPSO, and NSGA-II), and the stability of IMODA-ADBN network model is proved. Finally, IMODA-ADBN is applied to the diagnosis experiment of a two-stage four-op-amplifier double-second-order low-pass filter. The experimental results show that the proposed IMODA-ADBN can ensure classification accuracy on the basis of fast convergence, and IMODA-ADBN has higher diagnosis rate than other methods mentioned in this paper, which can realize the classification and location of high-difficulty faults.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023202
Abstract:
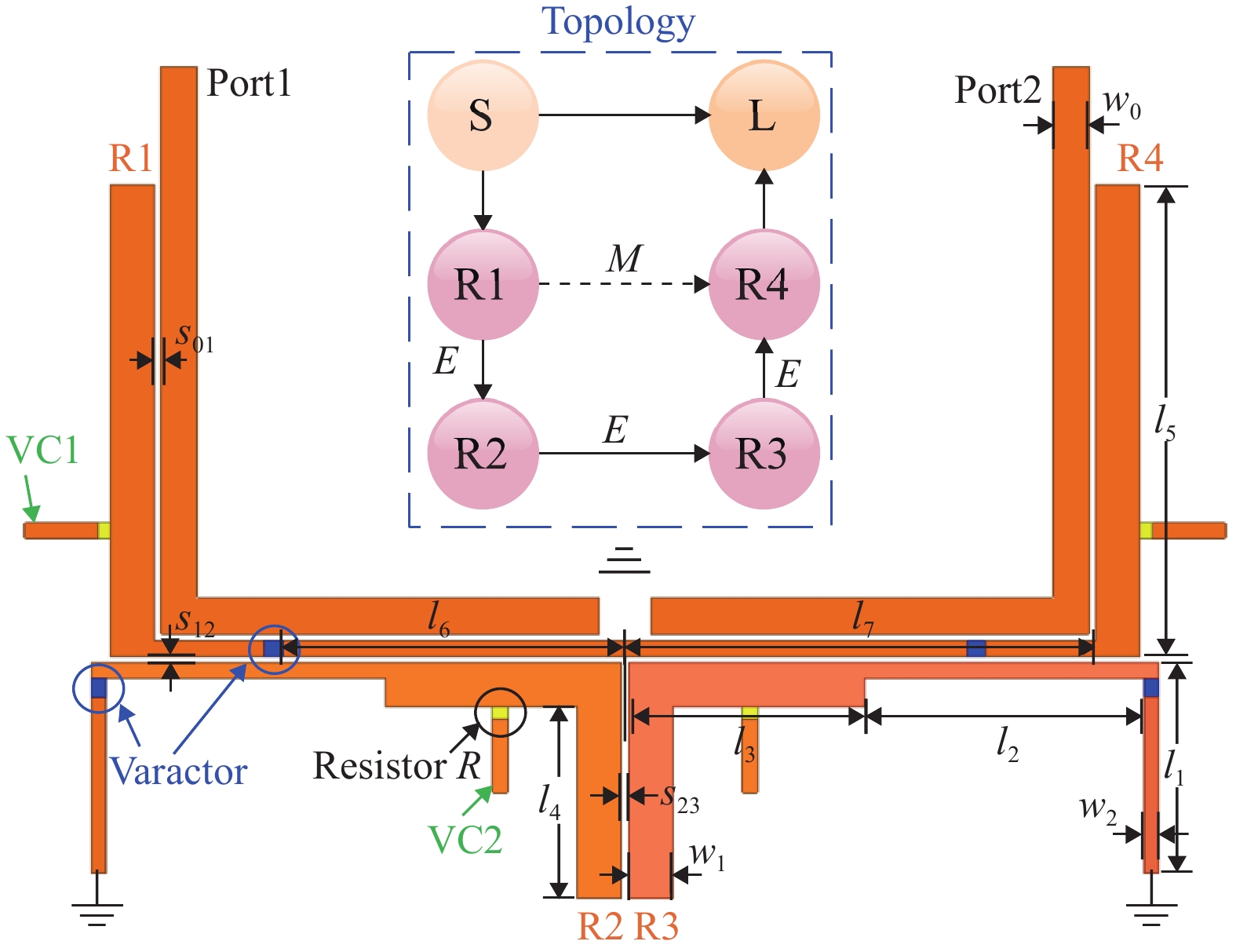
In this article, a compact fourth-order frequency tunable bandpass filter (BPF) with four Transmission Zeros (TZs) based on Varactor-Loaded Step-Impedance Resonators (VL-SIRs) is presented. With the utilization of VL-SIRs, the Tuning Range (TR) of the proposed fourth-order BPF is improved. Besides, by introducing cross coupling between VL-SIRs, a pair of TZs close to the passband are produced and the selectivity of the filter is enhanced significantly. Another pair of TZs are generated to improve the out-of-band rejection by using source-load coupling. Moreover, the Frequency-Dependent Coupling (FDC) structures based on VL-SIRs are employed to realize constant Absolute Bandwidth (ABW). The simulated and measured results are presented and show good agreement. The measured results exhibit a tuning range from 0.78 GHz to 1.15 GHz with a 3-dB constant ABW of about 55±3 MHz, the return loss of the filter is greater than 10 dB and the insertion loss is about 2.8 dB to 3.3 dB.
In this article, a compact fourth-order frequency tunable bandpass filter (BPF) with four Transmission Zeros (TZs) based on Varactor-Loaded Step-Impedance Resonators (VL-SIRs) is presented. With the utilization of VL-SIRs, the Tuning Range (TR) of the proposed fourth-order BPF is improved. Besides, by introducing cross coupling between VL-SIRs, a pair of TZs close to the passband are produced and the selectivity of the filter is enhanced significantly. Another pair of TZs are generated to improve the out-of-band rejection by using source-load coupling. Moreover, the Frequency-Dependent Coupling (FDC) structures based on VL-SIRs are employed to realize constant Absolute Bandwidth (ABW). The simulated and measured results are presented and show good agreement. The measured results exhibit a tuning range from 0.78 GHz to 1.15 GHz with a 3-dB constant ABW of about 55±3 MHz, the return loss of the filter is greater than 10 dB and the insertion loss is about 2.8 dB to 3.3 dB.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023011
Abstract:
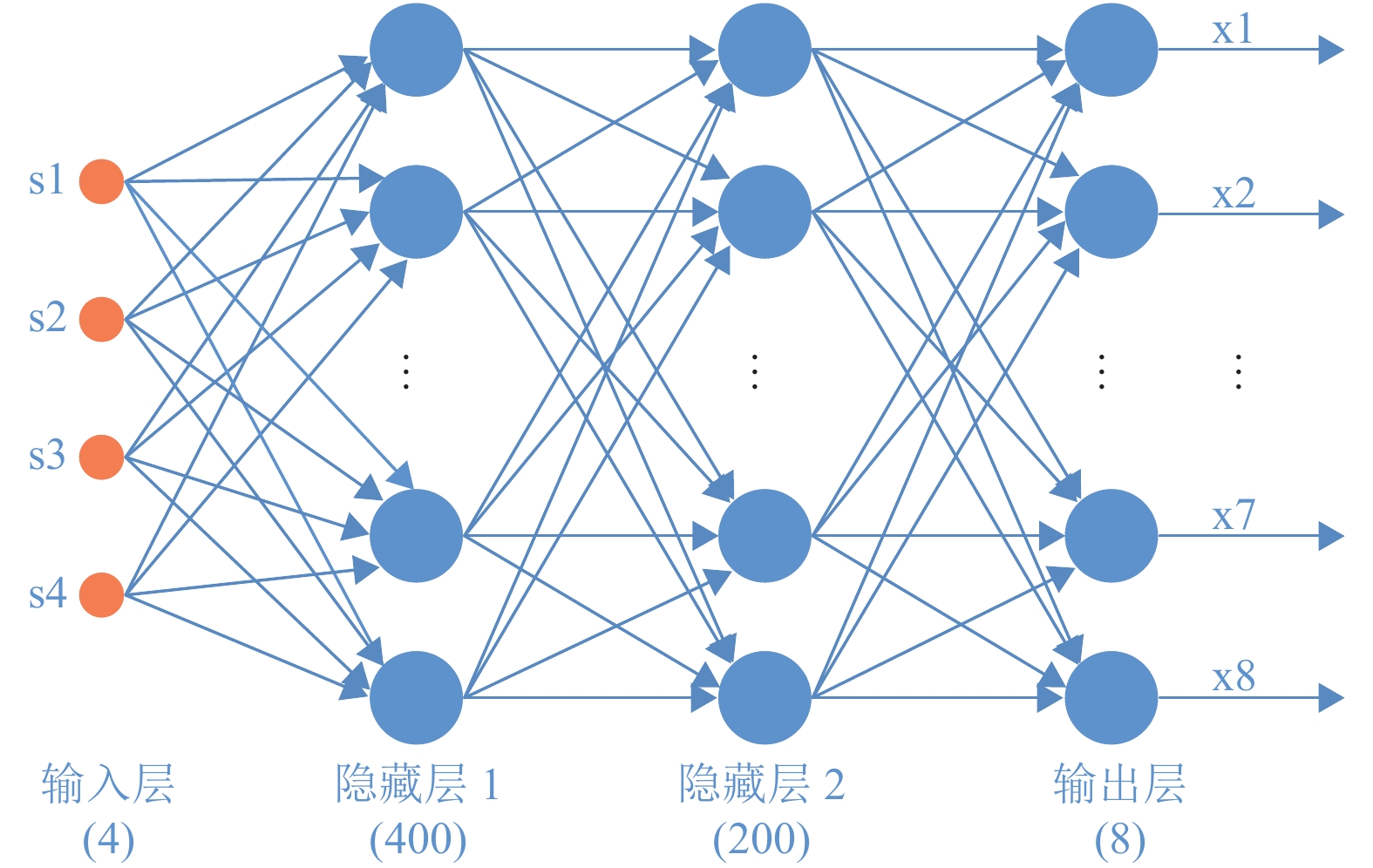
The traditional parameter optimization algorithm cannot meet the requirements of the application scenario with high real-time, large amount of calculation. Combining with the current mainstream machine learning methods, an improved parameter optimization method based on BP neural network was proposed. Using the data of the local search algorithm to train the network and predict the parameters, the proposed methods can obtain better real-time performance and lower computational complexity for the traditional search algorithm is replaced. Then it is compared with random forest and XGBoost methods. The simulation results show that the order of magnitude of the mean square error of each parameter predicted by BP neural network is\begin{document}$ {10^{-6}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
The traditional parameter optimization algorithm cannot meet the requirements of the application scenario with high real-time, large amount of calculation. Combining with the current mainstream machine learning methods, an improved parameter optimization method based on BP neural network was proposed. Using the data of the local search algorithm to train the network and predict the parameters, the proposed methods can obtain better real-time performance and lower computational complexity for the traditional search algorithm is replaced. Then it is compared with random forest and XGBoost methods. The simulation results show that the order of magnitude of the mean square error of each parameter predicted by BP neural network is
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023116
Abstract:
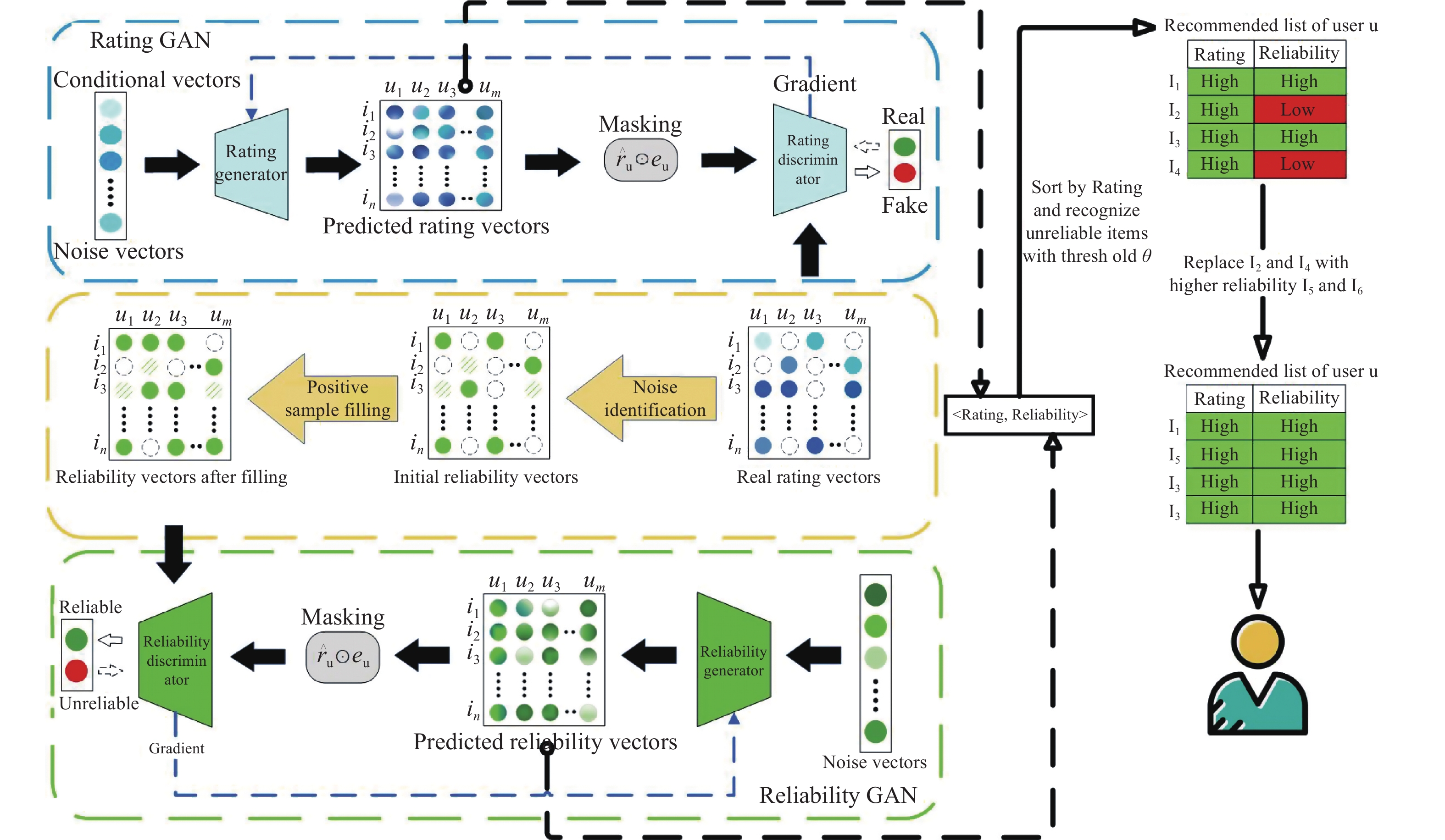
Existing deep learning-based recommendation models have mainly focused on improving the accuracy of recommendation systems. However, beyond recommendation accuracy, the reliability of the model's recommendations is also of great concern. Therefore, a rating-trustworthy recommendation model based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) is proposed to evaluate the effectiveness of prediction results and achieve a balance between recommendation accuracy and reliability. This model solely employs explicit user rating information to gauge the credibility of predicted ratings and screens out highly credible predicted ratings based on a predefined reliability threshold, thus ensuring the trustworthiness of recommended items. Furthermore, to enhance the prediction performance of the model and ensure fairness in training, a positive sample padding strategy is designed to mitigate the data imbalance problem in the rating reliability matrix. Experimental results on three real datasets show that the proposed model outperforms selected comparison methods in both Recall and NDCG metrics, effectively improving the performance of recommendation systems.
Existing deep learning-based recommendation models have mainly focused on improving the accuracy of recommendation systems. However, beyond recommendation accuracy, the reliability of the model's recommendations is also of great concern. Therefore, a rating-trustworthy recommendation model based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) is proposed to evaluate the effectiveness of prediction results and achieve a balance between recommendation accuracy and reliability. This model solely employs explicit user rating information to gauge the credibility of predicted ratings and screens out highly credible predicted ratings based on a predefined reliability threshold, thus ensuring the trustworthiness of recommended items. Furthermore, to enhance the prediction performance of the model and ensure fairness in training, a positive sample padding strategy is designed to mitigate the data imbalance problem in the rating reliability matrix. Experimental results on three real datasets show that the proposed model outperforms selected comparison methods in both Recall and NDCG metrics, effectively improving the performance of recommendation systems.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2023104
Abstract:
Conventional electronic devices are mainly composed of inorganic semiconductor materials such as silicon-based and rigid polymer insulating substrate materials, which are the basis of existing electronic technology. Although the traditional electronic technology has been developed, but due to the limitations of the material, resulting in the field of flexible electronics, its application still exists in a certain limit. Two-dimensional materials have high crystallinity, near-perfect lattice structure, atomic-level thickness and high mechanical tensile strength, and exhibit excellent charge-transfer properties, making them promising for applications in the field of flexible electronics. In this paper, we combine the excellent mechanical properties of graphene, molybdenum disulfide and hexagonal boron nitride to prepare molybdenum disulfide-based field-effect transistors by mechanical exfoliation method with dry transfer. We test the flexible electrical properties of the devices using a flexible test platform built in-house. The test results show that the designed two-dimensional heterojunction transistor has only a small change in electrical properties under static test conditions; however, under dynamic test conditions, due to the too small van der Waals force between layers, the sliding or displacement between layers makes the electrical properties of the device change significantly.
Conventional electronic devices are mainly composed of inorganic semiconductor materials such as silicon-based and rigid polymer insulating substrate materials, which are the basis of existing electronic technology. Although the traditional electronic technology has been developed, but due to the limitations of the material, resulting in the field of flexible electronics, its application still exists in a certain limit. Two-dimensional materials have high crystallinity, near-perfect lattice structure, atomic-level thickness and high mechanical tensile strength, and exhibit excellent charge-transfer properties, making them promising for applications in the field of flexible electronics. In this paper, we combine the excellent mechanical properties of graphene, molybdenum disulfide and hexagonal boron nitride to prepare molybdenum disulfide-based field-effect transistors by mechanical exfoliation method with dry transfer. We test the flexible electrical properties of the devices using a flexible test platform built in-house. The test results show that the designed two-dimensional heterojunction transistor has only a small change in electrical properties under static test conditions; however, under dynamic test conditions, due to the too small van der Waals force between layers, the sliding or displacement between layers makes the electrical properties of the device change significantly.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022226
Abstract:
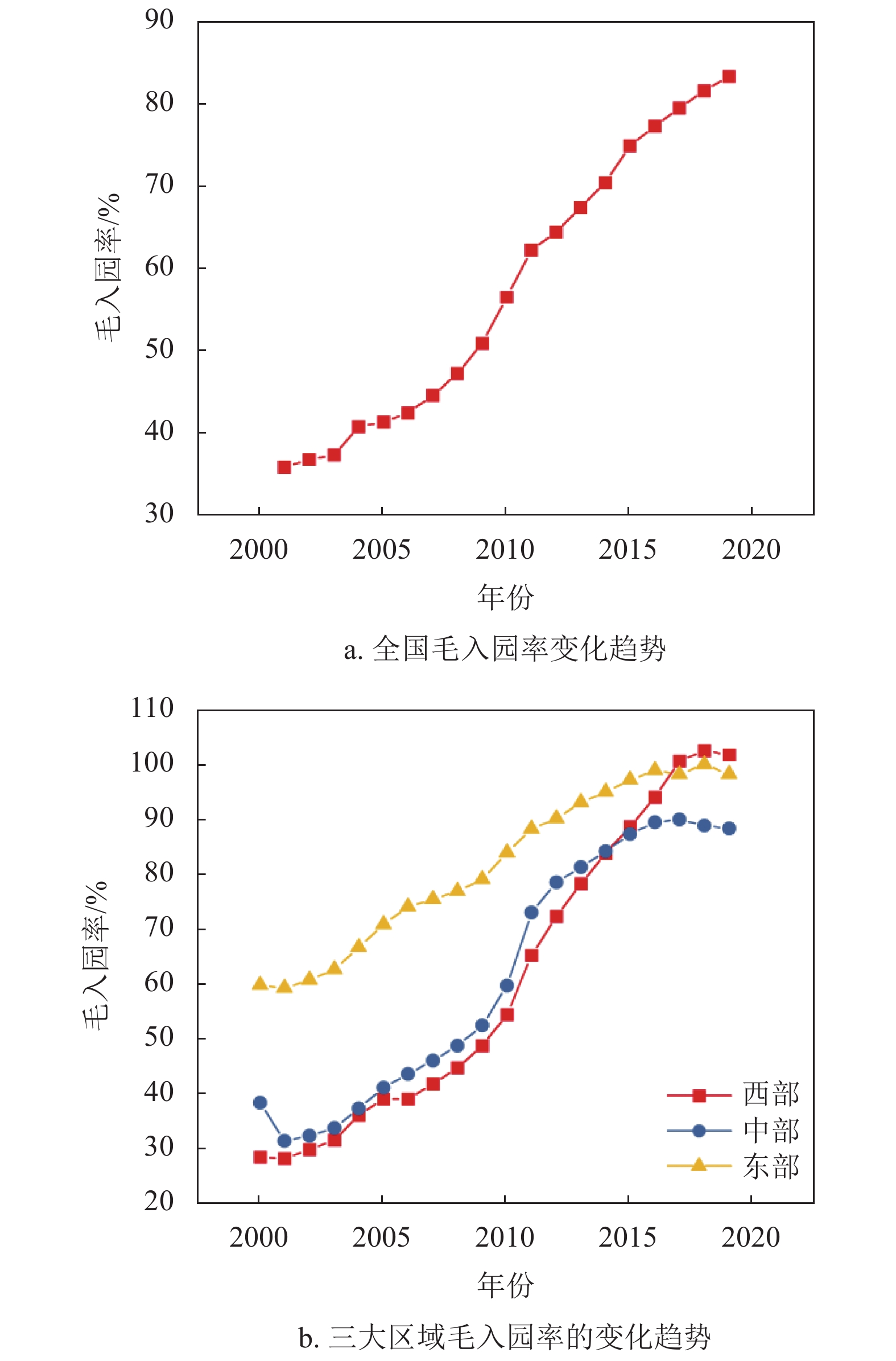
Preschool education is an essential people’s livelihood field related to the development of children, family happiness, and the future of the country, which has significance and value in promoting the fairness of social resources and welfare and maintaining the stability of social order. In order to guarantee the equality and accessibility of preschool education, the government has committed to making attributions to narrow both regional and urban-rural preschool education gap for a long time. Based on related data from the China Education Statistics Yearbook and China Population & Employment Statistics Yearbook, we analyze the evolution trend of preschool education at nation level, at region level, and at province level, respectively. The results show that the gross enrollment rate for three-year preschool education has dramatically enhanced in the past two decades, especially in the central and west regions. The distribution disparity of the gross enrollment rate has decreased, which is mainly attributable to intra-regional differences. During 2000-2015, the gross enrollment rate had a significantly positive spatial aggregation. During 2016-2019, the spatial aggregation pattern disappeared over time. The findings reveal that the level of preschool education has made remarkable progress in quantity and balanced development. In the end, this paper provides some suggestions for the balanced development of preschool education.
Preschool education is an essential people’s livelihood field related to the development of children, family happiness, and the future of the country, which has significance and value in promoting the fairness of social resources and welfare and maintaining the stability of social order. In order to guarantee the equality and accessibility of preschool education, the government has committed to making attributions to narrow both regional and urban-rural preschool education gap for a long time. Based on related data from the China Education Statistics Yearbook and China Population & Employment Statistics Yearbook, we analyze the evolution trend of preschool education at nation level, at region level, and at province level, respectively. The results show that the gross enrollment rate for three-year preschool education has dramatically enhanced in the past two decades, especially in the central and west regions. The distribution disparity of the gross enrollment rate has decreased, which is mainly attributable to intra-regional differences. During 2000-2015, the gross enrollment rate had a significantly positive spatial aggregation. During 2016-2019, the spatial aggregation pattern disappeared over time. The findings reveal that the level of preschool education has made remarkable progress in quantity and balanced development. In the end, this paper provides some suggestions for the balanced development of preschool education.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022314
Abstract:
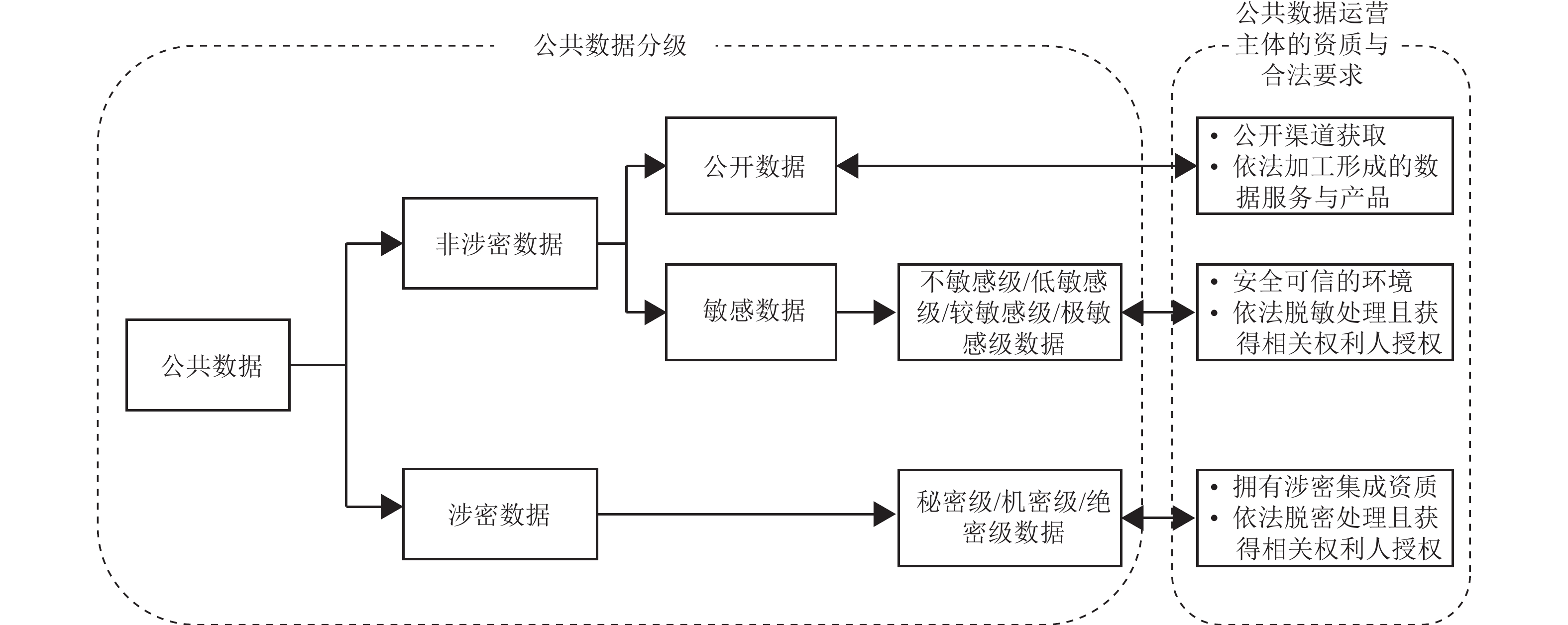
Public data paid service is the path to the valued and factored public data. However, there is still a lack of sufficient research and feasible solutions on the legitimacy, effective path and risk prevention of public data paid service. This paper analyzes the concept of public data, analyzes the scope of public data paid service, and from the social economic value, data ownership and the rationality and necessity of charging three aspects, demonstrate the legitimacy of public data paid service. This paper deeply analyzes the effective path to develop public data paid service and clearly proposes the strategies and solutions that should be adopted in the four key links of authorization and operation mode, service delivery mode, pricing strategy and benefit compensation mechanism. At the end of the paper, it also discusses the possible risks and preventive measures in the public data paid service, and summarizes and refines the six specific suggestions. This paper can be an important reference for promoting the paid service of public data continuously and healthily.
Public data paid service is the path to the valued and factored public data. However, there is still a lack of sufficient research and feasible solutions on the legitimacy, effective path and risk prevention of public data paid service. This paper analyzes the concept of public data, analyzes the scope of public data paid service, and from the social economic value, data ownership and the rationality and necessity of charging three aspects, demonstrate the legitimacy of public data paid service. This paper deeply analyzes the effective path to develop public data paid service and clearly proposes the strategies and solutions that should be adopted in the four key links of authorization and operation mode, service delivery mode, pricing strategy and benefit compensation mechanism. At the end of the paper, it also discusses the possible risks and preventive measures in the public data paid service, and summarizes and refines the six specific suggestions. This paper can be an important reference for promoting the paid service of public data continuously and healthily.
, Available online , doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2022419
Abstract:
Aiming at the problem of network structure influence on the control strategy on delaying the spatial spread of epidemic, the dual-population structure, hub structure, one-dimensional linear structure, and path superposition structure existing in the composite population network are studied, and the effects of patient isolation strategy and air traffic control strategy on delaying the first time of epidemic are analyzed, and the simulation verification is carried out through the American Airlines network. The results show that in the early stage of the outbreak, the control effect of timely patient isolation strategy is better than that of air traffic control strategy. The length of the epidemiological transmission structure is an important factor affecting the time of first arrival; The path overlay structure hardly affects the control effect of air traffic control strategy, but to a large extent, it inhibits the control effect of patient isolation strategy.
Aiming at the problem of network structure influence on the control strategy on delaying the spatial spread of epidemic, the dual-population structure, hub structure, one-dimensional linear structure, and path superposition structure existing in the composite population network are studied, and the effects of patient isolation strategy and air traffic control strategy on delaying the first time of epidemic are analyzed, and the simulation verification is carried out through the American Airlines network. The results show that in the early stage of the outbreak, the control effect of timely patient isolation strategy is better than that of air traffic control strategy. The length of the epidemiological transmission structure is an important factor affecting the time of first arrival; The path overlay structure hardly affects the control effect of air traffic control strategy, but to a large extent, it inhibits the control effect of patient isolation strategy.

 ISSN
ISSN